Timeline of Substack
This is a timeline of Substack, a United States online platform that provides users with tools to publish paid (or free) subscription newsletters.
Contents
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
Big picture
Summary by year
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Early Success | Substack attracts initial users and begins to grow its user base, offering writers the ability to earn money through paid subscriptions.[1] |
| 2019 | Funding and Growth | Substack raises $15.3 million from investors including Andreessen Horowitz, Y Combinator, and Fifty Years, facilitating further expansion.[1] |
| 2020 | Growth and Prominence | Substack grows in prominence as several well-known opinion journalists, including Heather Cox Richardson, Glenn Greenwald, Andrew Sullivan, and Matt Taibbi, abandon their longtime employers to start their own subscriptions on the platform. During this time, Substack refines its revenue-sharing model, taking a 10% cut of the revenue generated by paid subscriptions and introducing features like tipping.[2][1] |
| 2022 | User Base Expansion | Substack reports over 500,000 paid subscribers and more than 100,000 writers, solidifying its position as a leading newsletter platform.[1] |
| 2023 | Evolution | Substack evolves into a platform with algorithmically ranked digests and mutual user recommendations.[3] |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | May | Initial launch | Substack is launched by Chris Best, Jairaj Sethi, and Hamish McKenzie[4] with the mission to make it simple to start publications that make money from subscriptions.[5] |
| 2017 | October 16 | Founding | Substack is founded in San Francisco, California, by Chris Best, Jairaj Sethi, and Hamish McKenzie. The platform aims to provide independent writers with a way to publish newsletters and monetize their content through subscriptions, offering simple infrastructure for email newsletters without heavy content moderation.[6][3][1][7][8] |
| 2017 | October 18 | Launch | Bill Bishop launches the first paid newsletter on Substack, marking its official introduction to the public. The success of this launch demonstrates the platform's potential for monetizing content through subscriptions.[6] |
| 2018 | May 1 | Funding | Substack receives its first seed funding round where they raise $2 million. Investors in this round include Fifty Years, Garage Capital, and several others. This initial capital helps Substack establish its platform and start attracting writers and subscribers.[9] |
| 2019 | February | Service | Substack launches audio content support for creators who want to sell podcast subscriptions to their audience.[10] |
| 2019 | July 17 | Funding | Substack experiences significant growth with its Series A round, securing $19.1 million. The funding is led by prominent investors such as a16z and Y Combinator. This round marks a pivotal moment for Substack, allowing them to expand their team, enhance their platform features, and attract more high-profile writers to their subscription-based publishing model |
| 2020 | April | Expansion | Substack launches Notes, a text-based social network similar to Twitter.[3] |
| 2020 | November 17 | An article by The Guardian explores how Substack is disrupting traditional media by offering an alternative publishing platform. According to the article, Substack's model empowers individual writers, providing them with financial independence and editorial freedom. However, it also raises concerns about the sustainability of journalism and the potential for misinformation as writers operate without the oversight of traditional editorial processes.[11] | |
| 2020 | December 2 | An article from NPR explores the growing trend of journalists transitioning from social media to Substack, in search of more creative control and financial independence. Frustrated with the pressures of traditional media and social media's algorithm-driven environment, these writers are attracted to Substack's model, which allows them to directly connect with their audience and monetize their work through subscriptions. While this shift provides new opportunities, it also raises concerns about the long-term sustainability of this model and its impact on traditional journalism.[12] | |
| 2020 | July 30 | Growth | A Business Insider article details how Substack saw its user base double and revenue increase by 60% during the first three months of the COVID-19 pandemic. This growth was driven by readers with more time at home and writers from traditional media seeking new monetization methods.[13] |
| 2020 | November 17 | Criticism | An article from *The Guardian* critiques Substack for its growing influence in the media landscape. The piece argues that Substack's model, which allows writers to earn directly from subscribers, disrupts traditional media but also raises concerns about the platform's role in shaping public discourse, its lack of editorial oversight, and the potential for fostering echo chambers. The article questions whether Substack's rise will ultimately benefit or harm the broader media ecosystem.[14] |
| 2020 | December 28 | Review | Anna Wiener at the The New Yorker writes that while "Substack has advertised itself as a friendly home for journalism, [...] few of its newsletters publish original reporting; the majority offer personal writing, opinion pieces, research, and analysis."[15] |
| 2021 | January 28 | Competition | Twitter's acquisition of Revue, a newsletter platform, marks its entry into the email subscription business, directly competing with Substack. Revue offers similar services to Substack, which has been popular among journalists for monetizing newsletters. Twitter’s move includes reducing Revue's fee to 5% and plans to integrate newsletter subscriptions with Twitter accounts. Despite Twitter's vast resources and potential advantages, analysts like Ben Thompson caution that successful execution is crucial. Substack, backed by significant investments and notable writers, may still hold a strong position in the market. Critics question if Substack perpetuates media inequities by favoring already influential voices.[16] |
| 2021 | March 16 | Competition | Facebook announces it has plans to launch its paid newsletter product “in the coming months.”[17] |
| 2021 | March 17 | Statement | Substack publishes a statement titled Substack is for independent writers.[18] |
| 2021 | March 19 | Controversy | Substack faces backlash from some writers, like Jude Doyle, who leave due to the platform's support for controversial authors accused of hate speech. Substack's business model, which includes paying large advances to attract high-profile writers, causes further tension. By this time, the lack of transparency regarding these deals and concerns about supporting divisive figures have led to criticism. With competitors like Facebook and Twitter entering the newsletter market, Substack risks losing writers. The company's identity crisis between being a platform and a publisher exacerbates these issues, challenging its long-term stability. |
| 2021 | March 24 | Criticism | An article by Eric Levitz argues that while Substack has been criticized for its secretive financial arrangements and potentially misleading new writers about the profitability of newsletter writing, these issues are not unique to Substack but are endemic to the entire journalism industry. Levitz suggests that the real problem lies in the broader structural challenges faced by the media, including the collapse of traditional revenue models and the resulting mass underemployment of journalists. He proposes that a solution to these deeper issues might require public financing of journalism to support its vital civic function.[2][19] |
| 2021 | April 23 | Competition | An article discusses Substack's strategy of attracting prominent journalists from traditional media outlets like The New York Times by offering lucrative financial incentives and greater editorial freedom. This approach intensifies competition in the media industry as Substack aims to build a robust subscription-based model, challenging established media companies' dominance. The piece explores the implications of this shift for journalism and the broader media landscape.[20] |
| 2021 | May 6 | Substack launches a new feature called "Sections", which allows writers and content creators to manage multiple newsletters or podcasts within one main publication, akin to traditional media outlets. Subscribers can choose which sections of the publication they want delivered to their inbox, potentially intensifying competition with established media organizations. This development underscores Substack's growing influence in the digital content space.[21] | |
| 2021 | May 30 | Funding | Substack confirms US$65 million raise in new venture capital funding that values the company at around US$650 million. Andreessen Horowitz leads the investor round.[22][23] |
| 2021 | June 7 | An article by The Wired discusses the rise of Ghost, a content management system that offers a platform for independent publishers and writers. It highlights how Ghost provides an alternative to larger, more commercial platforms, allowing users more control over their content and monetization strategies. The article also examines Ghost's features, its appeal to content creators seeking autonomy from traditional publishing models, and its role in the evolving landscape of digital media and independent publishing.[24] | |
| 2021 | August 12 | An article from *Rest of World* discusses Substack's international expansion efforts, focusing on how the platform is attracting writers and journalists outside the United States. As Substack grows globally, it aims to diversify its user base by offering local-language support and adapting to different cultural and market dynamics. By this time, the platform's model gains traction among international creators who seek financial independence and greater control over their work.[25] | |
| 2021 | September | Funding | Substack raises a $65 million Series B round led by Andreessen Horowitz, valuing the company at $650 million and emphasizing its rapid growth and market potential.[6] |
| 2021 | November 16 | Growth | Substack surpasses one million paid subscriptions, signaling significant growth and the platform's increasing influence in the media landscape. The company claims that these subscriptions represent new revenue for writers, not a shift from traditional media. High-profile writers like Glenn Greenwald, Matt Taibbi, Bari Weiss, and Matt Yglesias contribute to this success. In response, legacy media outlets like The New York Times and The Atlantic launch paid newsletter programs to retain and attract top writers. This trend would prompt new platforms like Lede and Workweek to offer hybrid options, balancing newsroom support with writer independence.[26][27] |
| 2022 | January 27 | Controversy | Substack faces criticism for hosting and profiting from content by anti-vaccine advocates like Joseph Mercola, who spreads debunked claims about COVID-19 vaccines. While major social media platforms ban or restrict such content, Substack's more lenient policies allow these figures to gain significant followings and generate substantial revenue. Substack argues that tolerating diverse viewpoints is essential for fostering trust in information, but critics warn that this approach may enable the spread of harmful misinformation. The platform's business model, which includes a 90-10 revenue split between authors and the company, draws scrutiny as it generates millions from controversial content. |
| 2022 | March 9 | Controversy | An article from Mashable discusses why some Substack creators, such as Grace Lavery, are leaving the platform. Lavery, a trans woman and University of Berkeley professor, departed due to Substack's failure to enforce its content guidelines against harassment and misinformation, particularly around transphobic content. This exodus includes other writers like K. Tempest Bradford and Kirsten Han, who criticize Substack's hands-off approach to content moderation. By this time, the platform's stance on free speech, prioritizing minimal censorship, has attracted controversial figures spreading misinformation and hate speech, which would drive many creators away despite Substack's financial appeal.[28] |
| 2023 | April 7 | Competition | Twitter restricts users from liking or retweeting posts that contain links to Substack. This action by Twitter limits the visibility and engagement of Substack content on its platform. The restriction raises concerns among users and creators who rely on both Twitter and Substack for content distribution and audience engagement.[29] |
| 2022 | April 13 | Coverage | A New York Times article discusses Substack's growth in the newsletter space. Despite facing challenges such as criticism from traditional media and competition from other platforms, by this time Substack managed to attract prominent writers and expand its user base. The platform's subscription-based model is described as appealing to both writers and readers, fostering a direct connection between them.[30] |
| 2022 | June 29 | Substack lays off 13 employees, roughly 14% of its workforce, in response to challenging economic conditions. The layoffs are part of a broader strategy to cut costs and extend the company's financial runway. [31] | |
| 2023 | January | Product Expansion | Substack launches private Substacks, signaling its move beyond newsletters to become a broader platform for multimedia content and social interaction.[6] |
| 2023 | February 9 | An article reveals that the 27 highest-earning newsletters on Substack generate over $22 million annually, with at least five making $1 million each per year. These top newsletters cover a range of topics, including politics, culture, and niche interests. Notable high earners include Heather Cox Richardson’s "Letters from an American," which brings in around $5 million annually. The analysis underscores Substack's potential as a lucrative platform for writers, particularly those with significant followings.[32] | |
| 2023 | April 17 | An article explores how Substack provides financial and editorial freedom for investigative journalists, allowing them to publish independently. Its growth during the COVID-19 pandemic was significant, boasting two million paid subscriptions by early 2023. Substack's benefits include built-in monetization, design support, and the Defender program for legal assistance. However, challenges such as sustaining an audience, publishing frequency, and monetization persist. Case studies like Geneva Health Files, SoCal Water Wars, Undue Influence, and 18 Degrees North Investigations highlight both the platform's potential and the hurdles faced by journalists in building a successful, independent investigative journalism presence. | |
| 2023 | May 30 | Funding | Substack continues to attract investment with an additional $3.29 million raised in a Series B extension round. While smaller compared to the previous Series B round, this funding is aimed at specific growth initiatives or strategic investments to further bolster their platform capabilities or market reach. |
| 2023 | June 1 | WordPress.com intro
duces a new feature that allows users to create paid newsletters, directly competing with Substack. This update enables users to monetize their newsletters by adding paid subscriptions and premium content, even on the free plan. WordPress.com will charge a transaction fee starting at 10% for free plan users, decreasing to 0% for paid plans. Payments are processed through Stripe. This move leverages WordPress's extensive customization options and large user base, providing an attractive alternative for newsletter creators looking to expand their offerings beyond just newsletters to include websites and online stores.[33][34][35] | |
| 2023 | June 5 | Substack introduces new video features, enabling creators to integrate video content into their newsletters and subscriptions. This update allows users to upload and share videos directly on Substack, providing an additional revenue stream and expanding content options beyond traditional text-based newsletters. This feature enhances the platform's capabilities, aiming to support creators in building richer and more engaging content for their subscribers.[36] | |
| 2023 | June 27 | Competition | An article discusses on Substack facing increased competition from platforms like WordPress and Beehiiv as it emerges from a period of defensive retrenchment. Despite setbacks, including controversies and layoffs, Substack remains a popular choice for many high profile writers. By this time, the platform has its Twitter-like Notes feature, which led to tensions with Twitter, notably under Elon Musk. Meanwhile, legacy media and newer platforms offer competitive newsletter options, with WordPress launching paid newsletters and Beehiiv securing $12.5 million in funding to expand its offerings. Substack cofounder Hamish McKenzie emphasizes the importance of helping writers grow to justify their 10% fee amidst this competition.[37] |
| 2023 | August 2 | Writer, interviewer, and podcaster Madeleine Dore reflects on her first year on Substack, embracing her inconsistent writing style and leveraging it alongside the support of paying readers to create a consistent schedule for paid content. She emphasizes the value of starting without perfect clarity, allowing her newsletter "On Things" to evolve organically. Dore advises against the comparison trap, preferring personal commitment over external metrics, and warns of the unsustainable pursuit of growth. Her measure of success focuses on personal fulfillment rather than subscriber numbers. Looking forward, she expresses plans to expand offerings for paid subscribers and sustain her independent writing career with diverse content and community engagement. This provides insights into how Substack serves as a platform that enables writers to embrace their unique writing styles and build a community around their creative pursuits.[38] | |
| 2023 | August 10 | Historical Reflection | Casey Botticello publishes an article detailing the history and impact of Substack on independent journalism and traditional media.[1] |
| 2023 | August 14 | Substack introduces a new feature allowing users to follow writers without subscribing to their newsletters. This feature lets followers stay updated on writers' activities, publications, and interactions through Substack's Notes feed and profiles. Positioned as a way to expand writers' audiences within Substack's network, the feature aims to complement, rather than replace, paid subscriptions.[39] | |
| 2023 | Aug 15 | Substack introduces a "Follow" button to make its platform more social network-like. This feature allows users to follow writers without subscribing to their newsletters, helping writers grow their audience. Followers can stay updated on writers' activities through the Notes feed and profiles. The platform aims to encourage subscriptions by notifying followers of new posts and milestones, making it easier to convert follows into subscriptions. This move aligns with Substack's strategy to compete with X (formerly Twitter) and expand beyond being just a newsletter platform.[40] | |
| 2023 | August 31 | Substack introduces new AI-powered audio transcription tools | |
| 2023 | September 17 | An article discusses how Substack newsletters became a significant trend in the literary world, offering writers a platform to connect directly with readers, generate income, and explore niche topics. Notable authors like Bri Lee, Salman Rushdie, and Chuck Palahniuk use Substack to publish content ranging from personal essays to serialized novels. The platform allows for a mix of free and paywalled content, supported by reader subscriptions. While some authors use Substack to provide early access to forthcoming works, others, like George Saunders and Mary Gaitskill, focus on essays, reviews, and literary criticism. However, the article notes that maintaining a regular newsletter can be demanding and may not be sustainable for all writers. Despite challenges, Substack remains a popular and accessible platform for literary and journalistic content.[41] | |
| 2023 | September 20 | Substack redesigns its mobile app to enhance discovery and engagement, featuring a new Home experience with a reading queue at the top for easier browsing and post sharing. This queue prioritizes new posts from paid subscriptions and frequently read content. Additionally, a discovery feed showcasing notes and post recommendations is introduced. The inbox is moved to the center tab with improved filtering, while notifications are placed in the top bar. Substack announces aim to make its platform more social, encouraging writers to share notes to attract and convert readers into subscribers.[42] | |
| 2023 | October 20 | Substack Takes a Swipe at X with New Link-Sharing Update | |
| 2023 | November 29 | Substack expands its services into video content, introducing new tools for creators to upload, manage, and monetize videos directly on its platform. This move positions Substack to compete with established platforms like Patreon and YouTube, aiming to attract creators who want to integrate video with their existing written content. The shift highlights Substack's strategy to diversify its offerings and impact the creator economy by providing an alternative to traditional video platforms, potentially altering how content creators engage with their audiences and manage revenue streams.[43] | |
| 2023 | December 15 | Controversy | Over 100 Substack writers, including prominent figures like George Washington professor Dave Karpf, sign a letter condemning Substack for allowing neo-Nazi and white supremacist writers, such as Richard Spencer, to monetize their content on the platform. Despite Substack’s terms prohibiting content inciting violence based on race, gender, ethnicity, and religion, a report by The Atlantic reveals several accounts linked to extremist leaders. Substack, known for its "hands-off" approach to content moderation, faces significant backlash but also receives support from some high-profile writers advocating for its current policies. The company declines to comment on the criticism.[45] |
| 2024 | January 3 | Controversy | Substack experiences a user revolt after its CEO defended hosting and handling payments for neo-Nazis on the platform, citing anti-censorship reasons. Chief Writing Officer Hamish McKenzie states that while Substack opposes Nazi views, it believes censorship exacerbates the problem. Prominent newsletter writers, including Casey Newton of Platformer, threaten to leave if Substack doesn't remove pro-Nazi content. By this time, Talia Lavin moved her newsletter to Buttondown. Substack, taking a firm stance against content moderation, remains committed to free expression despite criticism and potential revenue losses. The platform also faces scrutiny over its opaque Substack Pro service.[46] |
| 2024 | January 4 | Eric Newcomer, founder of the Substack newsletter "Newcomer," reports earning over $1 million in 2023. By this time, his newsletter, focused on startups and venture capital, has more than 75,000 free subscribers and over 2,000 paying $200 annually. Newcomer, who left Bloomberg in 2020, also generates revenue through an ad-supported podcast and events. His business, profitable with substantial cash reserves, remains independent without external funding. To expand, Newcomer hired his first reporter and plans more events. While expressing concerns about Substack's handling of pro-Nazi content, he credits the platform for facilitating his transition to independent journalism. [47] | |
| 2024 | January 4 | Controversy | Casey Newton publishes an article on Platformer criticizing Substack's policy on not demonetizing or removing openly Nazi accounts, sparking significant public debate.[3] |
| 2024 | January 17 | Substack implements ‘report’ feature amidst moderation controversies | |
| 2024 | January 29 | Substack launches new tools to support international writers and audiences, including local payment methods, support for more currencies, and default language settings for newsletters. By this time, the platform supports payments in 13 currencies such as USD, EUR, and BRL, removing the need for users to deal with dollar conversion rates. European subscribers can use local payment methods like direct debit. It is observed an 85% increase in paid conversions when local payment options are available. Additionally, Substack introduces default language options for newsletters, supporting Spanish, French, Italian, German, and Portuguese. However, geo-specific pricing is not yet available.[48] | |
| 2024 | January | Response | Substack co-founder Hamish McKenzie responds to the controversy, defending their stance on free speech and open discourse.[3] |
| 2024 | February 6 | An Axios article discusses how Substack assists creators in selling advertisements. By this time, Substack, is expanding its services to support creators in monetizing their content through ad sales. This initiative aims to provide more revenue opportunities for writers and content creators using Substack, allowing them to maintain financial independence while growing their audience.[49] | |
| 2024 | February 22 | Substack announces a milestone of over 3 million paid subscriptions, up from 2 million last year and 1 million in 2021. The platform raised significant funding based on achieving a critical mass of subscribers. Efforts to enhance its recommendations feature have contributed to subscriber growth, with plans to expand this feature to include more newsletters. Substack monetizes by taking a 10% cut from paid subscriptions, supporting writers and podcasters. While exploring new revenue avenues like aiding creators in selling ads, Substack continues to evolve its model amid ongoing growth opportunities.[50] | |
| 2024 | February 28 | Substack introduces direct messaging (DM) capabilities, enabling writers and readers to send private one-on-one messages, similar to features on social networks like X (formerly Twitter) and Instagram. This optional feature can be disabled, and DMs can be initiated from profiles or the Chat tab. Messages from non-connections land in a "Requests" folder. Writers can limit DMs to paid members. This addition is part of Substack’s evolution into a social network, following the launch of its Notes feature.[51] | |
| 2024 | April 11 | Partnership | Substack partners with Spotify to allow Substack podcast creators to distribute their content, both free and premium, on Spotify. This integration, part of Spotify Open Access, aims to expand the reach of Substack podcasts like Rich Text, Split Zone Duo, and Culture Study to Spotify’s 602 million monthly active users. From this time, podcast creators can effortlessly add Spotify distribution, enabling listeners to link their Substack and Spotify accounts or subscribe via Substack to access premium content. This partnership aims to enhance the podcast experience for both creators and subscribers, providing broader accessibility and control over content and revenue.[52] |
| 2024 | April 16 | Update | Substack enhances its Notes feature, a key revenue source for some creators, by making it easier to embed videos. Introduced a year earlier, Notes are designed for short, engaging updates, similar to tweets or snaps. These posts can now be embedded on external sites, increasing their reach. Substack also upgrades its video player, enhancing monetization options and making paywalls more flexible. This update is expected to make Notes more valuable and engaging. Testimonials highlight the revenue potential, with one creator earning $8,000 from a single short post. Substack's enhancements aim to expand the platform's influence across the web.[53] |
| 2024 | April 22 | Competition | Ghost, an open-source competitor to Substack, announces its plans to integrate with the fediverse in 2024. This move would allow Ghost's blog and newsletter authors to become part of the federated network, enabling users to follow, like, and interact with their content from various federated platforms like Mastodon, Threads, and others. This integration utilizes ActivityPub, similar to how WordPress interacts with the fediverse, enhancing user engagement and content distribution across decentralized networks. Ghost aims to add millions of users to the fediverse and provide more diverse subscription options, including email, RSS, and ActivityPub.[54] |
| 2024 | May 1 | Substack announces updates to its chat feature, allowing newsletter creators to paywall chat access for paid subscribers or founding members. Free subscribers and non-subscribers need to upgrade to access these chats. The updates also include improved navigation and usability, such as chat search on web and iOS, better access to notifications, and real-time messaging for live event participation. These enhancements aim to facilitate direct engagement between writers and their audiences, supporting Substack's growth alongside features like Notes and DMs.[55] | |
| 2024 | June 5 | Substack adds video capabilities to its Chat feature, allowing writers to share videos with subscribers. This follows the introduction of video to Notes, Substack’s short-form content platform similar to X/Twitter. The new feature aims to enhance communication between newsletter creators and their audiences, enabling them to share exclusive content and updates. Writers can upload or record videos up to five minutes long, add captions, and choose to put videos behind a paywall. Subscribers receive push notifications for new videos. This addition positions Substack as a competitor to social media platforms, expanding its appeal to various types of creators.[56] | |
| 2024 | June 11 | Substack launches the Substack Creator Studio, a year-long incubator program for TikTok creators to expand their reach and businesses. The program supports influencers like Coco Mocoe, Gabi Jones, and Jeauni Cassanova in using Substack's multimedia platform, which now includes video capabilities. This initiative aims to help creators move beyond TikTok’s algorithm-driven model, offering a more direct way to connect with audiences. Substack allows creators to charge for paywalled content and provides additional support to those in the program. The platform seeks to attract creators by offering a stable, responsive alternative to other social media platforms.[57] |
Numerical and visual data
Monthly active users
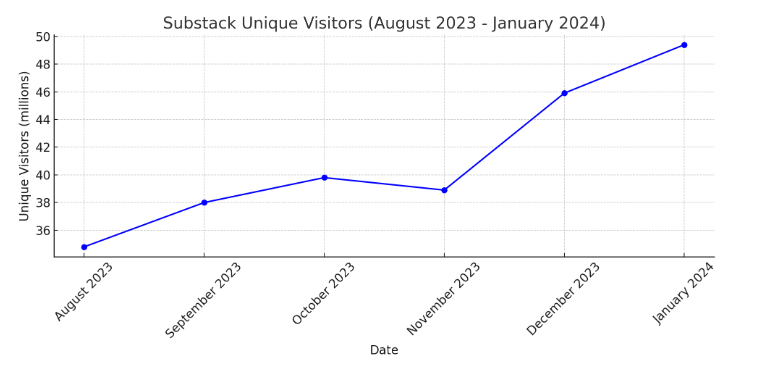
As of February 2023, Substack had over 20 million monthly active subscribers. In January 2024, the platform had 49.4 million unique visitors, a 41.95% increase since August 2023. This growth is reflected in monthly unique visitor counts, which rose from 34.8 million in August 2023 to 49.4 million in January 2024.[58]
| Year | Month | Unique Visitors (millions) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | August | 34.8 |
| 2023 | September | 38.0 |
| 2023 | October | 39.8 |
| 2023 | November | 38.9 |
| 2023 | December | 45.9 |
| 2024 | January | 49.4 |
Paying subscribers
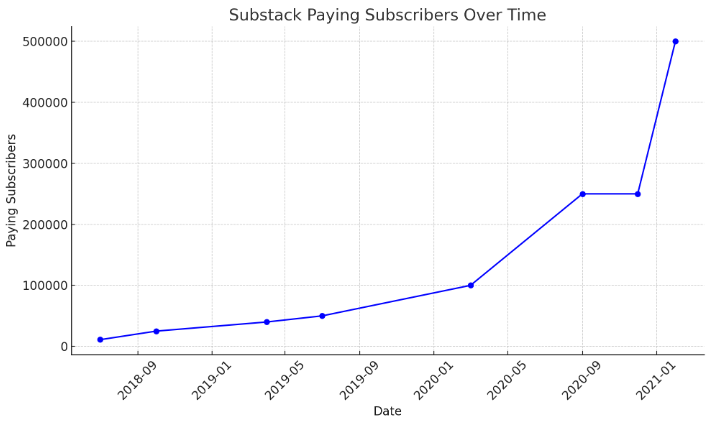
As of February 2021, Substack has over 500,000 paying subscribers, with notable growth since July 2018, when it had only 11,000 subscribers. Despite this rapid increase, Substack would no longer publicly update the number of unique paying subscribers.[58]
| Year | Month | Paying Subscribers |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | July | 11,000 |
| 2018 | October | 25,000 |
| 2019 | April | 40,000 |
| 2019 | July | 50,000 |
| 2020 | March | 100,000 |
| 2020 | September | 250,000 |
| 2020 | December | 250,000+ |
| 2021 | February | 500,000+ |
Funding
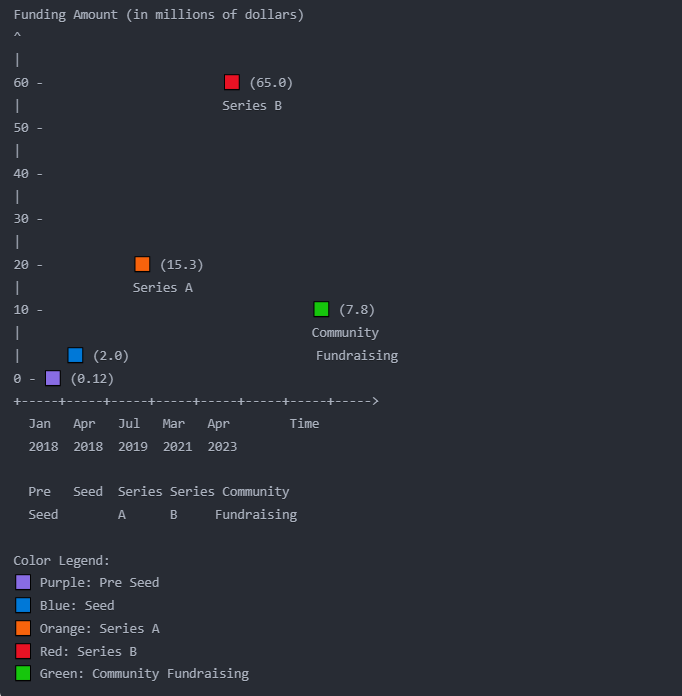
Substack has raised a total of $90.2 million through five funding rounds, with notable investors including Y Combinator and Andreessen Horowitz. The funding journey started with $120 thousand in January 2018 and culminated in a Series B round of $65 million in March 2021, along with a community fundraising of $7.8 million.[58]
| Year | Month | Funding Round | Funding Amount (millions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | January | Pre Seed | $0.12 |
| 2018 | April | Seed | $2.00 |
| 2019 | July | Series A | $15.3 |
| 2021 | March | Series B | $65.0 |
| 2023 | April | Community Fundraising (Wefunder)[59] | $7.8 |
Top author earnings
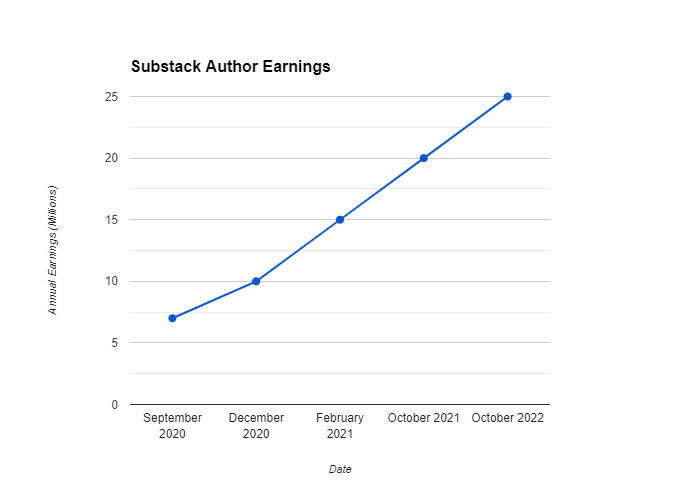
The annual earnings of the top 10 authors on Substack have shown a significant and steady increase from $7 million in September 2020 to $25 million by October 2022. This consistent growth reflects the platform's rising popularity and success in attracting both authors and subscribers, leading to higher revenue generation over the two-year period.[58]
| Year | Month | Annual Earnings (in millions of dollars) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | September | $7 |
| 2020 | December | $10 |
| 2021 | February | $15 |
| 2021 | October | $20 |
| 2022 | October | $25 |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "The History of Substack". Substack Course. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Levitz, Eric (24 March 2021). "Substack Is a Scam in the Same Way That All Media Is". Intelligencer.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Why Substack is at a Crossroads". Platformer. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ↑ "Substack History: An Overview of Substack". Blogging Guide. 21 June 2021. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ "Chris Best". linkedin.com. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Substack". Contrary Research. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ↑ "Substack Raises $2M to Help Writers Launch Subscription Newsletters". TechCrunch. 2017-10-16. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "Substack, a Publishing Platform for Independent Writers, Picks Up $15.3M Series A Led by a16z". TechCrunch. 2018-10-16. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ Kokalitcheva, Kia. "Substack raises $2 million to prove newsletters can help media". Axios. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ Botticello, Casey (21 June 2021). "What is Substack?". Substack Writing.
- ↑ "Substack: a new media platform that's shaking up publishing". The Guardian. November 17, 2020. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Tired Of The Social Media Rat Race, Journalists Move To Writing Substack Newsletters". NPR. Retrieved 12 August 2024.
- ↑ "Newsletter platform Substack sees number of users double from COVID-19". Business Insider. July 30, 2020. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack's Influence on Media: A Platform for Publishing or a Threat to Journalism?". The Guardian. Retrieved 12 August 2024.
- ↑ Nast, Condé (21 December 2020). "Is Substack the Media Future We Want?". The New Yorker. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ Ingram, Mathew (January 28, 2021). "Twitter gets into the newsletter business—should Substack be worried?". Columbia Journalism Review. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ "Supporting Independent Voices". Supporting Independent Voices | Facebook Media. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ Jairaj, Chris Best, Hamish McKenzie, and (17 March 2021). "Substack is for independent writers". Substack. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ "Why Substack's Scam Worked". New York Magazine. 2021-03-18. Retrieved 2024-06-27.
- ↑ "Substack and the New York Times Are Going to War for Talent". Slate. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ Financial Times https://www.ft.com/content/7b9fea53-db83-4cd4-a9bd-10af24aebfea. Retrieved 12 August 2024. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Primack, Kia Kokalitcheva,Dan. "Substack raising $65 million in venture capital amid newsletter boom". Axios. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ "Substack confirms $65M raise, promises to 'rapidly' expand its financial backing of newly independent writers". TechCrunch. Retrieved 26 September 2021.
- ↑ "The Rise of Ghost and Other Substack Platforms". Wired. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "Substack's Global Expansion Seeks to Empower International Writers". Rest of World. Retrieved 12 August 2024.
- ↑ "Substack hits major milestone, adding more paid subscribers than The New York Times and The Atlantic". Vanity Fair. 2021-11-19. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "How Investigative Journalists Are Using Substack Newsletters". Global Investigative Journalism Network. Retrieved 2024-06-27.
- ↑ "Why Some Substack Writers Are Leaving the Platform Over Misinformation". Mashable. Retrieved 2024-06-27.
- ↑ "Twitter restricts users from liking and retweeting posts with Substack links". NBC News. April 7, 2023. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack's Growth Amid Challenges". The New York Times. April 13, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack Lays Off 13 Employees Amid Economic Challenges". The New York Times. June 29, 2022. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Highest earning Substacks revealed". Press Gazette. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "WordPress.com Takes on Substack with New Paid Newsletter Feature". AlternativeTo. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "WordPress.com Disrupts Publishing Landscape, Takes on Substack with Launch of Paid Newsletters". LA Startups. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "WordPress.com Challenges Substack with Launch of Paid Newsletters". IndigiLife. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "Introducing Video to Substack Chat". Substack. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "Substack Newsletter Wars". Vanity Fair. 2023-06-27. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "One Year Anniversary". Substack. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "Substack adds 'Follow' button to help readers keep up with their favorite writers". The Verge. 14 August 2023. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ↑ "Substack expands further into social networking with a new follow button". TechCrunch. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "Substack newsletters are a literary trend. What's the appeal, and what should you read?". The Conversation. 2024-05-30. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "Substack redesigns its mobile app to boost discovery and engagement". TechCrunch. 2023-09-20. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "Substack Adds New Video Tools to Compete with Patreon and YouTube". Engadget. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ "Substack Expands into Video to Boost Its Competition in the Creator Economy". Washington Post. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ↑ Folk, Zachary (December 15, 2023). "Over 100 Substack Writers Sign Letter Condemning Site For Hosting Nazi And White Supremacist Newsletters". Forbes. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ Hern, Alex (2024-01-03). "Substack faces user revolt over anti-censorship stance on neo-Nazis". The Guardian. Retrieved 2024-06-20.
- ↑ "Substack Writer Eric Newcomer Says His Revenue Surpassed $1M in 2023". Axios. 4 January 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ↑ Mehta, Ivan (January 29, 2024). "Substack introduces new payment methods for international markets". TechCrunch. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack helping creators sell ads". Axios. February 6, 2024. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack hits 3 million paid subscriptions". Axios. 2024-02-22. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ Vasani, Sheena (February 28, 2024). "Substack's platform now has direct messages". The Verge. Vox Media. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ "Spotify and Substack Partner To Bring Even More Podcasts to Listeners". Spotify Newsroom. April 11, 2024. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ "Substack Notes Now Allows Users to Embed More Videos". Tubefilter. 2024-04-16. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "Substack rival Ghost confirms it will join the fediverse in 2024". TechCrunch. 2024-04-22. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ Navlakha, Meera (May 1, 2024). "Substack will allow writers to paywall the chat feature". Mashable. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ Lauren Forristal (June 5, 2024). "Substack brings video to its Chat feature". TechCrunch. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ Taylor Lorenz (June 11, 2024). "TikTok creators experiment with Substack". The Washington Post. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ↑ 58.0 58.1 58.2 58.3 "Substack Users: How Many People Use Substack in 2023?". Backlinko. Retrieved 2024-06-26.
- ↑ "In April 2023, Substack Raised $78M". LinkedIn. Retrieved 2024-06-26.