Timeline of poliomyelitis
This is a timeline of poliomyelitis, describing major events, such as vaccine releases, historic epidemics, and major organizations.
Big picture
| Year/period | Key developments |
|---|---|
| 1955 (pre-vaccine era) | Before the vaccine, poliomyelitis paralyze and kill up to half a million people every year at its peak, according to calculations.[1] |
| 1950s | The 1950s mark a change in the history of polio, with the development of both the Salk and Sabin vaccines.[1] |
| 1960s | Massive cut in polio transmission is achieved in the United States, where the vaccines are first administered.[2] |
| 1970s–1980s | Routine immunization is introduced worldwide as part of national immunization programs, helping to control poliomyelitis in many developing countries. Non–governmental organizations take action.[1][3] |
| 1990s–2000s | WHO regions of the Americas and Europe achieve polio–free certifications, while the number of endemic countries plummet in the rest of the world.[1][4] |
| 2010 onward | In the last years, massive immunization campaigns have proven to be successful, with an almost complete global eradication as of 2016. To date, only Afghanistan and Pakistan, remain endemic.[5] |
Full timeline
| Year/period | Type of event | Event | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1789 | Medical development | British physician Michael Underwood is the first to give a clinical description of poliomyelitis.[4] | United Kingdom |
| 1840 | Medical development | German orthopaedist Jakob Heine becomes the first to write a medical report on poliomyelitis, and the first to recognize the illness as a clinical entity.[4] | Germany |
| 1894 | Epidemic | First poliomyelitis epidemic breaks out in the United States. Eighteen deaths and 132 cases of permanent paralysis are reported.[6] | United States (Vermont) |
| 1905 | Epidemic | Poliomyelitis epidemic breaks out in the Scandinavian peninsula. 1,031 cases are reported.[7][8] | Sweden, Norway |
| 1908 | Scientific development | Austrian physicians Karl Landsteiner and Erwin Popper discover the etiologic agent of poliomyelitis by identifying a virus when transmitting the disease to a monkey.[7] | Austria (Vienna) |
| 1910 | Scientific development | American scientists Simon Flexner and Paul Lewis suggest that poliovirus gain access to the central nervous system via the nasal mucosa. This hypothesis is supported by experiments with monkeys performed by Flexner’s group and other researchers.[7] | |
| 1916 | Epidemic | Large epidemic of poliomyelitis breaks out in the United States. In New York City 9,000 cases and 2,343 deaths are reported, while toll nationwide is reported at 27,000 cases and 6,000 deaths.[9] | United States |
| 1927 | Organization | American politician Franklin D. Roosevelt founds Warm Springs Foundation for polio rehabilitation. In 1980 the facility is renamed Roosevelt Warm Springs Institute for Rehabilitation. Today, the organization treats patients with post-polio symptoms, spinal cord injuries, strokes, and other disabilities.[10] | United States (Georgia) |
| 1928 | Medical development | American industrial hygienist Philip Drinker along with Louis Agassiz Shaw, Jr. develop the iron lung, a negative pressure ventilator that enables a person to breathe when normal muscle control has been lost or the work of breathing exceeds the person's ability. It becomes popular after its successful first use in a girl with poliomyelitis, showing dramatic recovery in a very short period of time.[11] | United States |
| 1931 | Scientific development | Australian scientists Frank Macfarlane Burnet and Jean Macnamara discover the existence of antigenic differences between strains of poliovirus, comparing the famous Rockefeller MV strain with a local strain isolated in Melbourne and further finding striking differences in cross-immunity experiments and neutralization tests in monkeys.[7] | Australia |
| 1935 | Crisis | Canadian researcher Maurice Brodie works in the development of a vaccine made from a killed strain of poliovirus. While successful in twenty laboratory monkeys, the trials fail when performed on humans. The same year, American researcher John A. Kolmer, working on his own vaccine using weakened poliovirus, fails even worse when a large number of children who were administered his vaccine become ill and many die.[12] | United States |
| 1939 | Medical development | American physician Charles Armstrong manages to adapt the Lansing strain of poliovirus to mice, making available for research purposes an animal far less expensive than the monkey.[7] | United States |
| 1940 | Medical development | Australian nurse Elizabeth Kenny introduces new treatment for polio, using warm compresses to relax painful, contracting muscles and massage for rehabilitation. Unconventional and controversial at the beginning, eventually this treatment becomes part of standard care for poliomyelitis.[13] | United States |
| 1948 | Scientific development | Team led by American biomedical scientist John Franklin Enders, at Harvard University, succeeds in culturing poliovirus in the laboratory outside of a living body. In 1949, the team publishes the experiments and findings, which would make mass production of vaccine possible. In 1954 the researchers were awarded the Nobel Prize.[12] | United States |
| 1953 | Medical development | American medical researcher Jonas Salk and his associates develop a potentially safe, inactivated (killed), injected polio vaccine. By 1955, the Salk vaccine is recognized as safe, effective and potent. Salk is hailed a hero by the public and is granted a license to market his vaccine by the government.[12] | United States |
| 1955–1960 | Medical development | Polish American medical researcher Albert Sabin develops an oral polio vaccine. Initially overlooked due to Salk vaccine success, in 1957 the World Health Organization authorizes mass vaccination of children living in areas suffering from poliomyelitis epidemics. By 1959, about 4.5 million people in Russia have received the oral vaccine, making the incidence of polio in that country decrease markedly by 1959. Due to these results, the Sabin vaccine is licensed for use in the United States [12] | |
| 1955–1963 | Controversy | The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention admits that in this period over 98 million Americans received one or more doses of a polio shot which was contaminated with a cancer-causing virus called simian vacuolating virus 40 (SV40).[14][15] | United States |
| 1961 | Report | As a result of the first immunization campaigns, only 161 poliomyelitis cases are recorded in the United States, down from 35,000 in 1953 to 5,600 by 1957.[2] | United States |
| 1961 | Medical development | Albert Sabin develops oral polio vaccine types 1 and 2. Previously grown in monkey kidney cell culture, the vaccine would be licensed for use in the United States.[16] | United States |
| 1962–1970 | Medical development | The Salk vaccine is gradually replaced by the oral Sabin vaccine for most purposes because it is easier to administer and less expensive.[17][18] | Worldwide |
| 1974 | Program launch | Polio vaccine is included in the Expanded Programme on Immunization, created by the World Health Organization in response to poor immunization levels in developing countries (less than 5% of children in 1974).[16] | |
| 1979 | Program launch | Rotary International commits to provide oral polio vaccine to six million children in the Philippines as part of its new Health, Hunger and Humanity (3-H) program. Following the success of the program, Rotary begins to work with Albert Sabin on a plan to immunize all children against poliomyelitis.[1] | Philippines |
| 1979 | Infection | The last cases of wild type 1 poliovirus occur in the United States among unvaccinated Amish persons and members of other religious groups who did not accept vaccination.[16] | United States |
| 1980 | Program launch | Brazil implements National Immunization Days against infantile paralysis as part of the strategy to eliminate poliomyelitis. The initial objective is to achieve high coverage to interrupt transmission of poliovirus, with an established target of vaccinating 95% of children younger than five years with oral poliovirus vaccine. By 1989, a case of poliomyelitis in Brazil is confirmed for the last time.[19] | Brazil |
| 1981 | Scientific development | American researchers Vincent Racaniello and David Baltimore at Massachusetts Institute of Technology; and team led by German American virologist Eckard Wimmer at State University of New York, publish the poliovirus genome. The researchers used an enzyme to switch the single strands of viral RNA to double strands of DNA and then determined the sequence of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine encoding the five molecules that are the substance of the virus’s existence.[20] | United States |
| 1985 | Program launch | Rotary International announces a US$120 million pledge to its new PolioPlus program as a twenty-year commitment to immunize all children of the world against poliomyelitis by 2005. So far, Rotary has been the largest private sector donor to polio eradication, committing over US$600 million to the cause.[1][21] | Worldwide |
| 1985 | Program launch | The Universal Childhood Immunization Initiative is launched jointly by UNICEF and WHO, with the purpose of reducing child mortality through effective immunization.[1][22] | Worldwide |
| 1985 | Program launch | The Pan American Health Organization launches initiative to eradicate the indigenous transmission of wild poliovirus from the WHO region of the Americas by the end of 1990.[1] | Americas |
| 1988 | Program launch | The World Health Organization resolutes to eradicate poliomyelitis globally by 2000 through several delivery strategies, including reinforcement of existing initiatives such as National Immunization Days (NIDs) and sub-national immunization days. By 2016, the resolution was not achieved.[23] | |
| 1988 | Program launch | The World Health Assembly (WHA) launches a global goal to eradicate poliomyelitis by 2000. This goal is further moved to stopping transmission by end of 2005.[1] | Worldwide |
| 1990 | Medical development | Ipol, an enhanced-potency inactivated poliovirus vaccine, by Pasteur Méérieux Vaccins et Serums, is licensed.[16] | |
| 1991 | The last case of indigenous polio in the Western Hemisphere occurs in a 5-year-old Peruvian boy.[16] | Peru (Pichanaqui | |
| 1994 | Achievement | The entire Western Hemisphere is certified as "polio-free" by the International Commission for the Certification of Polio Eradication, from the World Health Organization.[16][19][5] | Western Hemisphere |
| 1996 | Program launch | South African politician Nelson Mandela launches Kick Polio out of Africa campaign, with aims at eradicating the disease from Africa. By 2003, poliomyelitis remains in only three countries (Nigeria, Niger and Egypt) out of 46.[1][24] | Africa |
| 1997 | The United States Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends adoption of a sequential series of two doses of inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) followed by two doses of oral polio vaccine (OPV) for all infants and children to decrease the rare occurrences of Vaccine Associated Paralytic Polio (VAPP) that were noted following the administration of live oral poliovirus vaccine.[16] | United States | |
| 1999 | Medical development | inactivated polio vaccine replaces oral polio vaccince as recommended method of polio immunization in the United States.[25] | United States |
| 1999 | Report | The last case of wild poliovirus (WPVs) type 2 is reported.[3] | India (Aligarh) |
| 1999 | The United States Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends exclusive use of inactivated poliovirus vaccine (IPV) for infants and children.[16] | United States | |
| 2000 | Achievement | The Western Pacific WHO Region is certified as polio-free[16] | |
| 2002 | Achievement | European WHO region is certified free of poliomyelitis.[4] | Europe, Turkey, ex USSR |
| 2002 | Medical development | Pediarix (by GlaxoSmithKline), a vaccine that combines the diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated polio, and hepatitis B antigens is licensed.[16] | |
| 2003 | Epidemic | Political and religious leaders of Kano, Zamfara, and Kaduna states in Nigeria bring the immunization campaign to a halt by calling on parents not to allow their children to be immunized. Polio immunization is suspended, thus leading to poliomyelitis outbreak and reinfecting at least other six countries (Burkina Faso, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte d’Ivoire, Mali, and Sudan).[1][26] | Africa |
| 2004 | Program launch | Upon emergency meeting of Health Ministers committed to end polio transmission, a massive immunization campaign is conducted in 22 African countries, reaching 80 million children, becoming one of the World’s largest public health campaigns.[1][27] | Africa |
| 2012 | Report | Poliovirus serotype WPV3 is last reported.[28] | Nigeria |
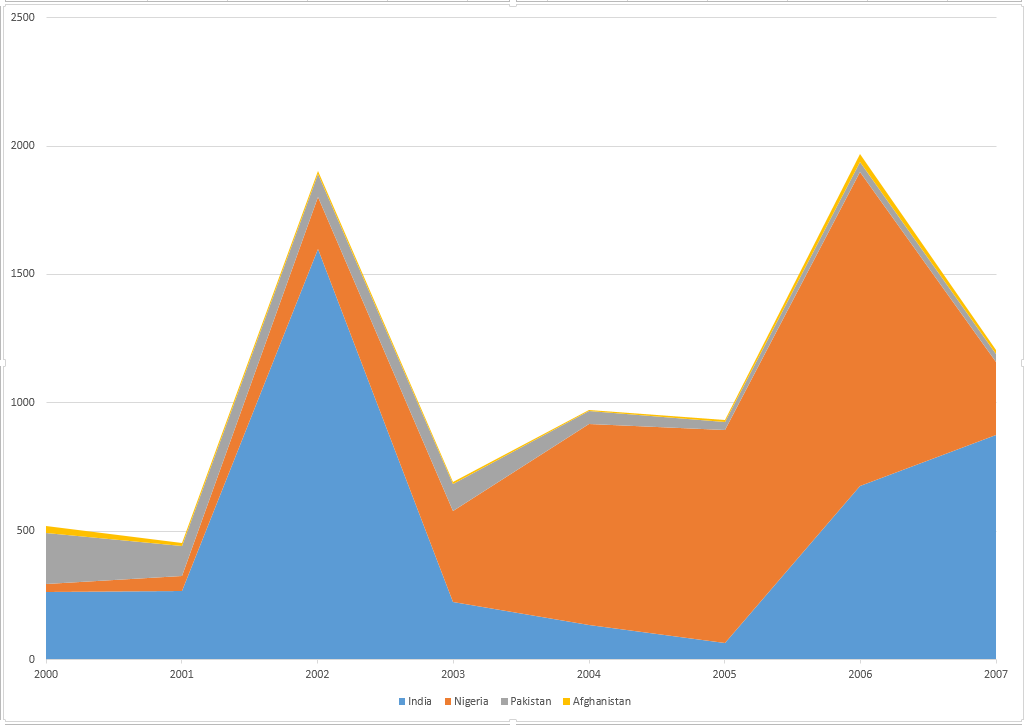
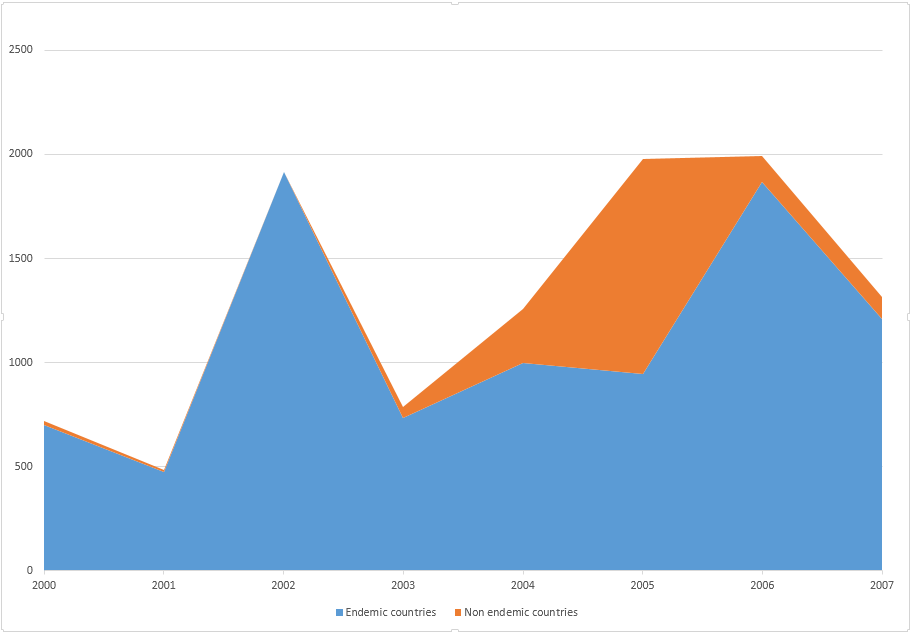
| 2012 | Report | Poliomyelitis remains officially endemic in four countries.[4] | Afghanistan, Nigeria, Pakistan, India |
| 2013 | Crisis | UNICEF and the World Health Organization condemn attacks on polio vaccination workers in Nigeria, where they are being killed by gunmen.[16][29] | Nigeria |
| 2014 | The World Health Organization Director-General Margaret Chan declares the international spread of wild poliovirus a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.[16] | ||
| 2015 | Achievement | Poliovirus serotype WPV2 is declared eradicated worldwide.[3][28] | |
| 2016 | Report | The only two endemic countries as of 2016 are Afghanistan and Pakistan.[5] | Afghanistan, Pakistan |
Google Scholar
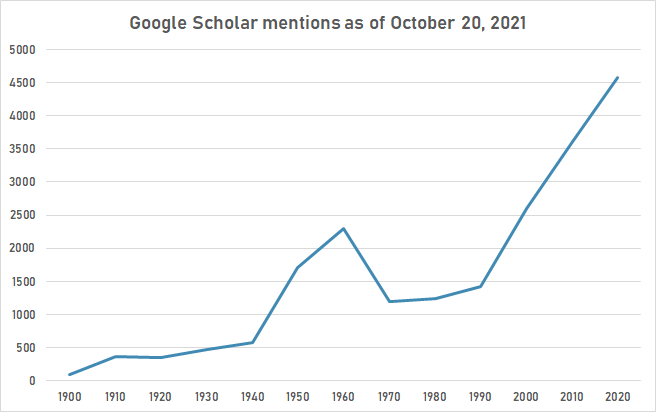
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of October 20, 2021.
| Year | poliomyelitis |
|---|---|
| 1900 | 97 |
| 1910 | 360 |
| 1920 | 354 |
| 1930 | 471 |
| 1940 | 573 |
| 1950 | 1,710 |
| 1960 | 2,290 |
| 1970 | 1,190 |
| 1980 | 1,240 |
| 1990 | 1,420 |
| 2000 | 2,600 |
| 2010 | 3,610 |
| 2020 | 4,570 |
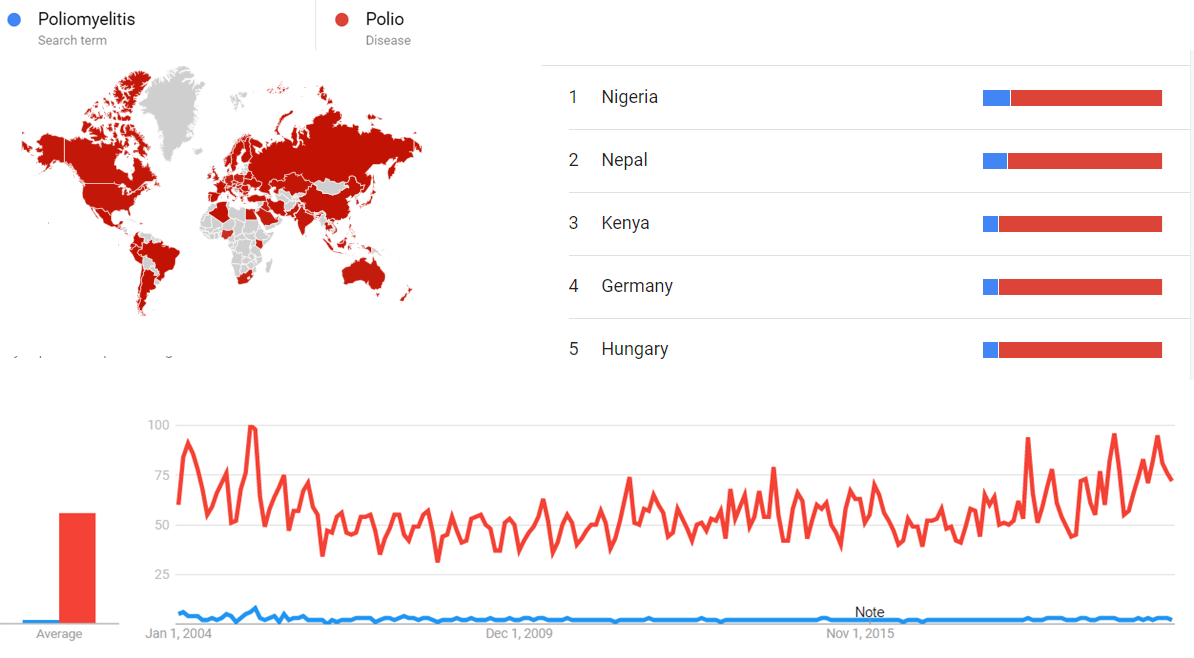
Google Trends
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for Poliomyelitis (Search term) and Polio (Disease), from January 2004 to April 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[30]
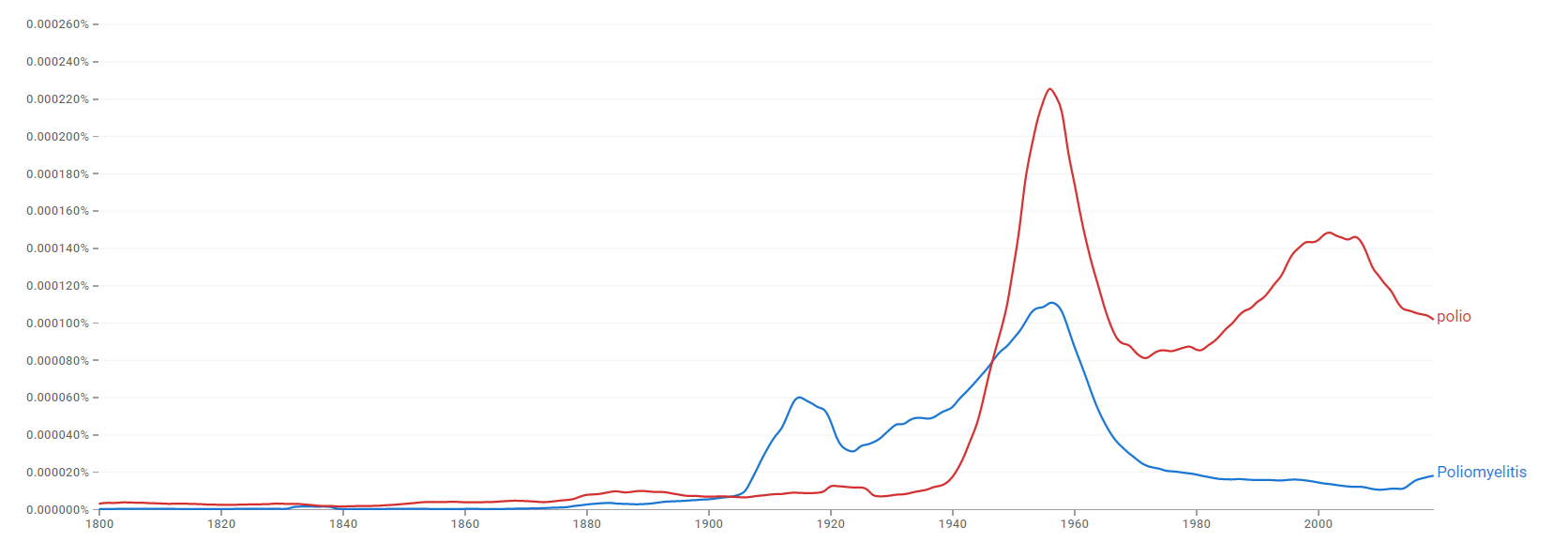
Google Trends
The comparative chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Poliomyelitis and Polio from 1800 to 2019.[31]
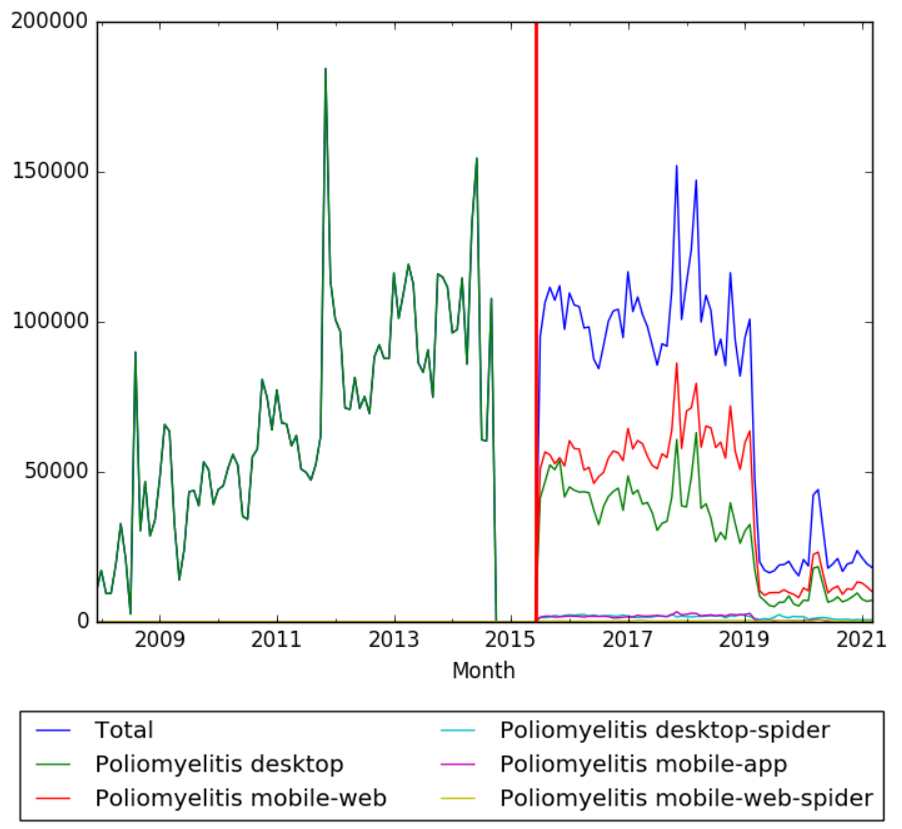
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Poliomyelitis, on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to March 2021. A data gap observed on desktop from October 2014 to June 2015 is the result of Wikipedia Views failure to retrieve data.[32]
Other
See also
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 "Kul Gautam – A History of Global Polio Eradication" (PDF). unicef.org. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "POLIO: A REVIEW". International Journal Of Pharmaceutical Sciences And Research. doi:10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.4(5).1714-24. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "History of Polio". polioeradication.org. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "History of polio BBC". BBC News. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "History of Polio ( Poliomyelitis )". historyofvaccines.org. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ "Polio cases report". historyofvaccines.org. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 Eggers, Hans J. "Milestones in Early Poliomyelitis Research (1840 to 1949)". PMC 112492.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Smallman-Raynor, Matthew. Poliomyelitis: Emergence to Eradication. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ "Whatever happened to polio?". amhistory.si.edu. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ "Roosevelt Warm Springs Institute for Rehabilitation". georgiaencyclopedia.org. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ "Today in History: Iron Lung Used for the First Time (1928)". english.tebyan.net. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 True Peters, Stephanie. The Battle Against Polio. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "Sister Kenny". amhistory.si.edu. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "CDC admits 98 million Americans were given cancer virus via the polio shot". vaccines.news. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ↑ "CDC ADMITS 98 MILLION AMERICANS RECEIVED POLIO VACCINE IN AN 8-YEAR SPAN WHEN IT WAS CONTAMINATED WITH CANCER VIRUS". cureyourowncancer.org. Retrieved 5 April 2018.
- ↑ 16.00 16.01 16.02 16.03 16.04 16.05 16.06 16.07 16.08 16.09 16.10 16.11 "Vaccine Timeline". immunize.org. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ↑ Pearce, J M S. "Salk and Sabin: poliomyelitis immunisation" (PDF). doi:10.1136/jnnp.2003.028530. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Persson, Sheryl. Smallpox, Syphilis and Salvation: Medical Breakthroughs that Changed the World. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Rocha MelloI, Maria Lúcia; Moraes, José Cássio; Brendan, Helena Aparecida; Flannery, Brendan. "Participation in national polio immunization days: results of a vaccine coverage survey among children in 27 Brazilian cities". Revista Brasileira de Epidemiologia. doi:10.1590/S1415-790X2010000200010. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "The polio genome". amhistory.si.edu. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ The Rotarian. 2001. p. 53. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "International Notes Update: Progress Toward Eradicating Poliomyelitis from the Americas". cdc.gov. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "National Immunization Day: a strategy to monitor health and nutrition indicators". Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "Address by President Nelson Mandela at the launch of the "Kick Polio Out of Africa" Campaign". mandela.gov.za. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ "Whatever happened to polio". si.edu. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ↑ Jegede, Ayodele Samuel. "What Led to the Nigerian Boycott of the Polio Vaccination Campaign?". doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0040073. PMC 1831725.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ↑ "West Africa mobilizes for final assault against polio". WHO. Retrieved 10 January 2017.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Global eradication of wild poliovirus type 2 declared". polioeradication.org. Retrieved 9 January 2017.
- ↑ "Gunmen Kill Nigerian Polio Vaccine Workers in Echo of Pakistan Attacks". nytimes.com. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ↑ "Poliomyelitis". Google Trends. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ↑ "Poliomyelitis". books.google.com. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ↑ "Poliomyelitis". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 12 April 2021.
- ↑ Gothefors, Leif. "The Impact of Vaccines in Low- and High-Income Countries". Department of Clinical Sciences/Paediatrics, Umeå University, Umeå, Sweden. doi:10.1159/000129623. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
- ↑ Gothefors, Leif. "The Impact of Vaccines in Low- and High-Income Countries". Department of Clinical Sciences/Paediatrics, Umeå University, Umeå , Sweden. doi:10.1159/000129623. Retrieved 14 January 2017.
Category:Poliomyelitis Category:Health-related timelines Category:Medicine timelines