Timeline of medical education
This is a timeline of medical education, attempting to describe important events in the development of medical education.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| Ancient history | Early medical traditions include those of Babylon, China, Egypt and India.[1] Scholars usually consider that medical education began with the ancient Greeks’ method of rational inquiry, which introduced the practice of observation and reasoning regarding disease.[2] The concepts of medical diagnosis, prognosis, and advanced medical ethics are intrduced by the Greeks.[1] Ayurveda is taught in India and traditional Chinese medicine develops. |
| Middle Ages | Apprenticeship training in monastic infirmaries and hospitals dominates medical education during the early Middle Ages. Universities begin systematic training of physicians around the years 1220 in Italy.[1] A medical school is established in Salerno in southern Italy between the 9th and 11th centuries. During the same period, medicine and medical education flourish in the Muslim world at such centres as Baghdad, Cairo, and Córdoba.[2] Formal medical education system in Europe starts in the late Middle Ages, with the rise of the universities in what is now Northern Italy.[3] |
| 16th – 17th centuries | In Europe, the first biological revolution takes place, whose best pedagogical expression is that of Boerhave (known as "the father of physiology") and the school of Leyden.[4] In the 16th century, the Portuguese first introduce Western medicine into India.[5] |
| 19th century | In Europe, until well into century, there is a sharp distinction between academically trained “learned gentlemen” and practically trained surgeons.[3] The century is the great era of Paris, London, and Edinburgh, where hospital-based teaching departs from Oxford's and Cambridge's academic methods. Experimental methods and specialization are pivotal to the second biological revolution and modern scientific medicine.[4] Physiology, pathology, and bacteriology merge, transforming basic teaching. This change constituted the great German epoch. In the mid-19th century upheavals were such that yesterday's medicine was no longer relevant.[4] In China there exists only a small Imperial College, with the role limited to the preparation of physicians attached to the Imperial Palace.[6] |
| 20th century | At the turn of the century, Western medical studies are the ideal mechanism for a respectable social promotion. At the top of the aristocracy of knowledge sits the doctor.[4] Preparing students for medical practice is not considered an academic responsibility until well into the 20th century.[3] During the 1950s and 1960s, dissatisfaction with the medical curriculum increases in Europe and the United States. Curricular overload is rampant and prevents all efforts to make the course more practical. In Europe, the aim of establishing an international market for professionals results in a 1975 European Union directive determining the minimum length and nomenclature of postgraduate medical education programs.[3] |
Visual data
Google Trends
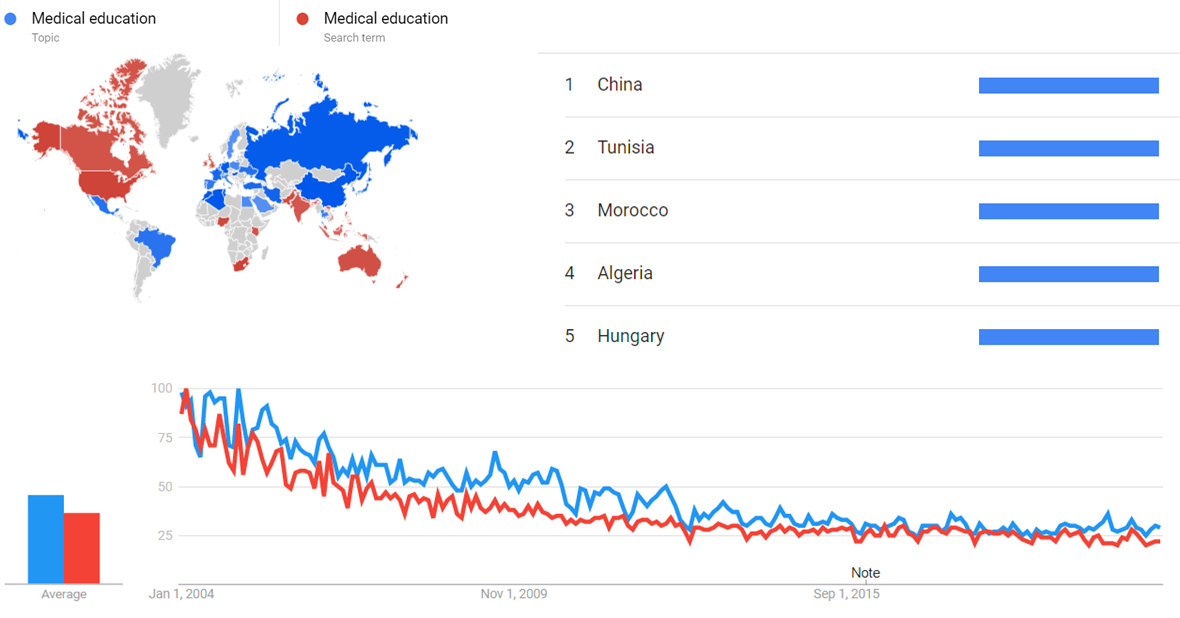
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for Medical education (Topic) and Medical education (Search term), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[7]
Google Ngram Viewer
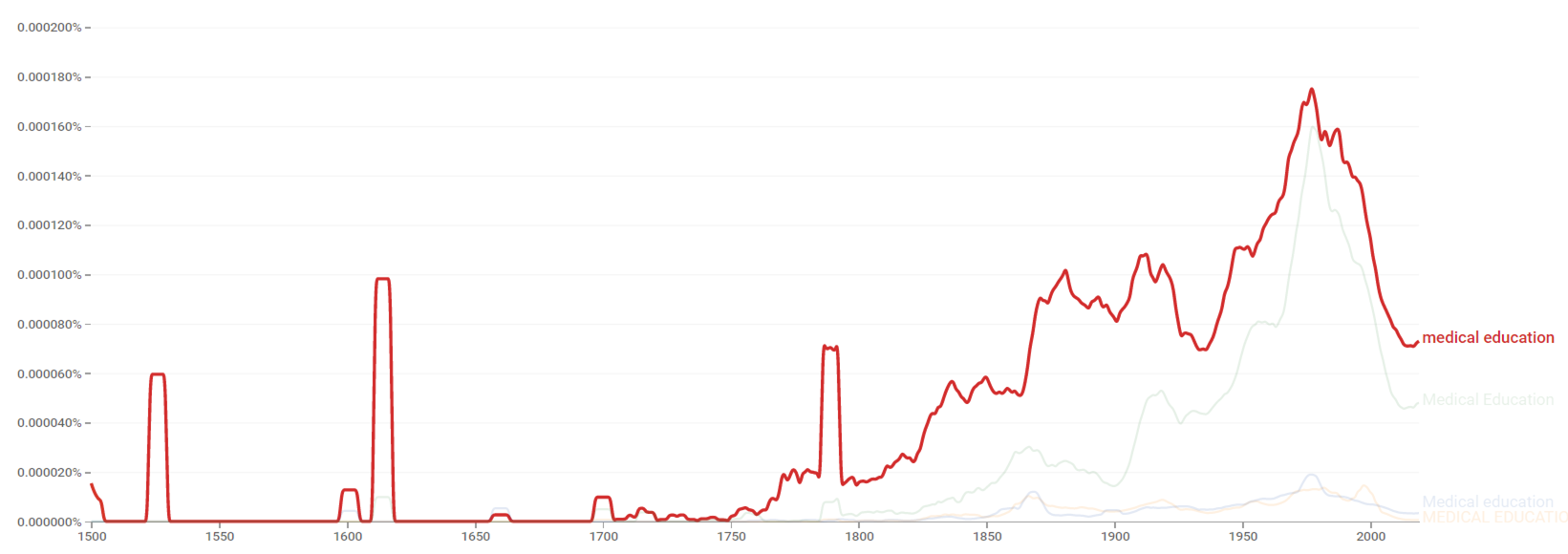
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Medical education, from 1500 to 2019.[8]
Wikipedia Views
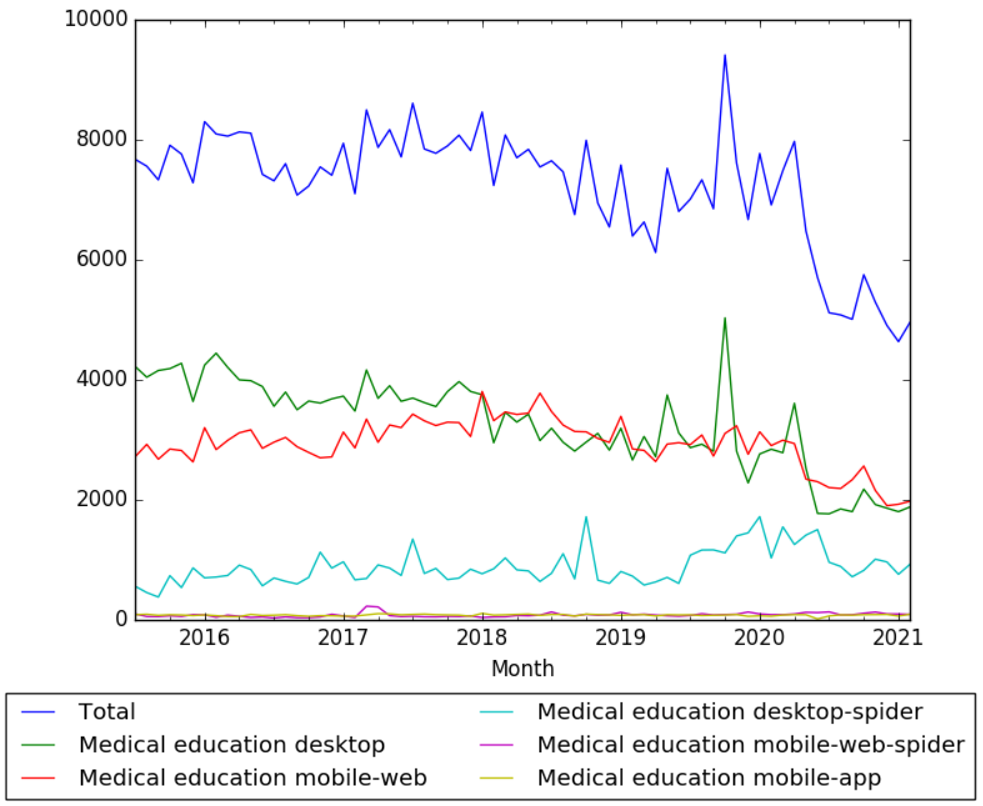
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Medical education, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to February 2021.[9]
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5th century BC | Greek physician Hippocrates teaches and originates the oath that would become a credo for practitioners through the ages.[2] | Greece | |
| 598 – 907 | The Tang Dynasty creates the tai-yi-chu (great medical service), an early example of medical instruction supervised by the state.[6] | China | |
| 931 | Hundreds of physicians in Baghdad are screened, and only those qualified are allowed to practice medicine. During the Abbasid period, the rulers want to ensure that physicians are skilled enough to practice medicine. Passing oral and written examinations are required to get licensed.[10] | Irak | |
| 1123 | Medical school | The Medical College of St Bartholomew’s Hospital is founded.[11][12][13] | United Kingdom |
| 1137 | Medical school | Medicine is taught at Montpellier, decades before the University of Montpellier is established.[11] | France |
| 1181 | Policy | William VIII of Montpellier act allows for licensed physicians to lecture in Montpellier without limit, thus attracting teachers and students from outside of the city.[11] | France |
| 1220 – 1255 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Oxford.[11] | United Kingdom |
| 1245 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Siena.[11] | Italy |
| 1290 | Medical school | The University of Coimbra is founded by Denis of Portugal in Lisbon, with four original faculties, including Medicine.[11][14] | Portugal |
| 1321 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Perugia.[11][15][16] | Italy |
| 1399 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Florence.[11] | Italy |
| 1343 | Medical school | The University of Pisa is established by Papal Bull from Pope Clement VI. A medical school is established among its original faculties.[11] | Italy |
| 1348 | Medical school | Charles University is established in Prague by Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor. A faculty of medicine is amongst its four original faculties.[11] | Czech Republic |
| 1364 | Medical school | Jagiellonian University, the oldest in Poland, is founded by Casimir III the Great, in Kazimierz (now a district of Krakow). A medical school is established among its original faculties.[11] | Poland |
| 1365 | Medical school | The University of Vienna is founded by Rudolf IV, Duke of Austria. A medical school is established among its original faculties.[11] | Austria |
| 1386 | Medical school | Heidelberg University, the oldest in Germany, is founded. A faculty of medicine is established as one of the original four faculties.[11] | Germany |
| 1399 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Padua.[11] | Italy |
| 1409 | Medical school | Leipzig University is established, with medicine amongst its four original faculties.[11] | Germany |
| 1413 | Medical school | The University of St Andrews School of Medicine is established in St Andrews, Scotland.[11] | United Kingdom |
| 1419 | Medical school | The University of Rostock is founded, including medicine amongst the original faculties.[11] | Germany |
| 1421 | Policy | The British Parliament petitions Henry V of England to pass a law determining that a medicine degree from a university be the only qualification granting the right to practice.[17] | United Kingdom |
| 1431 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the Sapienza University of Rome.[11][18] | Italy |
| 1434 | Medical school | Medicine is established amongst the original four faculties at the University of Catania.[11][19] | Italy |
| 1436 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Turin.[11][20] | Italy |
| 1456 | Medical school | A medical faculty established as one of the original faculties at the University of Greifswald.[11][21] | Germany |
| 1457 | Medical school | University of Freiburg is founded by Albert VII, Archduke of Austria. A medical faculty is established as one of the four original faculties.[11] | Germany |
| 1460 | Medical school | The University of Basel is established, with Medicine as one of the four original faculties.[11] | Switzerland |
| 1477 | Medical school | Uppsala University is founded by Papal Bull from Pope Sixtus IV. A medical faculty is established as one of the four original faculties.[11] | Sweden |
| 1477 | Medical school | The University of Tübingen is founded by Eberhard I, Duke of Württemberg. Medicine is established as one of the original faculties.[11] | Germany |
| 1479 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Copenhagen.[11] | Denmark |
| 1481 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Genoa.[11][22] | Italy |
| c.1509 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the Complutense University of Madrid.[11] | Spain |
| 1518 | Medical school | The Royal College of Physicians of London is established.[2][23][24] | United Kingdom |
| <1520 | Medical school | A medical faculty is established at the University of Pavia.[11] | Italy |
| 1542 | Medical school | A Medical faculty is established at the University of Zaragoza.[11][25] | Spain |
| 1669 | Publication | Muhammad Mumin publishes his Tufat al-Muminin, one of the most reliable books on medicine in medieval Islam.[10] | |
| 1765 | Medical school | The School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania, is founded. It is the oldest medical school in the United States.[11][26] | United States |
| 1785 | Medical school | The London Hospital Medical College is founded.[11] | United Kingdom |
| 1815 | Policy | A decree in the Netherlands establishes the structure of the academic medical curriculum and lists the disciplines to be included. However, nothing is stipulated about their content, which is determined by individual professors, being both teacher and examiner.[3] | Netherlands |
| 1822 | Medical school | The Native Medical Institution is established in Calcutta to provide medical training to Indians.[5] | India |
| 1827 | Medical school | Kasr Al-Ainy is established as a military teaching hospital near Cairo, giving rise to the modern history of Egyptian medical education.[27] | Egypt |
| 1842 | Medical school | A western formal medical school, Escola Medico-Cirurgica de Nova Goa, is established in Goa, in Portuguese India. Enrolment is limited to christians.[28][29][30] | India |
| 1847 | Organization | The American Medical Association (AMA) is founded with primary tasks to raise ethical standards in the medical field.[31] | United States |
| 1858 | Policy | The Medical Act of 1858 is passed in Britain, often termed the most important event in British medicine. It establishes the General Medical Council, controlling admission to the medical register, thus having great powers over medical education and examinations.[2] | |
| 1875 | Medical school | Madras Medical College becomes the first in India to open its doors to female students.[5] | India |
| 1876 | Medical school | The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) is founded with the purpose to reform medical education.[31] | United States |
| 1887 | Medical school | The Hong Kong College of Medicine is founded by private practitioners in western medicine to train Chinese doctors to serve the local community.[32] | Hong Kong |
| 1889 | Medical school | Johns Hopkins Hospital opens and offers the first “residency” program in the United States.[31] | United States |
| 1910 | Publication | American educator Abraham Flexner publishes report entitled report entitled Medical Education in the United states and Canada (Flexner Report), under the aegis of the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. The report would have an immediate impact on the improvement of the adequacy of medical schools in the United States.[2][33] | |
| 1915 | Organization | The Chinese Medical Association is established with aims at uniting medical professionals.[34][35][36] | China |
| 1916 | Policy | The "Indian Medical Degrees Act" is introduced in India in order to regulate medical practice in the country.[37] | India |
| 1933 | Organization | The American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) is established as the preeminent entity to oversee the certification of physician specialists in the United States.[31] | United States |
| 1933 | Organization | The Medical Council of India is founded with aims at establishing uniform and high standards of medical education in India.[38] | India |
| 1937 | Publication | The American College of Surgeons publishes Fundamental Requirements for Graduate Training in Surgery, setting its own standards for surgical education programs.[31] | United States |
| 1951 | Organization | The International Federation of Medical Students Associations (IFMSA) is founded. It represents a network of 1.3 million medical students in 127 countries.[39] | |
| 1953 | The World Health Organization publishes the first edition of the World Directory of Medical Schools. Successive editions would be published until the seventh and final print edition in 2000.[40] | ||
| 1962 | Organization | The Panamerican Federation of Association of Medical Schools (PAFAMS) is founded in Chile by a group of leading medical educators. It constitutes 343 medical schools from Latin America, United States and Canada, and adresses the prevailing problems in medical education in Latin America.[41] | Chile |
| 1972 | Organization | The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) is established in Copenhagen. WFME’s main objective is to "enhance the quality of medical education worldwide, with promotion of the highest scientific and ethical standards in medical education". The organization develops standards for medical education and promotes accreditation of medical schools. It also co-manages the World Directory of Medical Schools.[42][43] | Denmark |
| 1981 | Organization | The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) is established.[3] | United States |
| 1988 | Treaty | The Edinburgh declaration is approved at the World Conference on Medical Education, calling for greater co-operation between the health system and the education system, reflecting national needs in medical education and continuing lifelong education of medical staff to achieve quality in practice.[44] | United Kingdomm} |
| 1995 | Organization | The Global Alliance for Medical Education (GAME) is established.[45] | |
| 2000 | Organization | The Foundation for Advancement of International Medical Education and Research (FAIMER) is incorporated as a nonprofit foundation, with the purpose to "support the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG) as it promotes international health professions education through programmatic and research activities."[46][47][48] | |
| 2004 | The Guidelines for Accreditation of Basic Medical Education is developed by an international task force. In 2005, it would be published jointly by World Health Organization and the World Federation for Medical Education.[49][50] | ||
| 2005 | Organization | The International Association of Medical Colleges is founded with the purpose of peer evaluating of the medical education and maintaining uniform standards and recognition of physicians qualifications provided by individual medical schools anywhere in the world.[51] | |
| 2007 | Study | Studies conducted among the Generation Y of medical students in countries including the United Kingdom, Denmark, Austria, Tanzania, Colombia and Malaysia show that information technology (IT) has potential as an educational tool in enhancing teaching and learning in medical schools.[41] | |
| 2008 | The Avicenna Directory opens as a public database of worldwide medical schools, schools of pharmacy, schools of public health and educational institutions of other academic health professions.[40][52] | ||
| 2012 | Massive open online courses emerge as a popular mode of learning, with many courses on medicine and healthcare.[53][54] | ||
| 2013 | The Avicenna Directory merges with the International Medical Education Directory (IMED) to create the World Directory of Medical Schools.[55] | ||
| 2018 | Study | A published review shows that online teaching modalities are becoming increasingly prevalent in medical education, with associated high student satisfaction and improvement on knowledge tests.[56] |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "History of Medicine". ncrworks.com. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "Medical education". britannica.com. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Custers, Eugène; Cate, Olle. "The History of Medical Education in Europe and the United States, With Respect to Time and Proficiency". doi:10.1097/ACM.0000000000002079.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Danielle Gourevitch. "The history of medical teaching" (PDF). thelancet.com. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Supe, A. "Evolution of medical education in India: The impact of colonialism". PMC 5105212
 . PMID 27763484. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.191011.
. PMID 27763484. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.191011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 O'Malley, Charles Donald. The History of Medical Education: An International Symposium Held February 5-9, 1968, Volume 673.
- ↑ "Medical education". Google Trends. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ↑ "Medical education". books.google.com. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ↑ "Medical education". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Medical education in medieval Islam". hekint.org. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ↑ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 11.10 11.11 11.12 11.13 11.14 11.15 11.16 11.17 11.18 11.19 11.20 11.21 11.22 11.23 11.24 11.25 11.26 11.27 11.28 11.29 11.30 11.31 "30 OF THE OLDEST MEDICAL SCHOOLS IN THE WORLD". bestmedicaldegrees.com. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ↑ Mitchell, Piers. Anatomical Dissection in Enlightenment England and Beyond: Autopsy, Pathology and Display.
- ↑ Foster, J.; Sheppard, J. British Archives: A Guide to Archive Resources in the UK.
- ↑ O'Malley, Charles Donald. The History of Medical Education: An International Symposium Held February 5-9, 1968, Volume 673.
- ↑ "University of Perugia". retemuseiuniversitari.unimore.it. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ Rashdall, Hastings. The Universities of Europe in the Middle Ages: Volume 2, Part 1, Italy, Spain, France, Germany, Scotland, Etc.
- ↑ Watmough, Simon. Succeeding in Your Medical Degree.
- ↑ "Sapienza University of Rome". ready4study.eu. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ "University of Catania". esncatania.it. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ Siraisi, Nancy G. Medieval and Early Renaissance Medicine: An Introduction to Knowledge and Practice.
- ↑ "ERNST-MORITZ-ARNDT-UNIVERSITÄT GREIFSWALD". raids-fp7.eu. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ "University of Genoa (Università degli Studi di Genova)". genoa.university-guides.com. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ The Royal College of Physicians and Its Collections: An Illustrated History (Geoffrey Davenport, Ian McDonald, Caroline Moss-Gibbons ed.).
- ↑ Berkowitz, Carin; Lightman, Bernard. Science Museums in Transition: Cultures of Display in Nineteenth-Century Britain and America.
- ↑ "Historia". unizar.es. Retrieved 5 July 2018.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Health, Volume 18.
- ↑ Abdelaziz, Adel; Kassab, Salah Eldin; Abdelnasser, Asmaa; Hosny, Somaya. "Medical Education in Egypt: Historical Background, Current Status, and Challenges".
- ↑ Selin, Helaine. Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures.
- ↑ "1842, a history of healing". timesofindia.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ "ESCOLA MÉDICO-CIRÚRGICA DE GOA". abemdanacao.blogs.sapo.pt. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 31.4 "History of Medical Education". acgme.org. Retrieved 21 June 2018.
- ↑ "Introducing the Hong Kong College of Medicine". hkmms.org.hk. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ Schwartz, Gary S. Around the Eye in 365 Days.
- ↑ "Chinese Medical Association". en.cma.org.cn/. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ Tu, Ya; Fang, Tingyu. History and Philosophy of Chinese Medicine.
- ↑ Sullivan, Lawrence R.; Liu, Nancy Y. Historical Dictionary of Science and Technology in Modern China.
- ↑ Sharma. Concise Textbook Of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology.
- ↑ "Dark days for medical profession in India". PMID 20530169. doi:10.1503/cmaj.109-3279.
- ↑ "Who We Are?". ifmsa.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 "Mission of the World Directory of Medical Schools". wdoms.org. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Walsh, Kieran. Oxford Textbook of Medical Education.
- ↑ "World Directory of Medical Schools". wdoms.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ "About". wfme.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ "THE EDINBURGH DECLARATION". wfme.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ "History of GAME". game-cme.org. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- ↑ "FAIMER : About Us : Strategic Plan - Mission". Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ "FAIMER : About Us - Activities". Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ "History". faimer.org. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ "Accreditation". wfme.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ "WHO/WFME Guidelines for Accreditation of Basic Medical Education". wfme.org. Retrieved 28 July 2018.
- ↑ "International Association of Medical Colleges". iaomc.org. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ "Avicenna homepage – University of Copenhagen". Avicenna.ku.dk. 2012-07-19. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ Lewin, Tamar (20 February 2013). "Universities Abroad Join Partnerships on the Web". New York Times. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ Pappano, Laura. "The Year of the MOOC". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
- ↑ "World Directory of Medical Schools | About". www.wdoms.org. Retrieved 29 July 2018.
- ↑ Tang, Brandon; Coret, Alon; Qureshi, Aatif; Barron, Henry; Ayala, Ana Patricia; Law, Marcus (2018). "Online Lectures in Undergraduate Medical Education: Scoping Review". JMIR Medical Education. 4 (1). doi:10.2196/mededu.9091.