Difference between revisions of "Timeline of quantified self"
From Timelines
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline: | The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline: | ||
| + | * Concept introduction | ||
* Service launch | * Service launch | ||
* Device launch | * Device launch | ||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2012 || October || || "The Quantified Self web site listed over 500 tools as of October 2012 (http://quantifiedself.com/guide/), mostly concerning exercise, weight, health, and goal achievement."<ref name="The Quantified Se"/> | | 2012 || October || || "The Quantified Self web site listed over 500 tools as of October 2012 (http://quantifiedself.com/guide/), mostly concerning exercise, weight, health, and goal achievement."<ref name="The Quantified Se"/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2013 || || Concept introduction || Michael Savage uses the term 'lively data' in an article, to denote the constant generation of large masses of digital data as part of the digital data economy, and the implications of this practice for sociological research methods.<ref name="Lupton"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2014 || May 21 || || Wellness & Prevention, a division of {{w|Johnson & Johnson}}, launches self-tracking app Track Your Health, which allows users to track and aggregate data, set goals, and visualize their weight, movement and nutrition progress in the form of charts.<ref>{{cite web |title=Johnson & Johnson subsidiary launches self-tracking app |url=https://www.mobihealthnews.com/33348/johnson-johnson-subsidiary-launches-self-tracking-app |website=MobiHealthNews |access-date=20 March 2021 |language=en |date=21 May 2014}}</ref> | | 2014 || May 21 || || Wellness & Prevention, a division of {{w|Johnson & Johnson}}, launches self-tracking app Track Your Health, which allows users to track and aggregate data, set goals, and visualize their weight, movement and nutrition progress in the form of charts.<ref>{{cite web |title=Johnson & Johnson subsidiary launches self-tracking app |url=https://www.mobihealthnews.com/33348/johnson-johnson-subsidiary-launches-self-tracking-app |website=MobiHealthNews |access-date=20 March 2021 |language=en |date=21 May 2014}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 16:25, 18 July 2021
This is a timeline of quantified self. Covert surveillance or tracking of the self by others is not discussed in this timeline.
Contents
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- Concept introduction
- Service launch
- Device launch
- Literature
- Background technology
- Notable case
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient times | Early ideas | Monitoring, measuring and recording elements of one's body and life as a form of self-improvement or self-reflection is already discussed in ancient times.[1] |
| Latter half of the 20th century onwards | Early technologies | The Digital Revolution introduces technologies that facilitate tracking practices, leading to renewed interest in self-tracking.[1] The term database is introdiced in the 1960s. "Technically quantified self has been an idea since the 1970s"[2] |
| 21st century | Consolidation | The term quantified self is invented. "The Quantified Self movement was founded by Gary Wolf and Kevin Kelly in 2007"[3] |
Visual and numerical data
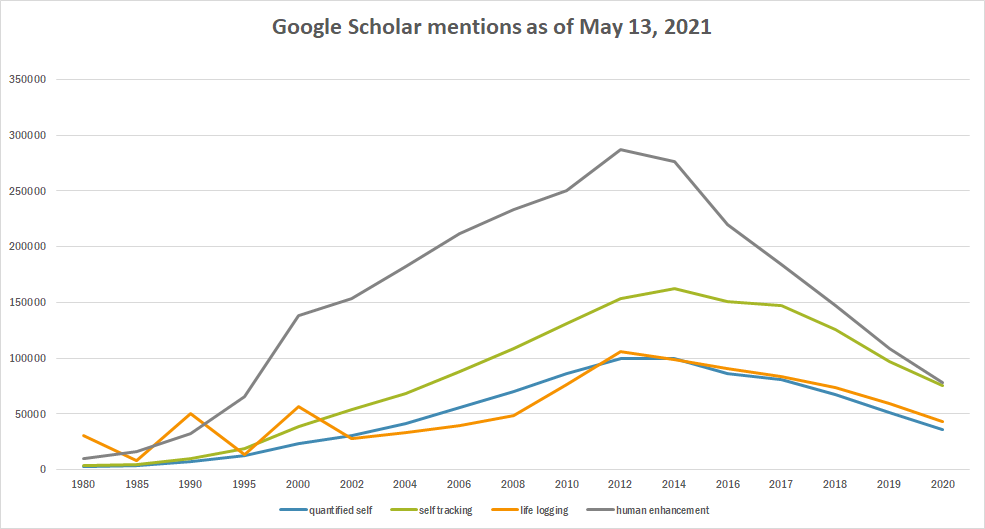
Mentions on Google Scholar
| Year | quantified self | self tracking | life logging | human enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 2,780 | 3,770 | 30,300 | 10,300 |
| 1985 | 3,460 | 4,660 | 7.830 | 15,900 |
| 1990 | 7,340 | 9,440 | 50,300 | 32,600 |
| 1995 | 12,300 | 18,500 | 13,400 | 65,700 |
| 2000 | 23,300 | 38,500 | 56,600 | 138,000 |
| 2002 | 30,500 | 54,000 | 28,100 | 153,000 |
| 2004 | 41,700 | 68,500 | 33,200 | 182,000 |
| 2006 | 56,000 | 88,000 | 39,700 | 212,000 |
| 2008 | 69,900 | 109,000 | 48,600 | 233,000 |
| 2010 | 86,500 | 131,000 | 76,500 | 250,000 |
| 2012 | 99,800 | 153,000 | 106,000 | 287,000 |
| 2014 | 99,500 | 162,000 | 99,100 | 276,000 |
| 2016 | 85,900 | 151,000 | 91,000 | 220,000 |
| 2017 | 80,400 | 147,000 | 83,200 | 184,000 |
| 2018 | 67,300 | 126,000 | 73,800 | 147,000 |
| 2019 | 51,300 | 97,200 | 59,300 | 109,000 |
| 2020 | 36,300 | 75,400 | 43,300 | 78,400 |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date (approximately) | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 | The first wireless ECG is invented. | ||
| 1999 | "eHealth is a relatively recent healthcare practice supported by electronic processes and communication, dating back to at least 1999."[4] | ||
| 2005 | MyFitnessPal is launched. It is a health smartphone app that tracks nutrition, exercise, and diet. In 2020, MyFitnessPal would be acquired by Francisco Partners for US$345 million.[5] | ||
| 2006 | April | 23andMe | |
| 2006 | August 24 | Background technology | Amazon.com releases its Elastic Compute Cloud product. Cloud computing starts being popularized.[6] |
| 2007 | January 15 | Service launch (reading tracker) | Goodreads is founded. It is a mobile and web app that allows its users to find, share, recommend, read, and review the books they like. In 2013, it would be acquired by Amazon.[7] As of 2021, Goodreads is the world’s largest site for readers and book recommendations.[8] |
| 2007 | January 28 | Service launch (task manager) | Todoist is founded. It keeps track of tasks, projects, and goals in one simple place, synching across all the users devices and integrating with all their favorite apps.[9] |
| 2007 | March 26 | Fitbit | |
| 2007 | The term quantified self is proposed in San Francisco by Wired magazine editors Gary Wolf and Kevin Kelly as "a collaboration of users and tool makers who share an interest in self knowledge through self-tracking."[10][11] | ||
| 2007 | September 25 | Domain name registration | quantifiedself.com is registered.[12]
|
| 2008 | "At the center of the quantified self movement is, appropriately, the Quantified Self community, which in October 2012 comprised 70 worldwide meetup groups with 5,000 participants having attended 120 events since the community formed in 2008 (event videos are available online at http://quantifiedself.com/)."[13] | ||
| 2009 | February | Literature | David Ewing Duncan publishes Experimental Man: What One Man's Body Reveals about His Future, Your Health, and Our Toxic World.[14] |
| 2012 | April | Literature | Bruce W. Perry publishes Fitness for Geeks: Real Science, Great Nutrition, and Good Health.[15] |
| 2012 | September | " The group's third conference was held at Stanford University in September 2012 with over 400 attendees."[13] | |
| 2012 | October | "At the center of the quantified self movement is, appropriately, the Quantified Self community, which in October 2012 comprised 70 worldwide meetup groups with 5,000 participants having attended 120 events since the community formed in 2008"[13] | |
| 2012 | October | "The Quantified Self web site listed over 500 tools as of October 2012 (http://quantifiedself.com/guide/), mostly concerning exercise, weight, health, and goal achievement."[13] | |
| 2013 | Concept introduction | Michael Savage uses the term 'lively data' in an article, to denote the constant generation of large masses of digital data as part of the digital data economy, and the implications of this practice for sociological research methods.[1] | |
| 2014 | May 21 | Wellness & Prevention, a division of Johnson & Johnson, launches self-tracking app Track Your Health, which allows users to track and aggregate data, set goals, and visualize their weight, movement and nutrition progress in the form of charts.[16] | |
| 2014 | July | "In July 2014 a smart technology footwear was introduced in Hyderabad, India. The shoe insoles are connected to a smartphone application that uses Google Maps, and vibrate to tell users when and where to turn to reach their destination.[17][18][19][20]" | |
| 2014 | October 28 | Health-tracking platform launch | Google Fit launches.[21] |
| 2016 | April 8 | Literature | Dawn Nafus publishes Quantified: Biosensing Technologies in Everyday Life, which elaborates on social, cultural, political, and economical aspects of quantified self. The book discusses empowering, social control, volunteering, enforcement, data interpretation, and how does all this affect the relationship between medical practice and self care, between scientific and lay knowledge.[22] |
| 2016 | May 2 | Literature | Deborah Lupton publishes The Quantified Self, which "critically analyses the social, cultural and political dimensions of contemporary self-tracking and identifies the concepts of selfhood and human embodiment and the value of the data that underpin them".[1] |
| 2016 | June 24 | Literature | Dawn Nafus and Gina Neff publish Self-Tracking: The Mit Press Essential Knowledge Series, which introduces the essential ideas and key challenges of self-tracking.[23] |
| 2016 | September 7 | Literature | Deborah Lupton publishes The Quantified Self.[24] |
| 2017 | September 11 | Literature | Phoebe V. Moore publishes The Quantified Self in Precarity: Work, Technology and What Counts, which attempts to demonstrate how workplace quantification leads to high turnover rates, workplace rationalization and worker stress and anxiety.[25] |
| 2017 | September 28 | Literature | Burkhardt Funk and Mark Hoogendoorn publish Machine Learning for the Quantified Self: On the Art of Learning from Sensory Data, which explains the complete loop to effectively use self-tracking data for machine learning.[26] |
| 2018 | May 8 | Health-tracking platform launch | "Google, Android P take on phone addiction with Android Dashboard"[27] |
| 2019 | Service launch (metabolic health tracker) | NutriSense is founded. It is a data-driven metabolic health platform that tracks key metabolic markers in real-time. It uses continuous glucose monitoring, AI-powered meal tracking, and expert coaching. It uses machine learning technology.[28][29] | |
| 2020 | June 1 | "Google updates Pixel devices with a new "bedtime" feature, new safety features"[30] | |
| 2020 | August 27 | Health-tracking platform launch | "AMAZON ANNOUNCES HALO, A FITNESS BAND AND APP THAT SCANS YOUR BODY AND VOICE"[31][32] |
| 2021 | March 31 | "Cisco is adding new "People Insights" to Webex to help you keep your professional screen time on track."[33] | |
| 2021 | April 15 | "Researchers in Japan have built a PV-powered device to measure volumetric variations in blood circulation. The system, which is just a few microns thick, was built with an organic solar module, a polymer light-emitting diode (PLED), and an organic photodetector."[34] |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
- Yuval Harari comments
- Quantified Self Apps
- [1] !!!!
- [2] (check also domain registration)
- [3] (check also domain registration)
- [4]
- [5]
- [6]
- Quantified self
- Wearable technology
- eHealth
- Human enhancement
- [7]
- [8]
- Internet of things
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lupton, Deborah (2 May 2016). The Quantified Self. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-5095-0059-8.
- ↑ Wong, Kai (15 November 2019). "The Quantified Self movement is dead". Medium.
- ↑ "The Quantified Self Movement: Self-Tracking in the Data Gold Rush". Bloomsoup. 23 July 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2021.
- ↑ Della Mea, Vincenzo (22 June 2001). "What is e-Health (2): The death of telemedicine?". Journal of Medical Internet Research. 3 (2): e22. PMC 1761900
 . PMID 11720964. doi:10.2196/jmir.3.2.e22
. PMID 11720964. doi:10.2196/jmir.3.2.e22 .
.
- ↑ "MyFitnessPal - Crunchbase Company Profile & Funding". Crunchbase. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ "Announcing Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) – beta". 24 August 2006. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ↑ "Amazon Acquires Social Reading Site Goodreads, Which Gives The Company A Social Advantage Over Apple". TechCrunch. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ "Goodreads - Crunchbase Company Profile & Funding". Crunchbase. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ "Todoist - Crunchbase Company Profile & Funding". Crunchbase. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ Wolf, Gary. "Quantified Self". Gary Wolf. Archived from the original (blog) on 2012-03-27. Retrieved 2012-03-26.
- ↑ Singer, Emily. "The Measured Life". MIT. Retrieved 2011-07-05.
- ↑ "quantifiedself.com whois lookup - who.is". who.is. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Swan, Melanie (June 2013). "The Quantified Self: Fundamental Disruption in Big Data Science and Biological Discovery". Big Data. 1 (2): 85–99. doi:10.1089/big.2012.0002.
- ↑ Duncan, David Ewing (2009). Experimental man : what one man's body reveals about his future, your health, and our toxic world. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley. ISBN 9780470176788.
- ↑ Perry, Bruce W. (2012). Fitness for geeks : real science, great nutrition, and good health (1st ed.). Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media. ISBN 1449399894.
- ↑ "Johnson & Johnson subsidiary launches self-tracking app". MobiHealthNews. 21 May 2014. Retrieved 20 March 2021.
- ↑ McGregor, Jay (25 July 2014). "India's Take On Google Glass, A Vibrating Smartshoe". Forbes. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ↑ Thoppil, Dhanya Ann Thoppil (24 July 2014). "India's Answer to Google Glass: The Smartshoe". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ↑ Anthony, Sebastian (24 July 2014). "The smartshoe: A much more sensible approach to wearable computing than Glass or a smartwatch". Extreme Tech. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ↑ "A smart shoe from Indian firm". Deccan Chronicle. 27 July 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ↑ Sawers, Paul (28 October 2014). "Google launches Google Fit app for Android, capturing all your fitness data in one place". TNW | Apps. Retrieved 5 May 2021.
- ↑ Nafus, Dawn (8 April 2016). Quantified: Biosensing Technologies in Everyday Life. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-03417-3.
- ↑ Neff, Gina; Nafus, Dawn (24 June 2016). Self-Tracking. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-52912-9.
- ↑ Lupton, Deborah. The Quantified Self. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-5095-0063-5.
- ↑ Moore, Phoebe V. (11 September 2017). The Quantified Self in Precarity: Work, Technology and What Counts. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-20160-1.
- ↑ Hoogendoorn, Mark; Funk, Burkhardt. Machine Learning for the Quantified Self: On the Art of Learning from Sensory Data. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-66308-1.
- ↑ Ng, Alfred. "Google wants to help you fight phone addiction". CNET. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ↑ Collier, Kara. "NutriSense V2.0 - Discover and reach your health potential". Product Hunt. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ "NutriSense - Crunchbase Company Profile & Funding". Crunchbase. Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ↑ Condon, Stephanie. "Google updates Pixel devices with a new "bedtime" feature, new safety features". ZDNet. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ↑ "Introducing Amazon Halo and Amazon Halo Band—A New Service that Helps Customers Improve Their Health and Wellness | Amazon.com, Inc. - Press Room". press.aboutamazon.com. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ↑ Bohn, Dieter (27 August 2020). "Amazon announces Halo, a fitness band and app that scans your body and voice". The Verge. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ↑ Condon, Stephanie. "Cisco adds new "People Insights" to Webex for a work-focused spin on digital wellness". ZDNet. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
- ↑ "I've got solar over my skin". pv magazine International. Retrieved 17 April 2021.