Timeline of speech and voice recognition
This is a timeline of speech and voice recognition, a technology which enables the recognition and translation of spoken language into text.
Overview
| Time period | Key developments |
|---|---|
| 1877–1971 | Speech recognition is at an early stage of development. Specialized devices can recognize few words and accuracy is not very high.[1] |
| 1971–1987 | Speech recognition rapidly improves, although the technology is still not commercially available.[1] |
| 1987–2014 | Speech recognition continues to improve, becomes widely available commercially, and can be found in many products.[1] |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date (if applicable) | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1877 | Invention | Thomas Edison's phonograph becomes the first device to record and reproduce sound. The method is fragile, however, and is prone to damage.[2] | |
| 1879 | Invention | Thomas Edison invents the first dictation machine, a slightly improved version of his phonograph.[2] | |
| 1936 | Invention | A team of engineers at Bell Labs, led by Homer Dudley, begins work on the Voder, the first electronic speech synthesizer.[3] | |
| 1939 | March 21 | Invention | Dudley is granted a patent for the Voder, US patent 2151091 A.[3] |
| 1939 | Demonstration | The Voder is demonstrated at the 1939 Golden Gate International Exposition in San Francisco. A keyboard and foot pedals were used to have the machine emit speech.[3] | |
| 1939–1940 | Demonstration | The Voder is demonstrated at the 1939-1940 World's Fair in New York City.[3] | |
| 1952 | Invention | A team at Bell Labs designs the Audrey, a machine capable of understanding spoken digits.[1] | |
| 1962 | Demonstration | IBM demonstrates the Shoebox, a machine that can understand up to 16 spoken words in English, at the 1962 Seattle World's Fair.[4] | |
| 1971 | Invention | IBM invents the Automatic Call Identification system, enabling engineers to talk to and receive spoken answers from a device.[5] | |
| 1971–1976 | Program | DARPA funds five years of speech recognition research with the goal of ending up with a machine capable of understanding a minimum of 1,000 words. The program led to the creation of the Harpy by Carnegie Mellon, a machine capable of understanding 1,011 words.[1] | |
| Early 1980s | Technique | The hidden Markov model begins to be used in speech recognition systems, allowing machines to more accurately recognize speech by predicting the probability of unknown sounds being words.[1] | |
| Early 1980s | Invention | IBM begins work on the Tangora, a machine that would be able to recognize 20,000 spoken words by the mid 1980s.[5] | |
| 1987 | Invention | The invention of the World of Wonder's Julie Doll, a toy children could train to respond to their voice, brings speech recognition technology to the home.[1] | |
| 1990 | Invention | Dragon launches Dragon Dictate, the first speech recognition product for consumers.[1] | |
| 1993 | Invention | Sphinx-II, the first large-vocabulary continuous speech recognition system, is invented by Xuedong Huang.[6] | |
| 1996 | Invention | IBM launches the MedSpeak, the first commercial product capable of recognizing continuous speech.[5] | |
| 2002 | Application | Microsoft integrates speech recognition into their Office products.[7] | |
| 2006 | Application | The National Security Agency begins using speech recognition to isolate keywords when analyzing recorded conversations.[8] | |
| 2007 | January 30 | Application | Microsoft releases Windows Vista, the first version of Windows to incorporate speech recognition.[9] |
| 2007 | Invention | Google introduces GOOG-411, a telephone-based directory service. This will serve as a foundation for the company's future Voice Search product.[10] | |
| 2008 | November 14 | Application | Google launches the Voice Search app for the iPhone, bringing speech recognition technology to mobile devices.[11] |
| 2011 | October 4 | Invention | Apple announces Siri, a digital personal assistant. In addition to being able to recognize speech, Siri is able to understand the meaning of what it is told and take appropriate action.[12] |
| 2014 | April 2 | Application | Microsoft announces Cortana, a digital personal assistant similar to Siri.[13] |
| 2014 | November 6 | Invention | Amazon announces the Echo, a voice-controlled speaker. The Echo is powered by Alexa, a digital personal assistant similar to Siri and Cortana. While Siri and Cortana are not the most important features of the devices on which they run, the Echo is dedicated to Alexa.[14] |
Numerical and visual data
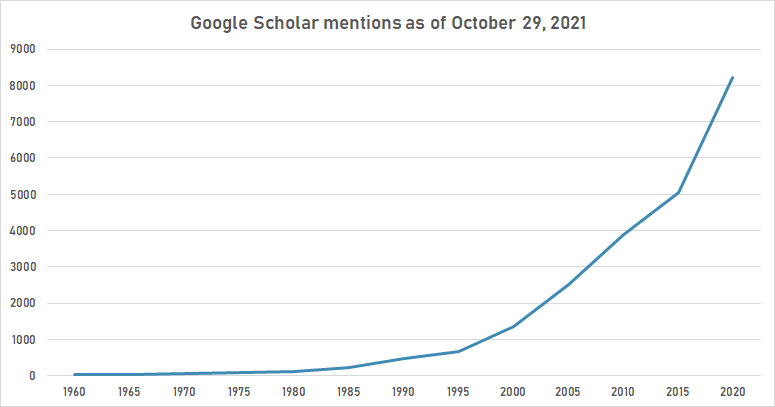
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of October 28, 2021.
| Year | "automatic speech recognition" |
|---|---|
| 1960 | 31 |
| 1965 | 35 |
| 1970 | 68 |
| 1975 | 94 |
| 1980 | 120 |
| 1985 | 219 |
| 1990 | 489 |
| 1995 | 675 |
| 2000 | 1,350 |
| 2005 | 2,520 |
| 2010 | 3,890 |
| 2015 | 5,050 |
| 2020 | 8,230 |
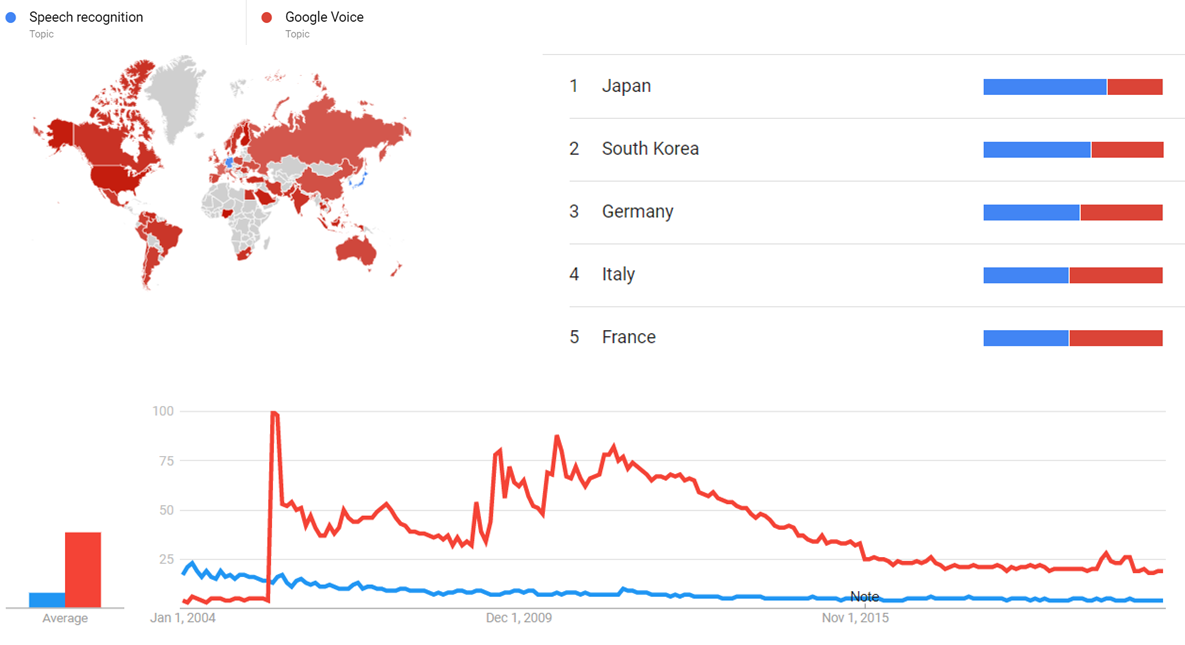
Google Trends
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for Speech recognition (Topic) and Google Voice (Topic), from January 2004 to April 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[15]
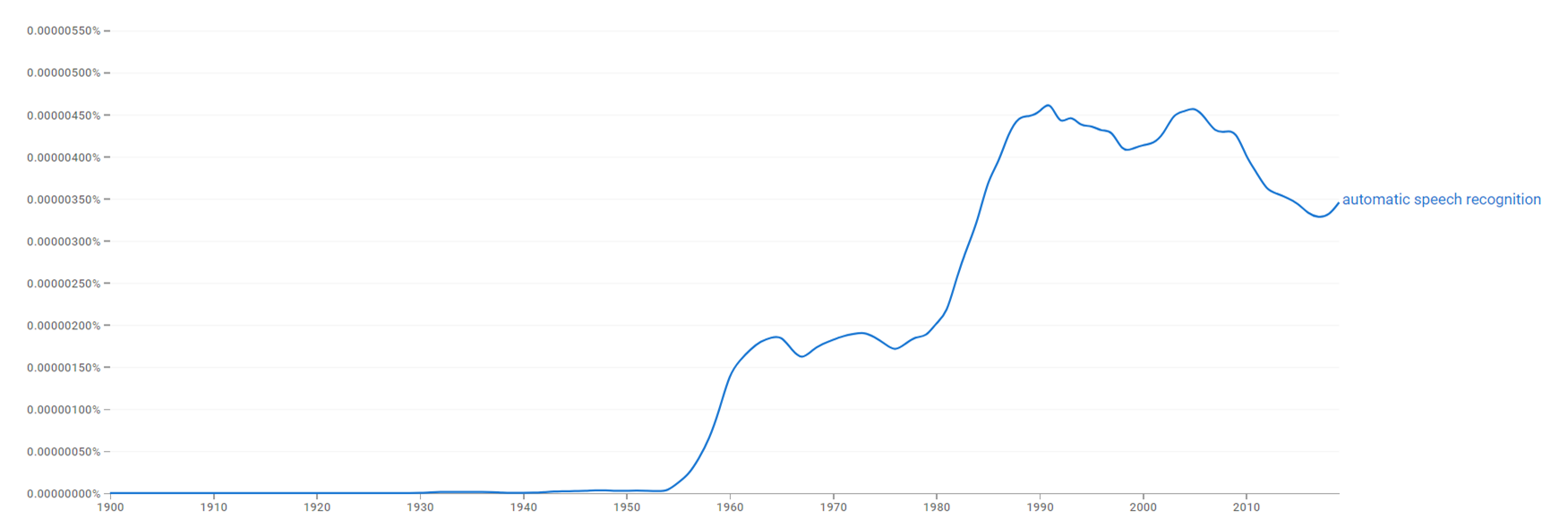
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Automatic speech recognition, from 1900 to 2019.[16]
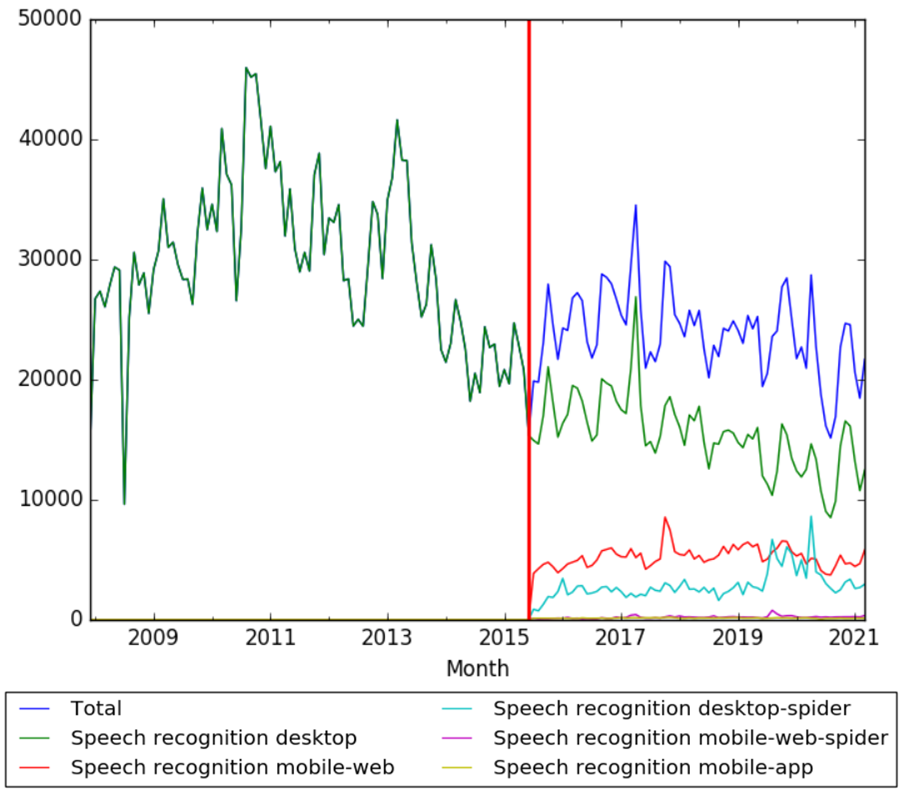
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Speech recognition, on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to March 2021.[17]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Pinola, Melanie. "Speech Recognition Through the Decades: How We Ended Up With Siri". PCWorld. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Newville, Leslie J. Development of the Phonograph at Alexander Graham Bell's Volta Laboratory. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "History of Information Database". Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ "IBM Shoebox". IBM. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Pioneering Speech Recognition". IBM. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Lee, Kai-Fu. "An Overview of the SPHINX Speech Recognition System" (PDF). Carnegie Mellon University. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Thompson, Terry. "DO-IT". University of Washington. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Froomkin, Dan. "The Computers Are Listening". The Intercept. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Shinder, Deb. "Speech recognition in Windows Vista". TechRepublic.
- ↑ Kincaid, Jason. "The Power Of Voice: A Conversation With The Head Of Google's Speech Technology". TechCrunch. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Markoff, John. "Google Is Taking Questions (Spoken, via iPhone)". New York Times. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Daw, David. "What Makes Siri Special?". PCWorld. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ "Microsoft Announces Cortana, Siri-Like Personal Assistant". NBC News. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ Welch, Chris. "Amazon just surprised everyone with a crazy speaker that talks to you". The Verge. Retrieved 21 June 2016.
- ↑ "Speech recognition and Google Voice". Google Trends. Retrieved 14 April 2021.
- ↑ "Automatic speech recognition". books.google.com. Retrieved 16 April 2021.
- ↑ "Speech recognition". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 16 April 2021.