Timeline of the World Health Organization
From Timelines
This is a timeline of the World Health Organization (WHO), describing significant events in the history of the agency.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 1940s | WHO is established in the late 1940s. |
| 1950s | WHO starts proposing programs to promote primary health care around the world.[1] Eradication campaigns are launched for yaws, smallpox and malaria, among other programs. |
| 1960s | WHO begins a planetwide campaign to eradicate the mosquitoes that transmit malaria. During the 1960s and early 1970s WHO functions as the omnipotent supplier and standardizing authority of the world's experimental pharmaceuticals.[2] |
| 1970s | WHO undertakes a massive smallpox eradication campaign.[3] The Expanded Program on Immunization is created in 1974. The Alma Ata Declaration is adopted in 1978. |
| 1980s | WHO becomes the first major organization and the first intergovernmental agency to begin mobilizing for HIV/AIDS prevention and care.[4] |
| 1990s | WHO remains one of only a few key players in global health, alongside organizations like the World Bank and other health-related UN organizations.[5] |
Visual Data
Google Trends
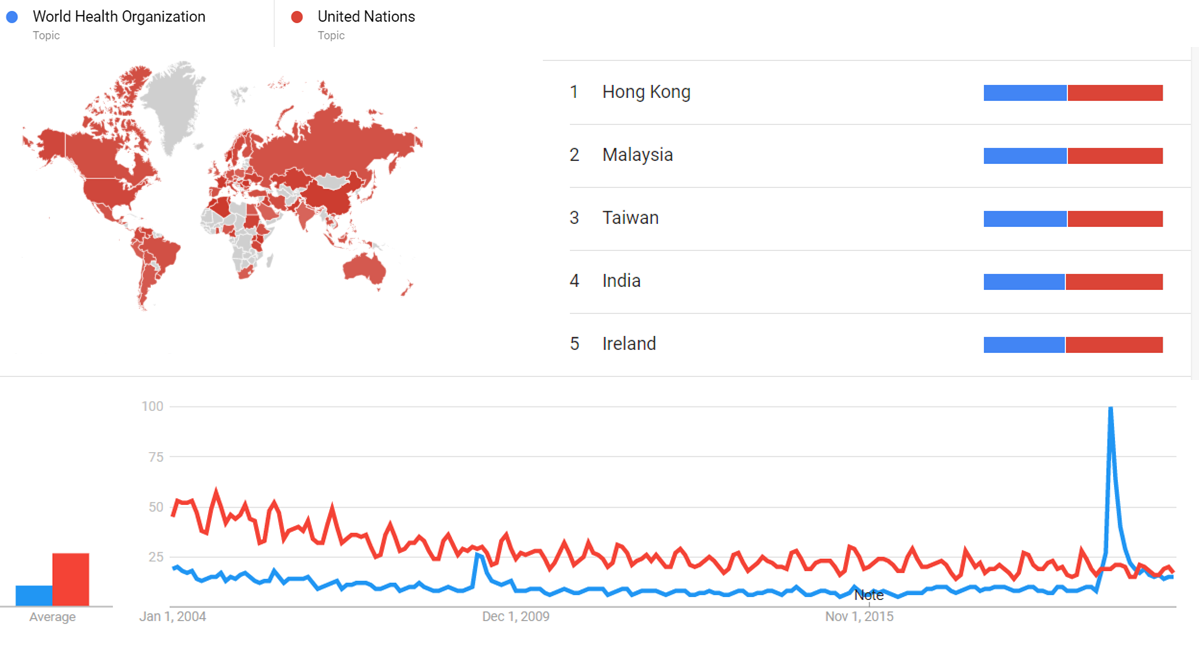
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for World Health Organization (Topic) and United Nations (Topic), from January 2004 to April 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[6]
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1945 | Prelude | The United Nations Conference in San Francisco unanimously approves the establishment of a new, autonomous international health organization.[7][8] | United States |
| 1946 (July) | The Constitution of the World Health Organization is approved by the International Health Conference in New York.[8] | United States | |
| 1947 (February 6) | The epidemiological information service is established.[8] | ||
| 1948 (April 7) | Creation | The World Health Organization Constitution comes into force.[7][8] | |
| 1948 (August 6) | The International Classification of Disease is created by WHO, as the global standard to report and categorize diseases, health-related conditions and external causes of disease and injury.[8] | ||
| 1948 (September 6) | Canadian doctor Brock Chisholm assumes office as WHO's first Director-General.[9] | ||
| 1949 | Publication | WHO publishes ICD-6, the sixth revision of the International statistical classification of diseases, which includes a section on mental disorders for the first time.[10] | |
| 1949 | The WHO's committee on mental health acknowledges that alcoholism is a public health issue.[11] | ||
| 1949 | Policy | WHO adopts a definition of health as “a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.”[12] | |
| 1950 (February 6) | The World Health Assembly establishes World Health Day to take place annually on 7 April.[8] | ||
| 1950 (May 6) | Program | WHO launches massive immunization with the bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccine, to protect children from tuberculosis.[8] | |
| 1950 | Epidemiology | WHO estimates that 160 million people are infected with yaws, 1 million with endemic syphilis, and 0.7 million with pinta.[13] | |
| 1951 | Policy | WHO adopts the International Sanitary Regulations – renamed International Health Regulations (IHR) in 1969 – with the objective of maximum prevention of the spread of infectious diseases with minimal disruption of travel and trade.[14] | |
| 1952 (Febuary 6) | Program | In partnership with UNICEF, WHO starts a massive international campaign to eradicate yaws, a tropical skin disease of the poor occurring in almost 100 countries.[15][8] | |
| 1952 | Program | WHO initiates a planetwide vaccination campaign to eradicate smallpox.[16] | |
| 1953 | Program | WHO launches an antimalaria program in the upcountry region of Central Province, Liberia, as a pilot project to determine the feasibility of malaria eradication in tropical Africa. The malaria control project in Monrovia constitutes the first large-scale use of synthetic insecticide to combat malaria in tropical Africa, and the WHO pilot project in Central Province is one of a first cluster of projects initiated to explore the efficacy of indoor residual spraying in a variety of African ecological zones.[17][18] | Liberia |
| 1953 (February 6) | Leadership | Brazilian medical doctor Marcolino Gomes Candau assumes office as WHO's Director-General. [9] | |
| 1954 | Growth | WHO reaches 81 members, nineteen more than the United Nations.[19] | |
| 1955 | Program | WHO launches the most ambitious public health program to date, the global eradication of malaria. The Global Malaria Eradication Programme is designed to rid the world of the parasitic disease at its source. Insecticide DDT is adopted as predominant method of insect control.[20] The program has the goal of eliminating the disease within 10 years.[21][22] | |
| 1956 | Program | WHO develops an international program to collect information about resistant populations of pests, methods of detection and evaluation of the resistance, and the use of alternative plant protection products.[23] | |
| 1957 | Program | WHO begins a US$ 6 billion campaign to rid the world of malaria using a combination of DDT and chloroquine.[24] | |
| 1957 | Program | WHO permits Polish American medical researcher Albert Sabin to test his polio vaccine in Chile, Holland, Japan, Mexico, Russia, and Sweden.[25] | Chile, Netherlands, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Sweden |
| 1957 | Publication | WHO publishes Requirements for Yellow Fever Vaccine, which standardizes the seed lot and manufacturing procedures.[26] | |
| 1958 | Policy | WHO sets the first International Drinking Water Standard for arsenic concentration at 200 µg L-1.[27] | |
| 1959 | Publication | WHO establishes the Advisory Committee for Medical Research (ACMR) to provide advice on medical research to the Director.[28] | |
| 1959 | Program | WHO initiates a plan to eradicate smallpox at a worldwide level.[29][30][31] | |
| 1960 | Publication | WHO publishes the first comprehensive report of the magnitude of iodine deficiency worldwide.[32] | |
| 1961 | Policy | WHO and Food and Agriculture Organization jointly create the joint Codex Alimentarius Commission in order to regulate the food safety by establishing international standards regarding processing, labeling, sampling of analysis, hygienic requirements, etc., of food commodities.[33] | |
| 1962 | Publication | WHO publishes the first international report on the importance of blood pressure control.[34] | |
| 1963 | The oral polio vaccine is licensed.[8] | ||
| 1963 | Policy | WHO recommends lowering the International Drinking Water Standard from 200 to 50 µg L-1 for arsenic concentration.[27] | |
| 1963 | Program | WHO establishes a system for the collection and distribution of information on viruses.[35] | |
| 1963 | Organization | WHO and FAO create the Codex Alimentarius Commission, joining 173 signatories from the European Community (EC) countries in order to control the tolerable limits of pollutants in food.[36] | |
| 1964 | Policy | WHO devises the Declaration of Helsinki, with 22 preconditions for human examination.[37] | Finland |
| 1964 | WHO introduces the concept of dependence, replacing and redefining the concept of addiction and encompassing the effects of the increasing variety of drugs available on the market.[38] | ||
| 1964 | WHO establishes the primary categories of residential satisfaction as safety, health, efficiency, and amenity.[39] | ||
| 1965 | Publication | WHO publishes diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus.[40] | |
| 1965 | Organization | The International Agency for Research on Cancer is established.[8] | |
| 1966 | The new headquarters building of the WHO is inaugurated in Geneva, Switzerland.[8] | Switzerland | |
| 1966 | Program | WHO launches the Smallpox Eradication Program, a mass vaccination campaign using new technology, freeze-dried vaccines, to allow for longer storage and transportation.[41] | |
| 1967 | Program | WHO launches the Intensified Global Smallpox Eradication Program, with the goal of vaccinating at least eighty percent of the world’s at-risk population.[42] | |
| 1968 | Publication | WHO publishes guidelines on the Principles and practice of screening for disease. Although these principles would be modified in 2008 and adjusted to screening based on genomic technologies, the main principles of screening, known as Wilson’s criteria, are still valid.[43] | |
| 1969 | The International Sanitary Regulations are renamed International Health Regulations.[8] | ||
| 1969 | Program | WHO suspends the Global Malaria Eradication Programme, after anopheles mosquitoes are found to develop resistance to DDT and continue to reproduce and spread disease in humans.[22] | |
| 1970 | Policy | WHO convenes a committee to classify and define the primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs). This expert committee accomplishes its task of creating a unified nomenclature for the then-known PIDs.[44] | |
| 1970 | Policy | WHO recognizes Ayurveda as a health science and as a traditional health system.[45] | India |
| 1972 | WHO introduces a classification of salivary gland tumors that would gain almost universal acceptance.[46] | ||
| 1972 | Policy | WHO declares noise as a pollutant.[47] | |
| 1973 | Growth | WHO celebrates its 25th anniversary with 138 member states.[19] | |
| 1973 | Leadership | Danish physician Halfdan T. Mahler assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 1974 | Program | WHO creates the Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI), a worldwide effort mobilized to help countries increase immunization coverage of basic childhood vaccines—diphtheria, measles, pertussis, polio, tetanus, and tuberculosis—using the third dose of diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (DTP3) as a measure of progress.[48] | |
| 1974 | Program | WHO launches the Onchocerciasis Control Programme in collaboration with the World Bank, the United Nations Development Programme and the Food and Agriculture Organization.[8] | |
| 1975 | Policy | WHO introduces the global concept of essential medicines as those that meet the health needs of the majority of the population.[49][50] | |
| 1975 | Program | WHO and the United States Agency for International Development embark on new programs aimed at developing a malaria vaccine.[51] | |
| 1975 | Epidemiology | WHO declares Europe free of malaria.[52] | Europe |
| 1975 | Program | WHO establishes the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases.[8] | |
| 1976 | WHO officially recognizes the potential value of traditional practitioners and folk healers to deliver healthcare.[53] | ||
| 1976 | Epidemiology | WHO estimates worldwide disability prevalence at 10%.[54] | |
| 1977 | Publication | WHO publishes the first essential medicines list.[8] | |
| 1978 | Treaty | WHO and UNICEF jointly host a conference in Kazakhstan that results in the Alma-Ata Declaration, in which primary health care is defined by leaders as ensuring that everyone, regardless of where they live, whether rich or poor, is able to access services and conditions necessary for realizing the best possible health.[55] The concept "Health for all by 2000" is introduced at the conference.[56] | Kazakhstan |
| 1978 | Program | WHO proposes a strategy for achieving Health For All, a programming goalenvisioning the secure of health and well being of people around the world.[57] | |
| 1979 | WHO holds an interregional seminar in which it defines a number of diseases for which acupuncture could be considered to be potentially helpful.[58] | ||
| 1980 | Epidemiology | WHO declares smallpox as officially eradicated from the world.[16] | |
| 1981 | Policy | WHO adopts the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes (International Code), with the purpose of contributing to the safe and adequate provision of nutrition for infants by protecting and promoting breastfeeding and ensuring that breast milk substitutes, when necessary, are used properly through adequate information and appropriate marketing and distribution.[59] | |
| 1982 | Program | WHO initiates the Cancer Pain Program, an initiative aimed at developing a global program for cancer pain relief with the help of specialists and pharmaceutical manufacturers. Through this program, three-step analgesic ladder would be developed, wih WHO recommending the use of strong opioids and adjuvants for cancer pain management.[60] | |
| 1982 | WHO asks an international group of investigators to develop a simple screening instrument to identify persons who are at risk of developing alcohol problems.[61] | ||
| 1983 | Program | WHO initiates the program "Smoking or Health" to focus public attention on the hazards of smoking.[62] | |
| 1984 | Policy | WHO develops a system of guidelines for the quality of drinking-water.[63] | |
| 1985 | WHO holds the first international meeting on maternal mortality.[64] | ||
| 1986 | Publication | WHO develops guidelines for cancer pain treatment.[65] | |
| 1987 | WHO recommends against universal mandatory HIV testing for all international travelers.[66] | ||
| 1988 | Leadership | Japanese doctor Hiroshi Nakajima assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 1988 | Program | WHO establishes as an objective the global eradication of poliomyelitis by the year 2000.[67] The Global Polio Eradication Initiative is established in collaboration with Rotary International, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and UNICEF.[8] | |
| 1988 | The World Health Assembly endorses a resolution on non-discrimination against people living with AIDS.[8] | ||
| 1989 | Program | WHO adopts the goal of eliminating neonatal tetanus as a public health problem worldwide.[68] | |
| 1990 | WHO establishes one of the first widely used definitions of palliative care: “the active, total care of patients whose disease is not responsive to curative treatment.”[69] | ||
| 1991 | Program | WHO initiates a project to simultaneously develop a quality of life (QOL) instrument in 15 countries: The World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL) instrument. This is intended as a generic QOL tool for use with patients across varying disease types, severities of illness, and cultural subgroups.[70] | |
| 1991 | Program | The World Health Assembly adopts a resolution to eliminate leprosy.[8] | |
| 1992 | Program | WHO sets a goal for all countries to introduce hepatitis B vaccine into national routine infant immunization programs by 1997.[71] | |
| 1993 | Policy | WHO declares tuberculosis a global emergency because of the scale of the epidemic and the urgent need to improve global tuberculosis control.[72] | |
| 1994 | WHO undergoes a major restructuring, in large part to meet the needs of the Children's Vaccine Initiative (CVI). A key result is the creation of the Global Program on Vaccines, which would later oversee the Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI), the Programme for Vaccine Development, and WHO's vaccine supply and quality-control operations.[73] | ||
| 1995 | Organization | WHO establishes the International Commission for the Certification of Dracunculiasis Eradication.[8] | |
| 1995 | Program | WHO launches the African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control (APOC) with the aim to control morbidity due to the parasitic infectious disease onchocerciasis (river blindness).[74] | Africa |
| 1995 | The Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal is launched by the Eastern Mediterranean Regional office of World Health Organisation.[75] | ||
| 1995 | Publication | WHO launches the Directly observed treatment, short-course (DOTS) strategy for tuberculosis control.[8] | |
| 1996 | Program | WHO establishes the International Electromagnetic Fields Project to investigate potential health risks associated with technologies emitting EMF.[76] | |
| 1996 | Organization | UNAIDS is created with six founding partner agencies.[8] | |
| 1997 | Growth | WHO turns 50 and reaches 191 member states.[19] | |
| 1998 | Leadership | Norwegian politician Gro Harlem Brundtland assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 1998 | Program | WHO establishes the Global Buruli Ulcer Initiative to draw attention to buruli ulcer (the third most common mycobacterial infection) and mobilize international efforts to understand and deal with it.[77] | |
| 1999 | Program | WHO initiates a series of meetings designed to create a Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC). Envisioned as a comprehensive, international, multilateral effort to reduce smoking rates, abate smoking-related illnesses, and regulate the trade, sale, and marketing of tobacco products, the FCTC marks the first truly global public health effort against tobacco consumption.[78] | |
| 2000 | Publication | WHO publishes The World Health Report 2000 – Health Systems: Improving Performance, which introduces a framework for evaluating and ranking healthcare with the stated objective of “improving the performance of health systems around the world”.[79] | |
| 2000 | Organization | The Global Outbreak Alert and Response Network is established.[8] | |
| 2000 | Program | 189 Member States of the United Nations unanimously adopt the United Nations Millennium Declaration, resulting in the Millennium Development Goals.[8] | |
| 2000 | Organization | The Commission on Macroeconomics and Health is established to assess the impact of health on development.[8] | |
| 2001 | Program | WHO launches a series of initiatives to put mental health on the global policy agenda and make it more visible throughout the world, and develops a set of instruments and programs.[80] | |
| 2001 | Program | WHO launches the Measles Initiative in partnership with the American Red Cross, UNICEF, the United Nations Foundation and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.[8] | |
| 2002 | Publication | WHO publishes a health system performance ranking for 191 member countries. The ranking is based on five indicators, with fixed weights common to all countries.[81] | |
| 2003 | Leadership | Korean public health doctor Lee Jong-wook assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 2003 | Publication | In order to emphasize the need to promote oral health, WHO publishes a guidance document for every nation to define their goals in oral health indicators by the year 2020.[82] | |
| 2003 | Treaty | The WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control is adopted.[83] | |
| 2004 | Policy | WHO releases the first global policy on physical activity and develops a set of programs and policies needed within each country to reverse the trend of inactivity.[84] | |
| 2005 | The WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control is adopted as WHO’s first global public health treaty.[85] | ||
| 2005 | Publication | WHO publishes a Resource Book (WHO-RB) on mental health, human rights and legislation, including a checklist of 175 specific items to be addressed in mental health legislation or policy in individual countries.[86] | |
| 2006 | Leadership | Swedish physician Anders Nordström assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 2006 | Policy | WHO launches new growth standards for application to all children regardless of ethnicity, socioeconomic status and feeding mode. By 2011, 125 countries would adopt these standards, with another 25 considering their adoption, and 30 not adopting them.[87] | |
| 2007 | Leadership | Chinese-Canadian physician Margaret Chan assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] | |
| 2007 | Program | WHO establishes an international network of biodosimetry laboratories, the BioDoseNet, with the goal to support international cooperation and capacity building in the area of biodosimetry around the world, including harmonisation of protocols and techniques to enable them to provide mutual assistance during a mass casualty event.[88] | |
| 2008 | Program | WHO launches the Safe Surgery Saves Lives campaign and produces the ‘Surgical Safety Checklist’ (SSC) designed to reduce complications and deaths associated with surgery.[89] | |
| 2008 | The WHO's annual World Health Statistics reports a global shift from infectious diseases to non-communicable diseases.[85] | ||
| 2009 | Program | WHO launches the Enhanced Global Strategy for Further Reducing the Disease Burden due to Leprosy for 2011–2015, under which the target becomes to reduce the number of new cases of leprosy with grade 2 disability per 100,000 total population by at least 35% between the end of 2010 and the end of 2015.[90] The goals are not likely to be met, with statistics indicating that new cases and those with G2D either stagnated or increased in the period.[91] | |
| 2010 | Policy | WHO issues a global Code of Practice with the purpose to control international migration of health professionals.[92] | |
| 2011 | Program | WHO develops a Global Monitoring Framework (GMF) to enable tracking of progress in preventing and controlling major noncommunicable diseases and their key risk factors – tobacco, harmful use of alcohol, unhealthy diets and physical inactivity.[93] | |
| 2012 | Publication | WHO publishes a roadmap that sets targets for the eradication, elimination and intensified control of 17 neglected tropical diseases.[94] | |
| 2012 | Program | WHO Member States set for the first time global targets to prevent and control heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and other non-communicable diseases.[85] | |
| 2012 (November 12) | Treaty | WHO adopts the Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products with the purpose of eliminating all forms of illicit trade in tobacco products.[95] | |
| 2013 | Program | WHO establishes the Global Forum on Innovation for Ageing Populations as an information exchange platform for diverse stakeholders to address the challenge of meeting the needs of older people in low resource settings with frugal innovations.[96] | |
| 2014 | Policy | WHO declares that polio is a public health emergency of international concern.[97] | |
| 2014 | Program | WHO develops the End TB Strategy in response to a World Health Assembly Resolution requesting Member States to end the worldwide epidemic of tuberculosis by 2035.[98] | |
| 2015 | Publication | WHO publishes its World report on aging and health, with aims at bringing to global attention a whole range of issues related to the health and well-being of older individuals and populations across the entire spectrum of high- middle- and low-income countries.[99] | |
| 2015 | The Sustainable Development Goals are adopted.[85] | ||
| 2016 | Program | WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launch the Global Hearts initiative, which focuses on the noncommunicable disease burden due to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and its risk factors. The initiative provides a simple framework that enables front-line health clinics to implement WHO’s call to integrate cardiovascular disease care into primary disease prevention.[100] | |
| 2017 | Publication | WHO publishes guidelines for the management of advanced human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease within a public health approach.[101] | |
| 2017 | Leadership | Ethiopian politician Tedros Adhanom assumes office as WHO's Director-General.[9] |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ Montegut, AJ. "To achieve "health for all" we must shift the world's paradigm to "primary care access for all".". PMID 17954857. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2007.06.070128.
- ↑ Eisen, Jonathan. Suppressed Inventions.
- ↑ "Successes and Setbacks in Disease Eradication". wnycstudios.org. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ AIDS in the World II: Global Dimensions, Social Roots, and Responses. Global AIDS Policy Coalition.
- ↑ "One chart that explains why the WHO is actually in crisis". vox.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "World Health Organization and United Nations". Google Trends. Retrieved 22 April 2021.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "History of WHO". who.int. Retrieved 10 October 2018.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 8.18 8.19 8.20 8.21 8.22 8.23 8.24 "The World Health Organization". media.timetoast.com. Retrieved 1 November 2018.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 9.8 "Former Directors-General". who.int. Retrieved 23 October 2018.
- ↑ Feinstein, Adam. A History of Autism: Conversations with the Pioneers.
- ↑ Mager, Anne Kelk. Beer, Sociability, and Masculinity in South Africa.
- ↑ "A Comparative Review of Contemporary Participation Measures' Psychometric Properties and Content Coverage". archives-pmr.org. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- ↑ Asiedu, Kingsley; Fitzpatrick, Christopher; Jannin, Jean. "Eradication of Yaws: Historical Efforts and Achieving WHO's 2020 Target".
- ↑ "Health crises and migration" (PDF). fmreview.org. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- ↑ Enserink, Martin. "A second chance". science.sciencemag.org. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "DNA screening for smallpox" (PDF). edvotek.com. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Webb, James L. A. "The First Large-Scale Use of Synthetic Insecticide for Malaria Control in Tropical Africa: Lessons from Liberia, 1945–1962".
- ↑ "History of Malaria". researchgate.net. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 "Leadership Change in the World Health Organization: Potential for Increased Effectiveness?" (PDF). files.ethz.ch. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Staples, Amy L. S.; Sayward, Amy L. The Birth of Development: How the World Bank, Food and Agriculture Organization, and World Health Organization Changed the World, 1945-1965.
- ↑ "The Connection: Malaria and DDT". sites.duke.edu. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Kinkela, David. DDT and the American Century: Global Health, Environmental Politics, and the Pesticide That Changed the World.
- ↑ Wojciechowska, M; Stepnowski, P; Gołębiowski, M. "The use of insecticides to control insect pests" (PDF).
- ↑ "Malaria". earthuntouched.com. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ "Albert Sabin". ohiohistorycentral.org. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Barnett, Elizabeth D. "Yellow Fever: Epidemiology and Prevention".
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 JOARDAR, JAGADISH CHANDRA. "Effect of arsenic both in soil and irrigation water on vegetable plants and promising soil additives for remedial measure of arsenic toxicity" (PDF). core.ac.uk. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ "A Historical Review of Its Contributions to Health, Health Care, and Health Policie: 1962-2008". iris.paho.org. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ "History of Smallpox". cdc.gov. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ "Smallpox and the development of vaccination". digital.nls.uk. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Voigt, Emily A.; Kennedy, Richard B.; Poland, Gregory A. "Defending Against Smallpox: a Focus on Vaccines". PMC 5003177
 . PMID 27049653. doi:10.1080/14760584.2016.1175305.
. PMID 27049653. doi:10.1080/14760584.2016.1175305.
- ↑ Wondisford, Fredric E.; Radovick, Sally. Clinical Management of Thyroid Disease E-Book.
- ↑ "Food Security:" (PDF). fao.org. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- ↑ Petursson, Halfdan; Getz, Linn; Sigurdsson, Johann A; Hetlevik, Irene. "Can individuals with a significant risk for cardiovascular disease be adequately identified by combination of several risk factors? Modelling study based on the Norwegian HUNT 2 population". PMC 2695852
 . PMID 19239589. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00962.x.
. PMID 19239589. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.00962.x.
- ↑ Assaad, F.; Borecka, I. "Nine-year study of WHO virus reports on fatal viral infections". PMC 2366686
 . PMID 304388.
. PMID 304388.
- ↑ "Computational Biology, Protein Engineering, and Biosensor Technology: a Close Cooperation for Herbicides Monitoring". researchgate.net. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- ↑ "Wrong site surgery & surgical time out". epubs.rcsi.ie. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Pereira, Margaret. "Governing drug use among young people: Crime, harm and contemporary drug use practices" (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Lee, Sangwon; Alzoubi, Hussain H.; Sooyoung Kim. "The Effect of Interior Design Elements and Lighting Layouts on Prospective Occupants' Perceptions of Amenity and Efficiency in Living Rooms". doi:10.3390/su9071119.
- ↑ Alshareef, Ahmad. "THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN OBESITY AND PERIODONTAL DISEASE" (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ "The UN by decade: 1970s". una.org.uk. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Glomski, Matthew; Ohanian, Edward. "Eradicating a Disease: Lessons from Mathematical Epidemiology" (PDF). Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Litwin, Mieczysław. "Why should we screen for arterial hypertension in children and adolescents?". PMC 5700235
 . PMID 28717934. doi:10.1007/s00467-017-3739-8.
. PMID 28717934. doi:10.1007/s00467-017-3739-8.
- ↑ Notarangelo, Luigi; Casanova, Jean-Laurent; Fischer, Alain; Puck, Jennifer; Rosen, Fred; Seger, Reinhard; Geha, Raif. "Primary immunodeficiency diseases: An update".
- ↑ "Globalization and Alternative Medicines". globalization101.org. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Diagnosis of salivary gland disorders (K. Graamans, Hans Becker ed.).
- ↑ de Paiva Vianna, Karina Mary; Alves Cardoso, Maria Regina; Calejo Rodrigues, Rui Manuel. "Noise pollution and annoyance: An urban soundscapes study". PMC 4918656
 . PMID 25913551.
. PMID 25913551.
- ↑ Shen, Angela K.; Clay, Robert; Pablos-Mendez, Ariel. "Global Immunization through the Lens of Development". PMC 4121879
 . PMID 25100884. doi:10.1177/00333549141295S302.
. PMID 25100884. doi:10.1177/00333549141295S302.
- ↑ "Toward Sustainable Access to Medicines. (MDS-3: Managing Access to Medicines and Health Technologies, Chapter 1)". apps.who.int. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Albert, Michael A; Fretheim, Atle; Maïga, Diadié. "Factors influencing the utilization of research findings by health policy-makers in a developing country: the selection of Mali's essential medicines". PMC 1820594
 . PMID 17338810. doi:10.1186/1478-4505-5-2.
. PMID 17338810. doi:10.1186/1478-4505-5-2.
- ↑ Trager, W; Jensen, J B. "Human malaria parasites in Continuous culture" (PDF).
- ↑ "From Shakespeare to Defoe: Malaria in England in the Little Ice Age". cdc.gov. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Incayawar, Mario; Wintrob, Ronald; Bouchard, Lise; Bartocci, Goffredo. Psychiatrists and Traditional Healers: Unwitting Partners in Global Mental Health.
- ↑ Fayed, Nora. "Linking health and health-related information to the ICF: a systematic review of the literature from 2001 to 2008". Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ "Health progress and challenges, 30 years after the Alma-Ata Declaration". unicef.org. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ De Haan, Merle; Dennill, Kathleen; Vasuthevan, Sharon. The Health of Southern Africa.
- ↑ "Summary of Achievements in Primary Care Research". jhsph.edu. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ↑ Cheung, Lily; Li, Peng; Wong, Cheng. Mechanism of Acupuncture Therapy and Clinical Case Studies.
- ↑ "Recommendations for Adopting the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes into United States Policy". PMC 5515674
 . PMID 28418755. doi:10.1177/0890334417703063.
. PMID 28418755. doi:10.1177/0890334417703063.
- ↑ Sharma, Kailash S. "Development of Specialist Palliative Care in Indian Cancer Care Setting: A Personal Journey of Three Decades". PMC 4973481
 . PMID 27559249. doi:10.4103/0973-1075.185024.
. PMID 27559249. doi:10.4103/0973-1075.185024.
- ↑ "From clinical research to secondary prevention: international collaboration in the development of the Alcohol Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)". galegroup.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Waalkens, H.J.; Cohen Schotanus, J.; Adriaanset, H.; Knol, K. "Smoking habits in medical students and physicians in Groningen, The Netherlands" (PDF). Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Concern for Europe's tomorrow" (PDF). euro.who.int.
- ↑ "The history of the Safe Motherhood Initiative. Introductory remarks.". popline.org. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Carlson, CL. "Effectiveness of the World Health Organization cancer pain relief guidelines: an integrative review.". PMC 4965221
 . PMID 27524918. doi:10.2147/JPR.S97759.
. PMID 27524918. doi:10.2147/JPR.S97759.
- ↑ Marlink, Richard G.; Kotin, Alison G. Global AIDS Crisis: A Reference Handbook.
- ↑ "World Health Day -- April 7, 1995". cdc.gov. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Dietz, V; Galazka, A; van Loon, F; Cochi, S. "Factors affecting the immunogenicity and potency of tetanus toxoid: implications for the elimination of neonatal and non-neonatal tetanus as public health problems.". PMC 2486988
 . PMID 9141753.
. PMID 9141753.
- ↑ "NCCN Palliative Care Guidelines 2007: integrating end-of-life care". healio.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Bonomi, AE; Patrick, DL; Bushnell, DM; Martin, M. "Validation of the United States' version of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL) instrument.". PMID 10693897.
- ↑ "Implementation of newborn hepatitis B vaccination--worldwide, 2006.". PMID 19023261.
- ↑ Maher, Dermot; Raviglione, Mario. "Global Epidemiology of Tuberculosis".
- ↑ Pearson, Greg W. The Children's Vaccine Initiative: Continuing Activities ; a Summary of Two Workshops Held September 12-13 and October 25-26, 1994.
- ↑ Coffeng, Luc E.; Stolk, Wilma A.; Zouré, Honorat G. M.; Veerman, J. Lennert; Agblewonu, Koffi B.; Murdoch, Michele E.; Noma, Mounkaila; Fobi, Grace; Richardus, Jan Hendrik; Bundy, Donald A. P.; Habbema, Dik; de Vlas, Sake J.; Amazigo, Uche V. "African Programme for Onchocerciasis Control 1995–2015: Model-Estimated Health Impact and Cost". PMC 3561133
 . PMID 23383355. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002032.
. PMID 23383355. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0002032.
- ↑ "About the journal". emro.who.int. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ↑ "Electromagnetic fields and public health". who.int. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Weir, Erica. "Buruli ulcer: the third most common mycobacterial infection". PMC 116159
 . PMID 12126327.
. PMID 12126327.
- ↑ "The World Health Organization Takes On The Tobacco Industry". encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Canada Versus the World: The Validity and Usefulness of Ranking Healthcare Systems by Country". mjmmed.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Background and historical development of PAHO Mental Health Program". paho.org. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Lauer, Jeremy A; Lovell, Knox; Murray, Christopher JL; Evans, David B. "World health system performance revisited: the impact of varying the relative importance of health system goals". PMC 506780
 . PMID 15271220. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-4-19.
. PMID 15271220. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-4-19.
- ↑ "Is periodontal disease a public health issue in Colombia?". colombiamedica.univalle.edu.co. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "About the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control". who.int. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ↑ "Monitoring Global Progress of Physical Activity: The Role and Progress of Civil Society in Holding Governments to Account". journals.humankinetics.com. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 85.2 85.3 "Milestones for health over 70 years". who.int. Retrieved 21 December 2018.
- ↑ Duffy, Richard M.; Kelly, Brendan D. "Concordance of the Indian Mental Healthcare Act 2017 with the World Health Organization's Checklist on Mental Health Legislation". International Journal of Mental Health Systems.
- ↑ "Nutrition and Growth".
- ↑ "An update of the WHO Biodosenet: Developments since its Inception". researchgate.net. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Haugen, A. S.; Søfteland, E.; Eide, G. E.; Sevdalis, N.; Vincent, C. A.; Nortvedt, W.; Harthug, S. "Impact of the World Health Organization's Surgical Safety Checklist on safety culture in the operating theatre: a controlled intervention study". PMC 3630285
 . PMID 23404986.
. PMID 23404986.
- ↑ Alberts, Catharina J; Cairns S Smith, W; Meima, Abraham; Wangd, Lamei; Richardus, Jan Hendrik. "Potential effect of the World Health Organization's 2011–2015 global leprosy strategy on the prevalence of grade 2 disability: a trend analysis" (PDF).
- ↑ Tuberculosis, Leprosy and Mycobacterial Diseases of Man and Animals: The Many Hosts of Mycobacteria (Harshini Mukundan, Mark Chambers, Ray Waters, Michelle Larsen ed.).
- ↑ "Bulletin of the World Health Organization". who.int. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "WHO's Global Monitoring Framework Tracks Progress in NCD Prevention and Control" (PDF). cdc.gov. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "WHO declares India free of yaws". who.int. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Protocol to Eliminate Illicit Trade in Tobacco Products". who.int. Retrieved 2 November 2018.
- ↑ "WHO Global Forum on Innovations for Ageing Populations Report of the forum, 10-12 December 2013, Kobe, Japan". extranet.who.int. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ Sisay G. Tegegne; Pascal MKanda; Yared G. Yehualashet; Tesfaye B. Erbeto; Kebba Touray; Peter Nsubuga; Richard Banda; Rui G. Vaz. "Implementation of a Systematic Accountability Framework in 2014 to Improve the Performance of the Nigerian Polio Program". PMC 4818547
 . PMID 26823334. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiv492.
. PMID 26823334. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiv492.
- ↑ Falzon, D; Timimi, H; Kurosinski, P; Migliori, GB; Van Gemert, W; Denkinger, C; Isaacs, C; Story, A; Garfein, RS; do Valle Bastos, LG; Yassin, MA; Rusovich, V; Skrahina, A; Van Hoi, L; Broger, T; Abubakar, I; Hayward A, I; Thomas, BV; Temesgen, Z; Quraishi, S; von Delft, D; Jaramillo, E; Weyer, K; Raviglione, MC. "Digital health for the End TB Strategy: developing priority products and making them work.". PMC 4929075
 . PMID 27230443. doi:10.1183/13993003.00424-2016.
. PMID 27230443. doi:10.1183/13993003.00424-2016.
- ↑ "Equity and healthy ageing". who.int. Retrieved 9 October 2018.
- ↑ "Beyond hypertension: integrated cardiovascular care as a path to comprehensive primary care". who.int.
- ↑ "Managing Advanced HIV Disease in a Public Health Approach". researchgate.net. Retrieved 9 October 2018.