Timeline of online video
This is a timeline of online video.
Overview
| Time period | Key developments in Online Video |
|---|---|
| 1995–2004 | Early days of the world wide web. Several container formats for streaming the first videos are released. Some sites, like Newgrounds, heavily rely on these container formats to display online video. |
| 2005–2010 | Mass-streaming services like YouTube and Netflix become massively popular for streaming online video. Broadband penetration increases, allowing significant fractions of the population to stream online video. Macromedia Flash is the most popular format for displaying online video, as it is used by YouTube and many other sites. |
| 2011–2016 | HTML5 starts to displace Flash. Livestreaming becomes increasingly popular, especially in the form of services like Twitch.tv. Many social media startups integrate the streaming of short segments of video, like Vine and Keek. These are, in turn, integrated into the most popular services like Instagram and Facebook. |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | September 5 | Technology | ESPN SportsZone streams a live radio broadcast of a baseball game between the Seattle Mariners and the New York Yankees to thousands of its subscribers worldwide using cutting-edge technology developed by a Seattle-based startup company named Real Networks – the first livestreaming event.[1] |
| 1995 | Technology | Adobe releases Shockwave Player for Netscape Navigator, which becomes the primary format of streaming media for the late 1990s and 2000s (until it is gradually supplanted by HTML5).[2] | |
| 1998 | Late | Technology | MPEG-4, a method of defining compression of audio and visual (AV) digital data, is introduced.[3][4][5][6][7] |
| 1999 | Technology | Microsoft introduces streaming feature in Windows Media Player 6.4. It introduces the ASF file format, which allows storage of multiple video and audio tracks inside a single file. It also introduces Windows Media streaming protocols that support switching streams during broadcast. This technology is most commonly referred to as Multiple Bit Rate ASF, or simply MBR.[8] | |
| 1999 | June | Technology | Apple introduces a streaming media format in its QuickTime 4 application.[9] |
| 2002 | October | Technology | Adaptive bit rate over HTTP is created by the DVD Forum at the WG1 Special Streaming group. |
| 2003 | May | Technology | The On2 TrueMotion VP6 codec is released.[10] |
| 2004 | June | Products | MindGeek is founded as Too Much Media. Its name is changed to Manwin in 2010, and then MindGeek in October 2013. Its operations are primarily related to Internet pornography, but also include other online properties such as the comedy video website videobash.com and celebrity gossip site celebs.com.[11][12] |
| 2005 | January 25 | Products | Google Video launches.[13] |
| 2005 | March 15 | Companies | Dailymotion, a French video-sharing website, is founded.[14] |
| 2005 | April 23 | Companies | YouTube opens for video uploads, and the first YouTube video uploaded on April 23, 2005 is titled Me at the zoo.[15] Between March and July 2006, YouTube grows from 30 to 100 million views of videos per day. |
| 2006 | May 14 | Companies | Crunchyroll, an American website and international online community focused on video streaming East Asian media including anime, manga, drama, music, electronic entertainment, and auto racing content, is founded.[16] |
| 2006 | October 1 | Companies | Justin.tv, a live-streaming service that is the parent company of Twitch, is founded by Justin Kan.[17] |
| 2006 | September 7 | Products | Amazon introduces video on demand service Amazon Video.[18] |
| 2006 | October 9 | Mergers | Google acquires YouTube.[19] |
| 2006 | October 31 | Companies | LiveLeak, a UK-based video sharing website that lets users post and share videos (often of reality footage, politics, war, and other world events), is founded.[20] |
| 2006 | December | Companies | Youku, one of China's top online video and streaming service platforms, is founded.[21] |
| 2007 | January 15 | Products | Netflix announces that it will launch streaming video.[22] |
| 2007 | February | Technology | HTML5 specification introduces the video element for the purpose of playing videos. This allows embedding video to no longer necessitate a third-party plugin, as it can be played natively in the browser. HTML5 would later overtake Flash as the primary mechanism for broadcasting video.[23] |
| 2007 | Early | Companies | PornHub, a pornographic video sharing website, is founded by the web developer Matt Keezer as a website within the company Interhub.[24] |
| 2007 | September | Companies | Vevo is founded. It offers music videos from two of the "big three" major record labels, Universal Music Group and Sony Music Entertainment.[25] |
| 2007 | September 5 | Technology | Microsoft introduces Microsoft Silverlight, an application framework for writing and running rich Internet applications, similar to Adobe Flash.[26] |
| 2008 | February 25 | Products | DivX announces that it will shut down Stage6,[27] stating that it is unable to continue to provide the attention and resources required for its continued operation.[28] |
| 2008 | March 10 | Technology | Macromedia Flash moves to the H.264 encoding codec.[29] |
| 2008 | March 12 | Companies | Hulu, an online streaming service for TV/movies, launches for public access in the United States.[30] |
| 2009 | January | Products | Google discontinues the ability to upload videos to Google Video.[31] |
| 2010 | March | Acquisitions | PornHub is purchased by Fabian Thylmann as part of the Manwin conglomerate, now known as MindGeek.[32] |
| 2010 | April 22 | Companies | iQiyi, an online video platform based in Beijing, China launches.[33] |
| 2010 | December | Companies | Viki, an international video website offering TV shows, movies, and other premium content, is founded and gets Series A round funding.[34] |
| 2011 | January | Technology | Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP – which enables high quality streaming of media content over the Internet delivered from conventional HTTP web servers – becomes a draft international standard.[35] The MPEG-DASH standard is published as ISO/IEC 23009-1:2012 in April, 2012. |
| 2011 | April | Companies | Vudu announces the launch of its online streaming service.[36] |
| 2011 | May | Acquisitions | Manwin/MindGeek acquires the pornographic video sharing website YouPorn.[37] |
| 2011 | June 6 | Companies | Justin.tv spins off its gaming division as Twitch.tv, which officially launches in public beta.[38] |
| 2011 | July | Companies | Keek – a free online social networking service that allows its users to upload video status updates, which are called "keeks" – launches.[39] |
| 2012 | January 29 | Companies | Megaupload (and Megavideo) are shut down by the feds.[40] |
| 2012 | June | Companies | Vine, a short-form video sharing service where users can share six-second-long looping video clips, is founded by Dom Hofmann, Rus Yusupov, and Colin Kroll.[41][42] |
| 2012 | December | Companies | Snapchat adds the ability to send video snaps in addition to photos.[43] |
| 2013 | June 13 | Product | Instagram launches video sharing.[44] |
| 2015 | January 27 | Products | YouTube drops Flash for HTML5 video as default.[45] |
| 2015 | March | Companies | Periscope, a live video streaming app for iOS and Android developed by Kayvon Beykpour and Joe Bernstein is launched (and acquired by Twitter before its launch).[46] |
| 2015 | May | Companies | Meerkat, a mobile app that enables users to broadcast live video streaming through their mobile device, releases its app for both iOS and Android.[47] |
| 2016 | January | Companies | Facebook launches livestreaming to everyone with Facebook Live.[48] |
Numerical and visual data
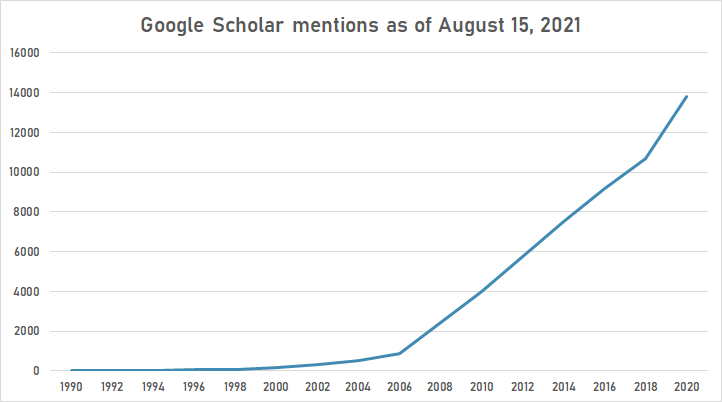
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of August 15, 2021.
| Year | "online video" |
|---|---|
| 1990 | 8 |
| 1992 | 20 |
| 1994 | 19 |
| 1996 | 68 |
| 1998 | 82 |
| 2000 | 179 |
| 2002 | 319 |
| 2004 | 517 |
| 2006 | 859 |
| 2008 | 2,430 |
| 2010 | 3,980 |
| 2012 | 5,740 |
| 2014 | 7,520 |
| 2016 | 9,160 |
| 2018 | 10,700 |
| 2020 | 13,800 |
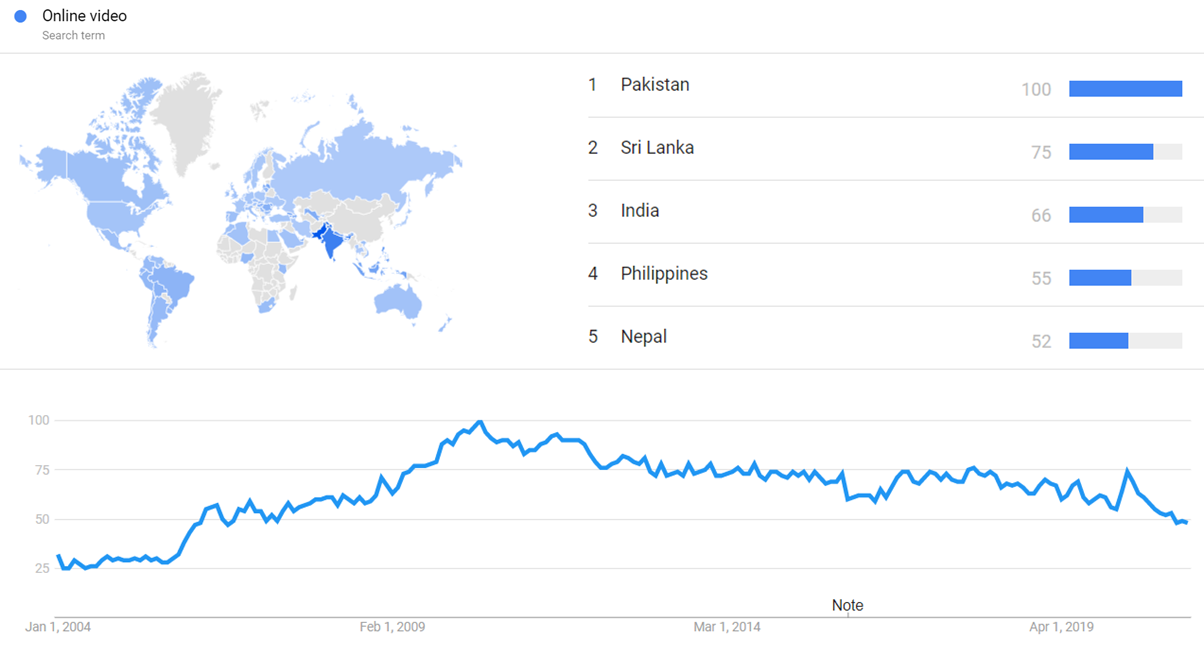
Google Trends
The image below shows Google Trends data for Online video (Search term), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[49]
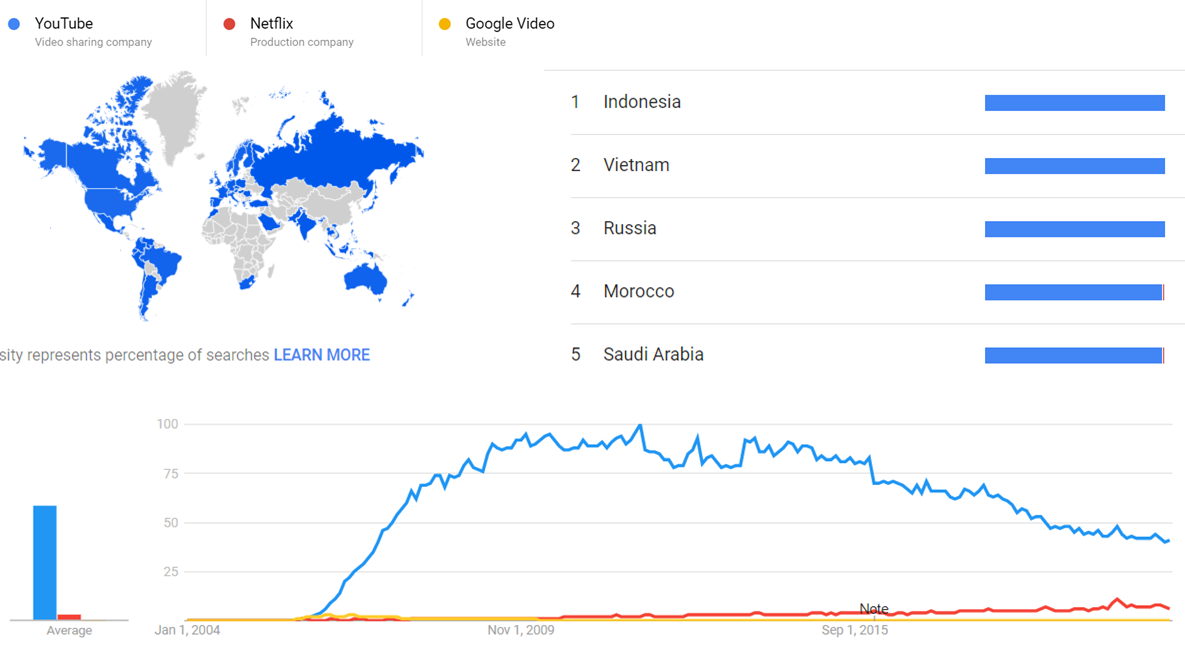
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for YouTube (Video sharing company), Netflix (Production company) and Google Video (Website), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[50]
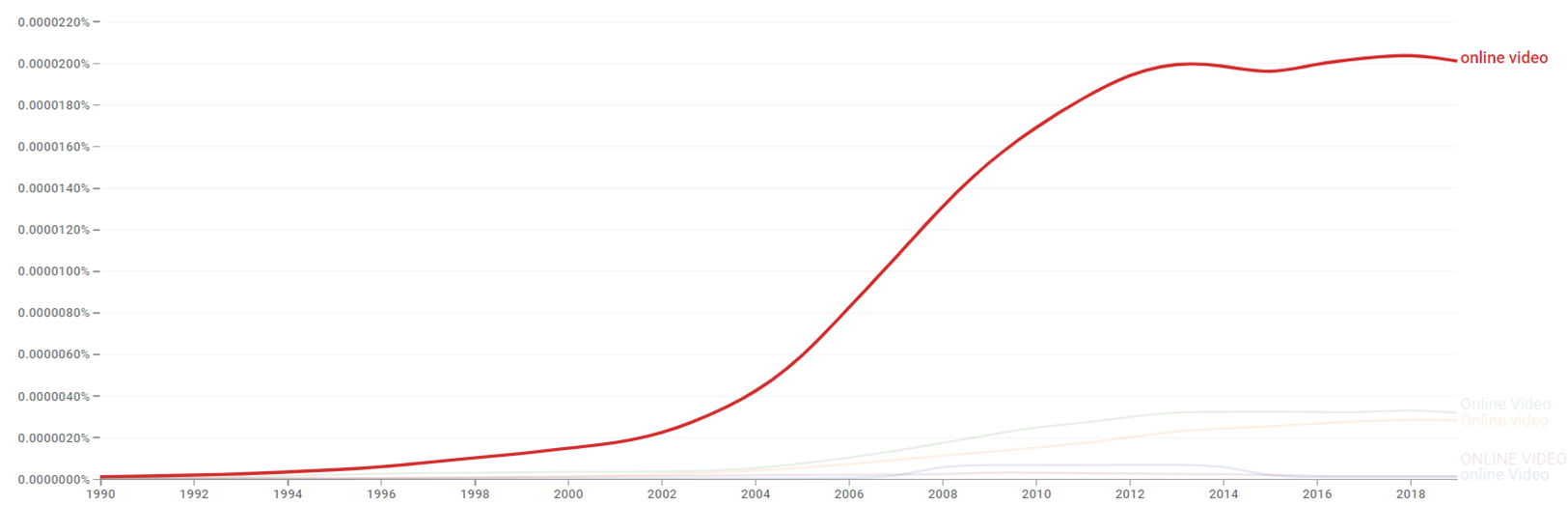
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Online video, from 1990 to 2019.[51]
Wikipedia Views
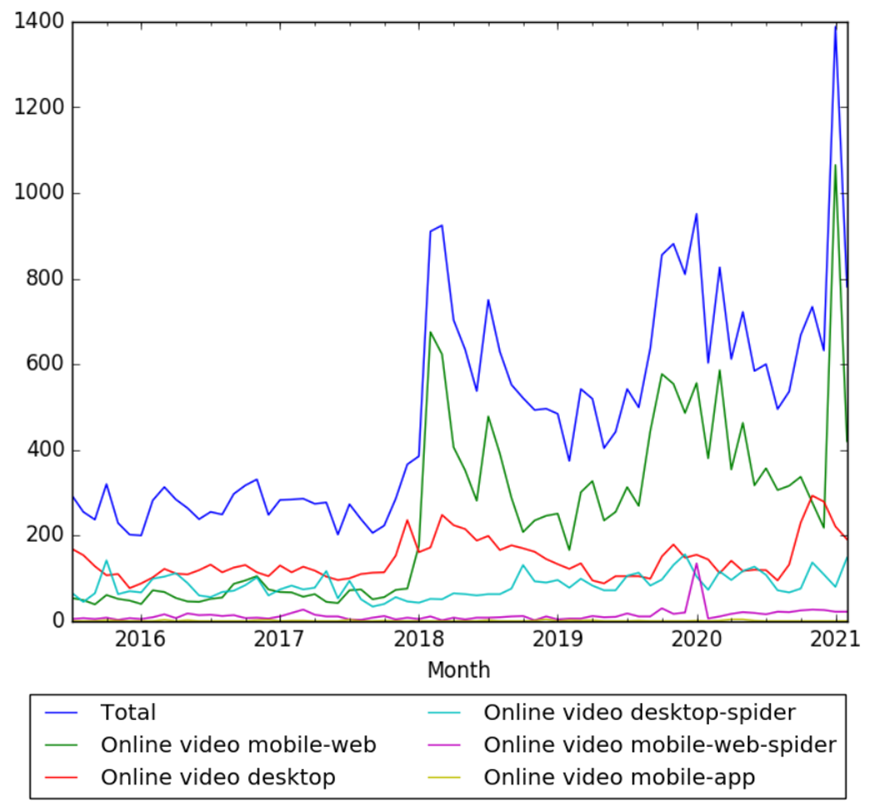
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Online video, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to February 2021.[52]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by FIXME.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "A history of media streaming and the future of connected TV". The Guardian. Retrieved July 28, 2016.
- ↑ ISO/IEC (2004-11-15), ISO/IEC 14496-1:2004 – Third edition 2004-11-15 – Information technology — Coding of audio-visual objects — Part 1: Systems (PDF), retrieved 2010-04-11Template:Fix/category[dead link]Template:Cbignore
- ↑ WG11 (MPEG) (March 2002). "Overview of the MPEG-4 Standard". Retrieved 2010-04-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ WG11 (1997-11-21), Text for CD 14496-1 Systems (MS Word .doc), retrieved 2010-04-11
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "MPEG-4 Systems Elementary Stream Management (ESM)". July 2001. Retrieved 2010-04-11.
- ↑ "MPEG Systems (1-2-4-7) FAQ, Version 17.0". July 2001. Retrieved 2010-04-11.
- ↑ "A Brief History of Multi-Bitrate Streaming". Alexzambelli.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ "Timeline of QuickTime Updates at the Apple Museum". Retrieved January 8, 2007.
- ↑ CNET News (2003-05-13) On2 blows trumpet for new codec, Retrieved on 2009-08-17
- ↑ MindGeek. "MindGeek". LinkedIn. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
Founded 2004
- ↑ "Manwin Canada: A Leader in Web Design, IT, Web Development & SEO!". ca.manwin.com. Archived from the original on 7 November 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
Established in June 2004, Manwin is an international organization, with corporate offices in Europe.
- ↑ Google Video Search Live
- ↑ Carvajal, Doreen. "Taking on the Godzilla of video-sharing sites. " The New York Times. Friday 21 March 2008. Retrieved 4 May 2011.
- ↑ Alleyne, Richard (July 31, 2008). "YouTube: Overnight success has sparked a backlash". The Daily Telegraph. London. Retrieved January 17, 2009.
- ↑ "Crunchyroll CEO: Making Online Anime Pay". ICv2. 2008-12-15. Retrieved 2008-12-15.
- ↑ "Justin.TV". Retrieved June 23, 2016.
- ↑ "Amazon.com Investor Relations: Press Release". corporate-ir.net.
- ↑ "Google closes $A2b YouTube deal". The Age. Melbourne. Reuters. November 14, 2006. Retrieved March 3, 2007.
- ↑ Damn, a year already? liveleak.com, October 31, 2007
- ↑ Kristen Nicole2007-11-21 06:47:07 UTC (2007-11-21). "Youku Hits the Jackpot with $25M". Mashable.com. Retrieved 2014-06-28.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Netflix to Deliver Movies to the PC". The New York Times. January 16, 2007. Retrieved May 21, 2016.
- ↑ "The history of online video: the state of the art and how we got there". Retrieved July 28, 2016.
- ↑ "The Geek-Kings of Smut". New York. Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ↑ "Queen Rania calls on music world to support 1GOAL education campaign". December 10, 2009. Retrieved September 3, 2015.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Silverlight architecture". Retrieved 2007-06-05.
- ↑ "DivX Announces Plans to Shut Down Stage6.com". DivX.com. February 25, 2008.
- ↑ "Stage6 Shut Down"., stage6.com
- ↑ "Exploring Flash Player support for high-definition H.264 video and AAC audio". Adobe.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ "Welcome to Hulu « The Hulu Blog". Blog.hulu.com. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ↑ Turning Down Uploads at Google Video, by Michael Cohen, Product Manager, January 14, 2009, Official Google Video Blog, accessed April 23, 2009
- ↑ Buse, Uwe (20 December 2012). "Harnessing the Internet: The German Porn King's Revolutionary Model". der Spiegel.
- ↑ "Baidu | Press Releases". ir.baidu.com. Retrieved 2015-12-29.
- ↑ "Viki". Crunchbase. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ ISO/IEC DIS 23009-1.2 Dynamic adaptive streaming over HTTP (DASH)
- ↑ "Vudu Launches Streaming Service". Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ↑ "Manwin Acquires YouPorn.com". AVN. 10 May 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2014. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ↑ Wilhelm, Alex (June 6, 2011). "Twitch TV: Justin.tv's killer new esports project". The Next Web.
- ↑ Dobby, Christine. "Toronto's Keek raises $18M for social video networking platform". Retrieved January 17, 2012.
- ↑ "Megaupload (and Megavideo) shut down by the Feds". Ew.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ Sippey, Michael (January 24, 2013). "Vine: A new way to share video". Twitter Blog. Twitter. Retrieved July 25, 2013.
- ↑ Crook, Jordan (January 24, 2013). "Twitter's 6-Second Video Sharing App, Vine, Goes Live In The App Store". TechCrunch. Retrieved January 26, 2013.
- ↑ J.J. Colao, "Snapchat Adds Video, Now Seeing 50 Million Photos A Day", Forbes, Dec 14, 2012. Retrieved May 16, 2016.
- ↑ "Instagram Launches 15-Second Video Sharing Feature, With 13 Filters And Editing". Techcrunch.com. Retrieved April 15, 2016.
- ↑ "YouTube drops Flash for HTML5 video as default". Theverge.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ Shontell, Alyson (26 March 2015). "What it's like to sell your startup for ~$120 million before it's even been launched: Meet Twitter's new prized possession, Periscope". Business Insider. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ↑ "Meerkat raises $12 million - Business Insider". Businessinsider.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ "Facebook Livestreaming Opens Up to Everyone With an iPhone". Wired.com. Retrieved July 31, 2016.
- ↑ "Online video". Google Trends. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- ↑ "YouTube, Netflix and Google Video". Google Trends. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- ↑ "Online video". books.google.com. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
- ↑ "Online video". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 25 March 2021.