Difference between revisions of "Timeline of NTT Docomo"
| (40 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
| 2010s || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces one of the earliest commercial LTE services.<ref name="Overviewdd"/> Tata Docomo becomes the first private sector telecom company to launch {{w|3G}} services in India. | | 2010s || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces one of the earliest commercial LTE services.<ref name="Overviewdd"/> Tata Docomo becomes the first private sector telecom company to launch {{w|3G}} services in India. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | | 2019 onward || {{w|NTT Docomo}} begins rolling out 5G service in Japan. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 90: | Line 91: | ||
| 1996 || || Device || Market growth || The adoption rate for mobiles in Japan reaches 25%.<ref name="Personal Media"/> | | 1996 || || Device || Market growth || The adoption rate for mobiles in Japan reaches 25%.<ref name="Personal Media"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1997 || || || | + | | 1997 || || Financial || Funding || NTT MCN increases capital investment to 652.6 million JPY.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 1997 || March || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || NTT MCN launches DoPa packet-data communications service, the first data communications service in Japan.<ref name="History"/><ref name="The Six Immutable"/> | | 1997 || March || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || NTT MCN launches DoPa packet-data communications service, the first data communications service in Japan.<ref name="History"/><ref name="The Six Immutable"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1998 || || || Administration || NTT MCN establishes its urban information systems division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | + | | 1998 || || {{w|Information system}} || Administration || NTT MCN establishes its urban information systems division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 1998 || || || Recognition || NTT MCN acquires ISO9001 accreditation, an international standard used by organizations to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.<ref>{{cite web |title=WHAT IS ISO 9001:2015 – QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS? |url=https://asq.org/quality-resources/iso-9001 |website=asq.org |accessdate=16 October 2019}}</ref><ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 1998 || || || Recognition || NTT MCN acquires ISO9001 accreditation, an international standard used by organizations to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.<ref>{{cite web |title=WHAT IS ISO 9001:2015 – QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS? |url=https://asq.org/quality-resources/iso-9001 |website=asq.org |accessdate=16 October 2019}}</ref><ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1998 || October 12 || || | + | | 1998 || October 12 || Financial || [[w:Listing (finance)|Stock exchange listing]] || NTT MCN goes public on the {{w|Nikkei 225}} average.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT Mobile Communications Network |url=https://money.howstuffworks.com/10-biggest-ipos8.htm |website=money.howstuffworks.com |accessdate=15 October 2019}}</ref> The company is registered under the ticker TYO:9437.<ref name="crunchbase.com"/> NTT sells 30% of DoCoMo to the public.<ref name="dfgghj"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1998 || October 22 || || | + | | 1998 || October 22 || Financial || [[w:Listing (finance)|Stock exchange listing]] || NTT MCN is listed on the {{w|Tokyo Stock Exchange}}.<ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 1998 || December || || Acquisition || NTT MCN assumes control of Personal Handyphone System (PHS) business from NTT Personal Group.<ref name="History"/><ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | | 1998 || December || || Acquisition || NTT MCN assumes control of Personal Handyphone System (PHS) business from NTT Personal Group.<ref name="History"/><ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | ||
| Line 122: | Line 123: | ||
| 2000 || Late year || {{w|Cellular network}} || Userbase || There are 50 million Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) subscribers in Japan.<ref name="The Six Immutable"/> | | 2000 || Late year || {{w|Cellular network}} || Userbase || There are 50 million Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) subscribers in Japan.<ref name="The Six Immutable"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2000 || || || {{w|License}} || The {{w|Japanese government}} awards {{w|3G}} licenses to {{w|NTT Docomo}}, {{w|KDDI}} and {{w|J-Phone}} at no charge. This allows NTT Docomo to free up its cash stock for overseas investment.<ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | + | | 2000 || || {{w|Cellular network}} || {{w|License}} || The {{w|Japanese government}} awards {{w|3G}} licenses to {{w|NTT Docomo}}, {{w|KDDI}} and {{w|J-Phone}} at no charge. This allows NTT Docomo to free up its cash stock for overseas investment.<ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2001 || || || Recognition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires ISO14001 accreditation<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/>, the international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system.<ref>{{cite web |title=WHAT IS ISO 14001:2015 – ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS? |url=https://asq.org/quality-resources/iso-14001 |website=asq.org |accessdate=16 October 2019}}</ref> | | 2001 || || || Recognition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires ISO14001 accreditation<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/>, the international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system.<ref>{{cite web |title=WHAT IS ISO 14001:2015 – ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS? |url=https://asq.org/quality-resources/iso-14001 |website=asq.org |accessdate=16 October 2019}}</ref> | ||
| Line 134: | Line 135: | ||
| 2001 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} relocates the head office to {{w|Akasaka}} from {{w|Nishigotanda}}.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 2001 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} relocates the head office to {{w|Akasaka}} from {{w|Nishigotanda}}.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2001 || || || | + | | 2001 || || Financial || Funding || {{w|NTT Docomo}} investment ratio increases to 100%.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2001 || October || {{w|Cellular network}} || Milestone (service launch) || {{w|NTT Docomo}} becomes the first cellular operator in the world to offer commercial {{w|3G}} services (based on {{w|WCDMA}}) called {{w|Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access}} (FOMA). The service becomes first available in the {{w|Greater Tokyo Area}}, {{w|Yokohama}} and {{w|Kawasaki}}.<ref name="History"/><ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | | 2001 || October || {{w|Cellular network}} || Milestone (service launch) || {{w|NTT Docomo}} becomes the first cellular operator in the world to offer commercial {{w|3G}} services (based on {{w|WCDMA}}) called {{w|Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access}} (FOMA). The service becomes first available in the {{w|Greater Tokyo Area}}, {{w|Yokohama}} and {{w|Kawasaki}}.<ref name="History"/><ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 145: | ||
| 2002 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its Operation Systems HQ, System Development Division and Service Operations Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 2002 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its Operation Systems HQ, System Development Division and Service Operations Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2002 || March || || | + | | 2002 || February 19 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces agreement licensing German company {{w|E-Plus}} Mobilfunk GmbH & Co. KG to use its patents and technology for {{w|i-mode}} in Germany.<ref>{{cite web |title=DoCoMo signs i-mode deal with German firm |url=https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2002/02/19/business/docomo-signs-i-mode-deal-with-german-firm/#.XjyCq2j0mUk |website=japantimes.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || March || Financial || [[w:Listing (finance)|Stock exchange listing]] || {{w|NTT Docomo}} is listed on [[w:London stock exchange|London]] and {{w|New York stock exchange}}s.<ref name="History"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2002 || May 8 || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} states in a memorandum of understanding plans to convert its regional subsidiaries into wholly owned subsidiaries by way of share exchange.<ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | | 2002 || May 8 || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} states in a memorandum of understanding plans to convert its regional subsidiaries into wholly owned subsidiaries by way of share exchange.<ref name="i-mode Wireless"/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || May 22 || Financial || {{w|Stock split}} || {{w|NTT Docomo}} stocks are split with a 3:1 ratio.<ref name="split"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2002 || June 1 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches its i-shot service, allowing subscribers to transmit still images taken with compatible mobile phones having built-in cameras to virtually any device capable of receiving {{w|e-mail}}.<ref name="dd"/> | | 2002 || June 1 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches its i-shot service, allowing subscribers to transmit still images taken with compatible mobile phones having built-in cameras to virtually any device capable of receiving {{w|e-mail}}.<ref name="dd"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2002 || June 20 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} and {{w|KG Telecom}} launch an {{w|i-mode}} service in {{w|Taiwan}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=i-mode ready for Taiwan launch |url=https://www.cbronline.com/uncategorised/i_mode_ready_for_taiwan_launch/ |website=cbronline.com |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || October 14 || {{w|Mobile web}} || Userbase || Subscriptions for {{w|i-mode}} in Japan reaches 35 million.<ref name="sds"/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || October 15 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || Belgian telecom service provider [[w:Base (mobile telephony provider)|Base]] launches {{w|i-mode}} service in {{w|Belgium}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=Base launches i-mode service in Belgium |url=http://www.digitimes.com/news/a20021015PR203.html |website=digitimes.com |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2002 || November 15 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|Bouygues Telecom}} launches the {{w|i-mode}} service in {{w|France}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=I-mode ready to launch in France |url=https://www.computerweekly.com/news/2240048289/I-mode-ready-to-launch-in-France |website=computerweekly.com |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || January 14 || Device || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} i-shot handsets (camera phone) sales exceed 5 million.<ref name="dd">{{cite web |title=DoCoMo Camera Phone Sales Exceed 5 Million |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000928.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=12 November 2019}}</ref> | | 2003 || January 14 || Device || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} i-shot handsets (camera phone) sales exceed 5 million.<ref name="dd">{{cite web |title=DoCoMo Camera Phone Sales Exceed 5 Million |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000928.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=12 November 2019}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2003 || March 6 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces plans to unveil an always-on internet access service, dubbed "@ | + | | 2003 || January 17 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces the N2051 {{w|3G}} handset, which offers extended stand-by time and the ability to e-mail video clips.<ref>{{cite web |title=DoCoMo to Introduce Enhanced FOMA Handset Offering Video Clip e-Mailing |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000931.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || January 18 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces the F2051 3G handset, which features extended stand-by and the ability to e-mail video clips taken with its own camera.<ref>{{cite web |title=DoCoMo's New FOMA F2051 Handset Goes on Sale Jan. 18 |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000929.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || March 6 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces plans to unveil an always-on internet access service, dubbed "@FreeD", for use with compatible {{w|Personal Handy-phone System}} (PHS) terminals.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch Flat-Rate Internet Access Service for PHS |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000937.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || March 11 || Device || Product launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the introduction of the P2102V, the company's first {{w|3G}} videophone handset capable of video clip e-mailing and extended stand-by time, and the first {{w|Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access}} model to accept memory cards.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce New FOMA Videophone Model |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000940.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || March 11 || Device || Product launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the introduction of the P2102V, the company's first {{w|3G}} videophone handset capable of video clip e-mailing and extended stand-by time, and the first {{w|Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access}} model to accept memory cards.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce New FOMA Videophone Model |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000940.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 161: | Line 176: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || March 27 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the introduction of the its first {{w|Global Positioning Service}} (GPS) compatible handset, dubbed F661i, to the market.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce First GPS Handset |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000943.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || March 27 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the introduction of the its first {{w|Global Positioning Service}} (GPS) compatible handset, dubbed F661i, to the market.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce First GPS Handset |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000943.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || April 16 || Device || GPS launch ||{{w|NTT Docomo}} announces its first {{w|Global Positioning System}} compatible handset, dubbed F661i.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch Sales of First GPS Handset |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000948.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || May 19 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces launch of WORLD WING, an international roaming service for DoCoMo 3G handset users.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch International Roaming Service for 3G FOMA Users |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000963.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || May 26 || {{w|Mobile web}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches online shopping mall and account aggregation portal DoCommerce, which enables both 2G and 3G SSL-compatible {{w|i-mode}} handset users to manage their finances and shop online with their credit cards. The online mall launches with 10 virtual shops selling items such as accessories, perfumes and healthcare goods.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo launches mobile shopping mall and account aggregation portal |url=https://www.finextra.com/newsarticle/8935/ntt-docomo-launches-mobile-shopping-mall-and-account-aggregation-portal |website=finextra.com |accessdate=18 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || May 26 || {{w|Mobile web}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches online shopping mall and account aggregation portal DoCommerce, which enables both 2G and 3G SSL-compatible {{w|i-mode}} handset users to manage their finances and shop online with their credit cards. The online mall launches with 10 virtual shops selling items such as accessories, perfumes and healthcare goods.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo launches mobile shopping mall and account aggregation portal |url=https://www.finextra.com/newsarticle/8935/ntt-docomo-launches-mobile-shopping-mall-and-account-aggregation-portal |website=finextra.com |accessdate=18 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || June 3 || Website || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces a payments service to enable customers using {{w|2G}} and {{w|3G}} handsets to shop online at a dedicated portal site and receive bills for purchases together with their monthly mobile phone invoices.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Start Trial of Online Payments Service |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000975.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || June 3 || Website || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces a payments service to enable customers using {{w|2G}} and {{w|3G}} handsets to shop online at a dedicated portal site and receive bills for purchases together with their monthly mobile phone invoices.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Start Trial of Online Payments Service |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000975.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || June 25 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces introduction of {{w|i-mode}} in {{w|Spain}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=Telefonica Moviles Espana to Launch i-mode Service in Spain |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000980.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || June 30 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces launch of the F2102V mobile videophone, the first model compatible with Docomo's new FirstPass SSL client authentication service.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch FOMA F2102V Videophone |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000983.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || June 30 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces launch of the F2102V mobile videophone, the first model compatible with Docomo's new FirstPass SSL client authentication service.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch FOMA F2102V Videophone |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/000983.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 179: | Line 200: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || November 10 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the release of the mova P505iS, the world's first camera phone equipped with auto focus.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce P505iS: World's First Auto-Focus Camera Phone |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/001119.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || November 10 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the release of the mova P505iS, the world's first camera phone equipped with auto focus.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Introduce P505iS: World's First Auto-Focus Camera Phone |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/001119.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2003 || November 19 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces release of {{w|i-mode}} service in {{w|Italy}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=Wind Telecomunicazioni S.p.A. to Launch i-mode Service in Italy |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/001120.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2003 || December 9 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the release of three handsets in the {{w|2G}} mova 505iS series: "the SO505iS, a mega-pixel camera phone equipped to play extended-length video files; the N505iS, the first NEC-made camera phone in the mova lineup with 1.3 mega-pixel resolution; and the SH505iS, which comes with a 2.02 mega-pixel, auto-focus camera."<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch Three New Models in mova 505iS Series |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/001126.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2003 || December 9 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces the release of three handsets in the {{w|2G}} mova 505iS series: "the SO505iS, a mega-pixel camera phone equipped to play extended-length video files; the N505iS, the first NEC-made camera phone in the mova lineup with 1.3 mega-pixel resolution; and the SH505iS, which comes with a 2.02 mega-pixel, auto-focus camera."<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch Three New Models in mova 505iS Series |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2003/001126.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 202: | Line 225: | ||
| 2004 || April 28 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces launch an international roaming-in service to enable mobile subscribers of Docomo's 21 international partners in 19 countries and territories to use the company's {{w|3G}} [[W:Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access|FOMA]] network while in Japan.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch 3G Roaming-In Service for Visitors to Japan |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001169.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2004 || April 28 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Service launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces launch an international roaming-in service to enable mobile subscribers of Docomo's 21 international partners in 19 countries and territories to use the company's {{w|3G}} [[W:Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access|FOMA]] network while in Japan.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch 3G Roaming-In Service for Visitors to Japan |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001169.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2004 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes a Mobile Network Division | + | | 2004 || June 3 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announes launch of {{w|i-mode}} service in {{w|Greece}} via mobile network operator {{w|Cosmote}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=COSMOTE Mobile Telecommunications S.A. to Launch i-mode Service in Greece |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001180.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || June 10 || {{w|Mobile web}} || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} and {{w|Telstra}} announce launch of {{w|i-mode}} in {{w|Australia}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo and Telstra Commence Strategic Partnership for i-mode in Australia |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001181.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || End of June || {{w|Mobile web}} || Userbase || {{w|i-mode}} users outside {{w|Japan}} ({{w|Belgium}}, {{w|France}}, {{w|Germany}}, {{w|Taiwan}}, {{w|Netherlands}}, {{w|Spain}}, {{w|Italy}}, and {{w|Greece}}) exceed 3 million.<ref>{{cite web |title=i-mode users outside Japan exceed 3 million |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001190.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || || {{w|Cellular network}} || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes a Mobile Network Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || || {{w|Digital security}} || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes a Security Services Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || November 8 || {{w|Mobile web}} || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} and {{w|Cellcom}} launch of {{w|i-mode}} in {{w|Israel}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo and Cellcom Israel Commence Strategic Partnership for i-mode in Israel |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001216.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2004 || November 17 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces the 901i series of {{w|3G}} FOMA handsets, featuring greatly enhanced audio.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch 901i Series of 3G FOMA Handsets |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001220.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2004 || December || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches the F901iC {{w|3G}} {{w|FOMA}} handset, the latest model in the 901i series.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch F901iC 3G FOMA Handset |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001233.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=12 November 2019}}</ref> | | 2004 || December || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} launches the F901iC {{w|3G}} {{w|FOMA}} handset, the latest model in the 901i series.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo to Launch F901iC 3G FOMA Handset |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2004/001233.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=12 November 2019}}</ref> | ||
| Line 234: | Line 269: | ||
| 2007 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its Business Solution Headquarters, a System Integration Division, a Service Provider Division, a System Infrastructure Division, an Enterprise System Division, and an Information Security Department.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 2007 || || || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its Business Solution Headquarters, a System Integration Division, a Service Provider Division, a System Infrastructure Division, an Enterprise System Division, and an Information Security Department.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2007 || September || || | + | | 2007 || September || || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes an office in {{w|Hanoi}}, {{w|Vietnam}}, its fourth overseas office, joining existing facilities in {{w|Beijing}}, {{w|Shanghai}} and {{w|Singapore}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo Establishes Office in Hanoi, Vietnam |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2007/001365.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=24 January 2020}}</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2007 || September 29 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} {{w|3G}} [[w:Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access|FOMA]] subscribers surpass 40 million.<ref>{{cite web |title=3G FOMA Subscribers Exceed 40 Million |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2007/001367.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=26 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2007 || September 29 || {{w|Cellular network}} || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} {{w|3G}} [[w:Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access|FOMA]] subscribers surpass 40 million.<ref>{{cite web |title=3G FOMA Subscribers Exceed 40 Million |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2007/001367.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=26 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 252: | Line 287: | ||
| 2008 || January 24 || {{w|Mobile web}} || {{w|Partnership}} || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces a partnership with {{w|Google}}, which allows all models after the {{w|FOMA}}904i models to view {{w|YouTube}} videos.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://plusd.itmedia.co.jp/mobile/articles/0801/24/news066.html |title=ドコモとGoogleが提携──各種サービスのiモード対応などを推進 |accessdate=2008-01-26 |publisher=ITMedia+D モバイル |language=Japanese}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://plusd.itmedia.co.jp/mobile/articles/0801/24/news104.html |title=YouTube、ドコモの904i/905iシリーズに対応 |accessdate=2008-01-26 |publisher=ITMedia+D モバイル |language=Japanese}}</ref> | | 2008 || January 24 || {{w|Mobile web}} || {{w|Partnership}} || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces a partnership with {{w|Google}}, which allows all models after the {{w|FOMA}}904i models to view {{w|YouTube}} videos.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://plusd.itmedia.co.jp/mobile/articles/0801/24/news066.html |title=ドコモとGoogleが提携──各種サービスのiモード対応などを推進 |accessdate=2008-01-26 |publisher=ITMedia+D モバイル |language=Japanese}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://plusd.itmedia.co.jp/mobile/articles/0801/24/news104.html |title=YouTube、ドコモの904i/905iシリーズに対応 |accessdate=2008-01-26 |publisher=ITMedia+D モバイル |language=Japanese}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2008 || February || || {{w|Joint venture}} || NTT Investment Partners, Inc. (NTT-IP) is | + | | 2008 || February || || {{w|Joint venture}} || NTT Investment Partners, Inc. (NTT-IP) is established as a corporate venture capital firm by [[w:Nippon Telegraph and Telephone|Nippon Telegraph]] and Telephone Corporation (NTT). The firm focuses on funding advanced/disruptive technologies, services and business models around the world and looks to leverage NTT Group companies’ business operations, technologies and vast network to its portfolio companies.<ref>{{cite web |title=Gengo Closes a New Round of Funding with Intel Capital, Atomico, Iris Capital, Infocomm Investments, NTT-IP Fund and STC Ventures |url=https://gengo.com/news/gengo-closes-funding-intel/ |website=gengo.com |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=NTT Investment Partners Fund LP |url=https://www.bloomberg.com/profile/company/NTTIFZ:JP |website=bloomberg.com |accessdate=6 February 2020}}</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2008 || March || Device || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} reaches more than 53 million customers, which is more than half of Japan's cellular market.<ref name="Historyh"/> | | 2008 || March || Device || Userbase || {{w|NTT Docomo}} reaches more than 53 million customers, which is more than half of Japan's cellular market.<ref name="Historyh"/> | ||
| Line 266: | Line 301: | ||
| 2008 || June || {{w|Mobile operating system}} || Partnership || {{w|NTT Docomo}} joins the non-profit {{w|Symbian Foundation}} led by {{w|Nokia}} to co-develop a new {{w|Symbian}} smartphone operating system based on the [[w:S60 (software platform)|S60]] platform, which results in Symbian^2 for the Japanese market.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.allaboutsymbian.com/news/item/11613_First_Symbian2_phones_ship_in_.php|title=First Symbian^2 phones ship in Japan|author=|date=|website=allaboutsymbian.com|accessdate=27 March 2018}}</ref> | | 2008 || June || {{w|Mobile operating system}} || Partnership || {{w|NTT Docomo}} joins the non-profit {{w|Symbian Foundation}} led by {{w|Nokia}} to co-develop a new {{w|Symbian}} smartphone operating system based on the [[w:S60 (software platform)|S60]] platform, which results in Symbian^2 for the Japanese market.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.allaboutsymbian.com/news/item/11613_First_Symbian2_phones_ship_in_.php|title=First Symbian^2 phones ship in Japan|author=|date=|website=allaboutsymbian.com|accessdate=27 March 2018}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2008 || July 9 || || | + | | 2008 || July 9 || || International expansion || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces establishment of DOCOMO China Co., Ltd. as a wholly owned subsidiary in {{w|Shanghai}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Establishes Subsidiary Company in Shanghai, China |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2008/001410.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=24 January 2020}}</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2008 || November 5 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces release of 22 handsets in four new series — docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series™, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Unveils 22 Handsets in Four All-new Series |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2008/001420.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=25 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2008 || November 5 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} announces release of 22 handsets in four new series — docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series™, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Unveils 22 Handsets in Four All-new Series |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2008/001420.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=25 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 296: | Line 331: | ||
| 2009 || December 3 || || Acquisition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires {{w|net mobile AG}}, a publicly traded {{w|business-to-business}} {{w|service provider}}.<ref name="crunchbase.com"/><ref>{{cite web |title=net mobile AG acquired by NTT DoCoMo |url=https://www.crunchbase.com/acquisition/ntt-docomo-acquires-net-m--081d0edc |website=crunchbase.com |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo Other Acquisitions |url=https://www.startupranking.com/acquisition/ntt-docomo-acquires-net-mobile-ag-8978 |website=startupranking.com |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2009 || December 3 || || Acquisition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires {{w|net mobile AG}}, a publicly traded {{w|business-to-business}} {{w|service provider}}.<ref name="crunchbase.com"/><ref>{{cite web |title=net mobile AG acquired by NTT DoCoMo |url=https://www.crunchbase.com/acquisition/ntt-docomo-acquires-net-m--081d0edc |website=crunchbase.com |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo Other Acquisitions |url=https://www.startupranking.com/acquisition/ntt-docomo-acquires-net-mobile-ag-8978 |website=startupranking.com |accessdate=19 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2010 || April || || | + | | 2010 || April || Financial || Funding || {{w|NTT Docomo}} raises fund size of NTT-IP Fund to {{w|JPY}} 15 billion.<ref name="Historyh"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2010 || May 18 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces 20 new handsets, including 17 models in the four main series of {{w|FOMA}} {{w|3G}} handsets - docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series - plus three docomo Smartphone models.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Unveils 20 New Handsets |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2010/001476.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=25 January 2020}}</ref> | | 2010 || May 18 || Device || Mobile phone launch || {{w|NTT Docomo}} introduces 20 new handsets, including 17 models in the four main series of {{w|FOMA}} {{w|3G}} handsets - docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series - plus three docomo Smartphone models.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Unveils 20 New Handsets |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2010/001476.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=25 January 2020}}</ref> | ||
| Line 385: | Line 420: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2014 || October || {{w|Cellular network}} || {{w|Research and development) || {{w|NTT Docomo}} annpounces having successfully trialed {{w|network functions virtualization}} NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems.<ref>{{cite web |title=DOCOMO Successfully Trials NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2014/1014_00.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=28 October 2019}}</ref> | | 2014 || October || {{w|Cellular network}} || {{w|Research and development) || {{w|NTT Docomo}} annpounces having successfully trialed {{w|network functions virtualization}} NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems.<ref>{{cite web |title=DOCOMO Successfully Trials NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems |url=https://www.nttdocomo.co.jp/english/info/media_center/pr/2014/1014_00.html |website=nttdocomo.co.jp |accessdate=28 October 2019}}</ref> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2014 || || Financial || [[w:Listing (finance)|Stock exchange listing]] || {{w|NTT Docomo}} is delisted from the {{w|London stock exchange}}.<ref name="History"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2015 || || {{w|Computer security}} || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its IT Security Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 2015 || || {{w|Computer security}} || Administration || {{w|NTT Docomo}} establishes its IT Security Division.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
| Line 396: | Line 433: | ||
| 2015 || October 1 || || Merger || Docomo Capital announces its merger with Docomo Innovations.<ref>{{cite web |title=GATEWAY TO JAPAN |url=https://www.docomoinnovations.com/ |website=docomoinnovations.com |accessdate=18 November 2019}}</ref> | | 2015 || October 1 || || Merger || Docomo Capital announces its merger with Docomo Innovations.<ref>{{cite web |title=GATEWAY TO JAPAN |url=https://www.docomoinnovations.com/ |website=docomoinnovations.com |accessdate=18 November 2019}}</ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 2015 || Year round || || | + | | 2015 || Year round || Financial || Revenue generation || {{w|NTT Docomo}} generates JPY 4.4 trillion in annual revenue, down from JPY 4.5 trillion recorded in 2014.<ref name="Careers at NTT DoCoMo"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2016 || || || Acquisition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires "Kurumin", a next generation support certification logo.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | | 2016 || || || Acquisition || {{w|NTT Docomo}} acquires "Kurumin", a next generation support certification logo.<ref name="docomo-sys.co.jp"/> | ||
| Line 485: | Line 522: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Numerical and visual data == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Scholar === | ||
| + | |||
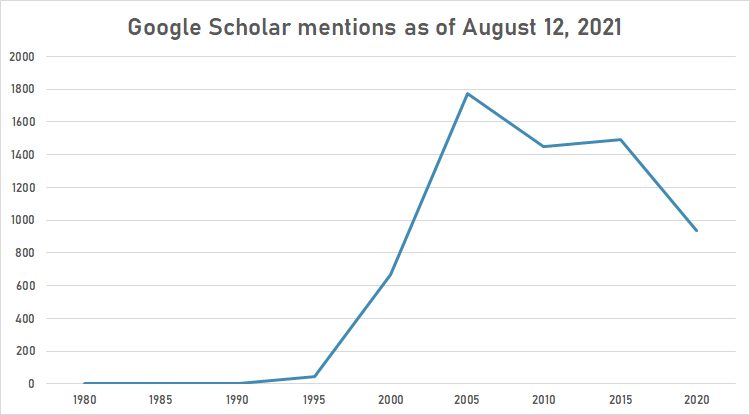
| + | The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of August 12, 2021. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="sortable wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Year | ||
| + | ! "NTT Docomo" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1980 || 1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1985 || 3 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1990 || 4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1995 || 42 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2000 || 665 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2005 || 1,770 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010 || 1,450 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2015 || 1,490 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2020 || 936 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NTT DoCoMo google schoolar.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
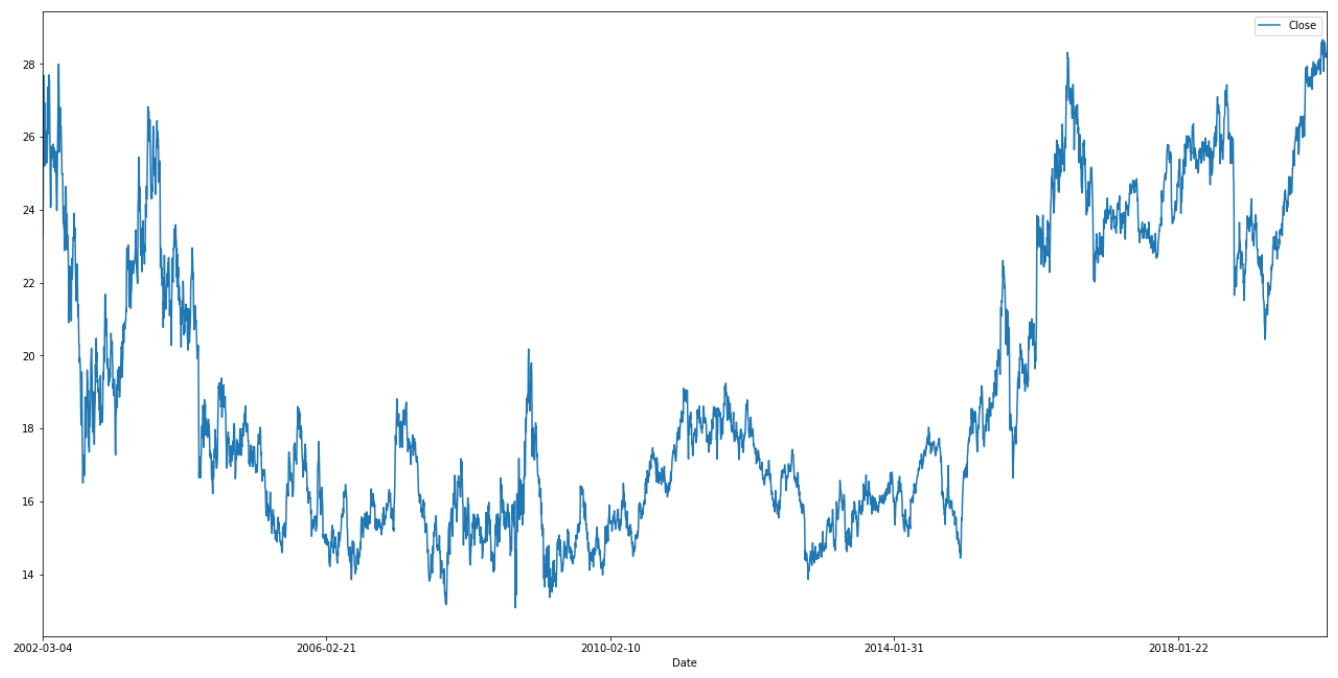
| + | The image shows NTT Docomo daily stock close price from March 4, 2002 to February 19 2020.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO |url=https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/DCMYY/history?p=DCMYY |website=finance.yahoo.com |accessdate=20 February 2020}}</ref> Note: A 3:1 ratio split on May 22 2002<ref name="split">{{cite web |title=NTT DOCOMO Inc Stock Splits History |url=https://www.netcials.com/stock-splits-history-nyse/DCM-NTT-DOCOMO-Inc/ |website=netcials.com |accessdate=14 March 2020}}</ref> is not reflected on the graph, therefore prices before that date should be multiplied by three if one is interested in the price per stock. | ||
| + | [[File:NTT Docomo daily stock close price.png|thumb|center|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Trends === | ||
| + | |||
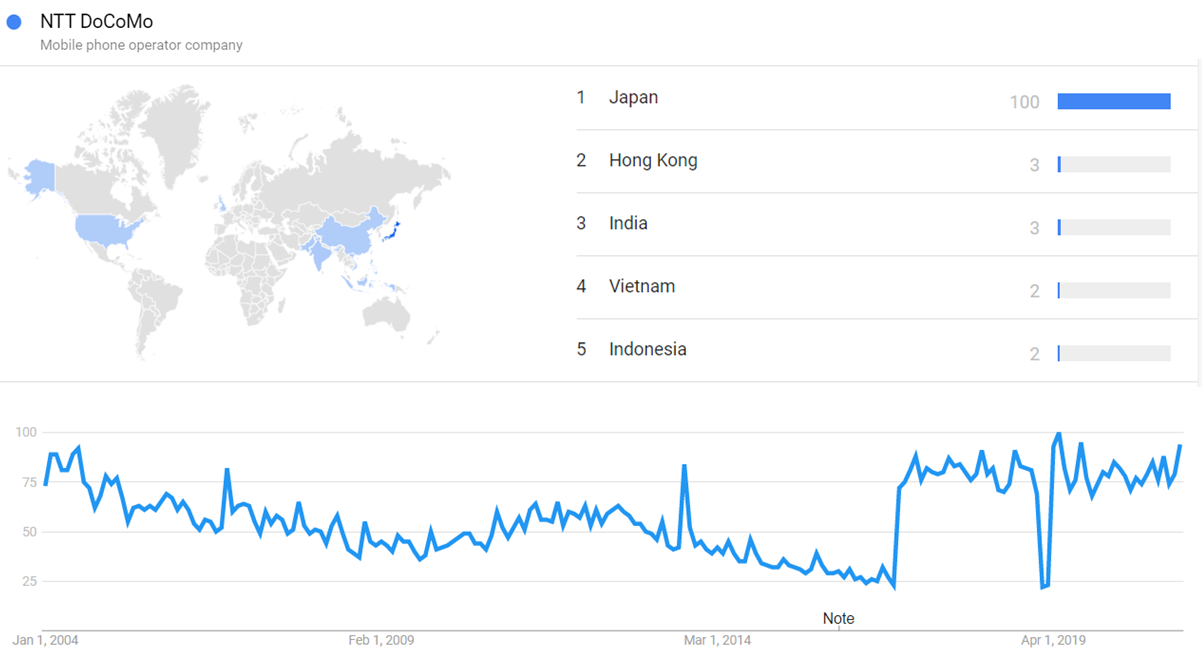
| + | The image below shows {{w|Google Trends}} data for NTT DoCoMo (Mobile phone operator company), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo |url=https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=%2Fm%2F020t9w |website=Google Trends |access-date=24 March 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NTT DoCoMo gt.png|thumb|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Ngram Viewer === | ||
| + | |||
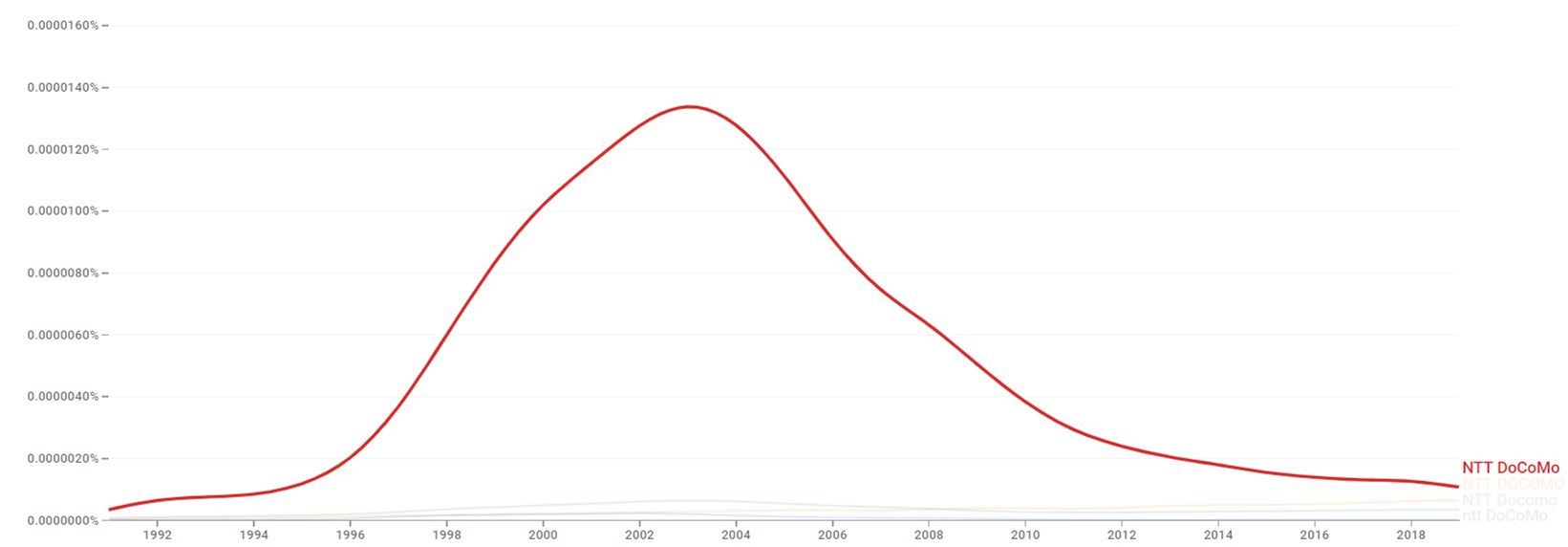
| + | The chart below shows {{w|Google Ngram Viewer}} data for NTT Docomo, from 1991 to 2019.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT Docomo |url=https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=NTT+Docomo&year_start=1991&year_end=2019&corpus=26&smoothing=3&case_insensitive=true |website=books.google.com |access-date=24 March 2021 |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NTT DoCoMo ngram.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Wikipedia Views === | ||
| + | |||
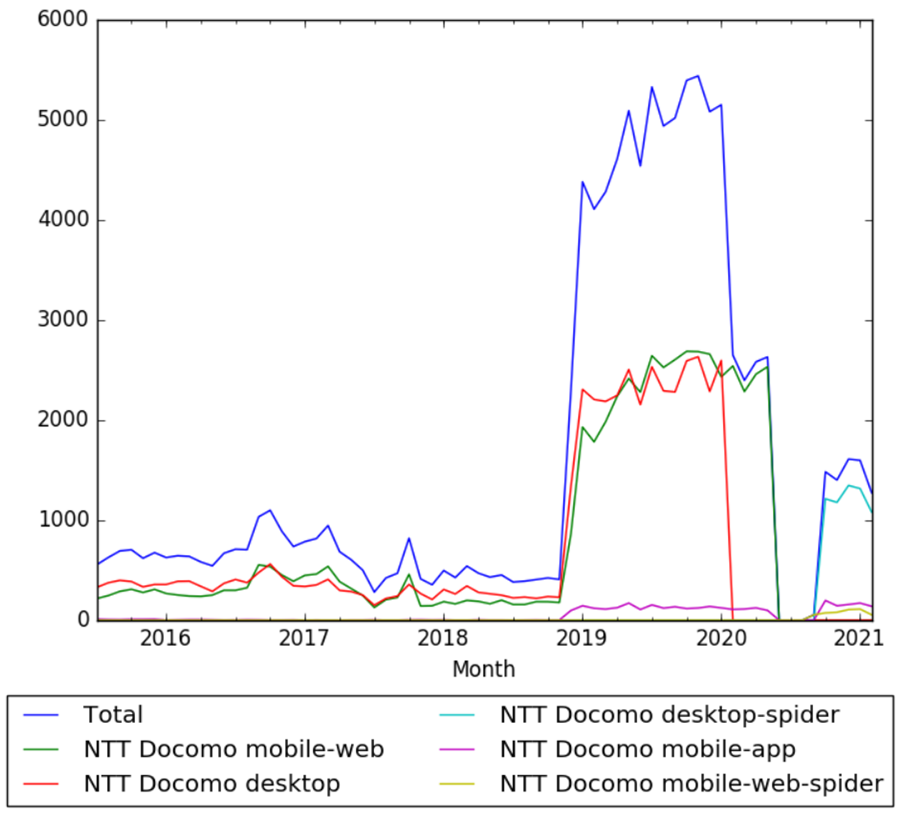
| + | The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article {{w|NTT DoCoMo}}, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to February 2021.<ref>{{cite web |title=NTT DoCoMo |url=https://wikipediaviews.org/displayviewsformultiplemonths.php?page=NTT+Docomo&allmonths=allmonths-api&language=en&drilldown=all |website=wikipediaviews.org |access-date=24 March 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NTT DoCoMo wv.png|thumb|center|450px]] | ||
==Meta information on the timeline== | ==Meta information on the timeline== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:06, 21 March 2024
This is a timeline of NTT Docomo, a Japanese mobile telecommunication services provider.
Contents
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- How did userbase evolve across different NTT Docomo products and services?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Userbase".
- You will see evolution of figures across a variety of services.
- What are some of the numerous R&D enterprises by NTT Docomo?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Research and development".
- You will se some important developments, some of them conducted in partnerships with other companies/organizations.
- Which worldwide technology milestones were pioneered by NTT Docomo?
- What are important company acquisitions by NTT Docomo?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Acquisition".
- What are some notable services launched by the company?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Service".
- You will see a variety of services launched by the company, including the i-mode, billing plans, international roaming, services through Tata Docomo, and a credit card.
- What are some notable products launched by the company?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Product".
- You will see a variety of products, including smartphones, mini tablets, SIM cards, etc.
- What are some important partnerships?
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 1952–1985 | Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (NTTPC) prelude era. NTTPC is established as a corporation. |
| 1985–1992 | Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT) prelude era. NTT is established as a private company. |
| 1992 onwards | NTT Docomo era, which is formally established taking over the mobile communications business of Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (“NTT Group”) as part of its corporate reorganization.[1] in 1993, the company launches the mobile phone service (PDC).[2] In 1997 it launches a packet communications service.[2] In 1999, the company launches i-mode, the world's first mobile internet service.[3] |
| 2000s | NTT Docomo becomes the first cellular operator in the world to offer commercial 3G services. By the late decade, the company reaches more than half of Japan's cellular market. |
| 2010s | NTT Docomo introduces one of the earliest commercial LTE services.[3] Tata Docomo becomes the first private sector telecom company to launch 3G services in India. |
| 2019 onward | NTT Docomo begins rolling out 5G service in Japan. |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Category | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1952 | Early development | Nippon Denshin Denwa Kosha (Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (NTTPC)) is launched as a public corporation and becomes the main engine for Japanese telecommunications R&D.[4][5] | ||
| 1985 | May 30 | Early development | State-owned Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corp. is privatized as Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT) amid liberalization of the telecommunications sector.[5][6][7] Operating domestic telecommunications, it is considered "one of the most powerful sparks that lit the communications revolution in Japan".[8] | |
| 1985 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT develops the first 'Shoulder phone', a car phone, that can be carried around in a shoulder trap.[9] | |
| 1987 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT offers the first handheld cellular phone, primarily for professional and organizational purposes.[9] | |
| 1989 | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT launches a new digital standard, which creates a fast growth for subscribers.[9] | |
| 1991 | August | Founding | NTT Mobile Communications Network is established by the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT) as a subsidiary to take over the mobile cellular operations.[10][11][12][13] This unit would soon adopt the nickname DoCoMo, which stands for "Do Communications Over the Mobile Network".[14] Operations commence at the Osaka Regional Marketing Branch.[6] | |
| 1991 | Cellular network | Userbase | There are about 5.75 million pager subscribers in Japan, of which NTT has some 3.5 million.[8] | |
| 1992 | Administration | NTT MCN relocates head office to Ikebukuro from Koji-Machi, Chiyoda-Ku.[6] | ||
| 1992 | Personnel | NTT MCN number of employees reaches 300.[6] | ||
| 1992 | July 1 | Reorganization | NTT MCN becomes an independent company and begins operations assuming control of mobile communications business of the reorganizing Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT).[8][15] This event is considered to be the birth of NTT DoCoMo, after the cellular communications services of NTT are carved out from the former telecom monopolist's other lines of business.[16] | |
| 1992 | Cellular network | Milestone (service launch) | NTT MCN launches the first analog cellular phone service.[13] | |
| 1993 | Service | Japan moves to digital mobile services as NTT MCN launches a new service based on Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) technology.[17] | ||
| 1993 | March | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT MCN Launches mova 2G (800 MHz), its first digital cellular phone service.[15][13] |
| 1993 | July | Administration | NTT MCN is reorganized into nine regional companies within Japan.[16] | |
| 1993 | Administration | NTT MCN establishes its Main Sales Division.[6] | ||
| 1993 | Userbase | Nearly 70 percent of new NTT pager subscribers are individuals instead of companies.[8] | ||
| 1994 | Background | The mobile phone market is opened to competition.[17] | ||
| 1994 | April | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT MCN launches CITYPHONE 1.5 GHz digital cellular phone service in urban areas.[15] |
| 1996 | Administration | NTT MCN relocates the head office to Nishigotanda from Ikebukuro.[6] | ||
| 1996 | Mid-year | Personnel | NTT MCN employs about 500 engineers.[18] | |
| 1996 | Device | Market growth | The adoption rate for mobiles in Japan reaches 25%.[9] | |
| 1997 | Financial | Funding | NTT MCN increases capital investment to 652.6 million JPY.[6] | |
| 1997 | March | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT MCN launches DoPa packet-data communications service, the first data communications service in Japan.[15][13] |
| 1998 | Information system | Administration | NTT MCN establishes its urban information systems division.[6] | |
| 1998 | Recognition | NTT MCN acquires ISO9001 accreditation, an international standard used by organizations to demonstrate the ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.[19][6] | ||
| 1998 | October 12 | Financial | Stock exchange listing | NTT MCN goes public on the Nikkei 225 average.[20] The company is registered under the ticker TYO:9437.[12] NTT sells 30% of DoCoMo to the public.[17] |
| 1998 | October 22 | Financial | Stock exchange listing | NTT MCN is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.[16] |
| 1998 | December | Acquisition | NTT MCN assumes control of Personal Handyphone System (PHS) business from NTT Personal Group.[15][16] | |
| 1998–1999 | Milestone (product launch) | NTT MCN morking team designer Shigetaka Kurita invents the Emoji, a pictographic language being adopted around the world. The first set of 176 12×12 pixel emoji is created as part of i-mode's messaging features to help facilitate electronic communication, and also to serve as a distinguishing feature from other services.[21] | ||
| 1999 | February | Mobile web | Milestone (service launch) | NTT MCN introduces its 2.5G i-mode, the first such service with national coverage.[13] i-mode is the world's first mobile internet service available through the handset itself. Before this, there no terminal other than personal computers for accessing the internet.[22] |
| 1999 | August 8 | Mobile web | Userbase | i-mode grows to 1 million subscribers.[13] |
| 1999 | December | Mobile web | Userbase | i-mode grows to 3 million subscribers.[13] |
| 2000 | April | Rebranding | Around its 15th anniversary, NTT Mobile Communications Network changes official name to NTT Docomo.[15][6] | |
| 2000 | August 6 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 10 million.[23] |
| 2000 | September | Facility | The NTT Docomo Yoyogi Building opens. One of the tallest buildings in Tokyo, it houses base station equipment and switching equipment.[24] | |
| 2000 | November 22 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 10 million.[23][13] |
| 2000 | Late year | Cellular network | Userbase | There are 50 million Personal Digital Cellular (PDC) subscribers in Japan.[13] |
| 2000 | Cellular network | License | The Japanese government awards 3G licenses to NTT Docomo, KDDI and J-Phone at no charge. This allows NTT Docomo to free up its cash stock for overseas investment.[16] | |
| 2001 | Recognition | NTT Docomo acquires ISO14001 accreditation[6], the international standard that specifies requirements for an effective environmental management system.[25] | ||
| 2001 | March 4 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 20 million.[23] |
| 2001 | May | Mobile web | Userbase | i-mode grows to 23 million subscribers.[13] |
| 2001 | July 1 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 25 million.[23] |
| 2001 | Administration | NTT Docomo relocates the head office to Akasaka from Nishigotanda.[6] | ||
| 2001 | Financial | Funding | NTT Docomo investment ratio increases to 100%.[6] | |
| 2001 | October | Cellular network | Milestone (service launch) | NTT Docomo becomes the first cellular operator in the world to offer commercial 3G services (based on WCDMA) called Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA). The service becomes first available in the Greater Tokyo Area, Yokohama and Kawasaki.[15][16] |
| 2001 | December 25 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 30 million.[23] |
| 2002 | Personnel | NTT Docomo reaches 700 employees.[6] | ||
| 2002 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes its Operation Systems HQ, System Development Division and Service Operations Division.[6] | ||
| 2002 | February 19 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo announces agreement licensing German company E-Plus Mobilfunk GmbH & Co. KG to use its patents and technology for i-mode in Germany.[26] |
| 2002 | March | Financial | Stock exchange listing | NTT Docomo is listed on London and New York stock exchanges.[15] |
| 2002 | May 8 | Administration | NTT Docomo states in a memorandum of understanding plans to convert its regional subsidiaries into wholly owned subsidiaries by way of share exchange.[16] | |
| 2002 | May 22 | Financial | Stock split | NTT Docomo stocks are split with a 3:1 ratio.[27] |
| 2002 | June 1 | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT Docomo launches its i-shot service, allowing subscribers to transmit still images taken with compatible mobile phones having built-in cameras to virtually any device capable of receiving e-mail.[28] |
| 2002 | June 20 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo and KG Telecom launch an i-mode service in Taiwan.[29] |
| 2002 | October 14 | Mobile web | Userbase | Subscriptions for i-mode in Japan reaches 35 million.[23] |
| 2002 | October 15 | Mobile web | International expansion | Belgian telecom service provider Base launches i-mode service in Belgium.[30] |
| 2002 | November 15 | Mobile web | International expansion | Bouygues Telecom launches the i-mode service in France.[31] |
| 2003 | January 14 | Device | Userbase | NTT Docomo i-shot handsets (camera phone) sales exceed 5 million.[28] |
| 2003 | January 17 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the N2051 3G handset, which offers extended stand-by time and the ability to e-mail video clips.[32] |
| 2003 | January 18 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the F2051 3G handset, which features extended stand-by and the ability to e-mail video clips taken with its own camera.[33] |
| 2003 | March 6 | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces plans to unveil an always-on internet access service, dubbed "@FreeD", for use with compatible Personal Handy-phone System (PHS) terminals.[34] |
| 2003 | March 11 | Device | Product launch | NTT Docomo announces the introduction of the P2102V, the company's first 3G videophone handset capable of video clip e-mailing and extended stand-by time, and the first Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access model to accept memory cards.[35] |
| 2003 | March 21 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the introduction of the D505i mobile phone, the first model in the company's 505i series of enhanced-PDC (2G) handsets that incorporate a Flash browser.[36] |
| 2003 | March 27 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the introduction of the its first Global Positioning Service (GPS) compatible handset, dubbed F661i, to the market.[37] |
| 2003 | April 16 | Device | GPS launch | NTT Docomo announces its first Global Positioning System compatible handset, dubbed F661i.[38] |
| 2003 | May 19 | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces launch of WORLD WING, an international roaming service for DoCoMo 3G handset users.[39] |
| 2003 | May 26 | Mobile web | Service launch | NTT Docomo launches online shopping mall and account aggregation portal DoCommerce, which enables both 2G and 3G SSL-compatible i-mode handset users to manage their finances and shop online with their credit cards. The online mall launches with 10 virtual shops selling items such as accessories, perfumes and healthcare goods.[40] |
| 2003 | June 3 | Website | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces a payments service to enable customers using 2G and 3G handsets to shop online at a dedicated portal site and receive bills for purchases together with their monthly mobile phone invoices.[41] |
| 2003 | June 25 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo announces introduction of i-mode in Spain.[42] |
| 2003 | June 30 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces launch of the F2102V mobile videophone, the first model compatible with Docomo's new FirstPass SSL client authentication service.[43] |
| 2003 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes ERP Division and Technical Center.[6] | ||
| 2003 | September | Userbase | After achieving a peak of more than 62 million subscribers for PDC services in Japan, the Japanese mobile market embraces next-generation technologies based on CDMA technology.[13] | |
| 2003 | October 1 | Cellular network | Userbase | The number of subscribers to the NTT Docomo 3G FOMA service nationwide passes the 1 million mark, two years after launch of the service.[44] |
| 2003 | October 30 | Mobile web | Userbase | Total subscribers to 2G and 3G i-mode mobile internet service in Japan surpass 40 million.[23] |
| 2003 | October 31 | Device | Product launch | NTT Docomo announces development of the first FOMA compact flash card, P2402, which enables 3G videophone and other wireless data communication via PCs and PDAs, such as Docomo's sigmarion III.[45] |
| 2003 | November 10 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the release of the mova P505iS, the world's first camera phone equipped with auto focus.[46] |
| 2003 | November 19 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo announces release of i-mode service in Italy.[47] |
| 2003 | December 9 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the release of three handsets in the 2G mova 505iS series: "the SO505iS, a mega-pixel camera phone equipped to play extended-length video files; the N505iS, the first NEC-made camera phone in the mova lineup with 1.3 mega-pixel resolution; and the SH505iS, which comes with a 2.02 mega-pixel, auto-focus camera."[48] |
| 2003 | December 18 | Subsidiary liquidation | NTT Docomo announces liquidation of NTT Docomo Telecomunicações do Brasil Limitada, a wholly owned subsidiary of Docomo.[49] | |
| 2004 | January 9 | Emergency management | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces the launch of an i-mode Disaster Message Board service allowing i-mode subscribers in Japan to post personal messages at a special i-mode site (provided in Japanese only) in the event of major calamities such as high-magnitude earthquakes.[50] |
| 2004 | January 29 | Application service provider | Subsidiary liquidation | NTT Docomo announces the decision to liquidate its subsidiary, Mobimagic Co., an application service provider for medium and small-sized companies.[51] |
| 2004 | January 29 | Cellular network | Userbase | NTT Docomo announces that subscribers to the 3G FOMA service surpassed two million, two years and four months after the service was launched.[52] |
| 2004 | February 26 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces release of the P900i, the third handset in the new 3G FOMA 900i series.[53] |
| 2004 | March 24 | Subsidiary liquidation | NTT Docomo announces the decision to liquidate DCM Capital LDN (United Kingdom) Limited, DCM Capital HKG (UK) Limited and DCM Capital 3G HKG (UK) Limited, each of which is a wholly owned subsidiary of DoCoMo.[54] | |
| 2004 | March 31 | Cellular network | Userbase (3G FOMA service) | NTT Docomo announces that subscribers to the 3G FOMA service surpassed the three million mark.[55] |
| 2004 | April 1 | Research and development | NTT Docomo establishes its Mobile Society Research Institute, which would study the social impact of mobile phone use.[56] | |
| 2004 | April | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo launches mova 506i series of three PDC (2G) i-mode mobile phones, a series of handsets featuring cameras with effective resolutions of more than one million pixels.[57] |
| 2004 | April 28 | Cellular network | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces launch an international roaming-in service to enable mobile subscribers of Docomo's 21 international partners in 19 countries and territories to use the company's 3G FOMA network while in Japan.[58] |
| 2004 | June 3 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo announes launch of i-mode service in Greece via mobile network operator Cosmote.[59] |
| 2004 | June 10 | Mobile web | Userbase | NTT Docomo and Telstra announce launch of i-mode in Australia.[60] |
| 2004 | End of June | Mobile web | Userbase | i-mode users outside Japan (Belgium, France, Germany, Taiwan, Netherlands, Spain, Italy, and Greece) exceed 3 million.[61] |
| 2004 | Cellular network | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes a Mobile Network Division.[6] | |
| 2004 | Digital security | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes a Security Services Division.[6] | |
| 2004 | November 8 | Mobile web | International expansion | NTT Docomo and Cellcom launch of i-mode in Israel.[62] |
| 2004 | November 17 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the 901i series of 3G FOMA handsets, featuring greatly enhanced audio.[63] |
| 2004 | December | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo launches the F901iC 3G FOMA handset, the latest model in the 901i series.[64] |
| 2004 | December 16 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the N900iG, the first FOMA 3G handset for fully functional mobile communications in approximately 115 countries/regions.[65] |
| 2005 | January 7 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the 2G mova N506iS, the world's first mobile phone to contain a flat panel display that also functions as a speaker.[66] |
| 2005 | November 24 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces launch of the FOMA SA800i, a child-friendly 3G mobile phone.[67] |
| 2005 | December | Service launch | NTT Docomo launches iD credit brand.[15] | |
| 2005 | December 29 | Cellular network | Userbase | The number of subscribers to Docomo's 3G FOMA service surpasses the 20 million mark.[68] |
| 2006 | February 23 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces achievement of 2.5Gbps packet transmission in the downlink while moving at 20km/h, in a 4G radio access field experiment.[69] |
| 2006 | April | Service launch | NTT Docomo launches DCMX mobile credit-card service.[15] | |
| 2006 | Information security | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes Information Security Services Division.[6] | |
| 2007 | January 16 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the development of new 3G FOMA handsets: the 703i Series, D800iDS and SO903iTV.[70] |
| 2007 | February 9 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces achievement of the world's first 5Gbps packet transmission in 4G field experiment, using 100MHz frequency bandwidth to a mobile station moving at 10km/h.[71] |
| 2007 | March 14 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the 3G FOMA F903iBSC business-use handset "to enable companies to address security issues such as information leaks and non-work-related use of corporate phones".[72] |
| 2007 | April 3 | Device | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces having developed a speech coding technology that provides "exceptionally high-quality voice for mobile phones, yet only requires the low-level computing power of conventional mobile telephony technologies".[73] |
| 2007 | July | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo begins testing an experimental Super 3G system for mobile communications, with aims at achieving a downlink transmission rate of 300Mbps over a high-speed wireless network.[74] |
| 2007 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes its Business Solution Headquarters, a System Integration Division, a Service Provider Division, a System Infrastructure Division, an Enterprise System Division, and an Information Security Department.[6] | ||
| 2007 | September | International expansion | NTT Docomo establishes an office in Hanoi, Vietnam, its fourth overseas office, joining existing facilities in Beijing, Shanghai and Singapore.[75] | |
| 2007 | September 29 | Cellular network | Userbase | NTT Docomo 3G FOMA subscribers surpass 40 million.[76] |
| 2007 | October | Device | Mobile phone launch | The prototype Wellness mobile phone of NTT Docomo and Mitsubishi Electric Corp. is launched at annual Japanese trade show CEATEC. It checks health with a motion sensor that detects body movement and measures calories, and includes a breathalyzer.[77] |
| 2007 | November 1 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces 23 new handsets available in a total of 75 colors in the new 905i and 705i series.[78] |
| 2007 | December | Acquisition | NTT Docomo and KT Freetel jointly invest US$200 million for a total of 33% stake in U Mobile Malaysia.[79] | |
| 2007 | December 10 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces launch of the F801i handset, which offers improved child-friendly features for security, theft/loss prevention, and ease of use.[80] |
| 2008 | January 3 | Userbase | NTT Docomo announces having surpassed 15 million subscribers to the i-channel news and information service.[81] | |
| 2008 | Earthquake Early Warning | Service launch | NTT Docomo begins offering a service called the "Area Mail Disaster Information Service" which broadcasts Earthquake Early Warning messages produced by the Japan Meteorological Agency to its subscribers with compatible handsets.[82] | |
| 2008 | January 24 | Mobile web | Partnership | NTT Docomo announces a partnership with Google, which allows all models after the FOMA904i models to view YouTube videos.[83][84] |
| 2008 | February | Joint venture | NTT Investment Partners, Inc. (NTT-IP) is established as a corporate venture capital firm by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT). The firm focuses on funding advanced/disruptive technologies, services and business models around the world and looks to leverage NTT Group companies’ business operations, technologies and vast network to its portfolio companies.[85][86] | |
| 2008 | March | Device | Userbase | NTT Docomo reaches more than 53 million customers, which is more than half of Japan's cellular market.[87] |
| 2008 | March | Venture capital | NTT Docomo establishes a JPY 10 billion venture fund, the NTT Investment Partners Fund, L.P. (NTT-IP Fund).[87] | |
| 2008 | March 27 | Molecular communication | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces having successfully demonstrated the world's first molecular delivery system for molecular communication.[88] |
| 2008 | April 19 | Leadership | Ryuji Yamada is promoted as the president of NTT Docomo. Masao Nakamura stays as a director and senior adviser. [89] | |
| 2008 | May 27 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces the new 906i and 706i series comprising 19 handsets and 64 body colors.[90] |
| 2008 | June | Mobile operating system | Partnership | NTT Docomo joins the non-profit Symbian Foundation led by Nokia to co-develop a new Symbian smartphone operating system based on the S60 platform, which results in Symbian^2 for the Japanese market.[91] |
| 2008 | July 9 | International expansion | NTT Docomo announces establishment of DOCOMO China Co., Ltd. as a wholly owned subsidiary in Shanghai.[92] | |
| 2008 | November 5 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces release of 22 handsets in four new series — docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series™, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series.[93] |
| 2008 | November | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires a 26% stake in Tata Teleservices for US$2.7 billion.[94] | |
| 2008 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes a Customer Information Systems Division, a Billing Systems Division, an Enterprise Information Systems Division, an Information Systems Infrastructure Division, a Business Intelligence Systems Division, a Service Platform Division, a System Development Division, and a Public Enterprise Business Division.[6] | ||
| 2009 | May 11 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of a "highly efficient mobile spatial audio transmission technology that enables a mobile phone user to assign a spatial position to each sound source when listening to multiple sound sources, such as during a game or a conference call".[95] |
| 2009 | May 19 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces its lineup of 18 new handsets, including models in four main series of FOMA 3G handsets: docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series, as well as the new Evangelion Phone based on the anime film.[96] |
| 2009 | June 6 | Cellular network | Service | The Tata Docomo service is commercially launched in India.[97] |
| 2009 | July 2 | Money transfer | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces a new service enabling an individual subscriber to use their Docomo mobile phone to easily and quickly remit money to another Docomo user.[98] |
| 2009 | July 5 | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires San Diego, California-based PacketVideo for US$157.1 million. PacketVideo produces software for wireless multimedia that includes the display of video on mobile handsets.[12] | |
| 2009 | July 15 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces development of the SOLAR HYBRID, a solar-powered, waterproof mobile phone.[99] |
| 2009 | August 24 | Userbase | Subscribers to DCMX, Docomo's credit payment service, surpasses 10 million in Japan.[100] | |
| 2009 | September 24 | Device | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of mobile phone prototype made with the surplus wood of trees culled during thinning operations to maintain healthy forests.[101] |
| 2009 | October 27 | Mobile web | Service | NTT Docomo introduces a new service that allows FOMA users to send and receive domestic i-mode mails.[102] |
| 2009 | November 10 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces 19 new handsets, as well as a 3G-capable digital photo frame. The lineup includes models in the four main series of FOMA 3G handsets —docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series, docomo SMART series, and docomo PRO series.[103] |
| 2009 | December 3 | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires net mobile AG, a publicly traded business-to-business service provider.[12][104][105] | |
| 2010 | April | Financial | Funding | NTT Docomo raises fund size of NTT-IP Fund to JPY 15 billion.[87] |
| 2010 | May 18 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces 20 new handsets, including 17 models in the four main series of FOMA 3G handsets - docomo STYLE series, docomo PRIME series, docomo SMART series and docomo PRO series - plus three docomo Smartphone models.[106] |
| 2010 | Healthcare | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes CliNIC Division.[6] | |
| 2010 | June | Userbase | Tata Docomo reaches about 32.82 million users.[107] | |
| 2010 | September 28 | Electronic publishing | Service launch | NTT Docomo announces trial of e-book distribution service, with aims at gaining feedback from customers prior to the start of a full-scale e-book retail service with Dai Nippon Publishing.[108] |
| 2010 | November 5 | Cellular network | Service launch | Tata Docomo becomes the first private sector telecom company to launch 3G services in India.[109] |
| 2010 | November 8 | Mobile web | Service | NTT Docomo announces launch of an i-mode version of its “docomo market” mobile portal to provide the more than 48 million Docomo customers using i-mode-enabled handsets with simplified access to a range of mobile applications, music and electronic books.[110] |
| 2010 | November 22 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces a Japanese-market version of Samsung’s GALAXY Tab smart media device to be released in Japan.[111] |
| 2010 | December | Cellular network | Milestone (service launch) | NTT Docomo launches one of world's first Long-Term Evolution (LTE) services, Xi (read "crossy").[15] |
| 2011 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes its Enterprise Solution Division.[6] | ||
| 2011 | January 11 | Joint venture | NTT Docomo announces joint venture with 2Dfacto, Inc. for the launch of a digital/physical hybrid bookstore that would open to sell electronic books to users of smartphones and e-book readers marketed by NTT Docomo.[112] | |
| 2011 | March 28 | Facility | NTT Docomo announces the establishment of a dedicated Smart Communication Services Department, with aims at strengthening its growing smartphone business.[113] | |
| 2011 | June | Internet security | Partnership | NTT Docomo announces team with McAfee to provide McAfee VirusScan Mobile for its Android mobile users.[114] |
| 2011 | September 8 | Device | Tablet launch | NTT Docomo introduces the first tablets compatible with its extra-high-speed next-generation LTE service, Xi (read “Crossy”). The “docomo Tablet GALAXY Tab 10.1 LTE SC-01D” and the “docomo Tablet ARROWS Tab LTE F-01D” are announced for sale.[115] |
| 2011 | September 16 | Recognition | NTT Docomo announces having achieved top ranking in business customer satisfaction for mobile phone and PHS services.[116] | |
| 2011 | Mid–November | Mobile web | Service | NTT Docomo launches two new services for smartphones, “dmenu” and “dmarket.” The dmenu portal is aimed to provide a wide range of apps and other content from diverse providers, as well as enriched versions of the popular i-mode content, optimized for easy-to-use smartphone interfaces. The new dmarket content store is aimed at offering a large amount of other content, including movies, music, e-books and Android.[117] |
| 2011 | November 24 | Recognition | NTT Docomo announces having received the highest marks among mobile phone operators in the 2011 Japan Mobile Phone Service StudySM, a customer-satisfaction study conducted by J.D. Power Asia Pacific.[118] | |
| 2012 | February 1 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo and The Walt Disney Company (Japan) announce launch of an exclusive smartphone brand, “Disney Mobile on docomo”. Exclusive content and services include access to Disney full-length animations, live actions and overseas dramas, digital content from Disney, such as puzzle and music game applications for children and family-entertainment, original Disney applications, and various customer benefits in cooperation with Tokyo Disney Resort.[119] |
| 2012 | March | Cellular network | Service | NTT Docomo shifts customer base completely to 3G and LTE services.[15] |
| 2012 | March 11 | Cellular network | Userbase | NTT Docomo mobile subscribers surpass 60 million. The figure includes customers who subscribe to the company’s LTE, 3G and 2G mobile services.[120] |
| 2012 | June 8 | Cellular network | Userbase | NTT Docomo announces that subscribers to Xi, the company’s extra-high-speed LTE mobile service offering a maximum downlink of 75 Mbps, surpassed three million.[121] |
| 2012 | July | Healthcare | Joint venture launch | NTT Docomo and Japanese electronics company Omron establish docomo Healthcare Inc, a new company with the purpose to design, develop and provide healthcare support services.[122] |
| 2012 | July 26 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces the Raku-Raku smart phone, the first one designed for users who are new to touchscreen operations.[123] |
| 2012 | August 10 | Mobile web | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires Italian mobile commerce ecosystem company Buongiorno for US$260 million.[12][124] |
| 2012 | October 1 | Mobile translation | Research and development) | NTT Docomo announces launch the world’s first commercial mobile service for translation of conversations between people speaking Japanese and other languages. The company also announces a translator with word recognition camera, which translates foreign menus and signage by simply placing a smartphone camera in front of text.[125] |
| 2012 | October 11 | Mobile web | Service | NTT Docomo announces that it would begin operating platforms for gaming and online shopping via its dmarket portal of content and services for smartphones and tablets. The new mobile gaming platform, dgame, would offer games in cooperation with providers such as Bandai Namco Entertainment, Konami, Sega, and Square Enix, starting with 15 social gaming titles.[126] |
| 2012 | October 11 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces its 2012 winter lineup of 16 new models, including nine smartphones, one tablet, four feature phones, one photo panel and one mobile Wi-Fi router.[127] |
| 2012 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes a Web System Division, and a Corporate Social Responsibility Department.[6] | ||
| 2013 | January 10 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo announces development of the Smartphone for Juniors SH-05E, an entry-level model for upper elementary and junior high school students. The device enables parents to control voice calls and usage by setting restrictions on time of day and/or maximum amount of call time, as well as email and online activity. It is also equipped with an alarm.[128] |
| 2013 | January 22 | Device | Mobile phone, tablet, router launch | NTT Docomo introduces its 2013 spring lineup of 12 models, which includes 11 smartphones and tablets, plus one mobile Wi-Fi router.[129] |
| 2013 | February | Business incubation | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires NTT-IP with the purpose to strengthen cooperation with startup companies in terms of venture funding and incubation. The DOCOMO Innovation Fund Partnership is established as a JPY 10 billion new venture fund and the DOCOMO’s Incubation Program starts operating.[87] |
| 2013 | February 23 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces that in a joint experiment conducted with the Tokyo Institute of Technology it succeeded in the world's first packet transmission uplink rate of approximately 10 Gbps. The test is expected to help pave the way for future super-high-bit-rate mobile communications.[130] |
| 2013 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes its Enterprise Solution Division.[6] | ||
| 2013 | Recognition | NTT Docomo acquires ISO39001 accreditation.[6] | ||
| 2013 | November 25 | Service | NTT Docomo announces launch of a one-day (24-hour) flat-rate data communications billing plan for customers traveling overseas.[131] | |
| 2013 | July | Rebranding | NTT Docomo changes its trade name to NTT DOCOMO Ventures, Inc.[87] | |
| 2013 | August 27 | E-commerce | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires Austrian e-commerce solution provider Fine Trade.[132][12] |
| 2013 | August 30 | Recognition | NTT Docomo announces it has been ranked highest in business customer satisfaction for fifth straight year.[133] | |
| 2014 | January | Venture capital | NTT Docomo establishes a JPY 10 billion venture fund, NTT Investment Partners Fund II, L.P. (NTT-IP Fund II).[87] | |
| 2014 | May 14 | Cellular network | Service | NTT Docomo announces that its extra-high speed XiTM network would offer Japan's first LTE service for stable, high-quality voice and video calls using Voice-over-LTE (VoLTE) technology.[134] |
| 2014 | May 14 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces its 2014 summer lineup of mobile devices, comprising six smartphones, two tablets, two feature phones, one Raku-Raku ("easy-easy") phone and one USB data terminal.[135] |
| 2014 | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes Cloud Business Division, DOCOMO IT Systems Division, DOCOMO IT Infrastructure Division, DOCOMO Business Division, Legal & Contract Department, Internal Audit Department, and a Quality Control Department.[6] | ||
| 2014 | July | Program launch | NTT Docomo starts operating new business co-creation program in cooperation with startup, 39works.[87] | |
| 2014 | Emergency management | Service launch | Under Civil Protection Law of Japan, Docomo begins offering a service called the "Area Mail Disaster and Evacuation Information Service" which broadcasts J-Alert messages (including Earthquake Early Warning) produced by the Japan Fire and Disaster Management Agency to its subscribers with compatible handsets (e.g. Sony XPERIA, iPhone 5s, Samsung Galaxy).[136] | |
| 2014 | October | Cellular network | Research and development) | NTT Docomo annpounces having successfully trialed network functions virtualization NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems.[137] |
| 2014 | Financial | Stock exchange listing | NTT Docomo is delisted from the London stock exchange.[15] | |
| 2015 | Computer security | Administration | NTT Docomo establishes its IT Security Division.[6] | |
| 2015 | March 27 | Cellular network | Service | NTT Docomo launches Premium 4G, a LTE Advanced service.[138] |
| 2015 | May 13 | Mobile web | Service | NTT Docomo announces integration of DOCOMO's dmarket services with social networking functions offered by Facebook.[139] |
| 2015 | September 30 | Device | Smartphone, tablet, wouter launch | NTT Docomo its 2015 winter/2016 spring lineup of mobile devices, which includes 10 smartphones, one each tablet, feature phone and mobile Wi-Fi router.[140] |
| 2015 | October 1 | Merger | Docomo Capital announces its merger with Docomo Innovations.[141] | |
| 2015 | Year round | Financial | Revenue generation | NTT Docomo generates JPY 4.4 trillion in annual revenue, down from JPY 4.5 trillion recorded in 2014.[1] |
| 2016 | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires "Kurumin", a next generation support certification logo.[6] | ||
| 2016 | May 24 | Cellular network | Research and development | In a trial jointly conducted with Nokia, NTT Docomo announces having achieved the world's first wireless real-time transmission of 8K video deploying radio access technology for 5G mobile communications systems.[142] |
| 2016 | June 13 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo and Ericsson announce successful completion of a joint Proof of Concept (PoC) of dynamic network slicing technology for 5G core networks. NTT Docomo is responsible the network slice creation and selection functions, and Ericsson developed technologies to perform network slice lifecycle and service management.[143] |
| 2017 | January | International expansion | NTT Docomo launches its NTT DOCOMO Ventures' Silicon Valley branch in the United States.[87] | |
| 2017 | Recognition | NTT Docomo acquires the highest position of "Eruboshi", based on Act to advance women's success in their working life.[6] | ||
| 2017 | February | Device | SIM card launch | NTT Docomo announes a new eSIM platform that enables companion consumer devices embedded with subscriber identity modules (eSIM), including tablets and wearables, to connect to mobile networks through remote provisioning of the profile.[144] |
| 2017 | February 27 | Cellular network | Partnership | Qualcomm Technologies, Ericsson, and NTT Docomo announce collaboration on 5G New Radio (NR) trials to accelerate wide-scale 5G deployments in Japan.[145] |
| 2017 | April 17 | Device | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of the world's first spherical drone display, a vehicle able to display LED images on an omnidirectional spherical screen while in flight.[146] |
| 2017 | April 23 | Device | Mobile phone launch | NTT Docomo introduces five new 3G FOMA 904i models.[147] |
| 2017 | June 27 | Device | Research and development | China Mobile Communications Corporation and NTT Docomo announce joint development of the world's first multi-vendor embedded subscriber identity module (eSIM) system within their commercial environments based on the GSMA's Remote Provisioning Architecture for Embedded UICC3.1 (GSMAv3.1) standard.[148] |
| 2017 | October | Venture capital | NTT Docomo establishes a JPY 15 billion new venture fund, Docomo Innovation Fund II, L.P.[87] | |
| 2017 | November 28 | Device | SIM card launch | In collaboration with international digital security company Gemalto, NTT Docomo announces development of the world's first multi-profile SIM "for use through multi-carrier collaborations that can allow users to switch between profiles, which include data such as contract information and telephone numbers, on their smartphone or tablet in each country."[149] |
| 2018 | Administration | NTT Docomo Establishes IoT Division, Sales Channel Promotion Division Certified as a Health and Productivity Management Organization (White 500).[6] | ||
| 2018 | Recognition | NTT Docomo receives the Certification of Silver (Gin-no-Nintei).[6] | ||
| 2018 | March 16 | Artificial intelligence | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces the launch of an AI engine that "quickly, simply and accurately analyzes shelf allocation in stores and warehouses using photos taken with smartphones and other common devices".[150] |
| 2018 | May 9 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces that together with NEC Corporation and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT) it has achieved what is considered to be the first successful 28 GHz wireless data transmission between a 5G base station and a 5G mobile station in 5G field trials using a car moving at 305 km/h.[151] |
| 2018 | May 30 | Mobile web | Product launch | NTT Docomo launches My Daiz, a digital assistant that uses artificial intelligence to analyze the movements of smartphone and tablet users to recommend different services, including JapanTaxi's app, to users.[152][153] |
| 2018 | June 11 | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces successful development of population flow statistics for analyzing population mobility based on operational data from the company's nationwide mobile network in Japan.[154] | |
| 2018 | July 5 | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of the world's first 8K virtual reality (VR) live video streaming and viewing system for showing live events in 360° 8K VR video.[155] | |
| 2018 | November 29 | Research and development | NTT Docomo and Toyota announce having successfully controlled the Toyota-developed T-HR31 humanoid robot in trials using 5G under a test environment with control from a remote location (a distance of approximately 10 kilometers) using 5G in an area between two points.[156] | |
| 2019 | June 26 | Research and development | China Mobile and NTT Docomo announce launch of an eSIM solution to enable cross-vendor SIM profile switching from DOCOMO to China Mobile.[157] | |
| 2018 | July | Venture capital | NTT Docomo establishes a JPY 20 billion venture fund, NTT Investment Partners Fund III, L.P. (NTT-IP Fund III).[87] | |
| 2018 | Recognition | NTT Docomo manages employee health from business management standpoint and is certified “White 500” Recognition for Excellence in Health and Productivity Management.[158] | ||
| 2018 | October 25 | Internet of things | Program launch | NTT Docomo launches the "DOCOMO Asia IoT Program" (AIP), with aims at "fostering collaboration among IoT providers and expand the IoT market across the Asia region". Mobile operators from 15 countries in the region express their intention to participate in the program.[159] |
| 2018 | November 29 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo and Toyota announce successful joint control of the Toyota-developed T-HR31 humanoid robot in trials using 5G under a test environment with control from a remote location.[160] |
| 2018 | December 28 | Acquisition | NTT Docomo acquires Conobie, a Japanese website about parenting that provides articles and short comics about pregnancy, childbirth, childcare, and parenting.[12][161] | |
| 2019 | February 4 | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of the world's first 8K 3D virtual reality system for live video streaming and viewing at 60 frames per second (fps) over 5G mobile communications.[162] | |
| 2019 | February 18 | Recognition | NTT Docomo is ranked as the leading mobile operator in the world in terms of applications for candidate standard-essential patents (SEPs) for the new fifth-generation (5G) mobile communication standard. The company is also ranked first in terms of 5G technical proposals (contributions). The rankings are based on a study conducted by Japanese firm Cyber Creative Institute Co.[163] | |
| 2019 | May 29 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo, AGC Inc. and Ericsson announce having achieved the world's first 5G mobile telecommunications using an antenna embedded in synthetic fused silica glass to transmit and receive 28 GHz 5G radio signals for stable, high-speed mobile communication in buildings, vehicles and trains.[164] |
| 2019 | July 31 | Device | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of an application programming interface for its docomo sky drone-operation platform and uses the API to "successfully integrate docomo sky with NEXSYS-ONE's tower maintenance platform in a joint trial, demonstrating the possibility to use drones for automated inspections and maintenance of mobile-network base-station towers."[165] |
| 2019 | Administration | NTT Docomo Establishes Sales Channel Promotion Department, Security Operation Center, Web Systems Department, SE & Business Support Center, Human Resources and Development Department, and Western Branch.[6] | ||
| 2019 | May 17 | Device | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces development of a drone that is propelled safely through the air with ultrasonic vibrations, which make it appropriate for concert halls and other indoor spaces.[166] |
| 2019 | May 23 | Artificial intelligence | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces research in collaboration with Tohoku University, of an AI technology to detect periodontal disease simply by photographing a person's gums with a smartphone.[167] |
| 2019 | September 2 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces having joined the 5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation (5G-ACIA) "with the aim of further advancing the use of 5G technology in the manufacturing sector".[168] |
| 2019 | September 10 | Cellular network | Partnership | NTT Docomo announces agreement with Omron and Nokia Networks to collaborate in trials of 5G mobile communication technology inside factories, "with the aim of significantly enhancing future manufacturing productivity". [169] |
| 2019 | September 30 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces achievement of the world's first 28 GHz-band 5G mobile communications between base stations and a high-speed bullet train during experimental trials to verify further enhancement of 5G in collaboration with Central Japan Railway Company.[170] |
| 2019 | December 5 | Artificial intelligence | Research and development | NTT Docomo and Kyoto University announce joint development of what is believed to be the world's first artificial intelligence-based system for inspecting bridges based on vehicle weights and structural deflection estimated from video footage.[171] |
| 2019 | December 20 | Healthcare | Acquisition | NTT Docomo announces purchase of all shares of docomo Healthcare, Inc. and make it a wholly owned subsidiary of NTT Docomo.[172] |
| 2020 | January 17 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo announces world's first trial of a prototype transparent dynamic metasurface using 28 GHz 5G radio signals. The prototype is a collaboration with glass manufacturing company AGC Inc.[173] |
| 2020 | January 24 | Cellular network | Research and development | NTT Docomo releases a white paper on the topic of 6G, the sixth-generation mobile communications system that the company aims to launch on a commercial basis by 2030. The paper contains the company's views in the field of 5G evolution and 6G communications technology, areas that it has been researching since 2018.[174] |
| 2020 | July | Cellular network | Infrastructure | NTT Docomo plans to have 5G base stations in all 47 Japanese prefectures by this time.[175] |
| 2021 | Spring | Cellular network | Infrastructure | NTT Docomo plans to reach a total of 10,000 5G base stations by this time.[175] |
| 2026 | March | Mobile web | Service shutdown | NTT Docomo plans to discontinue its internet-capable mobile phone system i-mode (introduced in 1999) by this time, due to a dwindling number of users.[176] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of August 12, 2021.
| Year | "NTT Docomo" |
|---|---|
| 1980 | 1 |
| 1985 | 3 |
| 1990 | 4 |
| 1995 | 42 |
| 2000 | 665 |
| 2005 | 1,770 |
| 2010 | 1,450 |
| 2015 | 1,490 |
| 2020 | 936 |
The image shows NTT Docomo daily stock close price from March 4, 2002 to February 19 2020.[177] Note: A 3:1 ratio split on May 22 2002[27] is not reflected on the graph, therefore prices before that date should be multiplied by three if one is interested in the price per stock.
Google Trends
The image below shows Google Trends data for NTT DoCoMo (Mobile phone operator company), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[178]
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for NTT Docomo, from 1991 to 2019.[179]
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article NTT DoCoMo, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to February 2021.[180]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Careers at NTT DoCoMo". cleverism.com. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Trends in Mobile Technology and Business in the Asia-Pacific Region (Youngjin Yoo, Jae-Nam Lee, Chris Rowley ed.).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Overview". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ Okada, Yoshitaka. Struggles for Survival: Institutional and Organizational Changes in Japan's High-Tech Industries.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation History". fundinguniverse.com. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 6.12 6.13 6.14 6.15 6.16 6.17 6.18 6.19 6.20 6.21 6.22 6.23 6.24 6.25 6.26 6.27 6.28 6.29 6.30 6.31 6.32 "History". docomo-sys.co.jp. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ↑ Takano, Yoshirō. Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Privatization Study: Experience of Japan and Lessons for Developing Countries, Parts 63-179.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "Communication". features.japantimes.co.jp. Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Rasmussen, T. Personal Media and Everyday Life: A Networked Lifeworld.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo". pcmag.com. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ Jain, Vipul. Recent Trends in Intelligent Computing, Communication and Devices.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 "NTT DoCoMo". crunchbase.com. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ 13.00 13.01 13.02 13.03 13.04 13.05 13.06 13.07 13.08 13.09 13.10 Sugai, Philip; Koeder, Marco; Ciferri, Ludovico. The Six Immutable Laws of Mobile Business.
- ↑ Vesa, Jarkko. Mobile Services in the Networked Economy.
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 "History". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 11 September 2019.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 "NTT DoCoMo: i-mode Wireless Internet Services". bus.umich.edu. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Vesa, Jarkko. Mobile Services in the Networked Economy.
- ↑ Funk, Jeffrey L. Global Competition Between and Within Standards: The Case of Mobile Phones.
- ↑ "WHAT IS ISO 9001:2015 – QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS?". asq.org. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ↑ "NTT Mobile Communications Network". money.howstuffworks.com. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ Blagdon, Jeff (12 September 2019). "How emoji conquered the world". The Verge. Vox Media. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ↑ The Post-Mobile Society: From the Smart/Mobile to Second Offline (Hidenori Tomita ed.).
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 23.3 23.4 23.5 23.6 "i-mode Subscribers Surpass 40 million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Yoyogi Building". emporis.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "WHAT IS ISO 14001:2015 – ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS?". asq.org. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ↑ "DoCoMo signs i-mode deal with German firm". japantimes.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 "NTT DOCOMO Inc Stock Splits History". netcials.com. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "DoCoMo Camera Phone Sales Exceed 5 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "i-mode ready for Taiwan launch". cbronline.com. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "Base launches i-mode service in Belgium". digitimes.com. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "I-mode ready to launch in France". computerweekly.com. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "DoCoMo to Introduce Enhanced FOMA Handset Offering Video Clip e-Mailing". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "DoCoMo's New FOMA F2051 Handset Goes on Sale Jan. 18". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch Flat-Rate Internet Access Service for PHS". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Introduce New FOMA Videophone Model". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch First Handset in New 505i Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Introduce First GPS Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch Sales of First GPS Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch International Roaming Service for 3G FOMA Users". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo launches mobile shopping mall and account aggregation portal". finextra.com. Retrieved 18 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Start Trial of Online Payments Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Telefonica Moviles Espana to Launch i-mode Service in Spain". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch FOMA F2102V Videophone". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DoCoMo FOMA Subscribers Top 1 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Develops FOMA Compact Flash Card". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Introduce P505iS: World's First Auto-Focus Camera Phone". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Wind Telecomunicazioni S.p.A. to Launch i-mode Service in Italy". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch Three New Models in mova 505iS Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Liquidate a Brazilian Subsidiary". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch i-mode Disaster Message Board Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Liquidate a Subsidiary". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo FOMA Subscribers Top 2 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Release P900i - Third Handset in FOMA 900i Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Liquidate Some of its Subsidiaries". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo FOMA Subscribers Top 3 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Establish "Mobile Society Research Institute"". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Unveils New mova 506i i-mode Phone Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch 3G Roaming-In Service for Visitors to Japan". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "COSMOTE Mobile Telecommunications S.A. to Launch i-mode Service in Greece". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo and Telstra Commence Strategic Partnership for i-mode in Australia". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "i-mode users outside Japan exceed 3 million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo and Cellcom Israel Commence Strategic Partnership for i-mode in Israel". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch 901i Series of 3G FOMA Handsets". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch F901iC 3G FOMA Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Introduces First FOMA 3G Handset for International Roaming". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Develops World's First Mobile Phone with Flat Panel Speaker". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Develops Child-Friendly Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "3G FOMA Subscribers Top 20 Million Mark". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Achieves World's First 2.5Gbps Packet Transmission in 4G Field Experiment". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Unveils 3G FOMA 703i Series, D800iDS and SO903iTV Handsets". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Achieves World's First 5Gbps Packet Transmission in 4G Field Experiment". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Unveils Secure 3G FOMA F903iBSC Handset for Business Use". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Develops High-Quality Speech Coding Technology for Mobile Phones". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Begins Super 3G Experiment". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Establishes Office in Hanoi, Vietnam". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "3G FOMA Subscribers Exceed 40 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "The Associated Press: New Prototype Phone Gives Fitness Check". archive.org. 29 October 2007. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Unveils 23 Handsets in New 905i and 705i Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "STT to invest RM1b in U Mobile". theedgemarkets.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo to Launch Child-Friendly F801i Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "i-channel Subscribers Exceed 15 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "Area Mail Disaster Information Service". Archived from the original on 2011-10-25. Retrieved 2011-11-06.
- ↑ "ドコモとGoogleが提携──各種サービスのiモード対応などを推進" (in Japanese). ITMedia+D モバイル. Retrieved 2008-01-26.
- ↑ "YouTube、ドコモの904i/905iシリーズに対応" (in Japanese). ITMedia+D モバイル. Retrieved 2008-01-26.
- ↑ "Gengo Closes a New Round of Funding with Intel Capital, Atomico, Iris Capital, Infocomm Investments, NTT-IP Fund and STC Ventures". gengo.com. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT Investment Partners Fund LP". bloomberg.com. Retrieved 6 February 2020.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 87.2 87.3 87.4 87.5 87.6 87.7 87.8 87.9 "History". nttdocomo-v.com. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Demonstrates Molecular Delivery System for Molecular Communication". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ ドコモ社長に山田副社長が昇格へ (in Japanese). 2008-04-19. Archived from the original on 2008-04-22. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 19 Handsets in New 906i and 706i Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "First Symbian^2 phones ship in Japan". allaboutsymbian.com. Retrieved 27 March 2018.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Establishes Subsidiary Company in Shanghai, China". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 22 Handsets in Four All-new Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DoCoMo buys 26% of Tata Teleservices". vantageasia.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Spatial Audio Transmission Technology for Mobile Phones". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 18 New Handsets". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "Tata Group Announces Pan-India GSM Service with NTT DOCOMO" (PDF). corporate.tatateleservices.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Launch Mobile Remittance Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Develops Solar-powered Handset". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "Subscriptions to DOCOMO's Credit Payment Service Top 10 million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Mobile Phone Prototype Using Surplus Wood". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Offer Unlimited Domestic i-mode Mails". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 20 New Models". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "net mobile AG acquired by NTT DoCoMo". crunchbase.com. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Other Acquisitions". startupranking.com. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 20 New Handsets". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "joint-venture.ppt". scribd.com. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Conduct Trial E-Book Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "Tata DoCoMo launches 3G services". economictimes.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Launch i-mode Version of "docomo market" Portal". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Begin Selling Samsung GALAXY Tab on November 26". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "DNP-DOCOMO-CHI Joint Venture "2Dfacto" to Launch Initial E-book Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Create Dedicated Department for Smartphone Business". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo teams-up with McAfee to offer free malware protection for its Android users". intomobile.com. 2011. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Unveil First Tablets for LTE Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Achieves Top Ranking in Business Customer Satisfaction for Mobile Phone and PHS Services". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DoCoMo unveils 24 new mobile devices". japantoday.com. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Again Earns Highest Marks in Customer-Satisfaction Study". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Disney to Jointly Offer Smartphones and Mobile Services Under New "Disney Mobile on docomo" Brand". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Subscribers Top 60 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Xi® LTE Service Subscribers Top 3 Million". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "Docomo, Omron to establish docomo Healthcare Inc". japantoday.com. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Launch Smartphone for Beginners". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT Docomo acquires Italy's Buongiorno". Retrieved 2012-07-07.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Introduce Mobile Translation of Conversations and Signage". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Launch Mobile Gaming and E-commerce". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 16 New Mobile Devices". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Develops Smartphone for Preteens". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 12 New Mobile Devices — 5 Models to Link with Home Electronics and Play Full-HD under New Initiative —". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Tokyo Institute of Technology Achieve World's First 10 Gbps Packet Transmission in Outdoor Experiment". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Launch One-day International Data Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "Japan's NTT Docomo Buys Fine Trade, An Austrian E-Commerce Solution Provider, For 'Several Tens Of Millions Of Euros'". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Ranked Highest in Business Customer Satisfaction for Fifth Straight Year". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Launch Japan's First VoLTE Service". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO Unveils 12 New Mobile Devices in Summer Lineup". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "緊急速報「エリアメール」、及び「緊急速報メール」を利用した国民保護に関する情報の配信を開始". Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Successfully Trials NFV Using Multi-vendors' Virtualization Systems". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ↑ "DoCoMo starts on March 27 on "PREMIUM 4G" of the fastest 225 Mbps in Japan, in which the file DL speed exceeds 1.5 times the LTE". gigazine.net. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Integrate Mobile Services with Facebook". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Launches 13 New Mobile Devices for Winter/Spring Lineup". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "GATEWAY TO JAPAN". docomoinnovations.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Nokia Achieves World's First Real Time 8K Video Transmission Using 5G Radio Access Technology". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Ericsson Perform Successful Proof of Concept of Dynamic 5G Network Slicing". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 25 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops eSIM Platform for Consumer Devices". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "Qualcomm, Ericsson, and NTT DOCOMO announce collaboration on 5G NR trials to accelerate wide-scale 5G deployments in Japan". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops World's First Spherical Drone Display". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo Unveils New FOMA 904i Series". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "China Mobile Communications and NTT DOCOMO Develop World's First Multi-Vendor eSIM System for IoT". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Multi-Profile SIM for Smartphones and Tablets". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 12 November 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Launches AI Engine for Fast, Accurate Shelf Analysis". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Achieves World's First 5G Wireless Data Transmission in Ultra-high-mobility Environment Exceeding 300 km/h". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT Docomo steps on gas in car-related services". asia.nikkei.com. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT Docomo to launch AI system providing apt info based on user movements". mainichi.jp. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Population Flow Statistics as Transportation Big Data". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops World's First 360-degree 8K VR Live Video Streaming and Viewing System". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Toyota Conduct Successful Remote Control of T-HR3 Humanoid Robot Using 5G". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "China Mobile and NTT DOCOMO to Launch World's First IoT Multi-vendor eSIM Solution". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Labor Practices" (PDF). nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 15 October 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Launches "DOCOMO Asia IoT Program" to Further Expand IoT Market in the Region". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 26 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Toyota Conduct Successful Remote Control of T-HR3 Humanoid Robot Using 5G". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Like BabyCenter, L.L.C.". mandasoft.com. Retrieved 28 October 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops World's First 360-degree 8K 3D VR System for Live Video Streaming and Viewing at 60 fps". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Ranked World's Top Mobile Operator in 5G SEP Applications and Contributions to 5G Standard". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO, AGC and Ericsson Achieve World's First 5G Communication Using Glass Antenna for 28 GHz". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Drone Platform API for Expanded Drone Applications". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Develops Safe, Blade-free Drone Propelled with Ultrasonic Vibrations". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "Tohoku University and DOCOMO Launch Research Project to Develop Artificial-intelligence Technology for Periodontal Disease Detection". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Joins 5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO to Commence 5G Trials at Manufacturing Sites in Partnership with OMRON and Nokia". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Achieves World's First 5G Communication Between High-speed Bullet Train and Experimental Base Stations". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Kyoto University develop world's first AI system to detect bridge deterioration using video-based vehicle weights and structural deflection". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO to Absorb docomo Healthcare in Simplified, Short-form Merger". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Conducts World's First Successful Trial of Transparent Dynamic Metasurface". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 19 January 2020.
- ↑ "DOCOMO Releases White Paper Promoting 6G Communication System". nttdocomo.co.jp. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- ↑ 175.0 175.1 "NTT Docomo moves up Japan-wide 5G to June 2020, offers early access". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT Docomo to discontinue decades-old i-mode, world's first mobile internet service, in 2026". japantimes.co.jp. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- ↑ "NTT DOCOMO". finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 20 February 2020.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo". Google Trends. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ↑ "NTT Docomo". books.google.com. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ↑ "NTT DoCoMo". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 24 March 2021.