Difference between revisions of "Timeline of hygiene"
| (37 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This is a '''timeline of {{w|hygiene}}''', attempting to describe important aspects of human hygiene | + | This is a '''timeline of {{w|hygiene}}''', attempting to describe important aspects of human hygiene. {{w|Toilet}} developent is covered on the [[timeline of sanitation]]. |
==Big picture== | ==Big picture== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| Ancient times || Soap is already produced in the {{w|Middle East}}. Thoothbrushing is already developed by civilizations in [[w:Ancient Egypt|Egypt]] and {{w|Babylonia}}. Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the Roman civilization. | | Ancient times || Soap is already produced in the {{w|Middle East}}. Thoothbrushing is already developed by civilizations in [[w:Ancient Egypt|Egypt]] and {{w|Babylonia}}. Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the Roman civilization. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Middle Ages || {{w|Soap making}} becomes an established trade. | + | | Middle Ages || {{w|Soap making}} becomes an established trade. In Europe, Purity of the soul is emphasized over the cleanliness of the outer<ref name="The History of Shampoo">{{cite web|title=The History of Shampoo|url=http://hairstory.com/stories/2017/3/24/the-history-of-shampoo|website=hairstory.com|publisher=|accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref>, however, some scholars argue that people in [[w:Middle Ages|Medieval Europe]] probably bathed more than people in the 19th century.<ref name="Thorndike, ''Tales of the Middle Ages - Daily Life''">{{cite web |url=http://www.godecookery.com/mtales/mtales08.htm |title=Thorndike, ''Tales of the Middle Ages - Daily Life''|website=Gode Cookery|access-date=9 August 2017}}</ref>. In {{w|Japan}}, daily bathing becomes a common custom. In {{w|Iceland}}, pools warmed with water from hot springs are popular gathering places on Saturday evenings.<ref name="The History of Shampoo"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 19th Century || Modern sanitation starts becoming adopted. By the end of the century, deodorants can be found in many forms, including roll-ins, powders, creams, pads, solid, and dabbers.<ref name="Deodorants History - Invention of the Deodorant">{{cite web|title=Deodorants History - Invention of the Deodorant|url=http://www.historyofcosmetics.net/history-of-makeup/history-of-deodorants/|website=historyofcosmetics.net|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> | | 19th Century || Modern sanitation starts becoming adopted. By the end of the century, deodorants can be found in many forms, including roll-ins, powders, creams, pads, solid, and dabbers.<ref name="Deodorants History - Invention of the Deodorant">{{cite web|title=Deodorants History - Invention of the Deodorant|url=http://www.historyofcosmetics.net/history-of-makeup/history-of-deodorants/|website=historyofcosmetics.net|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 20th Century || Between 1963 and 1998, approximately 3000 toothbrush patents are filed worldwide.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> In the early 1980s, {{w|electronic bidet}}s are introduced in {{w|Japan}}. In the late 1990s and early part of the 21st century, [[w:Hand sanitizer|alcohol rub]] non-water-based hand hygiene agents (also known as alcohol-based hand rubs, antiseptic hand rubs, or hand sanitizers) begin to gain popularity. | + | | 20th Century || Commercially-made shampoo becomes available from the turn of the century.<ref name="Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood"/> Between 1963 and 1998, approximately 3000 toothbrush patents are filed worldwide.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> In the early 1980s, {{w|electronic bidet}}s are introduced in {{w|Japan}}. In the late 1990s and early part of the 21st century, [[w:Hand sanitizer|alcohol rub]] non-water-based hand hygiene agents (also known as alcohol-based hand rubs, antiseptic hand rubs, or hand sanitizers) begin to gain popularity. |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
| 1600 BC–1550 BC || Publication || The {{w|Ebers papyrus}}, an ancient Egyptian medical compendium, describes the practice of combining oils with alkaline salts to form a soap-like material for treating skin diseases and for washing. The papyrus indicates that the {{w|ancient Egypt}}ians bathed regularly. Egyptian documents also mention a soap-like substance was used in the preparation of {{w|wool}} for weaving.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/><ref>{{cite web|title=The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates back to around 2800 BC in ancient Babylon. A formula for soap consisting of water, alkali, and cassia oil was written on a Babylonian clay tablet around 2200 BC.|url=http://www.heritagedaily.com/2013/11/earliest-known-usage-of-soap/100304|website=heritagedaily.com|accessdate=20 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Egypt}} | | 1600 BC–1550 BC || Publication || The {{w|Ebers papyrus}}, an ancient Egyptian medical compendium, describes the practice of combining oils with alkaline salts to form a soap-like material for treating skin diseases and for washing. The papyrus indicates that the {{w|ancient Egypt}}ians bathed regularly. Egyptian documents also mention a soap-like substance was used in the preparation of {{w|wool}} for weaving.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/><ref>{{cite web|title=The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates back to around 2800 BC in ancient Babylon. A formula for soap consisting of water, alkali, and cassia oil was written on a Babylonian clay tablet around 2200 BC.|url=http://www.heritagedaily.com/2013/11/earliest-known-usage-of-soap/100304|website=heritagedaily.com|accessdate=20 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Egypt}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 753 BC–476 AD || || Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the [[w:Ancient Rome|Roman civilization]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Roman bath houses |url=http://www.channel4.com/history/microsites/T/timeteam/snapshot_rom_bath.html |website=Time Team |publisher=Channel Four Television Corporation |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070204115107/http://www.channel4.com/history/microsites/T/timeteam/snapshot_rom_bath.html |archivedate=4 February 2007 |deadurl=yes |df= }}</ref> || {{w|Italy}} | + | | 753 BC–476 AD || Body hygiene || Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the [[w:Ancient Rome|Roman civilization]].<ref>{{cite web|title=Roman bath houses |url=http://www.channel4.com/history/microsites/T/timeteam/snapshot_rom_bath.html |website=Time Team |publisher=Channel Four Television Corporation |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070204115107/http://www.channel4.com/history/microsites/T/timeteam/snapshot_rom_bath.html |archivedate=4 February 2007 |deadurl=yes |df= }}</ref> || {{w|Italy}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 600 BC || || The {{w|Phoenicians}} prepare {{w|soap}} from {{w|goat}}’s tallow and {{w|wood ash}}es.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || | + | | 600 BC || Body hygiene || The {{w|Phoenicians}} prepare {{w|soap}} from {{w|goat}}’s tallow and {{w|wood ash}}es.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 556–539 BC || || In the reign of {{w|Nabonidus}}, a recipe for soap consists of ''uhulu'' {{w|ashes}}, cypress {{w|oil}} and sesame {{w|seed oil}} "for washing the stones for the servant girls".<ref>Noted in {{cite journal|author=Levey, Martin |title=Gypsum, salt and soda in ancient Mesopotamian chemical technology|journal=Isis|volume=49|issue=3|year=1958|pages=336–342 (341)|jstor=226942|doi=10.1086/348678}}</ref> || | + | | 556–539 BC || Body hygiene || In the reign of {{w|Nabonidus}}, a recipe for soap consists of ''uhulu'' {{w|ashes}}, cypress {{w|oil}} and sesame {{w|seed oil}} "for washing the stones for the servant girls".<ref>Noted in {{cite journal|author=Levey, Martin |title=Gypsum, salt and soda in ancient Mesopotamian chemical technology|journal=Isis|volume=49|issue=3|year=1958|pages=336–342 (341)|jstor=226942|doi=10.1086/348678}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 500 BC || || Gentlemanly etiquette in China requires hand washing five times a day, hair washing every third day and a hot bath every fifth day.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|China}} | + | | 500 BC || Body hygiene || Gentlemanly etiquette in China requires hand washing five times a day, hair washing every third day and a hot bath every fifth day.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|China}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 460 BC – 377 BC || || “Hygiene” becomes known as the branch of medicine dedicated to the "art of health," (as distinct from therapeutics, the treatment of disease).<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF PUBLIC SANITATION">{{cite web|title=SNAPSHOTS OF PUBLIC SANITATION|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/public_sanitation.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=23 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Greece}} | | 460 BC – 377 BC || || “Hygiene” becomes known as the branch of medicine dedicated to the "art of health," (as distinct from therapeutics, the treatment of disease).<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF PUBLIC SANITATION">{{cite web|title=SNAPSHOTS OF PUBLIC SANITATION|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/public_sanitation.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=23 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Greece}} | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
| 460 – 377 BC || || Greek physician {{w|Hippocrates}} conceives hygiene as “an influence of atmosphere, soil, and water on human health”.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Pappas|first1=Georgios|title=Insights into infectious disease in the era of Hippocrates|journal=International Journal of Infectious Diseases|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1201971207002123|accessdate=10 August 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Greece}} | | 460 – 377 BC || || Greek physician {{w|Hippocrates}} conceives hygiene as “an influence of atmosphere, soil, and water on human health”.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Pappas|first1=Georgios|title=Insights into infectious disease in the era of Hippocrates|journal=International Journal of Infectious Diseases|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1201971207002123|accessdate=10 August 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Greece}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 312 BC || || In {{w|Rome}}, perfumed oils are used for bathing. Pumice and ashes are also rubbed over wet skin.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|Italy}} | + | | 312 BC || Body hygiene || In {{w|Rome}}, perfumed oils are used for bathing. Pumice and ashes are also rubbed over wet skin.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|Italy}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 47 AD || || Roman physician Scribonius Largus describes three different "toothpowder” mixtures, one containing {{w|vinegar}}, {{w|honey}} and {{w|salt}}; another with {{w|radish}} and finely {{w|ground glass}}; and a third using ground deer antler, a rare aromatic gum and rock salt. || | + | | 47 AD || Dental hygiene || Roman physician Scribonius Largus describes three different "toothpowder” mixtures, one containing {{w|vinegar}}, {{w|honey}} and {{w|salt}}; another with {{w|radish}} and finely {{w|ground glass}}; and a third using ground deer antler, a rare aromatic gum and rock salt. || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 100 – 200 AD || || Greek physician {{w|Galen}} recommends {{w|soap}} for cleaning and medicinal purposes.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP">{{cite web|last1=A brief history of…SOAP|title=A brief history of…SOAP|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/soap.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=20 September 2017}}</ref> || | + | | 100 – 200 AD || Body hygiene || Greek physician {{w|Galen}} recommends {{w|soap}} for cleaning and medicinal purposes.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP">{{cite web|last1=A brief history of…SOAP|title=A brief history of…SOAP|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/soap.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=20 September 2017}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 200 BC–450 AD || || Several Hindu texts, such as the {{w|Manusmriti}} and the {{w|Vishnu Purana}}, describe elaborate codes of hygiene. Bathing is one of the five {{w|Nitya karma}}s (daily duties) in Hinduism, and not performing it leads to sin, according to some scriptures.<ref>{{cite web|title=Aryan Code of Toilets (2nd Century AD)|url=http://www.sulabhtoiletmuseum.org/history-of-toilets/aryan-code-of-toilets-2nd-century-ad/|publisher=Sulabh International Museum of Toilets}}</ref> || {{w|India}} | | 200 BC–450 AD || || Several Hindu texts, such as the {{w|Manusmriti}} and the {{w|Vishnu Purana}}, describe elaborate codes of hygiene. Bathing is one of the five {{w|Nitya karma}}s (daily duties) in Hinduism, and not performing it leads to sin, according to some scriptures.<ref>{{cite web|title=Aryan Code of Toilets (2nd Century AD)|url=http://www.sulabhtoiletmuseum.org/history-of-toilets/aryan-code-of-toilets-2nd-century-ad/|publisher=Sulabh International Museum of Toilets}}</ref> || {{w|India}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 300 – 500 SD || || Indian women use a turmeric cream with antiseptic properties as an alternative to soap.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|India}} | + | | 300 – 500 SD || Body hygiene || Indian women use a turmeric cream with antiseptic properties as an alternative to soap.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|India}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 500 – 600 AD || || {{w|Japanese Buddhism}} teaches that bathing purifies the body of sin and also brings luck.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|Japan}} | + | | 500 – 600 AD || Body hygiene || {{w|Japanese Buddhism}} teaches that bathing purifies the body of sin and also brings luck.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || {{w|Japan}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 600 – 700 AD || Body hygiene || The "Turkish Bath" or {{w|Hammam}} becomes a major feature of {{w|Islam}}ic culture. The {{w|Quran}} requires cleanliness as an important part of Muslim faith: face, hand, forearm and feet washing before prayer, and whole body bathing after sex.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || | | 600 – 700 AD || Body hygiene || The "Turkish Bath" or {{w|Hammam}} becomes a major feature of {{w|Islam}}ic culture. The {{w|Quran}} requires cleanliness as an important part of Muslim faith: face, hand, forearm and feet washing before prayer, and whole body bathing after sex.<ref name="SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING"/> || | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
| 1100s || Body hygiene || Soap is highly taxed in England. It is considered a luxury item and is not widely used.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | | 1100s || Body hygiene || Soap is highly taxed in England. It is considered a luxury item and is not widely used.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1240 || || English physician {{w|Gilbertus Anglicus}} publishes his ''Compendium Medicinae'', which contains descriptions of hygiene and the care of one's appearance.<ref name="Thorndike, ''Tales of the Middle Ages - Daily Life''"/> || | + | | 1240 || Publication || English physician {{w|Gilbertus Anglicus}} publishes his ''Compendium Medicinae'', which contains descriptions of hygiene and the care of one's appearance.<ref name="Thorndike, ''Tales of the Middle Ages - Daily Life''"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1400s || Dental hygiene || The first precursor of the modern toothbrush is thought to come from {{w|China}} or {{w|Egypt}} in this century. It has a bamboo or bone handle and bristles from the back of the neck of the wild boar, or from horsehair. This design would spread to Europe.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> || | | 1400s || Dental hygiene || The first precursor of the modern toothbrush is thought to come from {{w|China}} or {{w|Egypt}} in this century. It has a bamboo or bone handle and bristles from the back of the neck of the wild boar, or from horsehair. This design would spread to Europe.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> || | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1791 || Body hygiene || French chemist {{w|Nicolas Leblanc}} patents the process for making soda ash, a major component of soap, from table salt.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || | | 1791 || Body hygiene || French chemist {{w|Nicolas Leblanc}} patents the process for making soda ash, a major component of soap, from table salt.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1800 || Hair care || Early colonial traders in {{w|India}} discover hair and body massage, called [[w:champo|shampoo]], and introduce “champing” to Europe.<ref name="The History of Shampoo"/> || {{w|India}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1815 || Dental hygiene || American dentist Dr. Levi Spear Parmly introduces the idea of using waxed silken thread as floss. Later in his career, Parmly would publish ''A Practical Guide to the Management of Teeth'', emphasizing the importance of brushing and flossing daily.<ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss"/><ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?"/> || {{w|United States}} | | 1815 || Dental hygiene || American dentist Dr. Levi Spear Parmly introduces the idea of using waxed silken thread as floss. Later in his career, Parmly would publish ''A Practical Guide to the Management of Teeth'', emphasizing the importance of brushing and flossing daily.<ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss"/><ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1823 || || French chemist {{w|Michel Eugène Chevreul}} reveals the chemical process of soap by showing how boiling fat with an alkali salt splits the fat molecule into the alkali salt of fatty acid (soap) and glycerol.<ref>{{cite web|title=Michel-Eugène Chevreul|url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Michel-Eugene-Chevreul|website=britannica.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || | + | | 1823 || Body hygiene || French chemist {{w|Michel Eugène Chevreul}} reveals the chemical process of soap by showing how boiling fat with an alkali salt splits the fat molecule into the alkali salt of fatty acid (soap) and glycerol.<ref>{{cite web|title=Michel-Eugène Chevreul|url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Michel-Eugene-Chevreul|website=britannica.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1824 || Dental hygiene || Dr Peabody, a dentist, introduces a soap-containing toothpaste.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || | | 1824 || Dental hygiene || Dr Peabody, a dentist, introduces a soap-containing toothpaste.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1844 || || The first 3-row brush is designed.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> || | + | | 1844 || Dental hygiene || The first 3-row brush is designed.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/> || |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1847 || Body Hygiene || Hungarian obstetrician {{w|Ignaz Semmelweis}} urges doctors at Vienna General Hospital to wash their hands. Prior to this, physicians weren't aware of the spread of infections due to lack of hand washing.<ref name="In 1850, Ignaz Semmelweis saved lives with three words: wash your hands">{{cite web|title=In 1850, Ignaz Semmelweis saved lives with three words: wash your hands|url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/health/ignaz-semmelweis-doctor-prescribed-hand-washing|website=pbs.org|accessdate=13 April 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Austria}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1853 || Body hygiene || English {{w|soap}} {{w|tax}} is abolished. Soap becomes widely used and is described by German chemist {{w|Justus von Liebig}} as an accurate measure of a country’s wealth and civilization.<ref name="A brief history of…SOAP"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1857 || Anal cleansing || {{w|Toilet paper}} comes on sale in the United States, at first being sold in sheets.<ref name="Panati's Extraordinary Origins of Everyday Things">{{cite book|last1=Panati|first1=Charles|title=Panati's Extraordinary Origins of Everyday Things|url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=utroDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA204&lpg=PA204&dq=%22in+1857+%22+%22toilet+paper%22&source=bl&ots=TDdk_HOFCz&sig=mXuzNzOmrwyj69CIoADhBg2r4z4&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi2p9GrgL7VAhXGlJAKHSFrCRk4ChDoAQhLMAc#v=onepage&q=%22in%201857%20%22%20%22toilet%20paper%22&f=false|accessdate=4 August 2017}}</ref><ref name="A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS"/> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1861 || Publication || {{w|Ignaz Semmelweis}} in {{w|Budapest}} publishes ''Die Aetiologie, der Begriff und die Prophylaxis des Kindbettfiebers'' (“The Etiology, the Concept, and the Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever”), in which he explains his theories on childbed fever, and the ways to avoid spreading it by means of vigorous hand-washing.<ref name="In 1850, Ignaz Semmelweis saved lives with three words: wash your hands"/> || {{w|Hungary}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 1874 || Dental hygiene || The first patent for dental floss is granted to Asahel M. Shurtleff for what is described as "an improved pocket thread carrier and cutter" that resembles modern floss packages.<ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?"/> || | | 1874 || Dental hygiene || The first patent for dental floss is granted to Asahel M. Shurtleff for what is described as "an improved pocket thread carrier and cutter" that resembles modern floss packages.<ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1880s || || {{w|Toothpaste}} is mass produced in jars in the {{w|United States}}, based on Dr Sheffield’s "Crème Dentifrice” invention of 1850.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || | + | | 1880s || Dental hygiene || {{w|Toothpaste}} is mass produced in jars in the {{w|United States}}, based on Dr Sheffield’s "Crème Dentifrice” invention of 1850.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1882 || Dental hygiene || Mass production of unwaxed silk floss begins in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS"/> || | | 1882 || Dental hygiene || Mass production of unwaxed silk floss begins in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS"/> || | ||
| Line 98: | Line 104: | ||
| 1888 || Body hygiene || The first cosmetic deodorant, a paste made from zinc chloride and wax, is patented under the name ‘Mum’.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT">{{cite web|title=A brief history of…DEODORANT|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/deodorant.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || | | 1888 || Body hygiene || The first cosmetic deodorant, a paste made from zinc chloride and wax, is patented under the name ‘Mum’.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT">{{cite web|title=A brief history of…DEODORANT|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/deodorant.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1890 || || {{w|Toilet paper}} is first sold in rolls in the {{w|United States}}.<ref name="A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS">{{cite web|title=A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS|url=http://www.localhistories.org/toilets.html|website=localhistories.org|accessdate=4 August 2017}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1890 || Anal cleansing || {{w|Toilet paper}} is first sold in rolls in the {{w|United States}}.<ref name="A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS">{{cite web|title=A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS|url=http://www.localhistories.org/toilets.html|website=localhistories.org|accessdate=4 August 2017}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1890s || || {{w|Aluminium chloride}} is added to deodorants to reduce sweating.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || | + | | 1890s || Body hygiene || {{w|Aluminium chloride}} is added to deodorants to reduce sweating.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1890s || Dental hygiene || {{w|Toothpaste}} | + | | 1890s || Dental hygiene || {{w|Toothpaste}} is sold in collapsible tubes.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE">{{cite web|title=A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/toothpaste.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1898 || Dental hygiene || The first dental floss patent is awarded in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS">{{cite web|title=A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/dental_floss.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref><ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss">{{cite web|title=A Brief History of Dental Floss|url=https://www.speareducation.com/spear-review/2013/01/a-brief-history-of-dental-floss|website=speareducation.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | | 1898 || Dental hygiene || The first dental floss patent is awarded in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS">{{cite web|title=A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS|url=http://www.hygieneforhealth.org.au/dental_floss.php|website=hygieneforhealth.org.au|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref><ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss">{{cite web|title=A Brief History of Dental Floss|url=https://www.speareducation.com/spear-review/2013/01/a-brief-history-of-dental-floss|website=speareducation.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1898 || Hair care || German chemist {{w|Hans Schwarzkopf}} in {{w|BErlin}} opens a {{w|drugstore}} dedicated to perfume and focuses his efforts on products for the hair. His popular water-soluble, powder {{w|shampoo}} still causes dulling, alkaline reactions.<ref name="The History of Shampoo"/> || {{w|Germany}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1914 || Hair care || British hair stylist Kasey Hebert in {{w|London}} invents the first commercial shampoo.<ref name="The History of Shampoo"/><ref name="Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood">{{cite web|title=Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood|url=http://www.independentpharmacist.co.uk/shampoo-taking-the-sting-out-of-childhood|website=independentpharmacist.co.uk|accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1939 || Dental hygiene || The first electric toothbrush is developed in Switzerland.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/><ref name="A Brief History of Dentistry">{{cite web|title=A Brief History of Dentistry|url=https://www.dentistsnearby.com/misc/patient-education/27-the-history-of-dentistry.html|website=dentistsnearby.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Switzerland | + | | 1927 || Hair care || {{w|Hans Schwarzkopf}} introduces one of the world’s premiere liquid shampoos.<ref name="Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood"/> || {{w|Germany}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1928 || Anal cleansing || {{w|Toilet paper}} is first sold in rolls in Europe.<ref name="A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS"/> || {{w|Europe}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1930 || Hair care || Shampoo as we know it today (with synthetic surfactants) is first introduced.<ref name="Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood"/><ref name="The History of Shampoo"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1939 || Dental hygiene || The first {{w|electric toothbrush}} is developed in Switzerland.<ref name="A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH"/><ref name="A Brief History of Dentistry">{{cite web|title=A Brief History of Dentistry|url=https://www.dentistsnearby.com/misc/patient-education/27-the-history-of-dentistry.html|website=dentistsnearby.com|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Switzerland}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1940s || Dental hygiene || Dr. Charles C. Bass creates a more shred-resistant nylon floss as a substitute for silk floss, thus promoting teeth flossing as an important part of oral hygiene.<ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?">{{cite web|title=Who Invented Dental Floss?|url=https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/who-invented-dental-floss|website=wonderopolis.org|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || | | 1940s || Dental hygiene || Dr. Charles C. Bass creates a more shred-resistant nylon floss as a substitute for silk floss, thus promoting teeth flossing as an important part of oral hygiene.<ref name="Who Invented Dental Floss?">{{cite web|title=Who Invented Dental Floss?|url=https://wonderopolis.org/wonder/who-invented-dental-floss|website=wonderopolis.org|accessdate=21 September 2017}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1942 || | + | | 1942 || Anal cleansing || Soft toilet paper comes on sale.<ref name="A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1945 || Dental hygiene || Soap is replaced by other ingredients in the making of toothpaste, following the invention of synthetic detergents, making toothpastes smoother.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || | | 1945 || Dental hygiene || Soap is replaced by other ingredients in the making of toothpaste, following the invention of synthetic detergents, making toothpastes smoother.<ref name="A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE"/> || | ||
| Line 119: | Line 133: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1952 || || The first roll-on deodorant, based on the design of the ballpoint pen, is marketed in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || {{w|United States}} | | 1952 || || The first roll-on deodorant, based on the design of the ballpoint pen, is marketed in the United States.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1952 || Journal || The ''American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene'' is formed.<ref name="Journals of the Century">{{cite book |last1=Cole |first1=Jim |last2=Stankus |first2=Tony |title=Journals of the Century |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Pv7sAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA422&lpg=PA422&dq=%22in+1962%22+%22Investigative+Ophthalmology%22&source=bl&ots=j2sCse0Izg&sig=cQpVjYIGUj4v7qkPpwEGfEoYcX0&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwju5pSLv7jdAhVBHJAKHQeOApwQ6AEwAXoECAkQAQ#v=onepage&q=%22in%201962%22%20%22Investigative%20Ophthalmology%22&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1965 || Body hygiene || The first anti-perspirant aerosol is launched to the market.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || | | 1965 || Body hygiene || The first anti-perspirant aerosol is launched to the market.<ref name="A brief history of…DEODORANT"/> || | ||
| Line 124: | Line 140: | ||
| 1975–1980 || || {{w|Sleep hygiene}} is developed as a recommended behavioral and environmental practice intended to promote better quality sleep. This recommendation is thought as a method to help people with mild to moderate {{w|insomnia}}. However, as of 2014, the evidence for effectiveness of individual recommendations is "limited and inconclusive".<ref name='SH2014'>{{cite journal|last1=Irish|first1=Leah A.|last2=Kline|first2=Christopher E|last3=Gunn|first3=Heather E|last4=Buysse|first4=Daniel J|last5=Hall|first5=Martica H|title=The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence|journal=Sleep Medicine Reviews|date=October 2014|doi=10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001|pmid= 25454674|pmc=4400203|volume=22|pages=23–36}}</ref> || | | 1975–1980 || || {{w|Sleep hygiene}} is developed as a recommended behavioral and environmental practice intended to promote better quality sleep. This recommendation is thought as a method to help people with mild to moderate {{w|insomnia}}. However, as of 2014, the evidence for effectiveness of individual recommendations is "limited and inconclusive".<ref name='SH2014'>{{cite journal|last1=Irish|first1=Leah A.|last2=Kline|first2=Christopher E|last3=Gunn|first3=Heather E|last4=Buysse|first4=Daniel J|last5=Hall|first5=Martica H|title=The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence|journal=Sleep Medicine Reviews|date=October 2014|doi=10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001|pmid= 25454674|pmc=4400203|volume=22|pages=23–36}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1980 || | + | | 1980 || Anal cleansing || Japanese electric toilet {{w|Washlet}}, with water spray feature for genital and {{w|anal cleansing}}, is released to the market.<ref name="363 Diffusion of Electronic Bidet Toilet in Japan Case Study: TOTO Washlet">{{cite web|last1=Akbar|first1=Adhiutama|last2=Seiichi|first2=Yoshikubo|title=363 Diffusion of Electronic Bidet Toilet in Japan Case Study: TOTO Washlet|url=http://www.sbm.itb.ac.id/wp-content/uploads/2010/01/Vol-2-No-2-December-2009-Diffusion-of-Electronic-Bidet-Toilet-in-Japan-Case-Study-TOTO-Washlet.pdf|website=itb.ac.id|publisher=Management of Technology Program, Shibaura Institute of Technology, Japan|accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref> || {{w|Japan}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 1980s || Dental hygiene || The interdental brush is invented as an alternative to [[w:Dental floss|flossing]].<ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss"/> || | | 1980s || Dental hygiene || The interdental brush is invented as an alternative to [[w:Dental floss|flossing]].<ref name="A Brief History of Dental Floss"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1985–1990 || Hand hygiene || {{w|Automatic faucet}}s are introduced for commercial use.<ref>{{cite web|title=Introduction of Automatic Faucets|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081007121913/http://www.macfaucets.com/education.htm|website=archive.org|accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1989 || || British epidemiologist {{w|David P. Strachan}} develops the {{w|hygiene hypothesis}}, which states that there is an inverse relationship between family size and development of atopic allergic disorders – the more children in a family, the less likely they are to develop these {{w|allergies}}.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Bloomfield et al|first1=SF|title=Too clean, or not too clean: the Hygiene Hypothesis and home hygiene|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1448690/|accessdate=9 August 2017|pmc=1448690}}</ref><ref name="Strachan2000">{{cite journal|last1=Strachan|first1=DP|title=Family size, infection and atopy: the first decade of the 'hygiene hypothesis'|journal=Thorax|date=August 2000|volume=55|issue=1|pages=S2–S10|pmc=1765943}}</ref> || | | 1989 || || British epidemiologist {{w|David P. Strachan}} develops the {{w|hygiene hypothesis}}, which states that there is an inverse relationship between family size and development of atopic allergic disorders – the more children in a family, the less likely they are to develop these {{w|allergies}}.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Bloomfield et al|first1=SF|title=Too clean, or not too clean: the Hygiene Hypothesis and home hygiene|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1448690/|accessdate=9 August 2017|pmc=1448690}}</ref><ref name="Strachan2000">{{cite journal|last1=Strachan|first1=DP|title=Family size, infection and atopy: the first decade of the 'hygiene hypothesis'|journal=Thorax|date=August 2000|volume=55|issue=1|pages=S2–S10|pmc=1765943}}</ref> || | ||
| Line 136: | Line 154: | ||
| 2000 || Statistics || 1229 million people worldwide practice {{w|open defecation}}.<ref name="Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017">{{cite web|title=Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/258617/1/9789241512893-eng.pdf?ua=1|website=who.int|accessdate=8 August 2017}}</ref> || | | 2000 || Statistics || 1229 million people worldwide practice {{w|open defecation}}.<ref name="Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017">{{cite web|title=Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/258617/1/9789241512893-eng.pdf?ua=1|website=who.int|accessdate=8 August 2017}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2015 || Statistics || 892 million people practice {{w|open defecation}}<ref name="Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017"/> || | + | | 2008 || Hand hygiene || The {{w|Global Handwashing Day}} is initiated by the [[w:Public-private partnership|Public Private Partnership]] for Handwashing (PPPHW) in August 2008 at the annual {{w|World Water Week}} in {{w|Stockholm}}.<ref>{{Cite web|url = http://globalhandwashing.org/about-us/our-history/|title = The Global Public Private Partnership for Handwashing – Our History|date = |accessdate = 28 September 2017|website = The Global Public Private Partnership for Handwashing|publisher = |last = |first = }}</ref> || {{w|Sweden}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2009 || Hand hygiene || The {{w|World Health Organization}} launches its New global Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care, developed with assistance from more than 100 renowned international experts. Also tested and given trials in different parts of the world.<ref name="a WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: a Summary">{{cite web|title=a WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: a Summary|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/70126/1/WHO_IER_PSP_2009.07_eng.pdf|website=who.int|accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2015 || Statistics || 892 million people practice {{w|open defecation}}.<ref name="Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2015 || Statistics || Study of {{w|handwashing}} in 54 countries finds that on average, 38.7% of households practice handwashing with {{w|soap}}.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.wssinfo.org/handwashing/|title=JMP handwashing dataset |quote=WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation |accessdate=28 September 2017}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2016 || Anal cleansing || [[w:Toilets in Japan|Bidet toilets]] are installed in 81.2% of Japanese households.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.esri.cao.go.jp/jp/stat/shouhi/2016/201603fukyuritsu.xls |publisher=Cabinet Office, Government of Japan |title=平成28年3月実施調査結果:消費動向調査 |trans_title=March 2016 consumer spending survey |date=March 2016 |deadurl=yes |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160623183155/http://www.esri.cao.go.jp/jp/stat/shouhi/2016/201603fukyuritsu.xls |archivedate=2016-06-23 |df= }}</ref> || {{w|Japan}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2018 || Scientific development || Study by the University of Connecticut School of Medicine shows that dryers sucking in bacteria and faecal particles from flushing toilets can spread it onto users' recently washed hands.<ref>{{cite web|title=Bathroom hand dryers may be blowing bacteria and faeces all over you, study suggests|url=https://www.irishexaminer.com/breakingnews/world/bathroom-hand-dryers-may-be-blowing-bacteria-and-faeces-all-over-you-study-suggests-837195.html|website=irishexaminer.com|accessdate=13 April 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Numerical and visual data == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Scholar === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of June 27, 2021. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="sortable wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Year | ||
| + | ! hygiene | ||
| + | ! hand hygiene | ||
| + | ! oral hygiene | ||
| + | ! personal hygiene | ||
| + | ! hygiene education | ||
| + | ! hygiene management | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1980 || 48,500 || 5,560 || 2,830 || 4,440 || 35,100 || 32,600 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1985 || 28,800 || 5,940 || 3,450 || 5,290 || 11,500 || 10,400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1990 || 90,400 || 8,460 || 5,280 || 7,580 || 60,800 || 51,900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1995 || 52,600 || 10,500 || 6,080 || 9,840 || 17,600 || 15,300 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2000 || 130,000 || 18,300 || 9,380 || 17,000 || 72,600 ||67,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || 107,000 || 21,100 || 11,600 || 20,300 || 35,600 || 35,900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || 121,000 || 25,000 || 14,400 || 23,700 || 45,200 || 42,100 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2006 || 147,000 || 31,300 || 18,500 || 30,700 || 57,000 || 52,500 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2008 || 162,000 || 37,700 || 25,000 || 39,100 || 65,500 || 61,400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010 || 210,000 || 48,000 || 30,300 || 47,500 || 97,800 || 98,400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2012 || 207,000 || 55,300 || 37,000 || 56,600 || 96,600 || 95,900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2014 || 191,000 || 56,100 || 41,000 || 61,400 || 96,100 || 93,500 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2016 || 168,000 || 55,700 || 41,300 || 61,200 || 85,800 || 85,200 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2017 || 174,000 || 54,500 || 40,900 || 59,500 || 79,300 || 81,500 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2018 || 136,000 || 50,200 || 39,500 || 54,500 || 71,400 || 75,100 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2019 || 116,000 || 44,500 || 39,300 || 49,000 || 65,900 || 63,700 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2020 || 85,800 || 37,300 || 32,900 || 49,500 || 52,300 || 60,500 |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hygiene tb.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Trends === | ||
| + | The comparative chart below shows {{w|Google Trends}} data for Hygiene (Topic) and Hygiene (Search term) from January 2004 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.<ref>{{cite web |title=Hygiene |url=https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=%2Fm%2F012sj0,Hygiene |website=Google Trends |access-date=26 February 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hygiene gt.png|thumb|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Ngram Viewer === | ||
| + | The chart below shows {{w|Google Ngram Viewer}} data for Hygiene from 1500 to 2019.<ref>{{cite web |title=Hygiene |url=https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=Hygiene&year_start=1500&year_end=2019&corpus=26&smoothing=3&case_insensitive=true |website=books.google.com |access-date=26 February 2021 |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hygiene ngram.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Wikipedia Views === | ||
| + | The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article {{w|Hygiene}} on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider,mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to January 2021. <ref>{{cite web |title=Hygiene |url=https://wikipediaviews.org/displayviewsformultiplemonths.php?page=Hygiene&allmonths=allmonths&language=en&drilldown=all |website=wikipediaviews.org |access-date=26 February 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hygiene wv.png|thumb|center|400px]] | ||
==Meta information on the timeline== | ==Meta information on the timeline== | ||
| Line 153: | Line 245: | ||
===What the timeline is still missing=== | ===What the timeline is still missing=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * {{w|School hygiene}} | ||
| + | * {{w|American School Hygiene Association}} | ||
===Timeline update strategy=== | ===Timeline update strategy=== | ||
| Line 161: | Line 256: | ||
* [[Timeline of water supply]] | * [[Timeline of water supply]] | ||
* [[Timeline of water treatment]] | * [[Timeline of water treatment]] | ||
| + | * [[Timeline of infection control]] | ||
| + | * [[Timeline of pollution]] | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 27 July 2023
This is a timeline of hygiene, attempting to describe important aspects of human hygiene. Toilet developent is covered on the timeline of sanitation.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| Ancient times | Soap is already produced in the Middle East. Thoothbrushing is already developed by civilizations in Egypt and Babylonia. Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the Roman civilization. |
| Middle Ages | Soap making becomes an established trade. In Europe, Purity of the soul is emphasized over the cleanliness of the outer[1], however, some scholars argue that people in Medieval Europe probably bathed more than people in the 19th century.[2]. In Japan, daily bathing becomes a common custom. In Iceland, pools warmed with water from hot springs are popular gathering places on Saturday evenings.[1] |
| 19th Century | Modern sanitation starts becoming adopted. By the end of the century, deodorants can be found in many forms, including roll-ins, powders, creams, pads, solid, and dabbers.[3] |
| 20th Century | Commercially-made shampoo becomes available from the turn of the century.[4] Between 1963 and 1998, approximately 3000 toothbrush patents are filed worldwide.[5] In the early 1980s, electronic bidets are introduced in Japan. In the late 1990s and early part of the 21st century, alcohol rub non-water-based hand hygiene agents (also known as alcohol-based hand rubs, antiseptic hand rubs, or hand sanitizers) begin to gain popularity. |
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | Present time country/location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3500 BC–3000 BC | Babylonians and the Egyptians already make toothbrushing tools by fraying the end of a twig. | ||
| 3000 BC | Dental hygiene | Ancient Egyptians develop an early form of toothbrush, a stick with one end flayed to soften the wood fibres. It is as well reported that Egyptians used tooth powder containing powdered ashes of ox hooves, myrrh, powdered burnt egg shells and pumice. Ancient Egyptians would also freshen their breath by chewing on fragrant mixtures with honey.[5][6] | Egypt |
| 2800 BC | Body hygiene | The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates from this time in ancient Babylon.[7] | |
| 2200 BC | Body hygiene | A formula for soap consisting of water, alkali, and cassia oil is written on a Babylonian clay tablet.[8] | |
| 1700 BC | Body hygiene | Palatial bathrooms with water supplied through terra cotta pipes are built in Knossos, Crete.[9] | Greece |
| 1600 BC–1550 BC | Publication | The Ebers papyrus, an ancient Egyptian medical compendium, describes the practice of combining oils with alkaline salts to form a soap-like material for treating skin diseases and for washing. The papyrus indicates that the ancient Egyptians bathed regularly. Egyptian documents also mention a soap-like substance was used in the preparation of wool for weaving.[10][11] | Egypt |
| 753 BC–476 AD | Body hygiene | Regular bathing is a distinctive feature of the Roman civilization.[12] | Italy |
| 600 BC | Body hygiene | The Phoenicians prepare soap from goat’s tallow and wood ashes.[10] | |
| 556–539 BC | Body hygiene | In the reign of Nabonidus, a recipe for soap consists of uhulu ashes, cypress oil and sesame seed oil "for washing the stones for the servant girls".[13] | |
| 500 BC | Body hygiene | Gentlemanly etiquette in China requires hand washing five times a day, hair washing every third day and a hot bath every fifth day.[9] | China |
| 460 BC – 377 BC | “Hygiene” becomes known as the branch of medicine dedicated to the "art of health," (as distinct from therapeutics, the treatment of disease).[14] | Greece | |
| 460 – 377 BC | Greek physician Hippocrates conceives hygiene as “an influence of atmosphere, soil, and water on human health”.[15] | Greece | |
| 312 BC | Body hygiene | In Rome, perfumed oils are used for bathing. Pumice and ashes are also rubbed over wet skin.[9] | Italy |
| 47 AD | Dental hygiene | Roman physician Scribonius Largus describes three different "toothpowder” mixtures, one containing vinegar, honey and salt; another with radish and finely ground glass; and a third using ground deer antler, a rare aromatic gum and rock salt. | |
| 100 – 200 AD | Body hygiene | Greek physician Galen recommends soap for cleaning and medicinal purposes.[10] | |
| 200 BC–450 AD | Several Hindu texts, such as the Manusmriti and the Vishnu Purana, describe elaborate codes of hygiene. Bathing is one of the five Nitya karmas (daily duties) in Hinduism, and not performing it leads to sin, according to some scriptures.[16] | India | |
| 300 – 500 SD | Body hygiene | Indian women use a turmeric cream with antiseptic properties as an alternative to soap.[9] | India |
| 500 – 600 AD | Body hygiene | Japanese Buddhism teaches that bathing purifies the body of sin and also brings luck.[9] | Japan |
| 600 – 700 AD | Body hygiene | The "Turkish Bath" or Hammam becomes a major feature of Islamic culture. The Quran requires cleanliness as an important part of Muslim faith: face, hand, forearm and feet washing before prayer, and whole body bathing after sex.[9] | |
| 600 – 700 AD | Body hygiene | Palestine, Iraq, Iran, Italy, Spain and France are the early centres of soapmaking, using vegetable and animal oils combined with ashes and fragrance.[10] | |
| 1000–1200 AD | Body hygiene | Bathing is essential to the Western European upper class. "The Cluniac monasteries to which they resorted or retired were always provided with bathhouses, and even the monks were required to take full immersion baths twice a year, at the two Christian festivals of renewal, though exhorted not to uncover themselves from under their bathing sheets."[17] | Europe |
| 1100s | Body hygiene | Soap is highly taxed in England. It is considered a luxury item and is not widely used.[10] | United Kingdom |
| 1240 | Publication | English physician Gilbertus Anglicus publishes his Compendium Medicinae, which contains descriptions of hygiene and the care of one's appearance.[2] | |
| 1400s | Dental hygiene | The first precursor of the modern toothbrush is thought to come from China or Egypt in this century. It has a bamboo or bone handle and bristles from the back of the neck of the wild boar, or from horsehair. This design would spread to Europe.[5] | |
| 1500s – 1600s | Body hygiene | “Dry cleaning”, the rubbing action of linen underclothing replaced bathing, is adopted in England. Underclothing is aired or laundered.[9] | |
| 1600s – 1700s | Body hygiene | Puritans in the United States prioritize cleanliness, with Sunday washing linked to spiritual cleansing. Cleanliness become linked to respectability and moral virtue.[9] | United States |
| 1710 | Body hygiene | The earliest reference to the bidet appears in Italy.[18] | Italy |
| 1791 | Body hygiene | French chemist Nicolas Leblanc patents the process for making soda ash, a major component of soap, from table salt.[10] | |
| 1800 | Hair care | Early colonial traders in India discover hair and body massage, called shampoo, and introduce “champing” to Europe.[1] | India |
| 1815 | Dental hygiene | American dentist Dr. Levi Spear Parmly introduces the idea of using waxed silken thread as floss. Later in his career, Parmly would publish A Practical Guide to the Management of Teeth, emphasizing the importance of brushing and flossing daily.[19][20] | United States |
| 1823 | Body hygiene | French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul reveals the chemical process of soap by showing how boiling fat with an alkali salt splits the fat molecule into the alkali salt of fatty acid (soap) and glycerol.[21] | |
| 1824 | Dental hygiene | Dr Peabody, a dentist, introduces a soap-containing toothpaste.[22] | |
| 1844 | Dental hygiene | The first 3-row brush is designed.[5] | |
| 1847 | Body Hygiene | Hungarian obstetrician Ignaz Semmelweis urges doctors at Vienna General Hospital to wash their hands. Prior to this, physicians weren't aware of the spread of infections due to lack of hand washing.[23] | Austria |
| 1853 | Body hygiene | English soap tax is abolished. Soap becomes widely used and is described by German chemist Justus von Liebig as an accurate measure of a country’s wealth and civilization.[10] | |
| 1857 | Anal cleansing | Toilet paper comes on sale in the United States, at first being sold in sheets.[24][25] | United States |
| 1861 | Publication | Ignaz Semmelweis in Budapest publishes Die Aetiologie, der Begriff und die Prophylaxis des Kindbettfiebers (“The Etiology, the Concept, and the Prophylaxis of Childbed Fever”), in which he explains his theories on childbed fever, and the ways to avoid spreading it by means of vigorous hand-washing.[23] | Hungary |
| 1874 | Dental hygiene | The first patent for dental floss is granted to Asahel M. Shurtleff for what is described as "an improved pocket thread carrier and cutter" that resembles modern floss packages.[20] | |
| 1880s | Dental hygiene | Toothpaste is mass produced in jars in the United States, based on Dr Sheffield’s "Crème Dentifrice” invention of 1850.[22] | |
| 1882 | Dental hygiene | Mass production of unwaxed silk floss begins in the United States.[26] | |
| 1888 | Body hygiene | The first cosmetic deodorant, a paste made from zinc chloride and wax, is patented under the name ‘Mum’.[27] | |
| 1890 | Anal cleansing | Toilet paper is first sold in rolls in the United States.[25] | United States |
| 1890s | Body hygiene | Aluminium chloride is added to deodorants to reduce sweating.[27] | |
| 1890s | Dental hygiene | Toothpaste is sold in collapsible tubes.[22] | |
| 1898 | Dental hygiene | The first dental floss patent is awarded in the United States.[26][19] | United States |
| 1898 | Hair care | German chemist Hans Schwarzkopf in BErlin opens a drugstore dedicated to perfume and focuses his efforts on products for the hair. His popular water-soluble, powder shampoo still causes dulling, alkaline reactions.[1] | Germany |
| 1914 | Hair care | British hair stylist Kasey Hebert in London invents the first commercial shampoo.[1][4] | United Kingdom |
| 1927 | Hair care | Hans Schwarzkopf introduces one of the world’s premiere liquid shampoos.[4] | Germany |
| 1928 | Anal cleansing | Toilet paper is first sold in rolls in Europe.[25] | Europe |
| 1930 | Hair care | Shampoo as we know it today (with synthetic surfactants) is first introduced.[4][1] | |
| 1939 | Dental hygiene | The first electric toothbrush is developed in Switzerland.[5][28] | Switzerland |
| 1940s | Dental hygiene | Dr. Charles C. Bass creates a more shred-resistant nylon floss as a substitute for silk floss, thus promoting teeth flossing as an important part of oral hygiene.[20] | |
| 1942 | Anal cleansing | Soft toilet paper comes on sale.[25] | |
| 1945 | Dental hygiene | Soap is replaced by other ingredients in the making of toothpaste, following the invention of synthetic detergents, making toothpastes smoother.[22] | |
| 1950s | Manufacturers start introducing aerosol technology.[3] | ||
| 1952 | The first roll-on deodorant, based on the design of the ballpoint pen, is marketed in the United States.[27] | United States | |
| 1952 | Journal | The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene is formed.[29] | United States |
| 1965 | Body hygiene | The first anti-perspirant aerosol is launched to the market.[27] | |
| 1975–1980 | Sleep hygiene is developed as a recommended behavioral and environmental practice intended to promote better quality sleep. This recommendation is thought as a method to help people with mild to moderate insomnia. However, as of 2014, the evidence for effectiveness of individual recommendations is "limited and inconclusive".[30] | ||
| 1980 | Anal cleansing | Japanese electric toilet Washlet, with water spray feature for genital and anal cleansing, is released to the market.[31] | Japan |
| 1980s | Dental hygiene | The interdental brush is invented as an alternative to flossing.[19] | |
| 1985–1990 | Hand hygiene | Automatic faucets are introduced for commercial use.[32] | |
| 1989 | British epidemiologist David P. Strachan develops the hygiene hypothesis, which states that there is an inverse relationship between family size and development of atopic allergic disorders – the more children in a family, the less likely they are to develop these allergies.[33][34] | ||
| 1990 | Publication | The WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme for Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygiene (JMP) starts producing regular estimates of national, regional and global progress on drinking water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH).[35] | |
| 1996 | Body hygiene | About 141 million people visit Japan’s 15,700 hot-spring inns during the year (out of a Japanese population of 125 million).[9] | Japan |
| 2000 | Statistics | 1229 million people worldwide practice open defecation.[35] | |
| 2008 | Hand hygiene | The Global Handwashing Day is initiated by the Public Private Partnership for Handwashing (PPPHW) in August 2008 at the annual World Water Week in Stockholm.[36] | Sweden |
| 2009 | Hand hygiene | The World Health Organization launches its New global Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care, developed with assistance from more than 100 renowned international experts. Also tested and given trials in different parts of the world.[37] | |
| 2015 | Statistics | 892 million people practice open defecation.[35] | |
| 2015 | Statistics | Study of handwashing in 54 countries finds that on average, 38.7% of households practice handwashing with soap.[38] | |
| 2016 | Anal cleansing | Bidet toilets are installed in 81.2% of Japanese households.[39] | Japan |
| 2018 | Scientific development | Study by the University of Connecticut School of Medicine shows that dryers sucking in bacteria and faecal particles from flushing toilets can spread it onto users' recently washed hands.[40] | United States |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
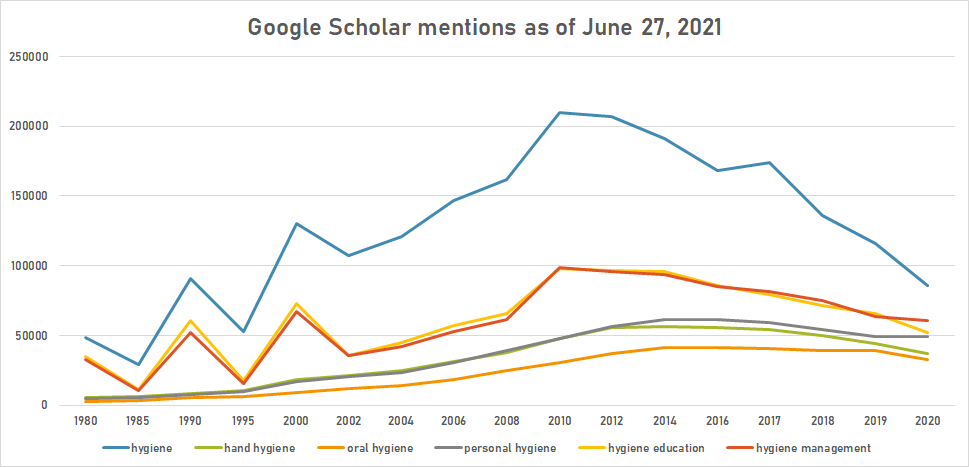
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of June 27, 2021.
| Year | hygiene | hand hygiene | oral hygiene | personal hygiene | hygiene education | hygiene management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 48,500 | 5,560 | 2,830 | 4,440 | 35,100 | 32,600 |
| 1985 | 28,800 | 5,940 | 3,450 | 5,290 | 11,500 | 10,400 |
| 1990 | 90,400 | 8,460 | 5,280 | 7,580 | 60,800 | 51,900 |
| 1995 | 52,600 | 10,500 | 6,080 | 9,840 | 17,600 | 15,300 |
| 2000 | 130,000 | 18,300 | 9,380 | 17,000 | 72,600 | 67,000 |
| 2002 | 107,000 | 21,100 | 11,600 | 20,300 | 35,600 | 35,900 |
| 2004 | 121,000 | 25,000 | 14,400 | 23,700 | 45,200 | 42,100 |
| 2006 | 147,000 | 31,300 | 18,500 | 30,700 | 57,000 | 52,500 |
| 2008 | 162,000 | 37,700 | 25,000 | 39,100 | 65,500 | 61,400 |
| 2010 | 210,000 | 48,000 | 30,300 | 47,500 | 97,800 | 98,400 |
| 2012 | 207,000 | 55,300 | 37,000 | 56,600 | 96,600 | 95,900 |
| 2014 | 191,000 | 56,100 | 41,000 | 61,400 | 96,100 | 93,500 |
| 2016 | 168,000 | 55,700 | 41,300 | 61,200 | 85,800 | 85,200 |
| 2017 | 174,000 | 54,500 | 40,900 | 59,500 | 79,300 | 81,500 |
| 2018 | 136,000 | 50,200 | 39,500 | 54,500 | 71,400 | 75,100 |
| 2019 | 116,000 | 44,500 | 39,300 | 49,000 | 65,900 | 63,700 |
| 2020 | 85,800 | 37,300 | 32,900 | 49,500 | 52,300 | 60,500 |
Google Trends
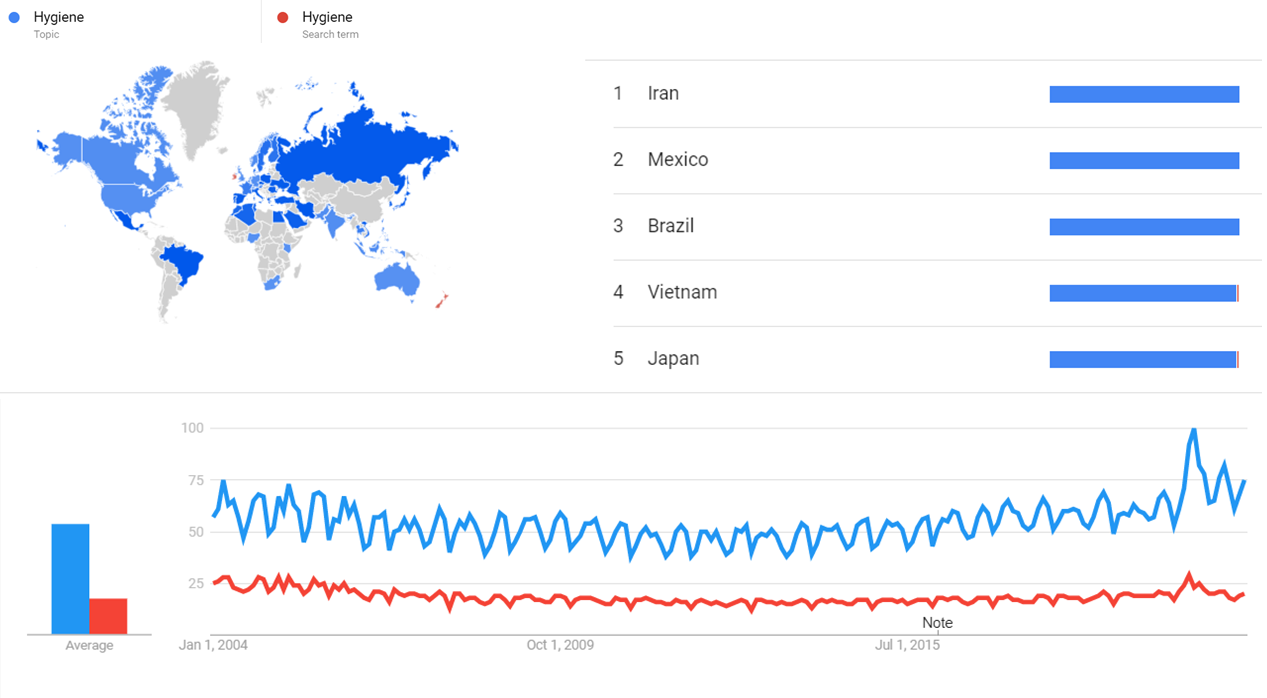
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for Hygiene (Topic) and Hygiene (Search term) from January 2004 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[41]
Google Ngram Viewer
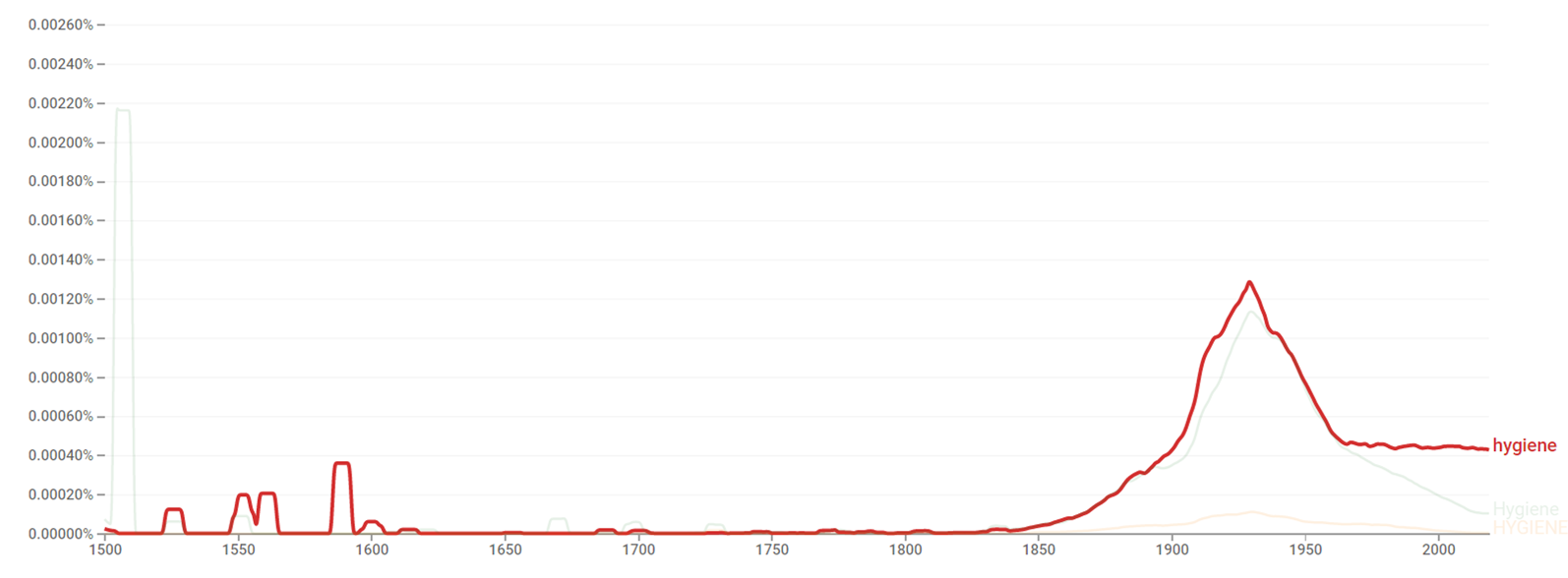
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Hygiene from 1500 to 2019.[42]
Wikipedia Views
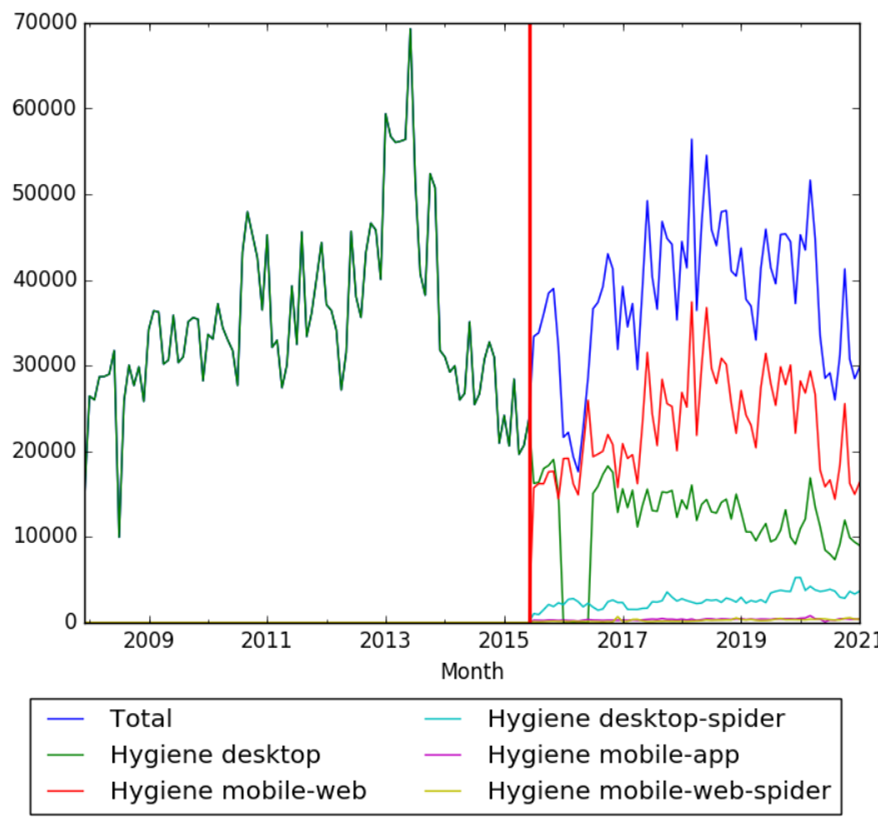
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Hygiene on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider,mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to January 2021. [43]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
- Timeline of sanitation
- Timeline of water supply
- Timeline of water treatment
- Timeline of infection control
- Timeline of pollution
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "The History of Shampoo". hairstory.com. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Thorndike, Tales of the Middle Ages - Daily Life". Gode Cookery. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Deodorants History - Invention of the Deodorant". historyofcosmetics.net. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Shampoo: Taking the sting out of childhood". independentpharmacist.co.uk. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "A brief history of…THE TOOTHBRUSH". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "History of Toothbrushes". colgateprofessional.com. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ Willcox, Michael (2000). "Soap". In Hilda Butler. Poucher's Perfumes, Cosmetics and Soaps (10th ed.). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers. p. 453. ISBN 0-7514-0479-9.
The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates back to around 2800 BCE in ancient Babylon.
- ↑ Birnbaum, David. Jews, Church & Civilization, Volume I. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 "SNAPSHOTS OF BATHING". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 A brief history of…SOAP. "A brief history of…SOAP". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "The earliest recorded evidence of the production of soap-like materials dates back to around 2800 BC in ancient Babylon. A formula for soap consisting of water, alkali, and cassia oil was written on a Babylonian clay tablet around 2200 BC.". heritagedaily.com. Retrieved 20 September 2017.
- ↑ "Roman bath houses". Time Team. Channel Four Television Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 February 2007.
- ↑ Noted in Levey, Martin (1958). "Gypsum, salt and soda in ancient Mesopotamian chemical technology". Isis. 49 (3): 336–342 (341). JSTOR 226942. doi:10.1086/348678.
- ↑ "SNAPSHOTS OF PUBLIC SANITATION". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 23 September 2017.
- ↑ Pappas, Georgios. "Insights into infectious disease in the era of Hippocrates". International Journal of Infectious Diseases. Retrieved 10 August 2017.
- ↑ "Aryan Code of Toilets (2nd Century AD)". Sulabh International Museum of Toilets.
- ↑ Philippe Braunstein "Solitude: eleventh to thirteenth century", in Georges Duby, ed. A History of Private Life: II. Revelations of the Medieval World 1988:525
- ↑ "Bidets for Beginners". italymagazine.com. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 "A Brief History of Dental Floss". speareducation.com. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Who Invented Dental Floss?". wonderopolis.org. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ "Michel-Eugène Chevreul". britannica.com. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "A brief history of…TOOTHPASTE". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "In 1850, Ignaz Semmelweis saved lives with three words: wash your hands". pbs.org. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ↑ Panati, Charles. Panati's Extraordinary Origins of Everyday Things. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 "A BRIEF HISTORY OF TOILETS". localhistories.org. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "A brief history of…DENTAL FLOSS". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 27.3 "A brief history of…DEODORANT". hygieneforhealth.org.au. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ "A Brief History of Dentistry". dentistsnearby.com. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ↑ Cole, Jim; Stankus, Tony. Journals of the Century.
- ↑ Irish, Leah A.; Kline, Christopher E; Gunn, Heather E; Buysse, Daniel J; Hall, Martica H (October 2014). "The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence". Sleep Medicine Reviews. 22: 23–36. PMC 4400203
 . PMID 25454674. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001.
. PMID 25454674. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001.
- ↑ Akbar, Adhiutama; Seiichi, Yoshikubo. "363 Diffusion of Electronic Bidet Toilet in Japan Case Study: TOTO Washlet" (PDF). itb.ac.id. Management of Technology Program, Shibaura Institute of Technology, Japan. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ "Introduction of Automatic Faucets". archive.org. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ Bloomfield, SF; et al. "Too clean, or not too clean: the Hygiene Hypothesis and home hygiene". PMC 1448690
 . Retrieved 9 August 2017.
. Retrieved 9 August 2017.
- ↑ Strachan, DP (August 2000). "Family size, infection and atopy: the first decade of the 'hygiene hypothesis'". Thorax. 55 (1): S2–S10. PMC 1765943
 .
.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 "Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2017" (PDF). who.int. Retrieved 8 August 2017.
- ↑ "The Global Public Private Partnership for Handwashing – Our History". The Global Public Private Partnership for Handwashing. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ "a WHO Guidelines on Hand Hygiene in Health Care: a Summary" (PDF). who.int. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- ↑ "JMP handwashing dataset". Retrieved 28 September 2017.
WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) for Water Supply and Sanitation
- ↑ "平成28年3月実施調査結果:消費動向調査" [March 2016 consumer spending survey]. Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. March 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-06-23.
- ↑ "Bathroom hand dryers may be blowing bacteria and faeces all over you, study suggests". irishexaminer.com. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ↑ "Hygiene". Google Trends. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ↑ "Hygiene". books.google.com. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- ↑ "Hygiene". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 26 February 2021.