Difference between revisions of "Timeline of gene therapy"
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This is a '''timeline of {{w|gene therapy}}'''. | + | This is a '''timeline of {{w|gene therapy}}''', attempting to describe significant events in the development of the field. |
==Big picture== | ==Big picture== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
! Year !! Event type !! Details !! Location | ! Year !! Event type !! Details !! Location | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1928 || || British bacteriologist {{w|Frederick Griffith}} describes the [[w:Griffith's experiment|transforming principle]].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Renneberg |first1=Reinhard |last2=Berkling |first2=Viola |last3=Loroch |first3=Vanya |title=Biotechnology for Beginners |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=r_BeBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA72&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Tmh |title=Target 2011: Biology 12 |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=aGJjU1wNF30C&pg=PA147&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Chamary |first1=JV |title=50 Biology Ideas You Really Need to Know |edition= |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Kr2xCAAAQBAJ&pg=PT69&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEINjAC#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | + | | 1928 || Field development || British bacteriologist {{w|Frederick Griffith}} describes the [[w:Griffith's experiment|transforming principle]].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Renneberg |first1=Reinhard |last2=Berkling |first2=Viola |last3=Loroch |first3=Vanya |title=Biotechnology for Beginners |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=r_BeBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA72&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Tmh |title=Target 2011: Biology 12 |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=aGJjU1wNF30C&pg=PA147&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Chamary |first1=JV |title=50 Biology Ideas You Really Need to Know |edition= |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Kr2xCAAAQBAJ&pg=PT69&dq=1928+British+bacteriologist+Frederick+Griffith+describes+the+transforming+principle.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwik7frzx5HeAhUDIpAKHXo9DsUQ6AEINjAC#v=onepage&q=1928%20British%20bacteriologist%20Frederick%20Griffith%20describes%20the%20transforming%20principle.&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1944 || || {{w|Oswald Avery}}, {{w|Colin MacLeod}}, and {{w|Maclyn McCarty}} describe that genetic information is carried in the form of {{w|DNA}}. The team finds that a {{w|gene}} is a part of {{w|DNA}} itself. This experimental demonstration is later called {{w|Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Ohya |first1=Masanori |last2=Watanabe |first2=Noboru |title=Selected Papers of M. Ohya |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=cXBpDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA368&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEILTAB#v=onepage&q=1944%20Avery%2C%20MacLeod%20and%20McCarty%20describe%20that%20genetic%20information%20is%20carried%20in%20the%20form%20of%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Principles and Applications of Molecular Diagnostics |edition=Nader Rifai, A. Rita Horvath, Carl T. Wittwer, Jason Park |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=nV1gDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA35&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEINDAC#v=onepage&q=1944%20Avery%2C%20MacLeod%20and%20McCarty%20describe%20that%20genetic%20information%20is%20carried%20in%20the%20form%20of%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Hoffee |first1=P. A. |title=Medical Molecular Genetics, Volume 698 |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=ssBqAAAAMAAJ&q=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEIVzAI}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1944 || Field development || {{w|Oswald Avery}}, {{w|Colin MacLeod}}, and {{w|Maclyn McCarty}} describe that genetic information is carried in the form of {{w|DNA}}. The team finds that a {{w|gene}} is a part of {{w|DNA}} itself. This experimental demonstration is later called {{w|Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Ohya |first1=Masanori |last2=Watanabe |first2=Noboru |title=Selected Papers of M. Ohya |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=cXBpDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA368&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEILTAB#v=onepage&q=1944%20Avery%2C%20MacLeod%20and%20McCarty%20describe%20that%20genetic%20information%20is%20carried%20in%20the%20form%20of%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Principles and Applications of Molecular Diagnostics |edition=Nader Rifai, A. Rita Horvath, Carl T. Wittwer, Jason Park |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=nV1gDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA35&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEINDAC#v=onepage&q=1944%20Avery%2C%20MacLeod%20and%20McCarty%20describe%20that%20genetic%20information%20is%20carried%20in%20the%20form%20of%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Hoffee |first1=P. A. |title=Medical Molecular Genetics, Volume 698 |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=ssBqAAAAMAAJ&q=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&dq=1944+Avery,+MacLeod+and+McCarty+describe+that+genetic+information+is+carried+in+the+form+of+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiInfKYkZ7eAhUEHpAKHQJHBlUQ6AEIVzAI}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1952 || || American molecular biologist {{w|Joshua Lederberg}} introduces [[W:Transduction (genetics)|transduction]] as a mechanism of genetic transfer.<ref>{{cite book |title=Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications |edition=P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Rxn1AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA379&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjqLvsyJHeAhWHW5AKHX0hBaUQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1952%20Joshua%20Lederberg%20introduces%20transduction%20as%20a%20mechanism%20of%20genetic%20transfer.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Maheshwari |first1=D.K. |title=A Textbook of Microbiology |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=WDIrDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA210&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg++transduction&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiUzpLLyZHeAhVHf5AKHRhiBpMQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1952%20Joshua%20Lederberg%20%20transduction&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Snyder |first1=Larry |last2=Champness |first2=Wendy |title=Molecular Genetics of Bacteria |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=IDtsAAAAMAAJ&q=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjqLvsyJHeAhWHW5AKHX0hBaUQ6AEITDAG}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1952 || Field development || American molecular biologist {{w|Joshua Lederberg}} introduces [[W:Transduction (genetics)|transduction]] as a mechanism of genetic transfer.<ref>{{cite book |title=Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications |edition=P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Rxn1AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA379&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjqLvsyJHeAhWHW5AKHX0hBaUQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1952%20Joshua%20Lederberg%20introduces%20transduction%20as%20a%20mechanism%20of%20genetic%20transfer.&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Maheshwari |first1=D.K. |title=A Textbook of Microbiology |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=WDIrDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA210&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg++transduction&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiUzpLLyZHeAhVHf5AKHRhiBpMQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=1952%20Joshua%20Lederberg%20%20transduction&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Snyder |first1=Larry |last2=Champness |first2=Wendy |title=Molecular Genetics of Bacteria |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=IDtsAAAAMAAJ&q=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&dq=1952+Joshua+Lederberg+introduces+transduction+as+a+mechanism+of+genetic+transfer.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjjqLvsyJHeAhWHW5AKHX0hBaUQ6AEITDAG}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1953 || || American molecular biologist {{w|James Watson}} and British molecular biologist {{w|Francis Crick}} identify the double-stranded structure of the {{w|DNA}}.<ref name="Gene therapy">{{cite web |title=Gene therapy |url=http://www.medlink.com/article/gene_therapy |website=medlink.com |accessdate=15 October 2018}}</ref> || | + | | 1953 || Field development || American molecular biologist {{w|James Watson}} and British molecular biologist {{w|Francis Crick}} identify the double-stranded structure of the {{w|DNA}}.<ref name="Gene therapy">{{cite web |title=Gene therapy |url=http://www.medlink.com/article/gene_therapy |website=medlink.com |accessdate=15 October 2018}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1961 || || American virologist {{w|Howard Martin Temin}} discovers that genetic mutation could be inherited as a result of virus infection.<ref>{{cite book |title=Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications |edition=P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Rxn1AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA379&dq=1961+Howard+Temin+discovers+that+genetic+mutation+could+be+inherited+as+a+result+of+virus+infection&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj2j6Kt1JHeAhWEkJAKHYqoB3gQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=1961%20Howard%20Temin%20discovers%20that%20genetic%20mutation%20could%20be%20inherited%20as%20a%20result%20of%20virus%20infection&f=false}}</ref> || | + | | 1961 || Field development || American virologist {{w|Howard Martin Temin}} discovers that genetic mutation could be inherited as a result of virus infection.<ref>{{cite book |title=Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications |edition=P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Rxn1AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA379&dq=1961+Howard+Temin+discovers+that+genetic+mutation+could+be+inherited+as+a+result+of+virus+infection&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwj2j6Kt1JHeAhWEkJAKHYqoB3gQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=1961%20Howard%20Temin%20discovers%20that%20genetic%20mutation%20could%20be%20inherited%20as%20a%20result%20of%20virus%20infection&f=false}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1961 || || Scientists first manage to incorporate functional DNA inside human cells in vivo.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today"/> || | + | | 1961 || Field development || Scientists first manage to incorporate functional DNA inside human cells in vivo.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1962 || || The possibility of gene therapy is speculated.<ref name="Gene therapy"/><ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer">{{cite book |last1=Wolff |first1=Jon A. |title=Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Xu_iBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA6&lpg=PA6&dq=1962(Lederberg+1968)+Possibility+of+gene+therapy+is+speculated&source=bl&ots=9klQHoV7cl&sig=Nu3ZlBNlfRSe0PG8kug_2ahajqY&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjr95yg5I3eAhXMIpAKHdf3AZMQ6AEwCnoECAEQAQ#v=onepage&q=1962(Lederberg%201968)%20Possibility%20of%20gene%20therapy%20is%20speculated&f=false}}</ref> || | + | | 1962 || Field development || The possibility of gene therapy is speculated.<ref name="Gene therapy"/><ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer">{{cite book |last1=Wolff |first1=Jon A. |title=Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Xu_iBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA6&lpg=PA6&dq=1962(Lederberg+1968)+Possibility+of+gene+therapy+is+speculated&source=bl&ots=9klQHoV7cl&sig=Nu3ZlBNlfRSe0PG8kug_2ahajqY&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjr95yg5I3eAhXMIpAKHdf3AZMQ6AEwCnoECAEQAQ#v=onepage&q=1962(Lederberg%201968)%20Possibility%20of%20gene%20therapy%20is%20speculated&f=false}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1962 || || Polish professor {{w|Wacław Szybalski}} coins the term {{w|gene therapy}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Twyman |first1=Richard |title=Gene Transfer to Animal Cells |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Wl56AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA31&lpg=PA31&dq=%22in+1962%22+%22Waclaw+Szybalski%22++gene+transfer+in+mammalian+cell+lines&source=bl&ots=O-AllUNFwj&sig=O-WfkDRB2Zzzhe_k3AaFTASahHU&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiEyM3-5ZHeAhXBDpAKHWMRAmAQ6AEwA3oECAUQAQ#v=onepage&q=%22in%201962%22%20%22Waclaw%20Szybalski%22%20%20gene%20transfer%20in%20mammalian%20cell%20lines&f=false}}</ref> || | + | | 1962 || Field development || Polish professor {{w|Wacław Szybalski}} coins the term {{w|gene therapy}}.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Twyman |first1=Richard |title=Gene Transfer to Animal Cells |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Wl56AgAAQBAJ&pg=PA31&lpg=PA31&dq=%22in+1962%22+%22Waclaw+Szybalski%22++gene+transfer+in+mammalian+cell+lines&source=bl&ots=O-AllUNFwj&sig=O-WfkDRB2Zzzhe_k3AaFTASahHU&hl=en&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwiEyM3-5ZHeAhXBDpAKHWMRAmAQ6AEwA3oECAUQAQ#v=onepage&q=%22in%201962%22%20%22Waclaw%20Szybalski%22%20%20gene%20transfer%20in%20mammalian%20cell%20lines&f=false}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1968 || || Early attempts at use of viral vectors.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> Rogers and Pfuderer demonstrate a proof-of-concept for virus mediated gene transfer.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Prazeres |first1=Duarte Miguel F. |title=Plasmid Biopharmaceuticals: Basics, Applications, and Manufacturing |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=CJHIlrsQDgEC&pg=PT25&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEINTAD#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer |edition=Jon A. Wolff |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Xu_iBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA14&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEILDAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=The Development of Human Gene Therapy |edition=Theodore Friedmann |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=KGMGpNVpwnIC&pg=PA3&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref> || | + | | 1968 || Application || Early attempts at use of viral vectors.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> Rogers and Pfuderer demonstrate a proof-of-concept for virus mediated gene transfer.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Prazeres |first1=Duarte Miguel F. |title=Plasmid Biopharmaceuticals: Basics, Applications, and Manufacturing |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=CJHIlrsQDgEC&pg=PT25&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEINTAD#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer |edition=Jon A. Wolff |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=Xu_iBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA14&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEILDAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=The Development of Human Gene Therapy |edition=Theodore Friedmann |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=KGMGpNVpwnIC&pg=PA3&dq=%22in+1968%22+Rogers+and+Pfuderer&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwieod76kp7eAhUCk5AKHTZLDWUQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=%22in%201968%22%20Rogers%20and%20Pfuderer&f=false}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1969 || || Aposhian proposes the use of pseudoviruses derived from the mouse virus, {{w|polyoma}}.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> || | + | | 1969 || Application || Aposhian proposes the use of pseudoviruses derived from the mouse virus, {{w|polyoma}}.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1970 || || {{w|Howard Martin Temin}} and {{w|David Baltimore}} discover {{w|reverse transcriptase}}, an enzyme used to generate {{w|complementary DNA}} (cDNA) from an {{w|RNA}} template.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Varmus |first1=Harold |title=The Art and Politics of Science |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=l8OcAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA60&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEIOjAD#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Pennington |first1=T. H. |title=Molecular Virology |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=iaLIAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA60&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEINDAC#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Snustad |first1=D. Peter |last2=Simmons |first2=Michael J. |title=Principles of Genetics, Binder Ready Version |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=NBB0CgAAQBAJ&pg=RA1-PA12&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEILTAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | + | | 1970 || Field development || {{w|Howard Martin Temin}} and {{w|David Baltimore}} discover {{w|reverse transcriptase}}, an enzyme used to generate {{w|complementary DNA}} (cDNA) from an {{w|RNA}} template.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Varmus |first1=Harold |title=The Art and Politics of Science |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=l8OcAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA60&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEIOjAD#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Pennington |first1=T. H. |title=Molecular Virology |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=iaLIAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA60&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEINDAC#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Snustad |first1=D. Peter |last2=Simmons |first2=Michael J. |title=Principles of Genetics, Binder Ready Version |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=NBB0CgAAQBAJ&pg=RA1-PA12&dq=%22in+1970%22+Discovery+of+reverse+transcriptase.+Copying+of+RNA+into+DNA&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiE35W2lJ7eAhWHUZAKHbchA64Q6AEILTAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201970%22%20Discovery%20of%20reverse%20transcriptase.%20Copying%20of%20RNA%20into%20DNA&f=false}}</ref><ref name="Gene therapy"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1971 || || A symposium on {{w|gene therapy}} is sponsored by the National Institute of Neuologic Disease and Stroke at the NIH and the Fogarty International Center.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> || | | 1971 || || A symposium on {{w|gene therapy}} is sponsored by the National Institute of Neuologic Disease and Stroke at the NIH and the Fogarty International Center.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1972 || || Professor Theodore Friedmann and his colleague Richard Roblin, from the {{w|University of California, San Diego}}, discuss gene therapy in an article published in ''[[w:Science (journal)|Science]]''.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> They suggest that transforming viruses could be used for therapeutic gene transfer.<ref name="Gene therapy"/><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy">{{cite web |title=TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/health-genetherapy-timeline/timeline-milestones-in-gene-therapy-idUSL5N0XK41J20150427 |website=reuters.com |accessdate=15 October 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Tramper |first1=J. |last2=Zhu |first2=Yang |title=Modern Biotechnology: Panacea or new Pandora's box? |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=WTS7BQAAQBAJ&pg=PA192&dq=%22in+1972%22+Friedmann+and+Roblin&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjZyf3zl57eAhWDIJAKHQw4DCQQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201972%22%20Friedmann%20and%20Roblin&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Shapiro |first1=Irving M. |last2=Risbud |first2=Makarand V. |title=The Intervertebral Disc: Molecular and Structural Studies of the Disc in Health and Disease |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=ixC7BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA385&dq=%22in+1972%22+Friedmann+and+Roblin&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjZyf3zl57eAhWDIJAKHQw4DCQQ6AEINTAC#v=onepage&q=%22in%201972%22%20Friedmann%20and%20Roblin&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1972 || Field development || Professor Theodore Friedmann and his colleague Richard Roblin, from the {{w|University of California, San Diego}}, discuss gene therapy in an article published in ''[[w:Science (journal)|Science]]''.<ref name="Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer"/> They suggest that transforming viruses could be used for therapeutic gene transfer.<ref name="Gene therapy"/><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy">{{cite web |title=TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/health-genetherapy-timeline/timeline-milestones-in-gene-therapy-idUSL5N0XK41J20150427 |website=reuters.com |accessdate=15 October 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Tramper |first1=J. |last2=Zhu |first2=Yang |title=Modern Biotechnology: Panacea or new Pandora's box? |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=WTS7BQAAQBAJ&pg=PA192&dq=%22in+1972%22+Friedmann+and+Roblin&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjZyf3zl57eAhWDIJAKHQw4DCQQ6AEILjAB#v=onepage&q=%22in%201972%22%20Friedmann%20and%20Roblin&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Shapiro |first1=Irving M. |last2=Risbud |first2=Makarand V. |title=The Intervertebral Disc: Molecular and Structural Studies of the Disc in Health and Disease |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=ixC7BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA385&dq=%22in+1972%22+Friedmann+and+Roblin&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjZyf3zl57eAhWDIJAKHQw4DCQQ6AEINTAC#v=onepage&q=%22in%201972%22%20Friedmann%20and%20Roblin&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 1973 || Field development || Graham and van der Erb introduce calcium phosphate {{w|transfection}}.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 1973 || Field development || Graham and van der Erb introduce calcium phosphate {{w|transfection}}.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
| 1983 || Field development || A group of scientists from {{w|Baylor College of Medicine}} in {{w|Houston}}, {{w|Texas}}, propose that gene therapy could one day be a viable approach for treating {{w|Lesch-Nyhan disease}}, a rare neurological disorder.<ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy">{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/medicine/divisions-diagnostics-and-procedures/medicine/gene-therapy |website=encyclopedia.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | | 1983 || Field development || A group of scientists from {{w|Baylor College of Medicine}} in {{w|Houston}}, {{w|Texas}}, propose that gene therapy could one day be a viable approach for treating {{w|Lesch-Nyhan disease}}, a rare neurological disorder.<ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy">{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/medicine/divisions-diagnostics-and-procedures/medicine/gene-therapy |website=encyclopedia.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1983 || || Scientists at the {{w|Massachussets Institute of Technology}} create the first retroviral vector suitable for use in gene therapy from a mouse leukemia virus.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today">{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today |url=https://premier-research.com/perspectives-gene-therapy-101-1960s-today/ |website=premier-research.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1983 || Field development || Scientists at the {{w|Massachussets Institute of Technology}} create the first retroviral vector suitable for use in gene therapy from a mouse leukemia virus.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today">{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today |url=https://premier-research.com/perspectives-gene-therapy-101-1960s-today/ |website=premier-research.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 1984 || Field development || Experiment shows that targeted insertion of corrective {{w|DNA}} is possible in {{w|mammalian cell}}s in vitro.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today"/> || | | 1984 || Field development || Experiment shows that targeted insertion of corrective {{w|DNA}} is possible in {{w|mammalian cell}}s in vitro.<ref name="Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today"/> || | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
| 1984 || Field development || Izant and Weintraub first demonstrate that antisense nucleic acid can be used to downregulate {{w|gene expression}}.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 1984 || Field development || Izant and Weintraub first demonstrate that antisense nucleic acid can be used to downregulate {{w|gene expression}}.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1984 || || A retrovirus vector system is designed that could efficiently insert foreign genes into mammalian chromosomes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cepko CL, Roberts BE, Mulligan RC | title = Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector | journal = Cell | volume = 37 | issue = 3 | pages = 1053–62 | date = July 1984 | pmid = 6331674 | doi = 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9 }}</ref> || | + | | 1984 || Field development || A retrovirus vector system is designed that could efficiently insert foreign genes into mammalian chromosomes.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cepko CL, Roberts BE, Mulligan RC | title = Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector | journal = Cell | volume = 37 | issue = 3 | pages = 1053–62 | date = July 1984 | pmid = 6331674 | doi = 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9 }}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1987 || Field development || Hoffman et al identify {{w|dystrophin}}, the protein product of Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene (basis of future gene therapy of this disorder).<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 1987 || Field development || Hoffman et al identify {{w|dystrophin}}, the protein product of Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene (basis of future gene therapy of this disorder).<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1988 || Literature || Eve K. Nichols publishes ''Human Gene Therapy''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Human Gene Therapy, Issue 617 |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Human_Gene_Therapy.html?id=MvunBZ0JKswC&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |website=books.google.com.ar |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1989 || Field development || The first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the United States {{w|National Institutes of Health}}, is conducted by American cancer researcher {{w|Steven A. Rosenberg}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rosenberg SA, Aebersold P, Cornetta K, Kasid A, Morgan RA, Moen R, Karson EM, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Topalian SL | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene transfer into humans--immunotherapy of patients with advanced melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes modified by retroviral gene transduction | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 323 | issue = 9 | pages = 570–8 | date = August 1990 | pmid = 2381442 | doi = 10.1056/NEJM199008303230904 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=March |first1=Keith L. |title=Gene Transfer in the Cardiovascular System: Experimental Approaches and Therapeutic Implications |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=aj8NVf_0f54C&pg=PA4&dq=Steven+A.+Rosenberg+%22in+1989%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi_xpTqzpHeAhVDF5AKHa4OAWAQ6AEIPzAE#v=onepage&q=Steven%20A.%20Rosenberg%20%22in%201989%22&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Barh |first1=Debmalya |last2=Azevedo |first2=Vasco |title=Omics Technologies and Bio-engineering: Volume 1: Towards Improving Quality of Life |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=9klkCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA509&dq=Steven+A.+Rosenberg+%22in+1989%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiY_IjazpHeAhXCH5AKHZqMD0oQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=Steven%20A.%20Rosenberg%20%22in%201989%22&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | | 1989 || Field development || The first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the United States {{w|National Institutes of Health}}, is conducted by American cancer researcher {{w|Steven A. Rosenberg}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Rosenberg SA, Aebersold P, Cornetta K, Kasid A, Morgan RA, Moen R, Karson EM, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Topalian SL | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene transfer into humans--immunotherapy of patients with advanced melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes modified by retroviral gene transduction | journal = The New England Journal of Medicine | volume = 323 | issue = 9 | pages = 570–8 | date = August 1990 | pmid = 2381442 | doi = 10.1056/NEJM199008303230904 }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=March |first1=Keith L. |title=Gene Transfer in the Cardiovascular System: Experimental Approaches and Therapeutic Implications |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=aj8NVf_0f54C&pg=PA4&dq=Steven+A.+Rosenberg+%22in+1989%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi_xpTqzpHeAhVDF5AKHa4OAWAQ6AEIPzAE#v=onepage&q=Steven%20A.%20Rosenberg%20%22in%201989%22&f=false}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Barh |first1=Debmalya |last2=Azevedo |first2=Vasco |title=Omics Technologies and Bio-engineering: Volume 1: Towards Improving Quality of Life |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=9klkCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA509&dq=Steven+A.+Rosenberg+%22in+1989%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiY_IjazpHeAhXCH5AKHZqMD0oQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=Steven%20A.%20Rosenberg%20%22in%201989%22&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1989 || || Trials for somatic gene therapy are run for various forms of {{w|cancer}}, {{w|familial hypercholesterolemia}}, {{w|hemophilia}}, and even {{w|AIDS}}.<ref name="The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies"/> || | + | | 1989 || Application || Trials for somatic gene therapy are run for various forms of {{w|cancer}}, {{w|familial hypercholesterolemia}}, {{w|hemophilia}}, and even {{w|AIDS}}.<ref name="The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1990 || || The first gene therapy widely accepted as a success is demonstrated when four-year-old Ashi DeSilva is treated for [[w:adenosine deaminase deficiency|ADA]]-[[w:severe combined immunodeficiency|SCID]].<ref name="Gene Therapy Finds Its Niche">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sheridan C | title = Gene therapy finds its niche | journal = Nature Biotechnology | volume = 29 | issue = 2 | pages = 121–8 | date = February 2011 | pmid = 21301435 | doi = 10.1038/nbt.1769 }}</ref> In the trial, Blaese et al manage to correct the adenosine deaminase deficiency in T-lymphocytes using retroviral-mediated gene transfer.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy"/> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1990 || Application || The first gene therapy widely accepted as a success is demonstrated when four-year-old Ashi DeSilva is treated for [[w:adenosine deaminase deficiency|ADA]]-[[w:severe combined immunodeficiency|SCID]].<ref name="Gene Therapy Finds Its Niche">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sheridan C | title = Gene therapy finds its niche | journal = Nature Biotechnology | volume = 29 | issue = 2 | pages = 121–8 | date = February 2011 | pmid = 21301435 | doi = 10.1038/nbt.1769 }}</ref> In the trial, Blaese et al manage to correct the adenosine deaminase deficiency in T-lymphocytes using retroviral-mediated gene transfer.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy"/> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1991 || || Hazinski et al make use of cationic liposome for gene transfer in experimental animals.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/> || | + | | 1991 || Field development || Hazinski et al make use of cationic liposome for gene transfer in experimental animals.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1991 || Financial || The {{w|United States Government}} provides US$58 million for gene therapy research, with increases in funding of US$15-40 million dollars a year over the following four years.<ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy"/> || {{w|United States}} | | 1991 || Financial || The {{w|United States Government}} provides US$58 million for gene therapy research, with increases in funding of US$15-40 million dollars a year over the following four years.<ref name="Gene TherapyGene Therapy"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| Line 83: | Line 85: | ||
| 1992 || Field development || Correction of myopathy is carried out in a transgenic mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by germline gene transfer of human dystrophin using a retroviral vector.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy of muscular dystrophy |url=http://www.medlink.com/article/gene_therapy_of_muscular_dystrophy |website=medlink.com |accessdate=25 October 2018}}</ref><ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 1992 || Field development || Correction of myopathy is carried out in a transgenic mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by germline gene transfer of human dystrophin using a retroviral vector.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy of muscular dystrophy |url=http://www.medlink.com/article/gene_therapy_of_muscular_dystrophy |website=medlink.com |accessdate=25 October 2018}}</ref><ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1992 || || {{w|Claudio Bordignon}}, working at the {{w|Vita-Salute San Raffaele University}}, performs the first gene therapy procedure using {{w|hematopoietic stem cell}}s as vectors to deliver genes intended to correct {{w|hereditary diseases}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Abbott A | title = Gene therapy. Italians first to use stem cells | journal = Nature | volume = 356 | issue = 6369 | pages = 465 | date = April 1992 | pmid = 1560817 | doi = 10.1038/356465a0}}</ref> || | + | | 1992 || Application || {{w|Claudio Bordignon}}, working at the {{w|Vita-Salute San Raffaele University}}, performs the first gene therapy procedure using {{w|hematopoietic stem cell}}s as vectors to deliver genes intended to correct {{w|hereditary diseases}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Abbott A | title = Gene therapy. Italians first to use stem cells | journal = Nature | volume = 356 | issue = 6369 | pages = 465 | date = April 1992 | pmid = 1560817 | doi = 10.1038/356465a0}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1992–1993 || | + | | 1992–1993 || Application || Cancer gene therapy is introduced by Trojan et al.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Trojan J, Johnson TR, Rudin SD, Ilan J, Tykocinski ML, Ilan J | title = Treatment and prevention of rat glioblastoma by immunogenic C6 cells expressing antisense insulin-like growth factor I RNA | journal = Science | volume = 259 | issue = 5091 | pages = 94–7 | date = January 1993 | pmid = 8418502 | doi = 10.1126/science.8418502}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1993 || | + | | 1993 || Application || Oldfield and Ram conduct the first clinical trial of {{w|herpes simplex virus}}/{{w|thymidine kinase}}/{{w|ganciclovir}} gene therapy system in glioblastoma multiforme.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1993 || || Experimental trials are run in {{w|London}} on a somatic gene therapy for cystic fibrosis (CF).<ref name="The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies">{{cite book |title=The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=KfNZdiCeiYMC&pg=PA124&dq=%22in+1993%22+somatic+treatment+genetic+change+is+performed.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjXopWuxZHeAhVQl5AKHYPFC3oQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=%22in%201993%22%20somatic%20treatment%20genetic%20change%20is%20performed.&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | + | | 1993 || Application || Experimental trials are run in {{w|London}} on a somatic gene therapy for cystic fibrosis (CF).<ref name="The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies">{{cite book |title=The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=KfNZdiCeiYMC&pg=PA124&dq=%22in+1993%22+somatic+treatment+genetic+change+is+performed.&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjXopWuxZHeAhVQl5AKHYPFC3oQ6AEIKDAA#v=onepage&q=%22in%201993%22%20somatic%20treatment%20genetic%20change%20is%20performed.&f=false}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1995 || | + | | 1995 || Application || Aebischer and Kato manage to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a gene therapy approach involving implantation of genetically engineered microencapsulated cells releasing neurotrophic factors.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 1996 || Organization || The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT) is established.<ref>{{cite web |title=ASGCT History |url=https://www.asgct.org/about/history |website=asgct.org |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | | 1996 || Organization || The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT) is established.<ref>{{cite web |title=ASGCT History |url=https://www.asgct.org/about/history |website=asgct.org |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| Line 97: | Line 99: | ||
| 1998 || Field development || Fire et al demonstrate {{w|RNA interference}}: injection of double stranded {{w|RNA}} shown to inhibit genes.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 1998 || Field development || Fire et al demonstrate {{w|RNA interference}}: injection of double stranded {{w|RNA}} shown to inhibit genes.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1999 || || American patient {{w|Jesse Gelsinger}} dies following a gene therapy experiment, impeding gene therapy research and setting the field back several years as U.S. regulators put some key experiments on hold.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/10/11/AR2010101102946.html |title=First patient treated in stem cell study |work=The Washington Post |date= 11 October 2010 | last = Stein | first = Rob | name-list-format = vanc | accessdate = 17 October 2018 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.medpagetoday.com/Genetics/GeneralGenetics/6275 |title=Death Prompts FDA to Suspend Arthritis Gene Therapy Trial |publisher=Medpage Today |date= 27 July 2007 |accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> As a result, the U.S. {{w|Food and Drug Administration}} suspends several clinical trials pending the reevaluation of ethical and procedural practices.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2000/01/22/us/gene-therapy-ordered-halted-at-university.html | last = Stolberg | first = Sheryl Gay | name-list-format = vanc | title=Gene Therapy Ordered Halted At University |work=The New York Times |date=22 January 2000 |accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1999 || Notable death || American patient {{w|Jesse Gelsinger}} dies following a gene therapy experiment, impeding gene therapy research and setting the field back several years as U.S. regulators put some key experiments on hold.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/10/11/AR2010101102946.html |title=First patient treated in stem cell study |work=The Washington Post |date= 11 October 2010 | last = Stein | first = Rob | name-list-format = vanc | accessdate = 17 October 2018 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.medpagetoday.com/Genetics/GeneralGenetics/6275 |title=Death Prompts FDA to Suspend Arthritis Gene Therapy Trial |publisher=Medpage Today |date= 27 July 2007 |accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> As a result, the U.S. {{w|Food and Drug Administration}} suspends several clinical trials pending the reevaluation of ethical and procedural practices.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2000/01/22/us/gene-therapy-ordered-halted-at-university.html | last = Stolberg | first = Sheryl Gay | name-list-format = vanc | title=Gene Therapy Ordered Halted At University |work=The New York Times |date=22 January 2000 |accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2000 || || American physician-geneticist {{w|Francis Collins}} completes the sequencing phase of the {{w|human genome project}}. Further developments in next-generation sequencing in the following years would have considerable impact on personalized medicine. For {{w|neurological disorder}}s, it would lead to improved diagnostics, identification of gene mutations, and development of therapies targeting these.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | + | | 1999 || Literature || Edmund C. Lattime and Stanton L. Gerson publish ''Gene Therapy of Cancer: Translational Approaches from Preclinical Studies to Clinical Implementation''.<ref>{{cite web |last1= |first1= |last2= |first2= |title=Gene Therapy of Cancer: Translational Approaches from Preclinical Studies to Clinical Implementation |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Gene_Therapy_of_Cancer.html?id=8ItrAAAAMAAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2000 || Field development || American physician-geneticist {{w|Francis Collins}} completes the sequencing phase of the {{w|human genome project}}. Further developments in next-generation sequencing in the following years would have considerable impact on personalized medicine. For {{w|neurological disorder}}s, it would lead to improved diagnostics, identification of gene mutations, and development of therapies targeting these.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || Literature || David T. Curiel and Joanne T. Douglas publish ''Adenoviral Vectors for Gene Therapy''.<ref>{{cite book |title=Adenoviral Vectors for Gene Therapy |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=SVGwl6bhxtkC&source=gbs_book_other_versions}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2002–2003 || || Cases of {{w|leukemia}} are diagnosed in French children undergoing gene therapy for genetic immunodeficiency.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref>{{cite web |title=somatic gene therapy |url=http://www.unifr.ch/nfp37/adverse.html |website=unifr.ch |accessdate=19 October 2018}}</ref> || | | 2002–2003 || || Cases of {{w|leukemia}} are diagnosed in French children undergoing gene therapy for genetic immunodeficiency.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref>{{cite web |title=somatic gene therapy |url=http://www.unifr.ch/nfp37/adverse.html |website=unifr.ch |accessdate=19 October 2018}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2003 || | + | | 2003 || Drug || The first commercial gene therapy, {{w|Gendicine}}, is approved in China for the treatment of head and neck cancer.<ref name="Gend">{{cite journal | vauthors = Pearson S, Jia H, Kandachi K | title = China approves first gene therapy | journal = Nature Biotechnology | volume = 22 | issue = 1 | pages = 3–4 | date = January 2004 | pmid = 14704685 | doi = 10.1038/nbt0104-3 }}</ref><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/> China becomes the first country to approve a gene therapy based product for clinical use. || {{w|China}} |
|- | |- | ||
| 2004 || Literature || David T. Curiel and Joanne T. Douglas publish ''Cancer Gene Therapy''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Cancer Gene Therapy |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=rvI8vgAACAAJ&source=gbs_book_other_versions |website=books.google.com.ar |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || | | 2004 || Literature || David T. Curiel and Joanne T. Douglas publish ''Cancer Gene Therapy''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Cancer Gene Therapy |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=rvI8vgAACAAJ&source=gbs_book_other_versions |website=books.google.com.ar |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2005 || | + | | 2005 || Drug || The China Food and Drug Administration approves its first {{w|oncolytic adenovirus}} drug Oncorine (H101), for treatment of advanced head and neck cancer.<ref name="The history of gene therapy drugs approval on the market">{{cite web |title=The history of gene therapy drugs approval on the market |url=http://stemcellassays.com/2011/12/history-gene-therapy-drugs-approval-market/ |website=stemcellassays.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> {{w|Adenovirus}} varieties have been explored extensively as a {{w|viral vector}} for {{w|gene therapy}} and also as an {{w|oncolytic virus}}.<ref>{{cite book|last=Pandha|first=K. J. Harrington ; edited by Richard G. Vile, Hardev|title=Viral therapy of cancer|year=2008|publisher=Wiley|location=Hoboken, N.J.|isbn=9780470019221|pages=1–13}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Wei |first1=D |last2=Xu |first2=J |last3=Liu |first3=XY |last4=Chen |first4=ZN |last5=Bian |first5=H |title=Fighting Cancer with Viruses: Oncolytic Virus Therapy in China. |doi=10.1089/hum.2017.212 |pmid=29284308 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29284308}}</ref> || {{w|China}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2006 (March) || | + | | 2006 (March) || Application || Researchers announce the successful use of gene therapy to treat two adult patients for X-linked {{w|chronic granulomatous disease}}, a disease which affects {{w|myeloid}} cells and damages the {{w|immune system}}. The study is the first to show that gene therapy can treat the {{w|myeloid}} system.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ott MG, Schmidt M, Schwarzwaelder K, Stein S, Siler U, Koehl U, Glimm H, Kühlcke K, Schilz A, Kunkel H, Naundorf S, Brinkmann A, Deichmann A, Fischer M, Ball C, Pilz I, Dunbar C, Du Y, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Lüthi U, Hassan M, Thrasher AJ, Hoelzer D, von Kalle C, Seger R, Grez M | display-authors = 6 | title = Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1 | journal = Nature Medicine | volume = 12 | issue = 4 | pages = 401–9 | date = April 2006 | pmid = 16582916 | doi = 10.1038/nm1393 | url = http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/531129 }}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2006 (May) || || A team reports a way to prevent the immune system from rejecting a newly delivered gene.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Brown BD, Venneri MA, Zingale A, Sergi Sergi L, Naldini L | title = Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable gene transfer | journal = Nature Medicine | volume = 12 | issue = 5 | pages = 585–91 | date = May 2006 | pmid = 16633348 | doi = 10.1038/nm1398 }}</ref> || | + | | 2006 (May) || Field development || A team reports a way to prevent the immune system from rejecting a newly delivered gene.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Brown BD, Venneri MA, Zingale A, Sergi Sergi L, Naldini L | title = Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable gene transfer | journal = Nature Medicine | volume = 12 | issue = 5 | pages = 585–91 | date = May 2006 | pmid = 16633348 | doi = 10.1038/nm1398 }}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2006 (August) || || Scientists successfully treat metastatic {{w|melanoma}} in two patients using [[w:Cytotoxic T cell|killer T cells]] genetically retargeted to attack the cancer cells.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Morgan RA, Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Hughes MS, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Royal RE, Topalian SL, Kammula US, Restifo NP, Zheng Z, Nahvi A, de Vries CR, Rogers-Freezer LJ, Mavroukakis SA, Rosenberg SA | display-authors = 6 | title = Cancer regression in patients after transfer of genetically engineered lymphocytes | journal = Science | volume = 314 | issue = 5796 | pages = 126–9 | date = October 2006 | pmid = 16946036 | pmc = 2267026 | doi = 10.1126/science.1129003}}</ref> || | + | | 2006 (August) || Application || Scientists successfully treat metastatic {{w|melanoma}} in two patients using [[w:Cytotoxic T cell|killer T cells]] genetically retargeted to attack the cancer cells.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Morgan RA, Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Hughes MS, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Royal RE, Topalian SL, Kammula US, Restifo NP, Zheng Z, Nahvi A, de Vries CR, Rogers-Freezer LJ, Mavroukakis SA, Rosenberg SA | display-authors = 6 | title = Cancer regression in patients after transfer of genetically engineered lymphocytes | journal = Science | volume = 314 | issue = 5796 | pages = 126–9 | date = October 2006 | pmid = 16946036 | pmc = 2267026 | doi = 10.1126/science.1129003}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2006 (November) || || Researchers report on the use of VRX496, a gene-based {{w|immunotherapy}} for the treatment of {{w|HIV}} that uses a [[w:lentivirus|lentiviral]] [[w:viral vector|vector]] to deliver an [[w:Sense (molecular biology)|antisense]] gene against the {{w|HIV envelope}}. This is the first evaluation of a lentiviral vector administered in a human clinical trial in the {{w|United States}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Levine BL, Humeau LM, Boyer J, MacGregor RR, Rebello T, Lu X, Binder GK, Slepushkin V, Lemiale F, Mascola JR, Bushman FD, Dropulic B, June CH | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 103 | issue = 46 | pages = 17372–7 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17090675 | pmc = 1635018 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.0608138103 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2009-02/uops-pmp021009.php|date=10 February 2009|title=Penn Medicine presents HIV gene therapy trial data at CROI 2009|accessdate=17 October 2018|publisher=EurekAlert!}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 2006 (November) || Application || Researchers report on the use of VRX496, a gene-based {{w|immunotherapy}} for the treatment of {{w|HIV}} that uses a [[w:lentivirus|lentiviral]] [[w:viral vector|vector]] to deliver an [[w:Sense (molecular biology)|antisense]] gene against the {{w|HIV envelope}}. This is the first evaluation of a lentiviral vector administered in a human clinical trial in the {{w|United States}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Levine BL, Humeau LM, Boyer J, MacGregor RR, Rebello T, Lu X, Binder GK, Slepushkin V, Lemiale F, Mascola JR, Bushman FD, Dropulic B, June CH | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector | journal = Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | volume = 103 | issue = 46 | pages = 17372–7 | date = November 2006 | pmid = 17090675 | pmc = 1635018 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.0608138103 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2009-02/uops-pmp021009.php|date=10 February 2009|title=Penn Medicine presents HIV gene therapy trial data at CROI 2009|accessdate=17 October 2018|publisher=EurekAlert!}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2007 (May) || || Researchers announce the first gene therapy trial for inherited {{w|retinal disease}}. The first operation is carried out on a 23-year-old British male, Robert Johnson, in early 2007.<ref>{{Cite news| url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/6609205.stm | publisher=BBC News | title=Gene therapy first for poor sight | date=1 May 2007 | accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> | + | | 2007 (May) || Application || Researchers announce the first gene therapy trial for inherited {{w|retinal disease}}. The first operation is carried out on a 23-year-old British male, Robert Johnson, in early 2007.<ref>{{Cite news| url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/6609205.stm | publisher=BBC News | title=Gene therapy first for poor sight | date=1 May 2007 | accessdate=17 October 2018}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2007 || | + | | 2007 || Application || Doctors in {{w|Great Britain}} conduct the world’s first operation using gene therapy to treat a serious sight disorder caused by a genetic defect.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/> || {{w|United Kingdom}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2007–2008 || || {{w|Timothy Ray Brown}} is cured of HIV by repeated {{w|hematopoietic stem cell transplantation}}.<ref>Rosenberg, Tina (29 May 2011) [http://nymag.com/health/features/aids-cure-2011-6/ The Man Who Had HIV and Now Does Not], ''[[w:New York (magazine)|New York]]''.</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 2007–2008 || Application || {{w|Timothy Ray Brown}} is cured of HIV by repeated {{w|hematopoietic stem cell transplantation}}.<ref>Rosenberg, Tina (29 May 2011) [http://nymag.com/health/features/aids-cure-2011-6/ The Man Who Had HIV and Now Does Not], ''[[w:New York (magazine)|New York]]''.</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2008 || Literature || Roland W. Herzog publishes ''Gene Therapy Immunology''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy Immunology |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Gene_Therapy_Immunology.html?id=dZ5PPgAACAAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |website=books.google.com.ar}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2009 (September) || || Using gene therapy, researchers manage to give {{w|trichromatic vision}} to {{w|squirrel monkeys}}.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Dolgin | first1 = E. | name-list-format = vanc | title = Colour blindness corrected by gene therapy | journal = Nature | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1038/news.2009.921 }}</ref> || | + | | 2009 (September) || Application || Using gene therapy, researchers manage to give {{w|trichromatic vision}} to {{w|squirrel monkeys}}.<ref>{{cite journal | last1 = Dolgin | first1 = E. | name-list-format = vanc | title = Colour blindness corrected by gene therapy | journal = Nature | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1038/news.2009.921 }}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2009 (November) || || Researchers halt a fatal {{w|genetic disorder}} called {{w|adrenoleukodystrophy}} in two children using a {{w|lentivirus}} vector to deliver a functioning version of {{w|ABCD1}}, the gene that is mutated in the disorder.<ref name="pmid19892975">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, Veres G, Schmidt M, Kutschera I, Vidaud M, Abel U, Dal-Cortivo L, Caccavelli L, Mahlaoui N, Kiermer V, Mittelstaedt D, Bellesme C, Lahlou N, Lefrère F, Blanche S, Audit M, Payen E, Leboulch P, l'Homme B, Bougnères P, Von Kalle C, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Aubourg P | display-authors = 6 | title = Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy | journal = Science | volume = 326 | issue = 5954 | pages = 818–23 | date = November 2009 | pmid = 19892975 | doi = 10.1126/science.1171242}}</ref> || | + | | 2009 (November) || Application || Researchers halt a fatal {{w|genetic disorder}} called {{w|adrenoleukodystrophy}} in two children using a {{w|lentivirus}} vector to deliver a functioning version of {{w|ABCD1}}, the gene that is mutated in the disorder.<ref name="pmid19892975">{{cite journal | vauthors = Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, Veres G, Schmidt M, Kutschera I, Vidaud M, Abel U, Dal-Cortivo L, Caccavelli L, Mahlaoui N, Kiermer V, Mittelstaedt D, Bellesme C, Lahlou N, Lefrère F, Blanche S, Audit M, Payen E, Leboulch P, l'Homme B, Bougnères P, Von Kalle C, Fischer A, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Aubourg P | display-authors = 6 | title = Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy | journal = Science | volume = 326 | issue = 5954 | pages = 818–23 | date = November 2009 | pmid = 19892975 | doi = 10.1126/science.1171242}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| 2010 || Field development || Critical components of the {{w|CRISPR}} (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 system are defined, which later forms the basis of gene editing.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | | 2010 || Field development || Critical components of the {{w|CRISPR}} (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 system are defined, which later forms the basis of gene editing.<ref name="Gene therapy"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2010 (April) || || A paper reports that gene therapy addresses {{w|achromatopsia}} (color blindness) in dogs by targeting [[w:Cone (vision)|cone]] photoreceptors. Cone function and day vision are restored for at least 33 months in two young specimens. The therapy is less efficient for older dogs.<ref name="Komáromy">{{cite journal | vauthors = Komáromy AM, Alexander JJ, Rowlan JS, Garcia MM, Chiodo VA, Kaya A, Tanaka JC, Acland GM, Hauswirth WW, Aguirre GD | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene therapy rescues cone function in congenital achromatopsia | journal = Human Molecular Genetics | volume = 19 | issue = 13 | pages = 2581–93 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20378608 | pmc = 2883338 | doi = 10.1093/hmg/ddq136 }}</ref> || | + | | 2010 (April) || Field development || A paper reports that gene therapy addresses {{w|achromatopsia}} (color blindness) in dogs by targeting [[w:Cone (vision)|cone]] photoreceptors. Cone function and day vision are restored for at least 33 months in two young specimens. The therapy is less efficient for older dogs.<ref name="Komáromy">{{cite journal | vauthors = Komáromy AM, Alexander JJ, Rowlan JS, Garcia MM, Chiodo VA, Kaya A, Tanaka JC, Acland GM, Hauswirth WW, Aguirre GD | display-authors = 6 | title = Gene therapy rescues cone function in congenital achromatopsia | journal = Human Molecular Genetics | volume = 19 | issue = 13 | pages = 2581–93 | date = July 2010 | pmid = 20378608 | pmc = 2883338 | doi = 10.1093/hmg/ddq136 }}</ref> || |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010 (September) || Application || Gene therapy successfully treates 18-year-old male patient in France with {{w|beta-thalassemia}}.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cavazzana-Calvo M, Payen E, Negre O, Wang G, Hehir K, Fusil F, Down J, Denaro M, Brady T, Westerman K, Cavallesco R, Gillet-Legrand B, Caccavelli L, Sgarra R, Maouche-Chrétien L, Bernaudin F, Girot R, Dorazio R, Mulder GJ, Polack A, Bank A, Soulier J, Larghero J, Kabbara N, Dalle B, Gourmel B, Socie G, Chrétien S, Cartier N, Aubourg P, Fischer A, Cornetta K, Galacteros F, Beuzard Y, Gluckman E, Bushman F, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Leboulch P | display-authors = 6 | title = Transfusion independence and HMGA2 activation after gene therapy of human β-thalassaemia | journal = Nature | volume = 467 | issue = 7313 | pages = 318–22 | date = September 2010 | pmid = 20844535 | pmc = 3355472 | doi = 10.1038/nature09328}}</ref> || {{w|France}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010–2011 || Field development || Cancer immunogene therapy using modified antigene, antisense/triple helix approach is introduced in {{w|South America}} in {{w|University of La Sabana}}, {{w|Bogota}}.<ref>Trojan An Aristizabal B, Jay LM, Castillo T, Penagos P, Trojan J. Testing of IGF-I biomarker in an ethical context. Adv Modern Oncol Res, 2(4); 2016</ref><ref>Castillo T, Trojan A, Noguera MC, Jay ML, Crane C, Alvarez A, Melo G, Penagos PJ, Shevelev A, Aristizabal BH, Briceño I, Ayala A, Duc HT, Trojan J. Epidemiologic experience in elaboration of molecular biology technology for immunogene therapy (in Spanish). Rev Cien, 2 (25); 2016</ref> || {{w|Colombia}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2011 || Drug || {{w|Neovasculgen}} is registered in Russia as the first-in-class gene-therapy drug for treatment of {{w|peripheral artery disease}}, including {{w|critical limb ischemia}}.<ref name="Neuvasculgen">{{cite news|title=Gene Therapy for PAD Approved|url=http://www.dddmag.com/news/2011/12/gene-therapy-pad-approved|accessdate=17 October 2018|date=6 December 2011}}</ref><ref name="The history of gene therapy drugs approval on the market"/> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2012 || Drug || {{w|Glybera}}, a treatment for a rare {{w|inherited disorder}}, becomes the first treatment to be approved for clinical use in both {{w|Europe}} and the {{w|United States}} after its endorsement by the {{w|European Commission}}.<ref name=Richards2012>{{cite web|last=Richards|first=Sabrina| name-list-format = vanc |title=Gene Therapy Arrives in Europe|url=http://www.the-scientist.com/?articles.view/articleNo/33166/title/Gene-Therapy-Arrives-in-Europe/|work=The Scientist|date=6 November 2012}}</ref><ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref name=Gallagher>Gallagher, James. (2 November 2012) [https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-20179561 BBC News – Gene therapy: Glybera approved by European Commission]. BBC. Retrieved 15 December 2012.</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2014 || Field development || Gene therapy clinical trials shows promise for inherited blood disorders, certain types of progressive blindness and {{w|HIV}}.<ref name="TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy"/><ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy trial shows promise for type of blindness |url=http://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2014-01-16-gene-therapy-trial-shows-promise-type-blindness |website=ox.ac.uk |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2014 || Literature || Gerhard Bauer and Joseph S. Anderson publish ''Gene Therapy for HIV''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene Therapy for HIV: From Inception to a Possible Cure |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Gene_Therapy_for_HIV.html?id=k6NJngEACAAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |website=books.google.com.ar |accessdate=26 October 2018}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2016 || Literature || Ravin Narain publishes ''Polymers and Nanomaterials for Gene Therapy''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Polymers and Nanomaterials for Gene Therapy |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Polymers_and_Nanomaterials_for_Gene_Ther.html?id=K5orjgEACAAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |website=books.google.com.ar}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2017 || Drug || The United States {{w|Food and Drug Administration}} approves the first gene therapy, {{w|tisagenlecleucel}} (Kymriah), for refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.<ref>{{cite web |title=The Past and Future of Gene Therapy |url=https://www.specialtypharmacytimes.com/news/the-past-and-future-of-gene-therapy |website=specialtypharmacytimes.com |accessdate=18 October 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2017 || || | + | | 2017 || Literature || Camiel J.F. Boon and Jan Wijnholds publish ''Retinal Gene Therapy: Methods and Protocols''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Retinal Gene Therapy: Methods and Protocols |url=https://books.google.com.ar/books/about/Retinal_Gene_Therapy.html?id=nWPcswEACAAJ&source=kp_book_description&redir_esc=y |website=books.google.com.ar}}</ref> || |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | == Numerical and visual data == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Scholar === | ||
| + | |||
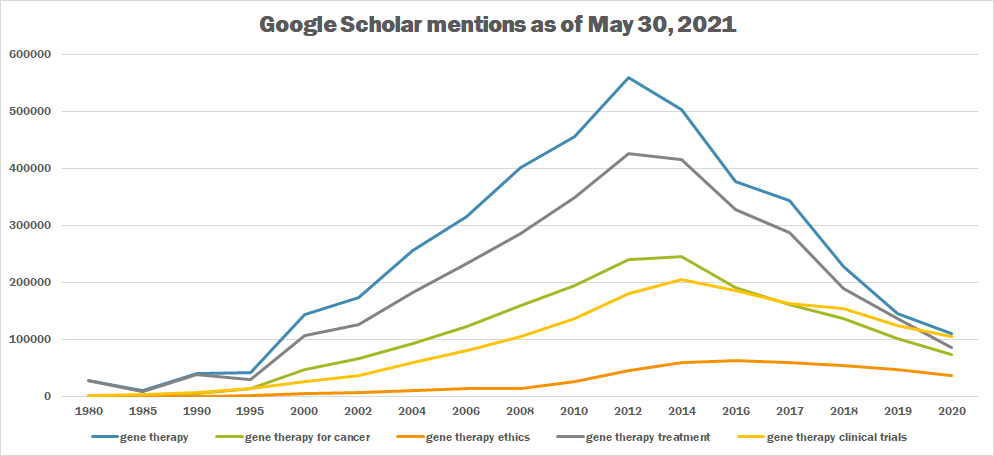
| + | The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of May 30, 2021. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="sortable wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Year | ||
| + | ! gene therapy | ||
| + | ! gene therapy for cancer | ||
| + | ! gene therapy ethics | ||
| + | ! gene therapy treatment | ||
| + | ! gene therapy clinical trials | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1980 || 28,000 || 1,020 || 125 || 27,800 || 2,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1985 || 10,700 || 2,220 || 315 || 9,370 || 3,290 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1990 || 41,000 || 5,130 || 629 || 38,900 || 6,350 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1995 || 41,400 || 13,900 || 1,780 || 30,000 || 13,500 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2000 || 144,000 || 47,300 || 5,820 || 107,000 || 26,900 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || 174,000 || 67,300 || 7,420 || 126,000 || 37,400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || 256,000 || 93,600 || 10,300 || 182,000 || 60,200 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2006 || 315,000 || 122,000 || 13,500 || 233,000 || 81,400 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2008 || 401,000 || 159,000 || 14,500 || 285,000 || 106,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010 || 455,000 || 195,000 || 26,600 || 349,000 || 137,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2012 || 560,000 || 241,000 || 46,000 || 426,000 || 181,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2014 || 504,000 || 246,000 || 59,000 || 416,000 || 206,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2016 || 377,000 || 192,000 || 62,300 || 328,000 || 185,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2017 || 343,000 || 162,000 || 60,100 || 287,000 || 163,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2018 || 228,000 || 136,000 || 54,100 || 189,000 || 154,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2019 || 145,000 || 102,000 || 47,800 || 137,000 || 125,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2020 || 110,000 || 73,800 || 37,200 || 85,400 || 105,000 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gene therapy tb.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Trends === | ||
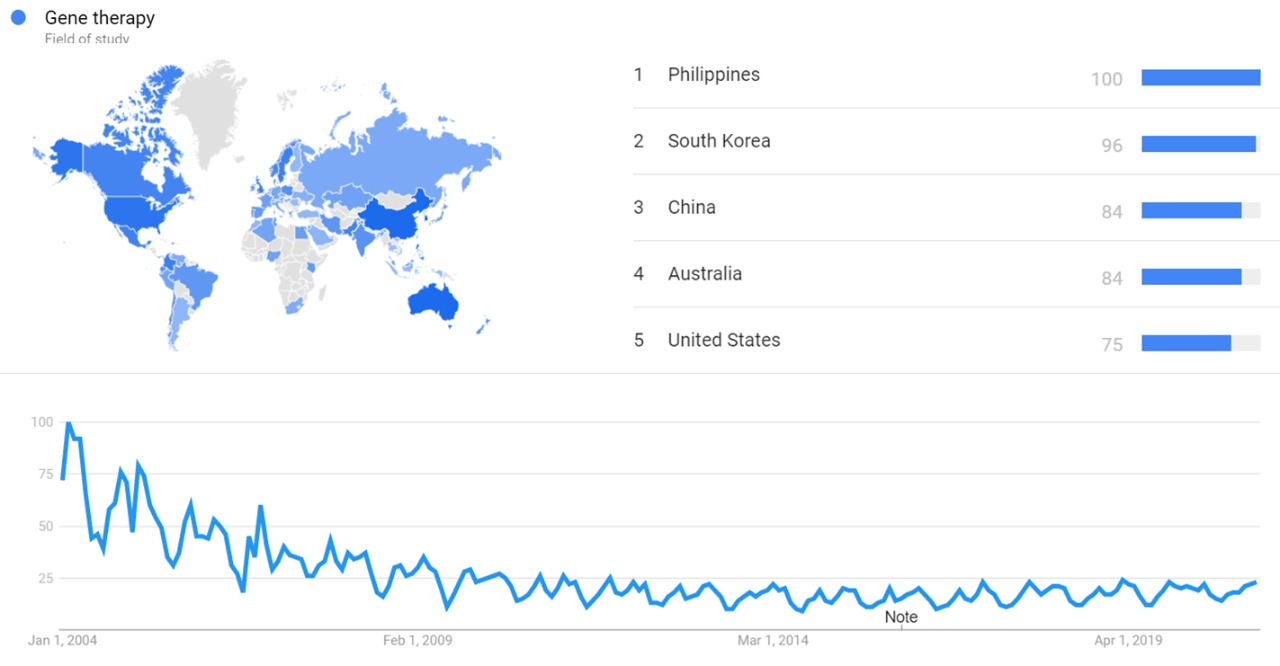
| + | The image below shows {{w|Google Trends}} data for Gene therapy (Field of study) from January 2004 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy |url=https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=%2Fm%2F03cpd |website=Google Trends |access-date=23 February 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gene therapy gt.jpg|thumb|center|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Ngram Viewer === | ||
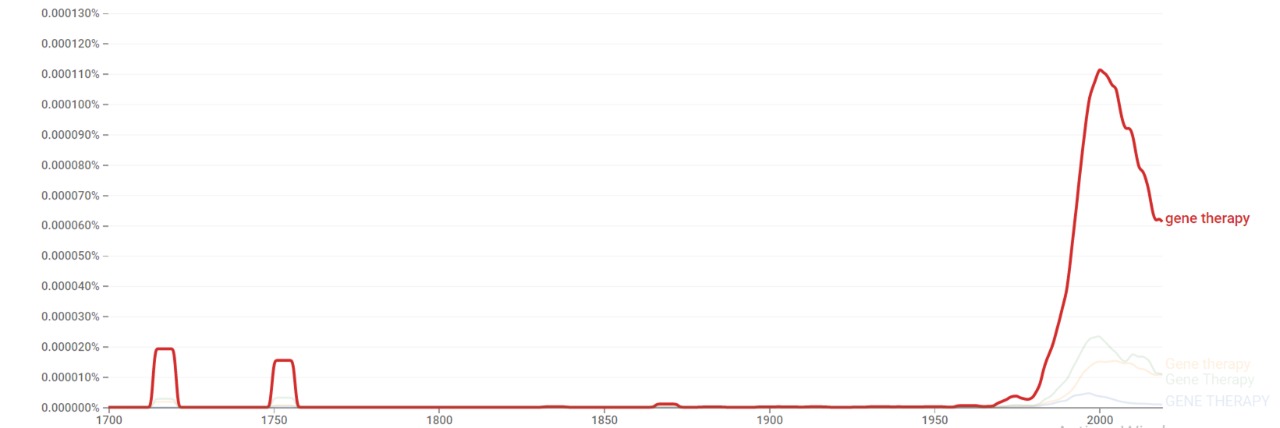
| + | The chart below shows {{w|Google Ngram Viewer}} data for Gene therapy from 1700 to 2019.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy |url=https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=Gene+therapy&year_start=1700&year_end=2019&corpus=26&smoothing=3&case_insensitive=true |website=books.google.com |access-date=23 February 2021 |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gene therapy ngram.jpg|thumb|center|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Wikipedia Views === | ||
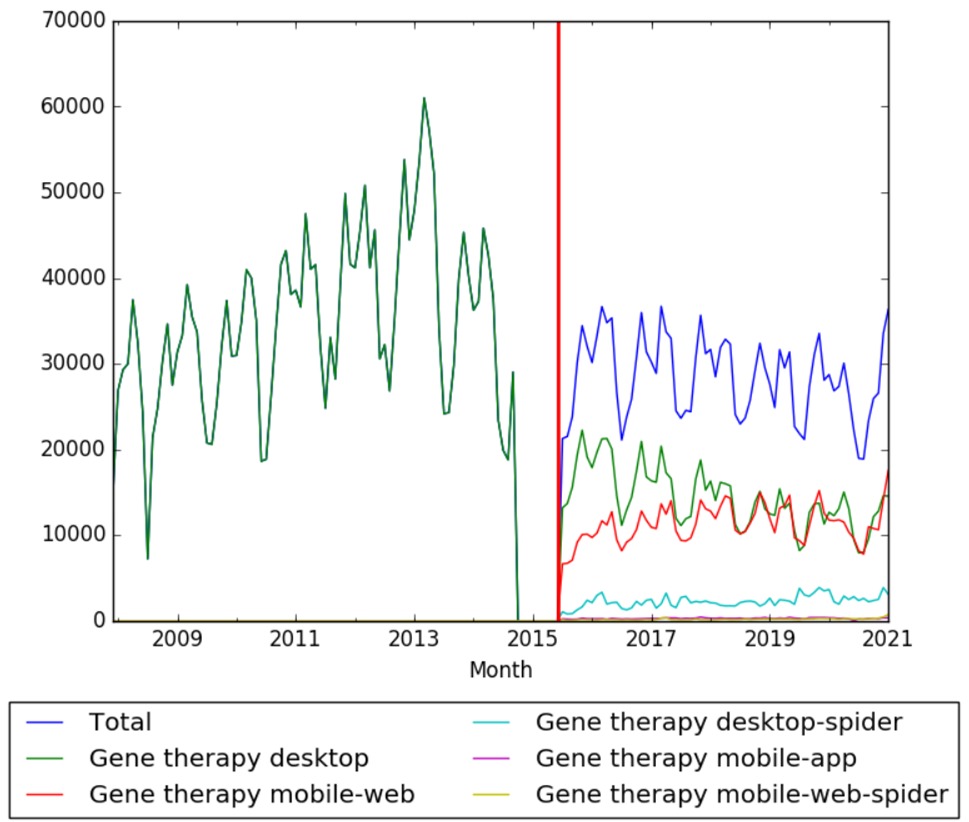
| + | The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article {{w|Gene therapy}} on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider,mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to January 2021.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gene therapy |url=https://wikipediaviews.org/displayviewsformultiplemonths.php?page=Gene+therapy&allmonths=allmonths&language=en&drilldown=all |website=wikipediaviews.org |access-date=23 February 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Gene therapy wv.jpg|thumb|center|600px]] | ||
==Meta information on the timeline== | ==Meta information on the timeline== | ||
| Line 160: | Line 240: | ||
===What the timeline is still missing=== | ===What the timeline is still missing=== | ||
| − | + | ||
===Timeline update strategy=== | ===Timeline update strategy=== | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Timeline of CRISPR]] | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:46, 26 July 2023
This is a timeline of gene therapy, attempting to describe significant events in the development of the field.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 1960s | Gene therapy as a concept is first introduced in the 1960s. Scientists are able to incorporate functional DNA inside human cells in vivo as early as 1961.[1] |
| By the late 1960s and early 1970s, gene therapy becomes the subject of an increasing number of articles and meetings.[2] | |
| 1980s | As the science of genetics advances throughout the decade, gene therapy gains an established foothold in the minds of medical scientists as a promising approach to treatments for specific diseases.[3] |
| 1990s | The decade brings further innovations, such as the first use of hematopoietic stem cells as vectors to deliver corrective genes. However, the death of Jesse Gelsinger in 1999, who dies following a major immune response to a vector used in clinical trial, has a major negative impact on the field of gene therapy.[1] |
| 2010s | Gene therapy is introduced in the European market first, and later in the United States.[1] |
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1928 | Field development | British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith describes the transforming principle.[4][5][6] | United Kingdom |
| 1944 | Field development | Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty describe that genetic information is carried in the form of DNA. The team finds that a gene is a part of DNA itself. This experimental demonstration is later called Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment.[7][8][9] | United States |
| 1952 | Field development | American molecular biologist Joshua Lederberg introduces transduction as a mechanism of genetic transfer.[10][11][12] | United States |
| 1953 | Field development | American molecular biologist James Watson and British molecular biologist Francis Crick identify the double-stranded structure of the DNA.[13] | |
| 1961 | Field development | American virologist Howard Martin Temin discovers that genetic mutation could be inherited as a result of virus infection.[14] | |
| 1961 | Field development | Scientists first manage to incorporate functional DNA inside human cells in vivo.[1] | |
| 1962 | Field development | The possibility of gene therapy is speculated.[13][2] | |
| 1962 | Field development | Polish professor Wacław Szybalski coins the term gene therapy.[15] | |
| 1968 | Application | Early attempts at use of viral vectors.[13] Rogers and Pfuderer demonstrate a proof-of-concept for virus mediated gene transfer.[16][17][18] | |
| 1969 | Application | Aposhian proposes the use of pseudoviruses derived from the mouse virus, polyoma.[2] | |
| 1970 | Field development | Howard Martin Temin and David Baltimore discover reverse transcriptase, an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template.[19][20][21][13] | |
| 1971 | A symposium on gene therapy is sponsored by the National Institute of Neuologic Disease and Stroke at the NIH and the Fogarty International Center.[2] | ||
| 1972 | Field development | Professor Theodore Friedmann and his colleague Richard Roblin, from the University of California, San Diego, discuss gene therapy in an article published in Science.[2] They suggest that transforming viruses could be used for therapeutic gene transfer.[13][22][23][24] | United States |
| 1973 | Field development | Graham and van der Erb introduce calcium phosphate transfection.[13] | |
| 1976 | Field development | A meeting sponsored by the New York Academy of Sciences discusses the new subject of gene therapy.[2] | United States |
| 1978 | Field development | American scientist Paul Zamecnik et al. suggest that oligonucleotides could be used therapeutically.[25][13] | United States |
| 1980 | Field development | Gene transfer mediated by liposomes is first described by Fengler.[26] | |
| 1980 | Field development | American scientist and physician Martin Cline from the University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), becomes the first investigator to attempt gene therapy using rDNA. Cline administers recombinant DNAwith the hope of effecting gene transfer in two patients with thalassemia, one in Israel and the other in Italy. The attempt fails.[27][28][29][30][31] | Israel, Italy |
| 1983 | Field development | A group of scientists from Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, propose that gene therapy could one day be a viable approach for treating Lesch-Nyhan disease, a rare neurological disorder.[3] | United States |
| 1983 | Field development | Scientists at the Massachussets Institute of Technology create the first retroviral vector suitable for use in gene therapy from a mouse leukemia virus.[1] | United States |
| 1984 | Field development | Experiment shows that targeted insertion of corrective DNA is possible in mammalian cells in vitro.[1] | |
| 1984 | Field development | Izant and Weintraub first demonstrate that antisense nucleic acid can be used to downregulate gene expression.[13] | |
| 1984 | Field development | A retrovirus vector system is designed that could efficiently insert foreign genes into mammalian chromosomes.[32] | |
| 1987 | Field development | Hoffman et al identify dystrophin, the protein product of Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene (basis of future gene therapy of this disorder).[13] | |
| 1988 | Literature | Eve K. Nichols publishes Human Gene Therapy.[33] | United States |
| 1989 | Field development | The first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the United States National Institutes of Health, is conducted by American cancer researcher Steven A. Rosenberg.[34][35][36] | United States |
| 1989 | Application | Trials for somatic gene therapy are run for various forms of cancer, familial hypercholesterolemia, hemophilia, and even AIDS.[37] | |
| 1990 | Application | The first gene therapy widely accepted as a success is demonstrated when four-year-old Ashi DeSilva is treated for ADA-SCID.[38] In the trial, Blaese et al manage to correct the adenosine deaminase deficiency in T-lymphocytes using retroviral-mediated gene transfer.[22][22][3] | United States |
| 1991 | Field development | Hazinski et al make use of cationic liposome for gene transfer in experimental animals.[22] | |
| 1991 | Financial | The United States Government provides US$58 million for gene therapy research, with increases in funding of US$15-40 million dollars a year over the following four years.[3] | United States |
| 1992 | Field development | Correction of myopathy is carried out in a transgenic mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy by germline gene transfer of human dystrophin using a retroviral vector.[39][13] | |
| 1992 | Application | Claudio Bordignon, working at the Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, performs the first gene therapy procedure using hematopoietic stem cells as vectors to deliver genes intended to correct hereditary diseases.[40] | |
| 1992–1993 | Application | Cancer gene therapy is introduced by Trojan et al.[41] | |
| 1993 | Application | Oldfield and Ram conduct the first clinical trial of herpes simplex virus/thymidine kinase/ganciclovir gene therapy system in glioblastoma multiforme.[13] | |
| 1993 | Application | Experimental trials are run in London on a somatic gene therapy for cystic fibrosis (CF).[37] | United Kingdom |
| 1995 | Application | Aebischer and Kato manage to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a gene therapy approach involving implantation of genetically engineered microencapsulated cells releasing neurotrophic factors.[13] | |
| 1996 | Organization | The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT) is established.[42] | United States |
| 1998 | Field development | Fire et al demonstrate RNA interference: injection of double stranded RNA shown to inhibit genes.[13] | |
| 1999 | Notable death | American patient Jesse Gelsinger dies following a gene therapy experiment, impeding gene therapy research and setting the field back several years as U.S. regulators put some key experiments on hold.[22][43][44] As a result, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration suspends several clinical trials pending the reevaluation of ethical and procedural practices.[45] | United States |
| 1999 | Literature | Edmund C. Lattime and Stanton L. Gerson publish Gene Therapy of Cancer: Translational Approaches from Preclinical Studies to Clinical Implementation.[46] | |
| 2000 | Field development | American physician-geneticist Francis Collins completes the sequencing phase of the human genome project. Further developments in next-generation sequencing in the following years would have considerable impact on personalized medicine. For neurological disorders, it would lead to improved diagnostics, identification of gene mutations, and development of therapies targeting these.[13] | |
| 2002 | Literature | David T. Curiel and Joanne T. Douglas publish Adenoviral Vectors for Gene Therapy.[47] | |
| 2002–2003 | Cases of leukemia are diagnosed in French children undergoing gene therapy for genetic immunodeficiency.[22][48] | ||
| 2003 | Drug | The first commercial gene therapy, Gendicine, is approved in China for the treatment of head and neck cancer.[49][22] China becomes the first country to approve a gene therapy based product for clinical use. | China |
| 2004 | Literature | David T. Curiel and Joanne T. Douglas publish Cancer Gene Therapy.[50] | |
| 2005 | Drug | The China Food and Drug Administration approves its first oncolytic adenovirus drug Oncorine (H101), for treatment of advanced head and neck cancer.[51] Adenovirus varieties have been explored extensively as a viral vector for gene therapy and also as an oncolytic virus.[52][53] | China |
| 2006 (March) | Application | Researchers announce the successful use of gene therapy to treat two adult patients for X-linked chronic granulomatous disease, a disease which affects myeloid cells and damages the immune system. The study is the first to show that gene therapy can treat the myeloid system.[54] | |
| 2006 (May) | Field development | A team reports a way to prevent the immune system from rejecting a newly delivered gene.[55] | |
| 2006 (August) | Application | Scientists successfully treat metastatic melanoma in two patients using killer T cells genetically retargeted to attack the cancer cells.[56] | |
| 2006 (November) | Application | Researchers report on the use of VRX496, a gene-based immunotherapy for the treatment of HIV that uses a lentiviral vector to deliver an antisense gene against the HIV envelope. This is the first evaluation of a lentiviral vector administered in a human clinical trial in the United States.[57][58] | United States |
| 2007 (May) | Application | Researchers announce the first gene therapy trial for inherited retinal disease. The first operation is carried out on a 23-year-old British male, Robert Johnson, in early 2007.[59] | |
| 2007 | Application | Doctors in Great Britain conduct the world’s first operation using gene therapy to treat a serious sight disorder caused by a genetic defect.[22] | United Kingdom |
| 2007–2008 | Application | Timothy Ray Brown is cured of HIV by repeated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.[60] | United States |
| 2008 | Literature | Roland W. Herzog publishes Gene Therapy Immunology.[61] | |
| 2009 (September) | Application | Using gene therapy, researchers manage to give trichromatic vision to squirrel monkeys.[62] | |
| 2009 (November) | Application | Researchers halt a fatal genetic disorder called adrenoleukodystrophy in two children using a lentivirus vector to deliver a functioning version of ABCD1, the gene that is mutated in the disorder.[63] | |
| 2010 | Field development | Critical components of the CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 system are defined, which later forms the basis of gene editing.[13] | |
| 2010 (April) | Field development | A paper reports that gene therapy addresses achromatopsia (color blindness) in dogs by targeting cone photoreceptors. Cone function and day vision are restored for at least 33 months in two young specimens. The therapy is less efficient for older dogs.[64] | |
| 2010 (September) | Application | Gene therapy successfully treates 18-year-old male patient in France with beta-thalassemia.[65] | France |
| 2010–2011 | Field development | Cancer immunogene therapy using modified antigene, antisense/triple helix approach is introduced in South America in University of La Sabana, Bogota.[66][67] | Colombia |
| 2011 | Drug | Neovasculgen is registered in Russia as the first-in-class gene-therapy drug for treatment of peripheral artery disease, including critical limb ischemia.[68][51] | |
| 2012 | Drug | Glybera, a treatment for a rare inherited disorder, becomes the first treatment to be approved for clinical use in both Europe and the United States after its endorsement by the European Commission.[69][22][70] | |
| 2014 | Field development | Gene therapy clinical trials shows promise for inherited blood disorders, certain types of progressive blindness and HIV.[22][71] | |
| 2014 | Literature | Gerhard Bauer and Joseph S. Anderson publish Gene Therapy for HIV.[72] | |
| 2016 | Literature | Ravin Narain publishes Polymers and Nanomaterials for Gene Therapy.[73] | |
| 2017 | Drug | The United States Food and Drug Administration approves the first gene therapy, tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah), for refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia.[74] | United States |
| 2017 | Literature | Camiel J.F. Boon and Jan Wijnholds publish Retinal Gene Therapy: Methods and Protocols.[75] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of May 30, 2021.
| Year | gene therapy | gene therapy for cancer | gene therapy ethics | gene therapy treatment | gene therapy clinical trials |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 28,000 | 1,020 | 125 | 27,800 | 2,000 |
| 1985 | 10,700 | 2,220 | 315 | 9,370 | 3,290 |
| 1990 | 41,000 | 5,130 | 629 | 38,900 | 6,350 |
| 1995 | 41,400 | 13,900 | 1,780 | 30,000 | 13,500 |
| 2000 | 144,000 | 47,300 | 5,820 | 107,000 | 26,900 |
| 2002 | 174,000 | 67,300 | 7,420 | 126,000 | 37,400 |
| 2004 | 256,000 | 93,600 | 10,300 | 182,000 | 60,200 |
| 2006 | 315,000 | 122,000 | 13,500 | 233,000 | 81,400 |
| 2008 | 401,000 | 159,000 | 14,500 | 285,000 | 106,000 |
| 2010 | 455,000 | 195,000 | 26,600 | 349,000 | 137,000 |
| 2012 | 560,000 | 241,000 | 46,000 | 426,000 | 181,000 |
| 2014 | 504,000 | 246,000 | 59,000 | 416,000 | 206,000 |
| 2016 | 377,000 | 192,000 | 62,300 | 328,000 | 185,000 |
| 2017 | 343,000 | 162,000 | 60,100 | 287,000 | 163,000 |
| 2018 | 228,000 | 136,000 | 54,100 | 189,000 | 154,000 |
| 2019 | 145,000 | 102,000 | 47,800 | 137,000 | 125,000 |
| 2020 | 110,000 | 73,800 | 37,200 | 85,400 | 105,000 |
Google Trends
The image below shows Google Trends data for Gene therapy (Field of study) from January 2004 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[76]
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Gene therapy from 1700 to 2019.[77]
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Gene therapy on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider,mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to January 2021.[78]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "Gene Therapy 101: From The 1960s To Today". premier-research.com. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Wolff, Jon A. Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Gene Therapy". encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- ↑ Renneberg, Reinhard; Berkling, Viola; Loroch, Vanya. Biotechnology for Beginners.
- ↑ Tmh. Target 2011: Biology 12.
- ↑ Chamary, JV. 50 Biology Ideas You Really Need to Know.
- ↑ Ohya, Masanori; Watanabe, Noboru. Selected Papers of M. Ohya.
- ↑ Principles and Applications of Molecular Diagnostics (Nader Rifai, A. Rita Horvath, Carl T. Wittwer, Jason Park ed.).
- ↑ Hoffee, P. A. Medical Molecular Genetics, Volume 698.
- ↑ Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications (P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe ed.).
- ↑ Maheshwari, D.K. A Textbook of Microbiology.
- ↑ Snyder, Larry; Champness, Wendy. Molecular Genetics of Bacteria.
- ↑ 13.00 13.01 13.02 13.03 13.04 13.05 13.06 13.07 13.08 13.09 13.10 13.11 13.12 13.13 13.14 "Gene therapy". medlink.com. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- ↑ Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: Novel Techniques and Applications (P. Dubruel, S. Van Vlierberghe ed.).
- ↑ Twyman, Richard. Gene Transfer to Animal Cells.
- ↑ Prazeres, Duarte Miguel F. Plasmid Biopharmaceuticals: Basics, Applications, and Manufacturing.
- ↑ Gene Therapeutics: Methods and Applications of Direct Gene Transfer (Jon A. Wolff ed.).
- ↑ The Development of Human Gene Therapy (Theodore Friedmann ed.).
- ↑ Varmus, Harold. The Art and Politics of Science.
- ↑ Pennington, T. H. Molecular Virology.
- ↑ Snustad, D. Peter; Simmons, Michael J. Principles of Genetics, Binder Ready Version.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 22.4 22.5 22.6 22.7 22.8 22.9 "TIMELINE-Milestones in gene therapy". reuters.com. Retrieved 15 October 2018.
- ↑ Tramper, J.; Zhu, Yang. Modern Biotechnology: Panacea or new Pandora's box?.
- ↑ Shapiro, Irving M.; Risbud, Makarand V. The Intervertebral Disc: Molecular and Structural Studies of the Disc in Health and Disease.
- ↑ "Zamecnik, P.C. & Stephenson, M.L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 280-284". researchgate.net. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ↑ "Gene Transfer Technique". mybiosource.com. Retrieved 25 October 2018.
- ↑ U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment (December 1984). Human gene therapy – A background paper. DIANE Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4289-2371-3.
- ↑ Sun M (October 1982). "Martin Cline loses appeal on NIH grant". Science. 218 (4567): 37. PMID 7123214. doi:10.1126/science.7123214.
- ↑ Kelly, Evelyn B. Gene Therapy.
- ↑ Preserving Public Trust: Accreditation and Human Research Participant Protection Programs. Institute of Medicine, Board on Health Sciences Policy, Committee on Assessing the System for Protecting Human Research Subjects.
- ↑ Serafini, Anthony. The Epic History of Biology.
- ↑ Cepko CL, Roberts BE, Mulligan RC (July 1984). "Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector". Cell. 37 (3): 1053–62. PMID 6331674. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9.
- ↑ "Human Gene Therapy, Issue 617". books.google.com.ar. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ Rosenberg SA, Aebersold P, Cornetta K, Kasid A, Morgan RA, Moen R, et al. (August 1990). "Gene transfer into humans--immunotherapy of patients with advanced melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes modified by retroviral gene transduction". The New England Journal of Medicine. 323 (9): 570–8. PMID 2381442. doi:10.1056/NEJM199008303230904.
- ↑ March, Keith L. Gene Transfer in the Cardiovascular System: Experimental Approaches and Therapeutic Implications.
- ↑ Barh, Debmalya; Azevedo, Vasco. Omics Technologies and Bio-engineering: Volume 1: Towards Improving Quality of Life.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 The Concise Encyclopedia of the Ethics of New Technologies.
- ↑ Sheridan C (February 2011). "Gene therapy finds its niche". Nature Biotechnology. 29 (2): 121–8. PMID 21301435. doi:10.1038/nbt.1769.
- ↑ "Gene therapy of muscular dystrophy". medlink.com. Retrieved 25 October 2018.
- ↑ Abbott A (April 1992). "Gene therapy. Italians first to use stem cells". Nature. 356 (6369): 465. PMID 1560817. doi:10.1038/356465a0.
- ↑ Trojan J, Johnson TR, Rudin SD, Ilan J, Tykocinski ML, Ilan J (January 1993). "Treatment and prevention of rat glioblastoma by immunogenic C6 cells expressing antisense insulin-like growth factor I RNA". Science. 259 (5091): 94–7. PMID 8418502. doi:10.1126/science.8418502.
- ↑ "ASGCT History". asgct.org. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ Stein R (11 October 2010). "First patient treated in stem cell study". The Washington Post. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ "Death Prompts FDA to Suspend Arthritis Gene Therapy Trial". Medpage Today. 27 July 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ Stolberg SG (22 January 2000). "Gene Therapy Ordered Halted At University". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ "Gene Therapy of Cancer: Translational Approaches from Preclinical Studies to Clinical Implementation". Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ Adenoviral Vectors for Gene Therapy.
- ↑ "somatic gene therapy". unifr.ch. Retrieved 19 October 2018.
- ↑ Pearson S, Jia H, Kandachi K (January 2004). "China approves first gene therapy". Nature Biotechnology. 22 (1): 3–4. PMID 14704685. doi:10.1038/nbt0104-3.
- ↑ "Cancer Gene Therapy". books.google.com.ar. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 "The history of gene therapy drugs approval on the market". stemcellassays.com. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- ↑ Pandha, K. J. Harrington ; edited by Richard G. Vile, Hardev (2008). Viral therapy of cancer. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley. pp. 1–13. ISBN 9780470019221.
- ↑ Wei, D; Xu, J; Liu, XY; Chen, ZN; Bian, H. "Fighting Cancer with Viruses: Oncolytic Virus Therapy in China.". PMID 29284308. doi:10.1089/hum.2017.212.
- ↑ Ott MG, Schmidt M, Schwarzwaelder K, Stein S, Siler U, Koehl U, et al. (April 2006). "Correction of X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by gene therapy, augmented by insertional activation of MDS1-EVI1, PRDM16 or SETBP1". Nature Medicine. 12 (4): 401–9. PMID 16582916. doi:10.1038/nm1393.
- ↑ Brown BD, Venneri MA, Zingale A, Sergi Sergi L, Naldini L (May 2006). "Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable gene transfer". Nature Medicine. 12 (5): 585–91. PMID 16633348. doi:10.1038/nm1398.
- ↑ Morgan RA, Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Hughes MS, Yang JC, Sherry RM, et al. (October 2006). "Cancer regression in patients after transfer of genetically engineered lymphocytes". Science. 314 (5796): 126–9. PMC 2267026
 . PMID 16946036. doi:10.1126/science.1129003.
. PMID 16946036. doi:10.1126/science.1129003.
- ↑ Levine BL, Humeau LM, Boyer J, MacGregor RR, Rebello T, Lu X, et al. (November 2006). "Gene transfer in humans using a conditionally replicating lentiviral vector". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (46): 17372–7. PMC 1635018
 . PMID 17090675. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608138103.
. PMID 17090675. doi:10.1073/pnas.0608138103.
- ↑ "Penn Medicine presents HIV gene therapy trial data at CROI 2009". EurekAlert!. 10 February 2009. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ "Gene therapy first for poor sight". BBC News. 1 May 2007. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ Rosenberg, Tina (29 May 2011) The Man Who Had HIV and Now Does Not, New York.
- ↑ "Gene Therapy Immunology". books.google.com.ar.
- ↑ Dolgin E (2009). "Colour blindness corrected by gene therapy". Nature. doi:10.1038/news.2009.921.
- ↑ Cartier N, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Bartholomae CC, Veres G, Schmidt M, Kutschera I, et al. (November 2009). "Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy with a lentiviral vector in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy". Science. 326 (5954): 818–23. PMID 19892975. doi:10.1126/science.1171242.
- ↑ Komáromy AM, Alexander JJ, Rowlan JS, Garcia MM, Chiodo VA, Kaya A, et al. (July 2010). "Gene therapy rescues cone function in congenital achromatopsia". Human Molecular Genetics. 19 (13): 2581–93. PMC 2883338
 . PMID 20378608. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq136.
. PMID 20378608. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq136.
- ↑ Cavazzana-Calvo M, Payen E, Negre O, Wang G, Hehir K, Fusil F, et al. (September 2010). "Transfusion independence and HMGA2 activation after gene therapy of human β-thalassaemia". Nature. 467 (7313): 318–22. PMC 3355472
 . PMID 20844535. doi:10.1038/nature09328.
. PMID 20844535. doi:10.1038/nature09328.
- ↑ Trojan An Aristizabal B, Jay LM, Castillo T, Penagos P, Trojan J. Testing of IGF-I biomarker in an ethical context. Adv Modern Oncol Res, 2(4); 2016
- ↑ Castillo T, Trojan A, Noguera MC, Jay ML, Crane C, Alvarez A, Melo G, Penagos PJ, Shevelev A, Aristizabal BH, Briceño I, Ayala A, Duc HT, Trojan J. Epidemiologic experience in elaboration of molecular biology technology for immunogene therapy (in Spanish). Rev Cien, 2 (25); 2016
- ↑ "Gene Therapy for PAD Approved". 6 December 2011. Retrieved 17 October 2018.
- ↑ Richards S (6 November 2012). "Gene Therapy Arrives in Europe". The Scientist.
- ↑ Gallagher, James. (2 November 2012) BBC News – Gene therapy: Glybera approved by European Commission. BBC. Retrieved 15 December 2012.
- ↑ "Gene therapy trial shows promise for type of blindness". ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ "Gene Therapy for HIV: From Inception to a Possible Cure". books.google.com.ar. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ↑ "Polymers and Nanomaterials for Gene Therapy". books.google.com.ar.
- ↑ "The Past and Future of Gene Therapy". specialtypharmacytimes.com. Retrieved 18 October 2018.
- ↑ "Retinal Gene Therapy: Methods and Protocols". books.google.com.ar.
- ↑ "Gene therapy". Google Trends. Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- ↑ "Gene therapy". books.google.com. Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- ↑ "Gene therapy". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 23 February 2021.