Difference between revisions of "Timeline of water desalination"
| (27 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This is a '''timeline of water desalination'''. | + | This is a '''timeline of water desalination''', attempring to describe major events in the development of the technology and production. Key developments in the reverse osmosis process are described. Also, major and historic desalination plants are described. |
==Big picture== | ==Big picture== | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
! Time period !! Development summary | ! Time period !! Development summary | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 16th century || Desalination contraptions based on evaporation are incorporated into boats, allowing them to be self-sufficient in the event of an emergency.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges">{{cite web|last1=KUMAR|first1=MANISH|last2=CULP|first2=TYLER|last3=SHEN|first3=YUEXIAO|title=Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges|url=https://www.nae.edu/19582/Bridge/164237/164313.aspx|website=nae.edu|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref> | + | | 16th century || Desalination contraptions based on evaporation are incorporated into boats, allowing them to be self-sufficient in the event of an emergency.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges">{{cite web|last1=KUMAR|first1=MANISH|last2=CULP|first2=TYLER|last3=SHEN|first3=YUEXIAO|title=Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges|url=https://www.nae.edu/19582/Bridge/164237/164313.aspx|website=nae.edu|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref><ref name="History - Drying Rivers">{{cite web|title=History - Drying Rivers|url=http://shalldesal.org/history|website=shalldesal.org|accessdate=5 March 2018}}</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
| 19th century || Distillation is commercialized by companies such as Caird & Rayner (a brand which still exists today), with firms located in various countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany and the United States.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> In the late century, the first major technical advance in desalination technology is the development of the Multiple Effect Distillation (MED) process.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> | | 19th century || Distillation is commercialized by companies such as Caird & Rayner (a brand which still exists today), with firms located in various countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany and the United States.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> In the late century, the first major technical advance in desalination technology is the development of the Multiple Effect Distillation (MED) process.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| 1970s || Fuel oil cost increases very sharply, affecting strongly the desalination cost, especially in processes with high specific energy consumption. A great effort is made in many countries to shift from desalination by distillation to desalination by other means.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> Low-pressure multi-effect distillation (MED) and improved reverse osmosis (RO) evolve as two new technologies capable to desalt seawater.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> The introduction of isobaric energy recovery technology significantly reduces the operating costs of seawater {{w|reverse osmosis}}.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> By the second half of the decade, the {{w|reverse osmosis}} process is considered in many regional developing programs as an option for small and large seawater desalination plants.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> Larger scale commercial {{w|reverse osmosis}} and electrodialysis/electrodialysis reversal systems begin to be used more extensively.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> | | 1970s || Fuel oil cost increases very sharply, affecting strongly the desalination cost, especially in processes with high specific energy consumption. A great effort is made in many countries to shift from desalination by distillation to desalination by other means.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> Low-pressure multi-effect distillation (MED) and improved reverse osmosis (RO) evolve as two new technologies capable to desalt seawater.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> The introduction of isobaric energy recovery technology significantly reduces the operating costs of seawater {{w|reverse osmosis}}.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> By the second half of the decade, the {{w|reverse osmosis}} process is considered in many regional developing programs as an option for small and large seawater desalination plants.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> Larger scale commercial {{w|reverse osmosis}} and electrodialysis/electrodialysis reversal systems begin to be used more extensively.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1980s || Synthetic membranes begin to play an increasingly crucial role in water desalination. Membrane distillation develops commercially on a small scale during the decade.<ref name="Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources"/> In the mid-1980s, low-pressure nanofiltration membranes | + | | 1980s || Desalination technology becomes a fully commercial enterprise.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> Synthetic membranes begin to play an increasingly crucial role in water desalination. Membrane distillation develops commercially on a small scale during the decade.<ref name="Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources"/> In the mid-1980s, low-pressure nanofiltration membranes are introduced by all of the major reverse osmosis companies.<ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1990s || The continuous improvement and cost reduction in RO technology increases, in most cases, the economic benefits of SWRO over the distillation process.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> | + | | 1990s || The use of {{w|reverse osmosis}} desalination technologies for municipal water supplies becomes commonplace.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> The continuous improvement and cost reduction in RO technology increases, in most cases, the economic benefits of SWRO over the distillation process.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Recent years || Today, desalination can be achieved by using thermal or membrane processes, or a hybrid combination.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination">{{cite web|title=Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination|url=http://www.filtsep.com/water-and-wastewater/features/current-challenges-in-energy-recovery-for/|website=filtsep.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> | + | | Recent years || Today, desalination can be achieved by using thermal or membrane processes, or a hybrid combination.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination">{{cite web|title=Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination|url=http://www.filtsep.com/water-and-wastewater/features/current-challenges-in-energy-recovery-for/|website=filtsep.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> Most of the desalinated water is currently produces in the {{w|Middle east}}. |
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 32: | Line 31: | ||
! Year !! Event type !! Details !! Geographical location | ! Year !! Event type !! Details !! Geographical location | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 400 BC–300 BC || || In his Meteorologica, Aristotle writes that "Salt water when it turns into vapour becomes sweet and the vapour does not form salt water again when it condenses".<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> || | + | | 400 BC–300 BC || || In his Meteorologica, Aristotle writes that "Salt water when it turns into vapour becomes sweet and the vapour does not form salt water again when it condenses".<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/><ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com">{{cite web|title=Desalination|url=https://www.britannica.com/technology/desalination|website=britannica.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1850s || || Pfeffer, Traube and others study osmotic phenomena with ceramic membranes.<ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications">{{cite book|last1=Baker|first1=Richard W.|title=Membrane Technology and Applications|url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=dLhSHOmdiOkC&pg=PA191&lpg=PA191&dq=%22in+1930..1940%22+%22desalination+plant%22+%22arabia%22&source=bl&ots=X-IZnLS9id&sig=Zo5FIaLK9sMxpSOqijnq7M7sFq8&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiNscuBgKzZAhUJF5AKHR8ZAvUQ6AEIWDAH#v=onepage&q=%22in%201930..1940%22%20%22desalination%20plant%22%20%22arabia%22&f=false|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1869 || || The first patent for a desalination process was granted in England.<ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com"/> || {{w|United Kingdom}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1869 || Facility || The first water-distillation plant is built by the British government at {{w|Aden}} in Yemen, to supply ships stopping at the {{w|Red Sea}} port.<ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com"/> || {{w|Yemen}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1881 || Facility || The world's first commercial traditional desalination plant is built in Sleima, Malta. || {{w|Malta}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1928 || Facility || The world's first land-based distillation plant is built in Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles. || {{w|Netherlands Antilles}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1930 || Facility || The first large still to provide water for commercial purposes is built in Aruba.<ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com"/> || {{w|Aruba}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1931 || Technology || The term reverse osmosis is coined, and the process is patented as a method of desalting water.<ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1950s || Technology || Weirs of Cathcart in Scotland develop the multi-stage flash distillation process, which would have significant development and wide application throughout the next decade due to both to its economical scale and its ability to operate on low-grade steam.<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Shatat|first1=Mahmoud|last2=Riffat|first2=Saffa B.|title=Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources|journal=International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, Volume 9, Issue 1, 1 March 2014, Pages 1–19|url=https://academic.oup.com/ijlct/article/9/1/1/663897|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United Kingdom}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1952 || Law || The United States Congress passes “The Saline Water Act” to provide federal support for desalination.<ref name="Desalination plant history"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1954 || Facility || The first desalination plant opens in {{w|Qatar}}.<ref>{{cite web|title=Historical Background|url=http://countrystudies.us/persian-gulf-states/68.htm|website=countrystudies.us|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Qatar}} | | 1954 || Facility || The first desalination plant opens in {{w|Qatar}}.<ref>{{cite web|title=Historical Background|url=http://countrystudies.us/persian-gulf-states/68.htm|website=countrystudies.us|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Qatar}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1955 || || Multi-stage flash distillation (MSF) appears as the first large-scale modern desalination process.<ref name="A short history of desalination">{{cite web|title=A short history of desalination|url=http://www.theenergyofchange.com/short-history-of-desalination|website=theenergyofchange.com|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|United States}} | + | | 1955 || Technology || Multi-stage flash distillation (MSF) appears as the first large-scale modern desalination process.<ref name="A short history of desalination">{{cite web|title=A short history of desalination|url=http://www.theenergyofchange.com/short-history-of-desalination|website=theenergyofchange.com|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref><ref name="History - Drying Rivers"/> || {{w|United States}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1957 || Facility || The first multi stage flash distillation plant is built in Kuwait. || {{w|Kuwait}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1959 || Scientific development || Reverse osmosis: Breton and Reid demonstrate the desalination capability of cellulose acetate film.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/><ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies">{{cite book|last1=Wang|first1=Lawrence K.|last2=Chen|first2=Jiaping Paul|last3=Hung|first3=Yung-Tse|last4=Shammas|first4=Nazih K.|title=Membrane and Desalination Technologies|url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=CMOBQ8ijJbwC&pg=PA9&dq=1972+Technology+The+interfacial+composite+membrane+is+developed&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiZ5p6M0dXZAhXDqFkKHdeBB_0Q6AEILTAB#v=onepage&q=1972%20Technology%20The%20interfacial%20composite%20membrane%20is%20developed&f=false}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1959 || Facility || The first multi-effect distillation (MED) plant is constructed in {{w|Aruba}}.<ref name="A short history of desalination"/><ref name="History - Drying Rivers"/> || {{w|Aruba}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1960 || Technology || The first synthetic and functional reverse osmosis membrane is produced at the {{w|University of California}}, made from cellulose acetate. This membrane is capable of blocking the salts while allowing water to pass through it at a reasonable rate of flow under high pressure.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1960-1965 || Technology || {{w|Electrodialysis}} is commercially introduced, providing a cost-effective way to desalt brackish water and spurring considerable interest in the whole field if using desalting technologies to produce potable water for municipal use.<ref name="Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources">{{cite journal|last1=Shatat|first1=Mahmoud|last2=Riffat|first2=Saffa B.|title=Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources|doi=10.1093/ijlct/cts025|url=https://academic.oup.com/ijlct/article/9/1/1/663897|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1962 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: Asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane is developed.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/><ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1963 || Scientific development || Loeb and Sourirajan at the {{w|University of California in Los Angeles}} show that an asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane can be used for desalination. The permeabilities of these early membranes are low and RO membranes are considered a novelty separation technique rather than a soution to desalination.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1963 || Facility || Reverse osmosis: first practical spiral-wound module is developed by {{w|General Atomics}}.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/><ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1963 || Scientific development || Reverse osmosis: the asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane structure is elucidated and the solution-diffusion model of membrane transport is identified.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1964 || Facility || In Spain, the first desalination plant is constructed in {{w|Lanzarote}}.<ref name="A short history of desalination"/><ref name="History - Drying Rivers"/> || {{w|Spain}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1964 || Technology || The cellulose acetate thin film composite membrane concept is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1965 || Facility || The first commercial desalination plant using reverse osmosis is inaugurated in California at the Coalinga desalination plant, used for brackish water.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges"/> || {{w|United States}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1965 || Facility || An 1 MGD (3,785 m3/year) MSF dual-purpose plant starts operating in {{w|Eilat}}, Israel, with an atual water cost amounted to about $0.3m3. The relatively low cost is due to the very low fuel-oil prices if $10-15/ton prevailing at the time.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations">{{cite web|last1=Glueckstern|first1=Pinhas|title=History of Desalination Cost Estimations|url=http://gwri-ic.technion.ac.il/pdf/IDS/71.pdf|website=gwri-ic.technion.ac.il|accessdate=16 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Israel}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | c.1965 || Production || Virtually all the world's seawater desalination capacity (about 1,000 m3/day) is in the {{w|Middle East}} and is produced by multistage flash (MSF) distillation.<ref name="Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1966 || Publication || ''Desalination'', the first international journal for desalting and purification of water, is founded by {{w|Miriam Balaban}}.<ref>{{cite web|title=Introduction to the special issue honoring Miriam Balaban|url=https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/elsevier/introduction-to-the-special-issue-honoring-miriam-balaban-UKddpJ2qNB|website=eepdyve.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1966 || Publication || Israel publishes a joint feasibility study of a 200 MW - 100 MGD (378,500 m3/year) nuclear dual-purpose plant.<ref name="History of Desalination Cost Estimations"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1967 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the B-15 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1967 || Technology || The first commercially successful hollow fiber module is released.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1970 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the cellulose acetate blend membrane is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1970 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the B-9 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1971–1974 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: The cellulose triacetate hollow fiber permeator is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1972 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: The interfacial composite membrane is developed.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1972 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: The B-10 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1973 || || Reverse osmosis: The PDC-1000 thin film composite membrane is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1974 || Facility || The first sea water reverse osmosis desalination plant comes into operation.<ref name="A short history of desalination"/><ref name="Tag Archives: Reverse Osmosis">{{cite web|title=Tag Archives: Reverse Osmosis|url=https://yatesenvironmentalservices.wordpress.com/tag/reverse-osmosis/|website=yatesenvironmentalservices.wordpress.com|accessdate=5 March 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Bermuda}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1975 || Facility || A large seawater desalination plant is built in Jiddah, using interfacial composite membranes, introduced by Fluid Systems. The construction of the plant is considered a milestone in reverse osmosis development.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> || {{w|Saudi Arabia}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1976 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: Fluid Systems starts commerciallization of aryl-alkyl polyetherurea thin film composite membrane.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1978 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the first fully aromatic thin film composite (FT-30) is developed.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/><ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1981 || Technology || John Cadotte patents the design for the three-layer TFC membrane that would later become industry standard. The layer provides high permeability while maintaining selectivity for water.<ref name="Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref>{{cite web|title=High-flux reverse osmosis membranes incorporated with hydrophilic additives for brackish water desalination|url=https://docslide.com.br/documents/high-flux-reverse-osmosis-membranes-incorporated-with-hydrophilic-additives.html|website=docslide.com.br|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Zhao|first1=Lin|title=ADVANCED REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANES FOR DESALINATION AND INORGANIC/POLYMER COMPOSITE MEMBRANES FOR CO2 CAPTURE|url=https://etd.ohiolink.edu/!etd.send_file?accession=osu1405729817&disposition=inline|website=etd.ohiolink.edu|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=BRIDGE. The FRONTIERS OF ENGINEERING. Computational Near-Eye Displays: Engineering the Interface to the Digital World Gordon Wetzstein|url=http://docplayer.net/43898871-Bridge-the-frontiers-of-engineering-computational-near-eye-displays-engineering-the-interface-to-the-digital-world-gordon-wetzstein.html|website=docplayer.net|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1986 || Technology || Low pressure nanofiltration membrane becomes widely available.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1986 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the B-15 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1986 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: several companies modify current membrane lines for low pressure operation.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1986 || Technology || Reverse osmosis: the fully aromatic polyamide thin film composite membrane is developed.<ref name="Membrane and Desalination Technologies"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1998 || Facility || Grace-Davison and Mobil install the first large hyperfiltration solvent separation plant at Beaumont Texas refinery.<ref name="Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges"/><ref name="Membrane Technology and Applications"/> || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2000 || Statistics || About 80 per cent of water demand for the domestic and industrial sectors in {{w|Kuwait}}, {{w|Bahrain}}, {{w|Qatar}} and {{w|United Arab Emirates}} is supplied by water production using desalination. In {{w|Saudi Arabia}} and {{w|Oman}}, water production using desalination supplies about 45 per cent of the water demands, with the remaining 55 per cent being supplied from ground waters.<ref>{{cite book|title=Energy Options for Water Desalination in Selected ESCWA Member Countries|publisher=United Nations, Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, 2001|url=https://books.google.com.ar/books?id=94zeAAAAMAAJ&q=%22desalination%22+%22in+1999..2004%22&dq=%22desalination%22+%22in+1999..2004%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjN7I7Y7NXZAhUSxVkKHQhpCuUQ6AEINDAC}}</ref> || {{w|Middle East}} |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2005 || Production || More than 10,500 desalination plants producing a total of more than 55 billion litres (in excess of 14.6 billion gallons) of potable water per day are in operation throughout the world.<ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2009 || Facility || The current largest desalination plant in the world is commissioned in Hadera, Israel. Built at a cost of around US$500 million, it uses reverse osmosis.<ref name="Desalination plant history">{{cite web|title=Desalination plant history|url=https://www.preceden.com/timelines/332386-desalination-plant-history|website=preceden.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Hadera Desalination Plant|url=http://www.water-technology.net/projects/hadera-desalination/|website=water-technology.net|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Hadera Desalination Plant|url=http://www.ide-tech.com/blog/b_case_study/hadera-project/|website=ide-tech.com|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Hadera Desalination Plant|url=https://www.technologyreview.com/s/534996/megascale-desalination/|website=technologyreview.com|accessdate=4 March 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Israel}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2009 (July) || Facility || The largest desalination plant in Europe is inaugurated in Spain. The Barcelona-Llobregat desal plant provides drinking water to 20% of the population in the region, nearly 1.3 million people.<ref name="Tag Archives: Reverse Osmosis"/> || {{w|Spain}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2010 || Production || The largest producers of desalinated water are {{w|Saudi Arabia}}, accounting for about 17 percent of total global output, and the {{w|United Arab Emirates}}, with 13.4 percent. The {{w|United States}} is third, accounting for roughly 13 percent of the total output (mostly in {{w|Florida}}, {{w|Texas}}, and {{w|California}}).<ref name="Desalinationbritannica.com"/> || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2014 || Production || As of 2014, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is the largest desalinated water producer in the world, and it currently produces about one-fifth of the world productions.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Ouda|first1=Omar K.M.|title=Domestic water demand in Saudi Arabia: assessment of desalinated water as strategic supply source|url=http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/19443994.2014.964332?src=recsys&journalCode=tdwt20|website=tandfonline.com|accessdate=17 February 2018}}</ref> || {{w|Saudi Arabia}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Numerical and visual data == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Scholar === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of November 7, 2021. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="sortable wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Year | ||
| + | ! "water desalination" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1950 || 0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1955 || 0 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1960 || 5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | 1965 || | + | | 1965 || 118 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1970 || 143 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1975 || 121 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1980 || 170 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1985 || 240 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1990 || 258 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 1995 || 354 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2000 || 475 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2005 || 868 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2010 || 2,010 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2015 || 4,140 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | 2020 || 8,000 |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Water desalination gscho.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Trends === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The chart below shows {{w|Google Trends}} data for Desalination (Topic), from January 2004 to April 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.<ref>{{cite web |title=Desalination |url=https://trends.google.com/trends/explore?date=all&q=%2Fm%2F014lg9 |website=Google Trends |access-date=18 April 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Desalination gt.png|thumb|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Google Ngram Viewer === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The chart below shows {{w|Google Ngram Viewer}} data for Water desalination, from 1900 to 2019.<ref>{{cite web |title=water desalination |url=https://books.google.com/ngrams/graph?content=Water+desalination&year_start=1900&year_end=2019&corpus=26&smoothing=3&case_insensitive=true |website=books.google.com |access-date=18 April 2021 |language=en}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Water desalination ngram.png|thumb|center|700px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Wikipedia Views === | ||
| + | |||
| + | The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article {{w|Water desalination}}, from July 2015 to March 2021.<ref>{{cite web |title=Water desalination |url=https://wikipediaviews.org/displayviewsformultiplemonths.php?page=Water+desalination&allmonths=allmonths-api&language=en&drilldown=all |website=wikipediaviews.org |access-date=18 April 2021}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Water desalination wv.png|thumb|center|450px]] | ||
| + | |||
==Meta information on the timeline== | ==Meta information on the timeline== | ||
| Line 97: | Line 211: | ||
[http://www.water-technology.net/projects/category/watersupply] | [http://www.water-technology.net/projects/category/watersupply] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[https://thisdayinwaterhistory.wordpress.com/tag/seawater-desalination/] | [https://thisdayinwaterhistory.wordpress.com/tag/seawater-desalination/] | ||
[https://www.sutori.com/story/saudi-arabia-desalination-plant] | [https://www.sutori.com/story/saudi-arabia-desalination-plant] | ||
| − | |||
===Timeline update strategy=== | ===Timeline update strategy=== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:47, 12 April 2024
This is a timeline of water desalination, attempring to describe major events in the development of the technology and production. Key developments in the reverse osmosis process are described. Also, major and historic desalination plants are described.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 16th century | Desalination contraptions based on evaporation are incorporated into boats, allowing them to be self-sufficient in the event of an emergency.[1][2] |
| 19th century | Distillation is commercialized by companies such as Caird & Rayner (a brand which still exists today), with firms located in various countries such as the United Kingdom, France, Germany and the United States.[3] In the late century, the first major technical advance in desalination technology is the development of the Multiple Effect Distillation (MED) process.[3] |
| 1930s | Thermal distillation begins use in several large plants, primarily in the Middle East.[4] |
| 1950s | Scientists begin looking at alternatives to thermal desalination by studying membrane processes. Electrodialysis (ED) is the first of these processes to be developed commercially.[3] |
| 1960s | Membrane technologies arise as a result of a breakthrough in the use of polymer films for separating salt from water in the late 1950s and early 1960s.[1] Anisotropic cellulose acetate membranes are the industry standard through the decade.[5] By the late 1960s, commercial desalination systems producing up to 8,000 m3/day begin to be installed in various parts of the world.[3] |
| 1970s | Fuel oil cost increases very sharply, affecting strongly the desalination cost, especially in processes with high specific energy consumption. A great effort is made in many countries to shift from desalination by distillation to desalination by other means.[6] Low-pressure multi-effect distillation (MED) and improved reverse osmosis (RO) evolve as two new technologies capable to desalt seawater.[6] The introduction of isobaric energy recovery technology significantly reduces the operating costs of seawater reverse osmosis.[3] By the second half of the decade, the reverse osmosis process is considered in many regional developing programs as an option for small and large seawater desalination plants.[6] Larger scale commercial reverse osmosis and electrodialysis/electrodialysis reversal systems begin to be used more extensively.[3] |
| 1980s | Desalination technology becomes a fully commercial enterprise.[3] Synthetic membranes begin to play an increasingly crucial role in water desalination. Membrane distillation develops commercially on a small scale during the decade.[7] In the mid-1980s, low-pressure nanofiltration membranes are introduced by all of the major reverse osmosis companies.[5] |
| 1990s | The use of reverse osmosis desalination technologies for municipal water supplies becomes commonplace.[3] The continuous improvement and cost reduction in RO technology increases, in most cases, the economic benefits of SWRO over the distillation process.[6] |
| Recent years | Today, desalination can be achieved by using thermal or membrane processes, or a hybrid combination.[3] Most of the desalinated water is currently produces in the Middle east. |
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | Geographical location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 400 BC–300 BC | In his Meteorologica, Aristotle writes that "Salt water when it turns into vapour becomes sweet and the vapour does not form salt water again when it condenses".[4][3][8] | ||
| 1850s | Pfeffer, Traube and others study osmotic phenomena with ceramic membranes.[5] | ||
| 1869 | The first patent for a desalination process was granted in England.[8] | United Kingdom | |
| 1869 | Facility | The first water-distillation plant is built by the British government at Aden in Yemen, to supply ships stopping at the Red Sea port.[8] | Yemen |
| 1881 | Facility | The world's first commercial traditional desalination plant is built in Sleima, Malta. | Malta |
| 1928 | Facility | The world's first land-based distillation plant is built in Curaçao, Netherlands Antilles. | Netherlands Antilles |
| 1930 | Facility | The first large still to provide water for commercial purposes is built in Aruba.[8] | Aruba |
| 1931 | Technology | The term reverse osmosis is coined, and the process is patented as a method of desalting water.[5] | |
| 1950s | Technology | Weirs of Cathcart in Scotland develop the multi-stage flash distillation process, which would have significant development and wide application throughout the next decade due to both to its economical scale and its ability to operate on low-grade steam.[9] | United Kingdom |
| 1952 | Law | The United States Congress passes “The Saline Water Act” to provide federal support for desalination.[10] | United States |
| 1954 | Facility | The first desalination plant opens in Qatar.[11] | Qatar |
| 1955 | Technology | Multi-stage flash distillation (MSF) appears as the first large-scale modern desalination process.[12][2] | United States |
| 1957 | Facility | The first multi stage flash distillation plant is built in Kuwait. | Kuwait |
| 1959 | Scientific development | Reverse osmosis: Breton and Reid demonstrate the desalination capability of cellulose acetate film.[4][1][5][13] | |
| 1959 | Facility | The first multi-effect distillation (MED) plant is constructed in Aruba.[12][2] | Aruba |
| 1960 | Technology | The first synthetic and functional reverse osmosis membrane is produced at the University of California, made from cellulose acetate. This membrane is capable of blocking the salts while allowing water to pass through it at a reasonable rate of flow under high pressure.[1] | |
| 1960-1965 | Technology | Electrodialysis is commercially introduced, providing a cost-effective way to desalt brackish water and spurring considerable interest in the whole field if using desalting technologies to produce potable water for municipal use.[7] | |
| 1962 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: Asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane is developed.[4][5][13] | |
| 1963 | Scientific development | Loeb and Sourirajan at the University of California in Los Angeles show that an asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane can be used for desalination. The permeabilities of these early membranes are low and RO membranes are considered a novelty separation technique rather than a soution to desalination.[1][3] | United States |
| 1963 | Facility | Reverse osmosis: first practical spiral-wound module is developed by General Atomics.[4][5][13] | United States |
| 1963 | Scientific development | Reverse osmosis: the asymmetric cellulose acetate membrane structure is elucidated and the solution-diffusion model of membrane transport is identified.[13] | |
| 1964 | Facility | In Spain, the first desalination plant is constructed in Lanzarote.[12][2] | Spain |
| 1964 | Technology | The cellulose acetate thin film composite membrane concept is developed.[13] | |
| 1965 | Facility | The first commercial desalination plant using reverse osmosis is inaugurated in California at the Coalinga desalination plant, used for brackish water.[1] | United States |
| 1965 | Facility | An 1 MGD (3,785 m3/year) MSF dual-purpose plant starts operating in Eilat, Israel, with an atual water cost amounted to about $0.3m3. The relatively low cost is due to the very low fuel-oil prices if $10-15/ton prevailing at the time.[6] | Israel |
| c.1965 | Production | Virtually all the world's seawater desalination capacity (about 1,000 m3/day) is in the Middle East and is produced by multistage flash (MSF) distillation.[3] | |
| 1966 | Publication | Desalination, the first international journal for desalting and purification of water, is founded by Miriam Balaban.[14] | |
| 1966 | Publication | Israel publishes a joint feasibility study of a 200 MW - 100 MGD (378,500 m3/year) nuclear dual-purpose plant.[6] | |
| 1967 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the B-15 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.[13] | |
| 1967 | Technology | The first commercially successful hollow fiber module is released.[4][5] | |
| 1970 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the cellulose acetate blend membrane is developed.[13] | |
| 1970 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the B-9 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.[13] | |
| 1971–1974 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: The cellulose triacetate hollow fiber permeator is developed.[13] | |
| 1972 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: The interfacial composite membrane is developed.[4] | |
| 1972 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: The B-10 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.[13] | |
| 1973 | Reverse osmosis: The PDC-1000 thin film composite membrane is developed.[13] | ||
| 1974 | Facility | The first sea water reverse osmosis desalination plant comes into operation.[12][15] | Bermuda |
| 1975 | Facility | A large seawater desalination plant is built in Jiddah, using interfacial composite membranes, introduced by Fluid Systems. The construction of the plant is considered a milestone in reverse osmosis development.[4][5] | Saudi Arabia |
| 1976 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: Fluid Systems starts commerciallization of aryl-alkyl polyetherurea thin film composite membrane.[13] | |
| 1978 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the first fully aromatic thin film composite (FT-30) is developed.[4][5][13] | |
| 1981 | Technology | John Cadotte patents the design for the three-layer TFC membrane that would later become industry standard. The layer provides high permeability while maintaining selectivity for water.[1][16][17][18] | |
| 1986 | Technology | Low pressure nanofiltration membrane becomes widely available.[4][5] | |
| 1986 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the B-15 polyamide hollow fiber permeator is developed.[13] | |
| 1986 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: several companies modify current membrane lines for low pressure operation.[13] | |
| 1986 | Technology | Reverse osmosis: the fully aromatic polyamide thin film composite membrane is developed.[13] | |
| 1998 | Facility | Grace-Davison and Mobil install the first large hyperfiltration solvent separation plant at Beaumont Texas refinery.[4][5] | |
| 2000 | Statistics | About 80 per cent of water demand for the domestic and industrial sectors in Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar and United Arab Emirates is supplied by water production using desalination. In Saudi Arabia and Oman, water production using desalination supplies about 45 per cent of the water demands, with the remaining 55 per cent being supplied from ground waters.[19] | Middle East |
| 2005 | Production | More than 10,500 desalination plants producing a total of more than 55 billion litres (in excess of 14.6 billion gallons) of potable water per day are in operation throughout the world.[8] | |
| 2009 | Facility | The current largest desalination plant in the world is commissioned in Hadera, Israel. Built at a cost of around US$500 million, it uses reverse osmosis.[10][20][21][22] | Israel |
| 2009 (July) | Facility | The largest desalination plant in Europe is inaugurated in Spain. The Barcelona-Llobregat desal plant provides drinking water to 20% of the population in the region, nearly 1.3 million people.[15] | Spain |
| 2010 | Production | The largest producers of desalinated water are Saudi Arabia, accounting for about 17 percent of total global output, and the United Arab Emirates, with 13.4 percent. The United States is third, accounting for roughly 13 percent of the total output (mostly in Florida, Texas, and California).[8] | |
| 2014 | Production | As of 2014, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is the largest desalinated water producer in the world, and it currently produces about one-fifth of the world productions.[23] | Saudi Arabia |
Numerical and visual data
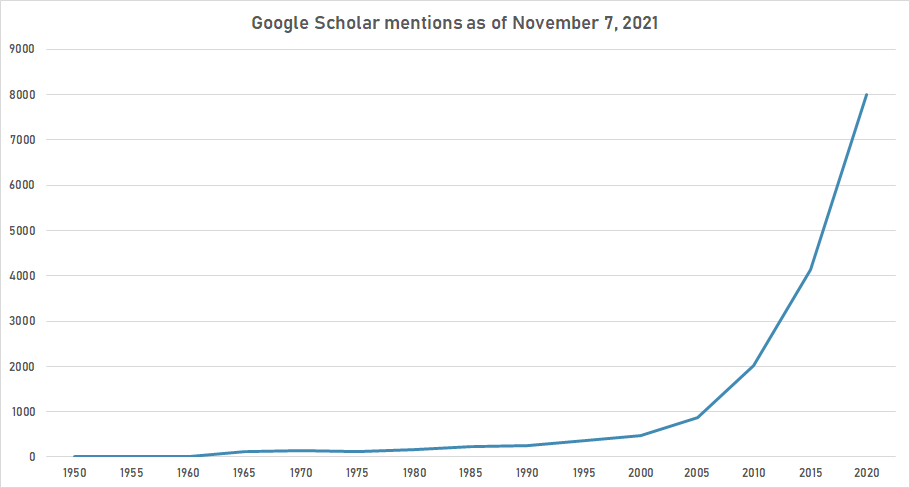
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of November 7, 2021.
| Year | "water desalination" |
|---|---|
| 1950 | 0 |
| 1955 | 0 |
| 1960 | 5 |
| 1965 | 118 |
| 1970 | 143 |
| 1975 | 121 |
| 1980 | 170 |
| 1985 | 240 |
| 1990 | 258 |
| 1995 | 354 |
| 2000 | 475 |
| 2005 | 868 |
| 2010 | 2,010 |
| 2015 | 4,140 |
| 2020 | 8,000 |
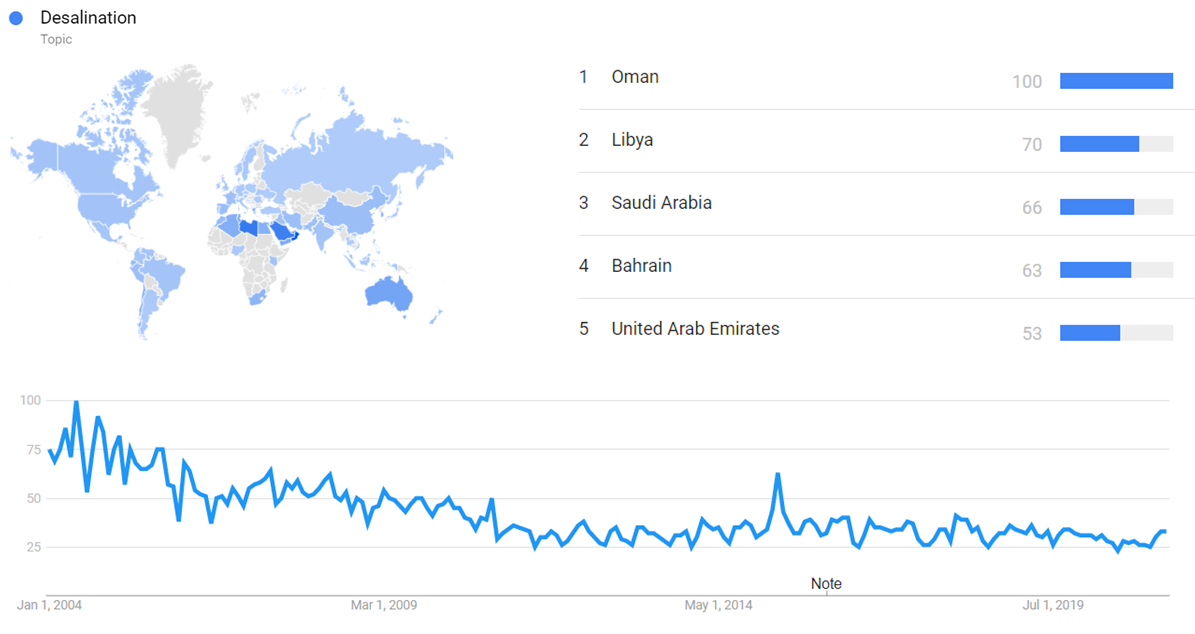
Google Trends
The chart below shows Google Trends data for Desalination (Topic), from January 2004 to April 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[24]
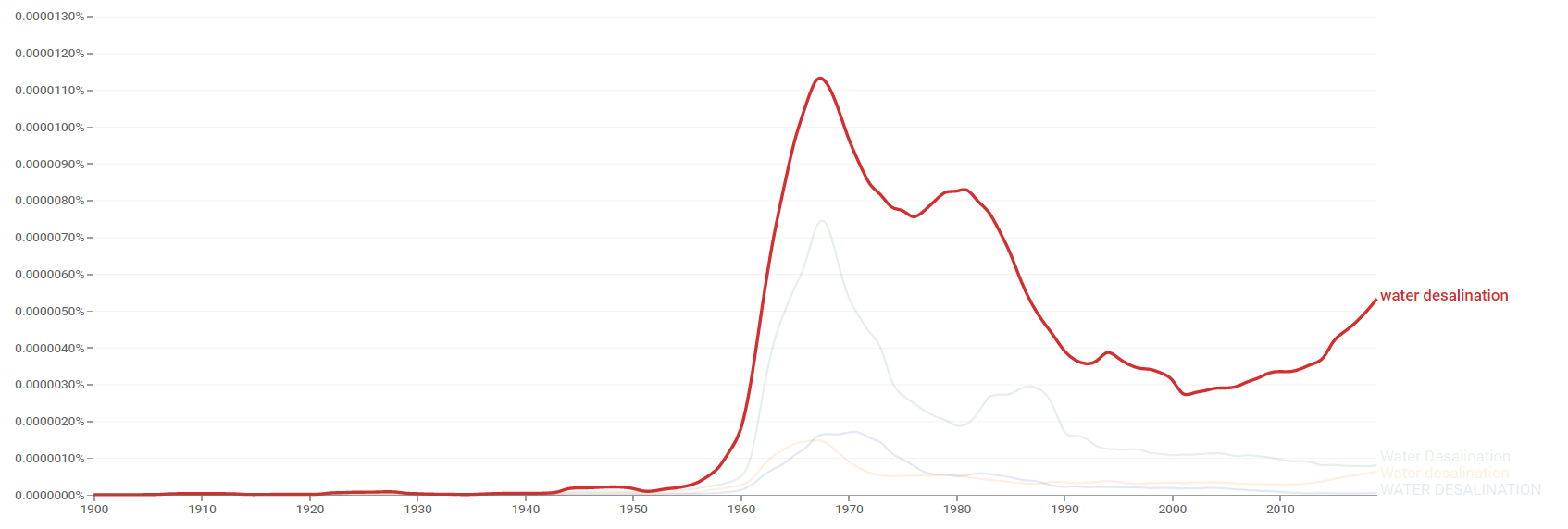
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Water desalination, from 1900 to 2019.[25]
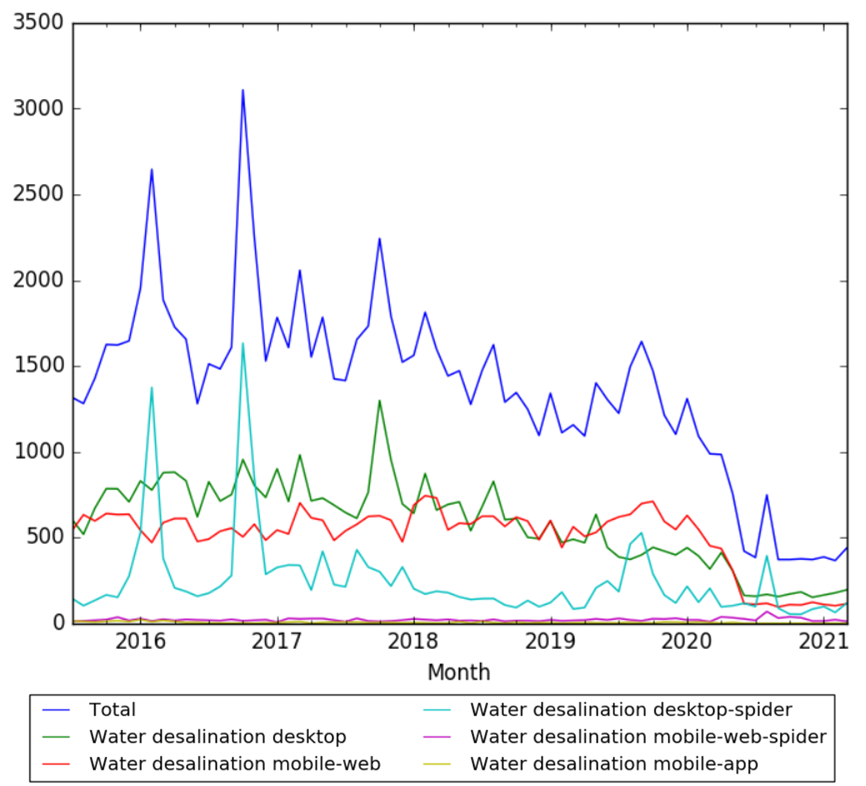
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Water desalination, from July 2015 to March 2021.[26]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 KUMAR, MANISH; CULP, TYLER; SHEN, YUEXIAO. "Water Desalination History, Advances, and Challenges". nae.edu. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "History - Drying Rivers". shalldesal.org. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 "Current challenges in energy recovery for desalination". filtsep.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 KUMAR, MANISH; CULP, TYLER; SHEN, YUEXIAO. "Water Desalination: History, Advances, and Challenges". nap.edu. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 Baker, Richard W. Membrane Technology and Applications. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Glueckstern, Pinhas. "History of Desalination Cost Estimations" (PDF). gwri-ic.technion.ac.il. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Shatat, Mahmoud; Riffat, Saffa B. "Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources". doi:10.1093/ijlct/cts025. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 "Desalination". britannica.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ Shatat, Mahmoud; Riffat, Saffa B. "Water desalination technologies utilizing conventional and renewable energy sources". International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies, Volume 9, Issue 1, 1 March 2014, Pages 1–19. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Desalination plant history". preceden.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ "Historical Background". countrystudies.us. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 "A short history of desalination". theenergyofchange.com. Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ 13.00 13.01 13.02 13.03 13.04 13.05 13.06 13.07 13.08 13.09 13.10 13.11 13.12 13.13 13.14 13.15 Wang, Lawrence K.; Chen, Jiaping Paul; Hung, Yung-Tse; Shammas, Nazih K. Membrane and Desalination Technologies.
- ↑ "Introduction to the special issue honoring Miriam Balaban". eepdyve.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Tag Archives: Reverse Osmosis". yatesenvironmentalservices.wordpress.com. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ↑ "High-flux reverse osmosis membranes incorporated with hydrophilic additives for brackish water desalination". docslide.com.br. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ Zhao, Lin. "ADVANCED REVERSE OSMOSIS MEMBRANES FOR DESALINATION AND INORGANIC/POLYMER COMPOSITE MEMBRANES FOR CO2 CAPTURE". etd.ohiolink.edu. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ "BRIDGE. The FRONTIERS OF ENGINEERING. Computational Near-Eye Displays: Engineering the Interface to the Digital World Gordon Wetzstein". docplayer.net. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ Energy Options for Water Desalination in Selected ESCWA Member Countries. United Nations, Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia, 2001.
- ↑ "Hadera Desalination Plant". water-technology.net. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ "Hadera Desalination Plant". ide-tech.com. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ "Hadera Desalination Plant". technologyreview.com. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ Ouda, Omar K.M. "Domestic water demand in Saudi Arabia: assessment of desalinated water as strategic supply source". tandfonline.com. Retrieved 17 February 2018.
- ↑ "Desalination". Google Trends. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ↑ "water desalination". books.google.com. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- ↑ "Water desalination". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 18 April 2021.