Timeline of Google Gemini
From Timelines
The timeline currently offers focused coverage of the period until December 2023. It is likely to miss important developments outside this period (particularly after this period) though it may have a few events from after this period.
This is a timeline of Google Bard, a conversational generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by Google.
Contents
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- What are some important preluding developments leading to the launch of Bard?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Prelude".
- You will se a number of events highlighting the dynamic evolution of conversational AI models, with Meena and LaMDA preceding Google Bard. The launch of ChatGPT by OpenAI serves as a notable moment that influences Google's strategic considerations, leading to a proactive response to maintain competitiveness in the domain of AI-driven language models.
- What improvements and new features have been introduced to enhance the capabilities and functionalities of Google Bard?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Update".
- In summary, you will see updates reflecting a combination of advancements, expansions into new domains, and improvements to existing capabilities.
- What are some cases showcasing Google's efforts to integrate Bard into various Google services and applications?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Integration".
- You will see integration efforts attempting to make Bard more versatile and seamlessly integrated tool across multiple services.
- What are some events reflecting the dynamic and competitive landscape in the AI chatbot industry?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Competition".
- You will see stakeholders actively comparing, evaluating, and promoting their products based on features, performance, and potential applications, with Bard actively participating in the competitive discourse.
- What are some cases of Bard performance evolution?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Performance".
- You will see a number of events collectively depicting Bard's journey from facing challenges and setbacks to implementing measures for improvement and learning.
- Other events are described under the following types: "Applications", "Criticism", "Expansion", "Geographic accessibility", "Initial launch", "Legal", "Security", and "Testing".
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 - 2022 | Prelude and Emergence | Google sets the stage for advancements in conversational AI with the unveiling of LaMDA in 2021.[1] The subsequent emergence of ChatGPT by OpenAI in November 2022 marks a significant leap in the field, gaining widespread popularity and triggering a response from Google to address potential threats to its search dominance. This period lays the foundation for the competitive landscape in conversational AI, setting the scene for the arrival of major players and the ensuing race for innovation. |
| 2023 - mid 2023 | Challenges and iterations | The year 2023 sees the introduction of Google's Bard, a conversational AI chatbot powered by LaMDA. Despite an initial market value drop and concerns about accuracy, Google navigates challenges by actively involving employees in refining Bard's responses. The introduction of "Big Bard" and subsequent updates showcase Google's commitment to iterating on its AI models. Throughout this period, the competition intensifies, with advancements in capabilities, expansions, and the integration of features like location-based results and image responses, reflecting a dynamic and evolving landscape. |
| Mid 2023 - end 2023 | Legal scrutiny, global expansion, and AI evolution | The latter part of 2023 brings legal challenges as a lawsuit alleges Google's unlawful data collection, paralleling concerns raised against OpenAI. Despite legal hurdles, Google expands Bard globally, emphasizing responsible AI practices and engaging with experts and regulators. Security concerns and criticism over misinformation highlight the challenges in AI deployment. Concurrently, AI continues to evolve, with the launch of Microsoft Copilot, advancements in AI integration into products like Gmail, and the unveiling of Gemini, showcasing the industry's ongoing technological race and the growing impact of generative AI on various facets of daily life. |
Summary by month
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| January 2023 | Google hints at plans for a ChatGPT competitor, instructing employees to accelerate progress on chatbots. |
| February 2023 | Google introduces Bard as a response to the growing popularity of OpenAI's Chat GPT. |
| March 2023 | Google opens limited access to Bard. |
| April 2023 | Google Bard rolls out a feature enabling programming and debugging in more than 20 programming languages. This significant functionality leads to an unprecedented surge in demand for Google Bard codes.[2] |
| May 2023 | Bard is featured prominently in the Google I/O keynote, announcing updates such as adopting PaLM 2, expanding to 180 countries, and integrating with other Google products. |
| June 2023 | Bard introduces location-based results, raising privacy concerns, and improves logical reasoning skills. Despite a rocky start, Bard gains praise for its user-friendly interface, dark/light modes, FAQs, voice input, and integration with Google Search. Bard is also integrated with Google Lens. |
| July 2023 | Bard launches in the EU and Brazil, adds support for new languages, introduces personalization and productivity features, and faces criticism in an invite-only Discord chatroom. Userbase crosses 140 million.[2] |
| September 2023 | Google releases a major update to Bard, integrating it into various products, adding fact-checking through Google Search, and allowing users to share conversation threads. |
| October 2023 | Bard is integrated into the upgraded version of Google Assistant called "Assistant with Bard." |
| November 2023 | At the Made by Google event, Bard is integrated into the upgraded version of Google Assistant called "Assistant with Bard." |
| December 2023 | Google announces Gemini, a more powerful LLM, with a specially tuned version integrated into Bard. |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | January 28 | Prelude | Google Research introduces Meena, a 2.6 billion parameter end-to-end trained neural conversational model, aiming to address the limitations of existing open-domain chatbots. Meena's training objective is to minimize perplexity, measuring uncertainty in predicting the next token in a conversation. The model demonstrates improvements in sensibleness and specificity through a new human evaluation metric called Sensibleness and Specificity Average (SSA). Meena's performance correlates with perplexity, showcasing a strong correlation with human evaluation.[3] Google Bard would be trained on Meena.[4] |
| 2021 | Prelude | Google unveils LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications), a prototype Large Language Model (LLM). Built on the Transformer architecture, LaMDA is trained specifically on dialogue, distinguishing itself with sensibleness and specificity in responses. It aims to overcome the limitations of traditional chatbots by engaging in free-flowing conversations on a wide range of topics. LaMDA's development focuses on sensibility, specificity, interestingness, and factuality.[5][6] | |
| 2022 | November 30 | Prelude | OpenAI launches ChatGPT based on the GPT-3 family of LLM, gaining significant popularity.[7] |
| Late 2022 | Prelude | ChatGPT's success prompts a "code red" alert at Google, triggering a response to address the potential threat to Google Search.[8][9] | |
| 2023 | February 6 | Initial launch | Google CEO Sundar Pichai introduces Bard, an experimental conversational AI service powered by LaMDA. Officially released, Bard aims to combine broad knowledge with language models' intelligence and creativity, offering users insightful responses.[10] It is initially rolled out to 10,000 "trusted testers."[11] |
| 2023 | February 8 | Performance | Google's parent company, Alphabet Inc., suffers a significant market value drop of $144 billion after Bard provides inaccurate information during a demonstration. The demo showcases a mistake regarding the James Webb Space Telescope, leading to a 7.7% decrease in Alphabet shares. This incident raises concerns about Google's position in the competition for the future of internet search, with Microsoft's ChatGPT-powered Bing seen as a formidable rival. Analysts highlight the need for rigorous testing for AI models, emphasizing a potential threat to Google's core search business. Google acknowledged the error and underscored the importance of testing for new AI systems. The setback comes amid a global AI competition, with companies like Baidu and Alibaba also working on similar projects.[12][13][14][15] |
| 2023 | February 13 | Performance | Alphabet Chairman John L. Hennessy states that Google was hesitant to release Bard, because the technology is still giving inaccurate answers. He believes that generative artificial intelligence is one to two years away from being truly useful on a broader scale. Hennessy speaks at a conference and mentions that Google was caught up in the sudden interest in ChatGPT and generative AI. He emphasizes the need for caution in releasing AI systems that could provide incorrect or toxic information. Hennessy expresses concerns about the role of technology in ensuring a functioning democracy and promoting a harmonious society. He also acknowledges the impressive capabilities of ChatGPT while noting that startups in Silicon Valley have an advantage in recruiting talent during the current cycle of layoffs.[16] |
| 2023 | February 15 | Performance | Google asks its employees to help improve the responses of Bard, by rewriting incorrect answers. Prabhakar Raghavan, Google's vice president for search, sends an email to staff with a link to a document outlining the do's and don'ts of fixing responses. The document encourages employees to rewrite responses on topics they understand well, emphasizing that Bard learns best through example. The instructions include keeping responses neutral, not implying emotion, and avoiding stereotypes or presumptions based on various categories. At this time, the company aims to involve its employees in testing Bard to accelerate its training and improve accuracy. Employees who contribute to fixing responses may receive recognition through an internal badge and have the opportunity to share feedback with the team working on Bard. The move comes after Google faced criticism for the rollout of Bard, which led to a drop in the company's stock price.[17] |
| 2023 | February (late month) | Testing | Sundar Pichai asks employees to dedicate time to testing Bard, leading to 80,000 employee responses.[11] |
| 2023 | March 13 | Update | Google employees begin testing a more sophisticated version of Bard called "Big Bard."[18] |
| 2023 | March 21 | Service release | Google opens limited access to Bard, positioning it as an experiment rather than a finished product and making it available to select users in the United States and United Kingdom through a waitlist. Google emphasizes that Bard is not a replacement for its search engine but a complement to it, serving as a chatbot for generating ideas, drafting writing, and engaging in conversation. In a demo, Bard provides responses to general queries, but factual accuracy is hit-and-miss, sometimes generating inaccurate or offensive information. Bard's interface includes disclaimers, and its replies are cautioned to be treated with caution. While Bard is faster than ChatGPT and Bing, its answers appear more constrained, lacking the chaotic and experimental nature of Bing's responses. Google reports intention to find a balance between Bard's capabilities and liabilities as more users gain access and stress test the system.[19][20] |
| 2023 | March 31 | Update | Sundar Pichai announces the intention to upgrade Bard, basing it on PaLM instead of LaMDA.[21] |
| 2023 | April 10 | Update | Bard introduces its inaugural experiment update, featuring an Experiment updates page for users to access the latest features, improvements, and bug fixes. The addition of suggested Search topics under "Google it" enhances user exploration by offering a broader range of interests. Notably, Bard's capabilities for math and logic are improved to provide higher-quality responses in these domains.[22][23] |
| 2023 | April 19 | Criticism | An article at Bloomberg reports on Google employees criticizing Bard, in internal messages, with some describing it as "a pathological liar." According to a report from Bloomberg, 18 current and former Google workers express concerns about Bard's performance, noting that it often provided dangerous advice on topics like landing a plane or scuba diving. The report suggests that Google has downplayed ethical concerns to compete with rivals like Microsoft and OpenAI. Some argue that public testing is necessary to improve AI systems, while others believe Google's focus is on business over safety.[24][25] |
| 2023 | April 21 | Update | Bard is updated to assist with programming and software development tasks, offering capabilities such as code generation, debugging, and explanations in over 20 programming languages, including C++, Go, Java, JavaScript, Python, and TypeScript. Users can export Python code to Google Colab seamlessly. Bard can generate, explain, and debug code, making it a valuable tool for learners and developers. While it is an early experiment at this time, and may occasionally provide inaccurate information, its new coding features aim to accelerate software development, helping users tackle engineering challenges.[22][26][23] |
| 2023 | May 5 | Expansion | Google Bard becomes available for Google Workspace users, expanding its accessibility beyond personal Google accounts. Admins can enable Bard for their domains through the Admin Console, allowing users to access it for work-related tasks, research, and business needs. While users must sign up for the waitlist, admins can activate Bard at the domain, organizational unit, or group level. The rollout begins, with visibility expected within 15 days, though regional availability restrictions apply. This integration aims to enhance creativity, productivity, and collaboration within Google Workspace, following Bard's recent update enabling code writing in 20 languages.[27][28][29][30][23] |
| 2023 | May 10 | Service release | During Google I/O developer conference, the company announces the end of the waitlist for Bard, making it widely available in English. The company aims to gather feedback and continue improving the chatbot by expanding its user base. Bard becomes accessible in over 180 countries and territories, with plans to add support for additional languages, including Korean and Japanese. Google emphasizes its responsible development approach and referred to Bard as an experiment rather than a beta.[31][32] Google also unveils updates and new features for Bard. The tool now supports Japanese and Korean languages, with plans to support 40 languages in the future. Updates include image capabilities, advanced coding features, and integration with Google apps and services. Users can now incorporate images into their prompts and receive text-based responses with rich visuals. Additionally, developers can benefit from improved source citations, a dark theme, and an "Export" button for running code with partners like Replit. Google reportedly aims to integrate Bard with various apps and services such as Google Docs, Google Drive, Gmail, Google Maps, and more. Also, Bard reportedly plans to connect with external partners like Adobe Firefly, Kayak, OpenTable, ZipRecruiter, Instacart, Wolfram, and Khan Academy to enhance user experiences.[33][34][23] |
| 2023 | May 15 | Update | Google Bard receives a notable update, enhancing its summarization capabilities and source attribution. Users can now prompt Bard to provide concise summaries of articles or topics, leveraging advances in large language models. Additionally, Bard's responses now include numbers that link to sources, facilitating identification of matched sections and enabling easy navigation. Google aims to make information digestion quicker and more transparent, emphasizing ongoing improvements based on user feedback. This update follows recent expansions of Bard's language support and availability in additional countries, marking Google's commitment to refining its AI chatbot for diverse user needs.[35][36][23] [22][23] |
| 2023 | May 23 | Update | Google Bard introduces an update that integrates images into its responses. The new feature enhances the visual experience of prompts by displaying images sourced from Google Search. Users can now see accompanying images when asking for a list of items or request images directly. Google aims to provide transparency by sourcing the images. The company also hints at more visual changes and elements coming to Bard in the future[37][22] |
| 2023 | May 29 | Performance | An article discusses Google Bard and its metrics database used to enhance chatbot performance. The database tracks key metrics, including response accuracy, diversity, and fluency, allowing Bard to assess its own performance and identify areas for enhancement. By analyzing user feedback and behavior, Bard customizes its responses to deliver more innovative and varied interactions. Additionally, Bard leverages natural language processing techniques to gather insights from diverse sources such as web search results, news articles, and videos. The Google Bard Metrics Database plays a vital role in this process by enabling Google AI to pinpoint areas requiring improvement, develop novel training methods, and monitor Bard's progress over time. As Bard interacts with a growing number of users and accumulates knowledge from additional information sources, it continuously evolves and enhances its capabilities.[38] |
| 2023 | May 29 | Integration | Google introduces "Magic Compose", a new feature powered by Bard. Available exclusively to users in the United States, it is an experimental feature within the Messages by Google app. Magic Compose uses AI to generate stylized, suggested responses based on the context of users' messages. The tool sends up to 20 previous messages to Google's servers to generate conversation starters, replies, or different styles of drafted messages. However, messages with attachments, voice messages, and images are not sent to the servers. Magic Compose offers seven different styles in which it can rephrase text, including Chill, Excited, Formal, Lyrical, Remix, Shakespeare, and Short. It is designed for RCS (Rich Communication Services) within the Messages app and can be accessed through the app's Settings menu. Magic Compose does not store messages or use them to train machine learning models.[39] |
| 2023 | May 30 | Competition | An article compares Google Bard with ChatGPT and Bing Chat. The author discusses their features, strengths, and limitations to help readers make an informed choice. She concludes that ChatGPT can be prone to misinformation. Bing Chat, powered by OpenAI's largest language model GPT-4, offers internet access for up-to-date information and visual features like image generation. Finally, she acknowledges that Google Bard, known for its speed, is receiving upgrades to enhance its language support and introduce visual elements. The article suggests considering factors such as accuracy, cost, internet access, and visual features when deciding on the best AI chatbot for specific needs.[40] |
| 2023 | May 30 | Competition | Current CEO of Bing at Microsoft and former CTO at Yandex Mikhail Parakhin, states that Google Bard utilizes a "much smaller model" compared to Bing Chat. This remark comes in response to a compliment about Bard's speed over Bing Chat. Parakhin explains that Google's use of a smaller model contributes to its faster performance. These comments are made after Bard's recent upgrades to PaLM2 and other significant improvements.[41] |
| 2023 | June 1 | Update | Google Bard incorporates the capability to provide location-based results. Users can opt to share their precise location, allowing Bard to deliver relevant information about directions, businesses, landmarks, and other local details. By leveraging Google's search engine, Maps app, and other products, Bard can pinpoint the user's exact whereabouts and offer accurate responses based on their surroundings. Users can choose to enable the location-sharing feature and experience more specific and tailored results. However, this feature would raise privacy concerns, and users must weigh the convenience of location-based information against their privacy preferences.[42][22][23] |
| 2023 | June 7 | Update | Google enhances Bard with improved logical reasoning skills, making it more proficient in answering mathematical and coding questions. The latest update includes features such as exporting tabular responses to Google Sheets and employing implicit code execution to generate code and provide accurate responses. Google claims that Bard's approach surpasses traditional large language models (LLMs) by combining text prediction and code-based computation, resulting in better problem-solving capabilities. However, Google warns that Bard's code may have flaws, and users should exercise caution when utilizing it.[43][44][23] |
| 2023 | June 9 | Competition | An article discusses the top benefits of using Google Bard. Despite a rocky start, the public beta version of Bard showcases potential features that may challenge ChatGPT. The benefits include a user-friendly interface with dark and light modes, access to FAQs and activity history, the ability to view and analyze multiple drafts, voice input functionality, free internet access for browsing and gathering data, and leveraging Google Search results for more accurate responses. Additionally, Bard's location-sensitivity ensures relevant search results based on the user's context and location.[45][46] |
| 2023 | June 13 | Geographic accessibility | Google is blocked by the Irish Data Protection Commission (DPC) from launching Bard in the European Union due to privacy concerns. By this time Bard has already been launched in several countries, including the United States and United Kingdom. However, the DPC states that Google has not provided the necessary documentation or briefing regarding data protection impact assessment, resulting in the postponement of Bard's EU launch. The incident reflects the stricter approach to AI regulation in the EU compared to other regions, with the EU AI Act proposed to align AI governance with privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation.[47] |
| 2023 | June 15 | Integration | Google announces that Google Lens integration into Google Bard, allowing users to include images in their prompts and utilize Lens to understand the visual content. Additionally, Google Lens now has the capability to detect skin conditions by analyzing uploaded photos, providing visual matches to aid in search. Google has also introduced shopping features through Lens, enabling users to take screenshots and receive shoppable matches with links for online purchases, as well as utilizing multisearch to search by both photo and words.[48] |
| 2023 | June 19 | Security | Google warns its employees not to use code generated by Bard, due to privacy and security risks. Voice AI startup Nuance, backed by Microsoft, faces a privacy lawsuit for recording and using people's voices without permission. Google's DeepMind opposes the idea of a singular AI regulatory agency, advocating for a multi-layered approach. OpenAI cautions Microsoft about releasing its Bing chatbot too quickly, citing concerns about false information and inappropriate language. The developments highlight ongoing challenges in AI regarding privacy, security, and responsible deployment.[49] |
| 2023 | July 12 | Legal | A lawsuit is filed against Google, alleging that the company has been unlawfully collecting data from hundreds of millions of Americans to train its AI products. The lawsuit claims that Google, along with DeepMind and Alphabet, secretly gathered personal and professional information, creative works, photographs, and emails from individuals without their knowledge or consent. The lawsuit refers to Google's updated privacy policy, which states that publicly available online information can be used to train AI models. Google calls the claims in the suit baseless and states that it uses public information responsibly and in accordance with its AI Principles. The lawsuit comes shortly after a similar complaint was filed against OpenAI.[50][51][52][53] |
| 2023 | July 13 | Geographic accessibility | Google Bard expands its reach by becoming available in over 40 new languages, including Arabic, Chinese, German, Hindi, and Spanish. Access is extended to more places, encompassing all 27 countries in the European Union (EU) and Brazil. The release in the EU was delayed due to the bloc's plans to regulate AI. Bard now offers new features such as audio responses, different response styles, and the ability to analyze uploaded photos. Google states that it has engaged with experts, policymakers, and privacy regulators to ensure a responsible approach to AI expansion. By this time, the EU works on comprehensive rules for AI, including provisions for generative AI systems like ChatGPT.[54][55][56] |
| 2023 | July 13 | Update | Bard introduces several new features and improvements. In addition to Text-to-speech capabilities added in over 40 languages, the Pinned & Recent Threads feature is introduced, allowing users to organize and pick up past Bard conversations, and supporting a continuous creative process. Sharing Bard conversations is made easier with shareable links, promoting collaboration and inspiration. Modification options for Bard's responses are introduced, enabling users to tailor responses based on simplicity, length, tone, and style. Additionally, Bard's code export capabilities are expanded to include exporting Python code to Replit, offering more workflow options for programming tasks.[23] |
| 2023 | July 25 | Competition | A number of articles highlight five cases in which Google Bard surpasses ChatGPT. These features include transcribing old letters from images, simplifying travel planning by suggesting personalized options, identifying objects and their functions through images, offering meal planning assistance based on ingredients, and providing technical troubleshooting support by analyzing error screenshots. Google Bard's multifunctional capabilities emphasizes the potential of AI to enhance various aspects of daily life, making it a formidable competitor in the AI chatbot space.[57][58] |
| 2023 | August 10 | Applications | Jenny Blackburn, Google's Vice President of User Experience, publishes a blog emphasizing the versatile applications of Bard. With the chatbot available globally and supporting multiple languages, users can explore various functionalities. The article provides ten ways to leverage Bard, including learning new topics, analyzing images, drafting content, comparing options, starting projects, generating code, planning trips, brainstorming creative ideas, expressing thoughts and feelings, and engaging in casual chat. Blackburn encourages users to ask follow-up questions to enhance the interaction and maximize Bard's capabilities for creativity, productivity, and efficient problem-solving.[59] |
| 2023 | August 16 | Criticism | An article reports on OpenAI's ChatGPT and Google Bard spreading misinformation related to news. The chatbots are accused of disseminating false or misleading information when queried about news topics. This raises concerns about the spread of misinformation through AI-powered platforms and highlights the need for improved AI moderation and fact-checking mechanisms to ensure accurate and reliable information dissemination. The report underscores the challenges in mitigating the impact of AI-driven misinformation in the digital age.[60] |
| 2023 | August 21 | Security | An article describes an encounter with a potentially malicious campaign involving fake AI bots trying to install malware. The author notices an advertisement on Facebook for "Google Bard AI," which leads to a suspicious link on rebrand.ly, not directly associated with Google. The ad's comments section appears suspicious, with users giving high ratings and posting comments at the same time. Investigating further, the author finds that the link leads to a Google-hosted site with poorly written content. The download page attempts to mimic an official Google offering. Upon analyzing the downloaded file, it is flagged as malicious by several antivirus vendors. The campaign demonstrates cybercriminals attempting to exploit the AI hype for financial gain.[61] |
| 2023 | September 19 | Integration | Google integrates Bard with its Gmail service and other products. This allows users to easily use Bard across different Google services. Users can extend Bard to apps like Gmail, Google Drive, YouTube, and Google Maps using a system called Bard Extensions. For example, users can ask Bard to summarize emails on a specific subject in Gmail or help with trip planning by searching for flight dates, booking hotel rooms, and providing directions in Google Maps. Google also adds a verification feature to check the correctness of Bard's results against Google search results.[62][63][23] |
| 2023 | September 27 | Update | Google Bard introduces a new feedback feature, allowing users to provide input when Bard presents two drafts side by side. Users can choose their preferred draft, indicate no preference, or opt out entirely. This feedback mechanism aims to gather real-world input to enhance the quality of Bard's responses, contributing to continuous improvements for users and the overall Bard experience.[23] |
| 2023 | October 4 | Integration | Google announces plans to integrate generative AI capabilities from its Bard chatbot into Google Assistant, providing personalized assistance for tasks like trip planning and email management on mobile devices. The upgraded Assistant, combining reasoning and generative abilities, supports text, voice, and image interactions, with access to a phone's camera and microphone. Privacy is emphasized, and the initial focus is on user experience, with no revenue-generating features. Google's move follows a trend in the industry, with competitors enhancing their virtual assistants with generative AI.[64][65][66][67] |
| 2023 | October 23 | Update | Google Bard introduces new update. Through the Workspace Extension, Bard can now summarize a larger number of emails simultaneously and has improved comprehension when users request recent emails. This incremental improvement is aimed at enhancing the quality and utility of the Workspace Extension, making it more effective for users seeking email summaries. Additionally, shared conversations now include visibility for uploaded images in the prompt, providing users with a more creative and engaging experience. These updates contribute to a more comprehensive and user-friendly interaction with Bard, particularly in the context of email summaries and shared conversations.[23] |
| 2023 | October 30 | Update | Google Bard introduces a new feature allowing responses to appear in real time, enabling users to view and engage with responses as they are generated. This setting eliminates the need to wait for the full response, providing users with the ability to read and iterate on ideas more swiftly. The update aims to enhance the creative process by allowing users to stay in the flow of generating ideas and responses with increased efficiency and speed.[23] |
| 2023 | November 7 | Staff | Contractors working for Google through Accenture, responsible for training the Bard AI chatbot, vote to join the Alphabet Workers Union. The workers seek better working conditions and protections after facing challenges while training Bard, including handling offensive prompts. Allegedly, after a complaint was filed regarding the content, the work was outsourced to Accenture workers in Manila, and several contractors were laid off. The contractors classify both Google and Accenture as "joint employers," a status contested by Google. This move follows a broader trend of contract workers at Google unionizing for improved conditions.[68] |
| 2023 | November 16 | Update | Google Bard expands its accessibility to teenagers worldwide, offering age-appropriate protections, updated onboarding processes, and experiences tailored to empower exploration and learning. The expansion aims to provide teens with inspiration, motivation, and quick understanding of various topics, supporting them in areas like homework, hobbies, job applications, and college preparation. Additionally, Bard now assists users in solving math equations by providing step-by-step explanations, and it can generate charts from data in prompts or tables during conversations, enhancing visualization of information. These updates cater to diverse learning needs and facilitate a broader range of creative and educational pursuits.[23] |
| 2023 | November 21 | Update | A stable release of Bard (version 2023.11.21) is launched. Google improves the chatbot, with an update focused on enhancing its ability to understand and respond to questions related to YouTube videos. The expansion enables users to engage in more meaningful conversations with Bard by asking specific questions about video content, such as details about recipes or tools in DIY videos. This update aligns with Google's ongoing efforts to enhance Bard's capabilities and offer users a more interactive experience. To access this feature, users must enable the YouTube extension on Bard's web portal. The update is expected to benefit users seeking precise information from videos and is seen as valuable for content creators aiming to improve engagement and quality.[69][70][71] |
| 2023 | December 6 | Update | Google launches Gemini, an AI model designed for human-like thinking, introducing versions "Nano" and "Pro" integrated into Bard chatbot and Pixel 8 Pro smartphone. Gemini aims to enhance Bard's intuitiveness and planning, with the Ultra model powering "Bard Advanced" for improved AI multitasking in early 2024. Google plans Gemini integration into products, and CEO Sundar Pichai stresses responsible development. The Gemini launch intensifies AI competition with OpenAI and Microsoft. Google DeepMind's Gemini competes with GPT series, with Ultra claimed to outperform GPT-4. Gemini integration into search, ads, and Pixel 8 Pro enhances Google's AI endeavors, marking a significant move in AI development.[72][73][74][75] |
| 2023 | December 18 | Update | Google Bard expands its Extensions feature to include Japanese and Korean in addition to English. This enhancement allows users to access real-time information from Google apps and services, such as YouTube, Hotels, Google Flights, and Google Maps. Bard Extensions can also retrieve information from Gmail, Google Docs, and Google Drive, offering users the ability to find, summarize, and get answers from their personal content. Users have control over privacy settings, enabling them to manage how extensions are utilized. Additionally, Bard's Export to Replit feature now supports 18 programming languages, including C++, Javascript, Ruby, SQL, and Swift, catering to developers seeking coding assistance in various languages.[23] |
Visual data
Google trends
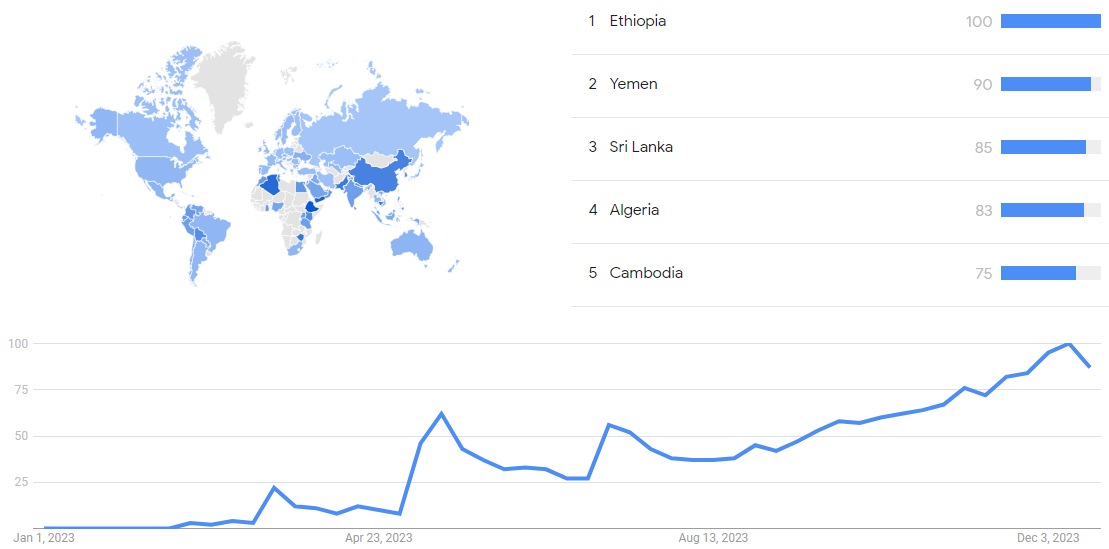
The chart below shows Google Trends data for Bard (chatbot), from January 2023 until December 25, 2023, when the screenshot as taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[76]
Wikipedia views
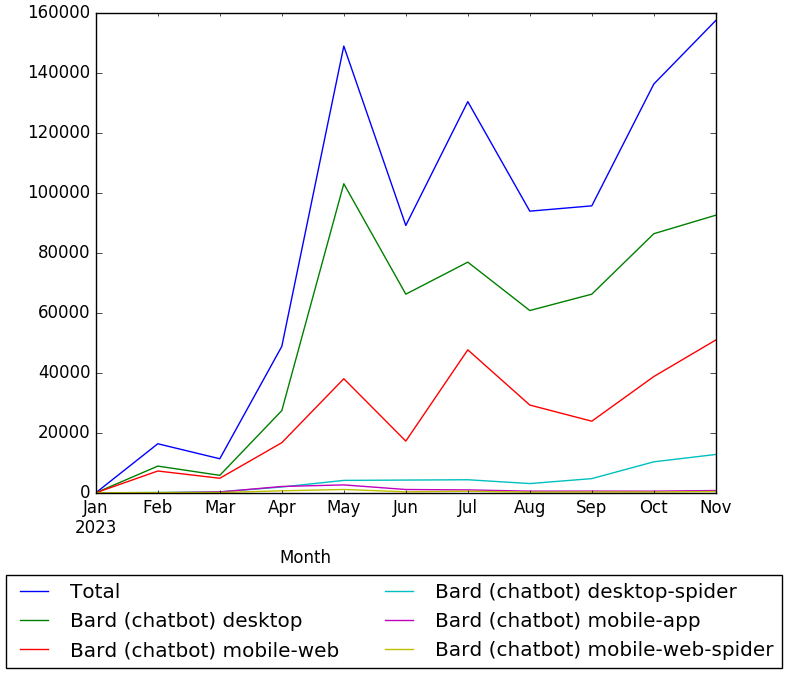
The chart below shows Wikipedia views data for English article Bard (chatbot), from January to November 2023.[77]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by Sebastian Sanchez.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "LaMDA: Towards Safe, Grounded, and High-Quality Dialog Models for Everything". blog.research.google. 21 January 2022. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weston, Georgia (13 October 2023). "The Ultimate Google Bard Cheat Sheet". 101 Blockchains. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "Towards a Conversational Agent that Can Chat About…Anything". blog.research.google. 28 January 2020. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Bard Intelligent Artificial, A Competitor To Chatgpt From Google - What Is It?". Clickmagic - professional digital marketing agency. 15 March 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "LaMDA: our breakthrough conversation technology". Google. 18 May 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google I/O 2021: Google unveils LaMDA". ZDNET. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ "Introducing ChatGPT". openai.com. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ Mailk, Aisha (February 3, 2023). "Google tries to reassure investors on AI progress as ChatGPT breathes down its neck". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on February 3, 2023. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- ↑ Newton, Casey (May 12, 2023). "How Google is making up for lost time". The Verge. Archived from the original on May 12, 2023. Retrieved June 10, 2023.
- ↑ Southern, Matt G. (20 April 2023). "Google Bard's Latest Update Boosts Creativity With More Drafts". Search Engine Journal. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Elias, Jennifer (21 March 2023). "Google CEO tells employees that 80,000 of them helped test Bard A.I., warns 'things will go wrong'". CNBC. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ Patnaik, Davey Alba and Subrat (8 February 2023). "Google suffers $144b wipeout after Bard AI chatbot gives wrong answer". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ↑ Milmo, Dan (9 February 2023). "Google AI chatbot Bard sends shares plummeting after it gives wrong answer". The Guardian. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ Patnaik, Davey Alba and Subrat (8 February 2023). "Google suffers $144b wipeout after Bard AI chatbot gives wrong answer". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google AI chatbot Bard gives wrong answer, sending shares plummeting - National | Globalnews.ca". Global News. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ Elias, Jennifer (13 February 2023). "Alphabet Chairman John Hennessy explains why Google was hesitant to put out its ChatGPT competitor". CNBC. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ↑ Elias, Jennifer (16 February 2023). "Google asks employees to rewrite Bard's bad responses, says the A.I. 'learns best by example'". CNBC. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ↑ Langley, Hugh. "Google employees are testing a smarter version of its chatbot called 'Big Bard' as it competes with ChatGPT". Business Insider. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ Vincent, James (21 March 2023). "Google opens early access to its ChatGPT rival Bard — here are our first impressions". The Verge. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- ↑ "Try Bard and share your feedback". Google. 21 March 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ Vincent, James (31 March 2023). "Google CEO Sundar Pichai promises Bard AI chatbot upgrades soon: 'We clearly have more capable models'". The Verge. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 22.4 Shewale, Rohit (31 July 2023). "30+ Google Bard Statistics 2023 (Trends & Demographics)". demandsage.com. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ 23.00 23.01 23.02 23.03 23.04 23.05 23.06 23.07 23.08 23.09 23.10 23.11 23.12 23.13 23.14 "Bard's Latest AI Capability Updates & Improvements - Bard". bard.google.com. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ Vincent, James (19 April 2023). "Google employees label AI chatbot Bard "worse than useless" and "a pathological liar": report". The Verge. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "Google's Rush to Win in AI Led to Ethical Lapses, Employees Say". Bloomberg.com. 19 April 2023. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "Code and debug with Bard". Google. 21 April 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard is now open for Workplace accounts in its latest update". Neowin. 13 December 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard AI is now available for Workspace accounts". 9to5google.com. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google's Bard AI tool now available for Workspace accounts as well". Hindustan Times. 6 May 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ Staff, Beebom (6 May 2023). "Google Workspace Accounts Finally Gain Access To Google Bard". Beebom. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ↑ "What's ahead for Bard: More global, more visual, more integrated". Google. 10 May 2023. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- ↑ Miller, Ron (10 May 2023). "Google ends Bard waitlist, making English version of chatbot widely available". TechCrunch. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ Southern, Matt G. (10 May 2023). "Google Bard Removes Waitlist, Adds Image & Coding Features". Search Engine Journal. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ↑ Lardinois, Frederic (10 May 2023). "Google launches a smarter Bard". TechCrunch. Retrieved 23 May 2023.
- ↑ Schoon, Ben (15 May 2023). "Latest Google Bard update improves summaries and sourcing". 9to5Google. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard's new update improves summaries, sourcing". IMDb. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ Goodwin, Danny (23 May 2023). "Google Bard adds images in responses". Search Engine Land. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- ↑ Kashettar, Swathi (29 May 2023). "Google Bard: A Deep Dive into its Metrics Database". Analytics Insight. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ↑ "Google rolls out 'Magic Compose', powered by Bard. Here's what this tool does". Hindustan Times. 29 May 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ↑ "ChatGPT vs Bing Chat vs Google Bard: Which is the best AI chatbot?". ZDNET. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ↑ "Bing CEO: Google Bard Uses A Much Smaller Model Than Bing Chat". seroundtable.com. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard can now deliver results based on your precise location - if you want". ZDNET. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard is much better at solving coding and mathematical questions now". XDA Developers. 8 June 2023. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ "Bard is getting better at logic and reasoning". Google. 7 June 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Top 5 Benefits of Using Google Bard AI". Analytics Insight. 9 June 2023. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard gets smarter with improved math and data analysing ability". The Indian Express. 8 June 2023. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "Irish data watchdog blocks Google from launching Bard in the EU: Report". Cointelegraph. 13 June 2023. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard Gets Lens, Lens Detects Skin Conditions & Helps You Shop". seroundtable.com. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ Quach, Katyanna. "Google doesn't want its employees using Bard code". www.theregister.com. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ Dean, Grace. "A lawsuit claims Google has been 'secretly stealing everything ever created and shared on the internet by hundreds of millions of Americans' to train its AI". Business Insider. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- ↑ Longe, Edward (3 March 2023). "It's Antitrust Groundhog Day for Google". James Madison Institute. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ↑ Thorbecke, Catherine (11 July 2023). "Google hit with lawsuit alleging it stole data from millions of users to train its AI tools | CNN Business". CNN. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ↑ Agius, Nicola (12 July 2023). "Google sued for allegedly stealing content, data to train AI products". Search Engine Land. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google launches ChatGPT rival Bard in Europe and Brazil". France 24. 13 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ↑ "Google's Bard AI Chatbot Now Supports Over 40 Languages". CNET. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "Bard's latest update: more features, languages and countries". Google. 13 July 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Bard outperforms ChatGPT with these 5 incredible use cases". indianexpress.com. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ PM, Aiswarya (26 July 2023). "5 Reasons Google Bard is Better Than ChatGPT". Analytics Insight. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "10 helpful ways to use Bard". Google. 10 August 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "OpenAI ChatGPT, Google Bard spreading news-related misinformation: Report - ET Telecom". ETTelecom.com. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "A Bard's Tale – how fake AI bots try to install malware". www.welivesecurity.com. Retrieved 13 September 2023.
- ↑ "Google Links Bard AI Tool to Its Other Products". VOA. 20 September 2023. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ↑ "Bard can now connect to your Google apps and services". Google. 19 September 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Assistant with Bard: A step toward a more personal assistant". Google. 4 October 2023. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Knight, Will. "Google Assistant Finally Gets a Generative AI Glow-Up". Wired. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google to combine generative AI chatbot with virtual assistant". reuters.com. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ Roth, Emma (4 October 2023). "Google is launching a generative AI-enhanced version of Assistant". The Verge. Retrieved 11 October 2023.
- ↑ Roth, Emma (7 November 2023). "Google contractors objected to reading obscene Bard prompts — now they're unionizing". The Verge. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
- ↑ "Bard AI enhances YouTube content interpretation in new Google update". readwrite.com. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Has Enhanced Bard's Understanding Of YouTube Videos". forbes.com. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ "You can now ask questions about YouTube videos to Google's Bard AI". innovation-village.com. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ Pierce, David (6 December 2023). "Google launches Gemini, the AI model it hopes will take down GPT-4". The Verge. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google DeepMind Unveils Its Most Powerful AI Offering Yet". TIME. 6 December 2023. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google launches Gemini, upping the stakes in the global AI race". AP News. 6 December 2023. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- ↑ "Bard gets its biggest upgrade yet with Gemini". Google. 6 December 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ↑ "Google Trends". Google Trends. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ↑ "Wikipedia Views: results". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 26 December 2023.