Timeline of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement
This is a timeline of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, attempting to describe significant historical events in the evolution of the societies related to the movement.
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 19th century | Henry Dunant activism leads to the creation of the International Committee of the Red Cross in the 1860s. In the same decade, the First Geneva Convention and the First International Conference of the Red Cross are held. The first National Societies are formed in Europe. |
| 20th century | In 1906, the 1864 Geneva Convention is revised for the first time. In 1907, the Hague Convention X extends the scope of the Geneva Convention to naval warfare. By 1914 there are already 45 national relief societies throughout the world. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is founded in the aftermath of World War I which showed a need for close cooperation between Red Cross Societies.[1] The League Of Red Cross Societies is formed in 1919. The International Council is created in 1928.[2] The four Geneva Conventions of 1949, for the protection of war victims, to which 166 States are party, and their two Additional Protocols of 1977 explicitly establish the role of the ICRC as a neutral and impartial humanitarian intermediary.[3] The period of decolonization from 1960 to 1970 is marked by a huge jump in the number of recognized national Red Cross and Red Crescent societies. In 1965, the Fundamental Principles of the Red Cross are proclaimed. By the end of the 1960s, there are more than 100 societies around the world. |
| 21st century | As late as in the early 21st century, Switzerland joins the United Nations. In 2004 the IFRC conducts its largest mission to date after the tsunami disaster in South Asia. By 2019, the IFRC is composed of 191 National Societies And 13.7 Million Volunteers, operating through some 166,000 branches, and nearly 14 million volunteers.[4] |
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Event type | Details | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1859 | Prelude | The idea of a Red Cross society is born when Swiss businessman Henry Dunant comes upon the scene of a bloody Battle of Solferino, Italy, between the armies of imperial Austria and the Franco-Sardinian alliance. An estimated 40,000 dead or dying men on the battlefield are found among lacking medical attention.[5][6] | Italy | |
| 1862 | Publication | Henry Dunant publishes book Un souvenir de Solférino (A Memory of Solferino). This publication would lead to the adoption of the first Geneva Convention in 1864, laying out rules to protect wounded soldiers and medics, and to the creation of relief societies in each country.[6] | Switzerland | |
| 1863 | February 17 | Founding | Inspired by Henry Dunant, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) is founded in Geneva.[7][8] In honor of Dunant’s nationality, the Swiss flag in reverse (a red cross on a white background) is chosen as emblem.[9][10] | Switzerland |
| 1863 | 26–29 October | Conference | The constituent Conference giving birth to the Red Cross is held in Geneva with the purpose to establish procedures to improve medical services on the battlefield and create national societies to aid the sick and wounded.[11][8] | Switzerland |
| 1863 | November 12 | Organization | The first National Society is formed in the Kingdom of Württemburg. The following year, National Societies are formed in the states of Baden, Bavaria, Hamburg, Hesse-Darmstadt, Mecklenburg-Schwerin, Oldenburg, Prussia and Saxe, all states in current-day Germany. The organization would merge in 1921 as the German Red Cross. The East German Red Cross would function between 1952 and 1991.[8] | Germany |
| 1864 | February 4 | Organization | The Belgian Red Cross is established.[8] | Belgium |
| 1864 | March 2 | Organization | The Spanish Red Cross is established.[8] | Spain |
| 1864 | May 25 | Organization | The French Red Cross is established.[12] | France |
| 1864 | June 15 | Organization | The Italian Red Cross is established.[13] | Italy |
| 1864 | August 22 | Treaty | The First Geneva Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded in Armies in the Field is held in Geneva. Twelve states sign 10 articles forming the convention.[14] The agreement, advocated by Henri Dunant, calls for nonpartisan care to the sick and wounded in times of war and provides for the neutrality of medical personnel. It also proposes the use of an international emblem to mark medical personnel and supplies.[9][8] | Switzerland |
| 1865 | February 11 | Organization | The Portuguese Red Cross is established.[8] | Portugal |
| 1865 | May 25 | Organization | The Swedish Red Cross is established.[15][8] | Sweden |
| 1865 | September 22 | Organization | The Norwegian Red Cross is established.[8] | Norway |
| 1866 | July 17 | Organization | The Swiss Red Cross is established.[16][8] | Switzerland |
| 1867 | Conference | The First International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Paris. Nine governments, 16 National Committees and the International Committee attend the conference.[14][17] | France | |
| 1867 | May 3 | Organization | The Russian Red Cross Society is established.[8] | Russia |
| 1867 | May 17 | Organization | The Austrian Red Cross is established.[8] | Austria |
| 1867 | July 19 | Organization | The Netherlands Red Cross is established.[18] | Netherlands |
| 1868 | June 11 | Organization | The Turkish Red Crescent is established.[19][8] | Turkey |
| 1869 | Conference | The Second International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Berlin.[14] The body created through one resolution leads to the creation of the Central Tracing Agency.[17] | Germany | |
| 1870 | August 4 | Organization | The British Red Cross is established as the National Aid Society. It would be renamed the British Red Cross in 1905.[20][8] | United Kingdom |
| 1875 | April 22 | Organization | The Danish Red Cross is established.[8] | Denmark |
| 1875 | November 29 | Organization | The Red Cross of Montenegro is established.[8] | Montenegro |
| 1876 – 1878 | Symbol | During the Russo-Turkish War, the Ottoman Empire declares that it would use the red crescent on a white background in place of the red cross. While respecting the red cross symbol, the Ottoman authorities believe that the red cross is offensive to Muslim soldiers. The red crescent is temporarily accepted for the duration of this conflict.[10] | ||
| 1876 | January 25 | Organization | The Red Cross of Serbia is established.[8] | Serbia |
| 1876 | July 4 | Organization | The Romanian Red Cross is established.[21][8] | Romania |
| 1877 | May 1 | Organization | The Japanese Red Cross Society is established.[22] | Japan |
| 1877 | May 7 | Organization | The Finnish Red Cross is established.[23] | Finland |
| 1877 | June | Organization | The Hellenic Red Cross is established.[24][8] | Greece |
| 1878 | Organization | The Croatian Red Cross is established within the Red Cross of the Austro-Hungarian monarchy. It would become independent since 10 October 1991.[8] | Croatia | |
| 1879 | Organization | The Chilean Red Cross is established. It would be disbanded in 1891, and re-established in 1903.[8] | Chile | |
| 1879 | April 17 | Organization | The Peruvian Red Cross is established.[8] | Peru |
| 1877 | Organization | The Slovenian Red Cross is established as a part of the Austrian Red Cross. It would become independent since 26 January 1993.[8] | Slovenia | |
| 1880 | June 13 | Organization | The Argentine Red Cross is established.[8] | Argentina |
| 1881 | May 16 | Organization | The Hungarian Red Cross is established.[8] | Hungary |
| 1881 | May 21 | Organization | The American Red Cross is founded by Clara Barton and Adolphus Solomons.[25][26][9] | United States |
| 1884 | Conference | The Third International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[14] | Switzerland | |
| 1885 | January 13 | Organization | The Bulgarian Red Cross is established.[8] | Bulgaria |
| 1885 | March 13 | Organization | The Salvadorean Red Cross Society is established.[8] | El Salvador |
| 1885 | April 4 | Organization | The Costa Rican Red Cross is established.[8] | Costa Rica |
| 1887 | Conference | The Fourth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Karlsruhe.[14] | Germany | |
| 1888 | December 31 | Organization | The Association Congolaise et Africaine is established. It would be recognized by the ICRC in 1889 but never part of the IFRC, ceasing to exist on 26 January 1909.[8] | Belgian Congo |
| 1892 | Conference | The Fifth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Rome.[14] | Italy | |
| 1893 | April 26 | Organization | The Thai Red Cross Society is established.[27] | Thailand |
| 1895 | January 30 | Organization | The Venezuelan Red Cross is established.[8] | Venezuela |
| 1896 | Organization | The Canadian Red Cross is established.[28] | Canada | |
| 1896 | July 22 | Organization | The South African Red Cross Society is established as the Transvaal Red Cross. The Orange Free State Red Cross would be founded in 1899 and a British Red Cross branch would be founded in Cape Colony in 1900. All would merge into an independent organization on 21 May 1913.[8] | South Africa |
| 1896 | October 10 | Organization | The Canadian Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent since 19 May 1909.[8] | Canada |
| 1896 | Organization | The Belarus Red Cross is established as the Grodno Province department of the Russian Red Cross. It would later become part of the Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies from 1926, gaining independence on 26 March 1992.[8] | Belarus | |
| 1897 | March 5 | Organization | The Uruguayan Red Cross is established.[8] | Uruguay |
| 1897 | Conference | The Sixth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Vienna.[14] | Austria | |
| 1899 | May–July | Treaty | The First Hague Peace Conference is convened. It adopts a convention on land warfare to which regulations are annexed.[14][29] | Netherlands |
| 1899 | Organization | Magen David Adom is established in Israel.[30] | Israel | |
| 1901 | Recognition | Henry Dunant is awarded the first Nobel Peace Prize.[9][31] | Sweden | |
| 1902 | Conference | The Seventh International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Saint Petersburg.[32] | Russia | |
| 1904 | March 10 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of China is established.[33] | China |
| 1905 | October 22 | Organization | The Republic of Korea National Red Cross is established. It would become a chapter of Japanese Red Cross after annexation in 1910. In South Korea, the Republic of Korea National Red Cross would function since 1947.[8] | Korea |
| 1906 | Treaty | The 1864 Geneva Convention is revised for the first time during a conference arranged by the Swiss Government.[34] | Switzerland | |
| 1907 | Conference | The Eighth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in London.[32] | United Kingdom | |
| 1907 | June–October | Treaty | The Second Hague Peace Conference of 1907 is held in The Hague, extending the scope of the Geneva Convention to naval warfare.[35] | Netherlands |
| 1907 | August 6 | Organization | The Mexican Red Cross is established.[8] | Mexico |
| 1908 | December 5 | Organization | The Brazilian Red Cross is founded.[8] | Brazil |
| 1909 | March 10 | Organization | The Cuban Red Cross is established.[8] | Cuba |
| 1912 | October 24 | Organization | The Egyptian Red Crescent Society is established.[30] | Egypt |
| 1912 | Conference | The Ninth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Washington, D.C. It establishes the respective wartime responsibilities of the National Societies and the ICRC "in providing protection and assistance not only for the wounded and sick but also for prisoners of war".[17] | United States | |
| 1914 | August 13 | Organization | The Australian Red Cross is established.[36][30] | Australia |
| 1914 | August 15 | Organization | Immediately after the start of the World War I, the ICRC esablishes its International Prisoners-of-War (POW) Agency.[37] | |
| 1914 | August 8 | Organization | The Luxembourg Red Cross is established.[38] | Luxembourg |
| 1915 | Organization | The New Zealand Red Cross is established as part of the British Red Cross. It becomes independent on 22 December 1931.[39][30] | New Zealand | |
| 1915 | July 30 | Organization | The Colombian Red Cross is established.[40] | Colombia |
| 1915 | August 8 | Organization | The Malagasy Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Madagascar |
| 1917 | January 13 | Organization | Red Cross Society of Panama is established.[30] | Panama |
| 1917 | Recognition | The Norwegian Nobel Committee awards the Nobel Peace Prize to the International Committee of the Red Cross, three years after the begining of World War I, during which there was no Nobel Peace Prize awarded.[41] It is the only Nobel Peace Prize awarded in the period from 1914 to 1918.[31] | Sweden | |
| 1917 | Organization | The Bolivian Red Cross is established.[30] | Bolivia | |
| 1918 | April 18 | Organization | The Ukrainian Red Cross Society is established. It would be incorporated as Part of the Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies from 1926, regaining independency on 28 October 1992.[30][42] | Ukraine |
| 1918 | September 8 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Georgia is established. It would be absorbed as part of the Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies in 1926, regaining indepencence on 26 March 1992.[30] | Georgia |
| 1918 | November 20 | Organization | The Latvian Red Cross is established.[43] | Latvia |
| 1919 | January 12 | Organization | The Lithuanian Red Cross Society is established. It would be absorbed as part of the Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies in 1940, later becoming independent.[30] | Lithuania |
| 1919 | January 22 | Organization | The Liberian Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Liberia |
| 1919 | February 6 | Organization | The Czech-Slovak Red Cross is established.[30] | Czechoslovakia |
| 1919 | February 12 | Organization | The Estonia Red Cross is established. It would be absorbed as part of the Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies from 1940; later becoming independent.[30] | Estonia |
| 1919 | February 14 | Organization | The Slovak Red Cross is established. It would be reformed in 1939 and again in 1993.[30] | Slovakia |
| 1919 | April 27 | Organization | The Polish Red Cross is established.[30] | Poland |
| 1919 | May 5 | Organization | The League of Red Cross Societies is established in Paris. The Articles of Association are signed by the governors of the Red Cross Societies of France, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. In June, the Covenant of the League of Nations is signed, with its own historic article containing an undertaking by member states to encourage and promote the formation of and cooperation between Red Cross Societies.[30] | France |
| 1919 | November 12 | Organization | The Paraguayan Red Cross is established.[30] | Paraguay |
| 1919 | Organization | The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) is founded in Paris in the aftermath of World War I.[5] | France | |
| 1920 | March 10 | Organization | The Azerbaijan Red Crescent Society is established.[44] | Azerbaijan |
| 1920 | March | Organization | The Indian Red Cross Society is established.[45] | India |
| 1920 | March | The First Meeting Of General Council Of The League Of Red Cross Societies is held.[4] | ||
| 1921 | October 4 | Organization | The Albanian Red Cross is established.[46] | Albania |
| 1921 | Conference | The Tenth International Conference is held in Geneva. A mandate results to the National Societies and to the ICRC to assist victims of civil war and internal disturbances.[17] | Switzerland | |
| 1922 | Organization | The Iranian Red Crescent Society is established.[47] | Iran | |
| 1922 | Program | The League of Red Cross Societies decides to focus its support to National Societies in three important fields: hygiene, nursing and youth.[4] | ||
| 1923 | Conference | The Eleventh International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 1925 | Conference | The Twelfth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 1926 | Organization | The Red Crescent Society of Turkmenistan is established.[48] | Turkmenistan | |
| 1928 | Conference | The Thirteenth International Conference is held in The Hague. The " Statutes of the International Red Cross " is adopted, which provides the Movement with a structural, operational and legal framework.[17] | Netherlands | |
| 1928 | Organization | The International Council is created to coordinate cooperation between the ICRC and the League of Red Cross Societies.[2] | ||
| 1929 | July 27 | Treaty | The Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War, Geneva July 27, 1929 is adopted. The Convention does not replace but only completes the provisions of the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907. It is the predecessor of the Third Geneva Convention signed in 1949.[49] | |
| 1930 | Conference | The Fourteenth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Brussels.[32] | Belgium | |
| 1932 | April 1 | Organization | The Iraqi Red Crescent Society is established.[50] | Iraq |
| 1932 | May 12 | Organization | The Haiti Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Haiti |
| 1934 | January 10 | Organization | The Nicaraguan Red Cross is established.[30] | Nicaragua |
| 1934 | April 4 | Organization | The Afghan Red Crescent Society is established.[51] | Afghanistan |
| 1934 | Conference | The Fifteenth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Tokyo.[32] | Japan | |
| 1935 | Organization | The Ethiopian Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Ethiopia | |
| 1936 | Organization | The Sri Lanka Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent since 1 April 1949.[52] | Sri Lanka | |
| 1937 | April 1 | Organization | The Myanmar Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Myanmar |
| 1937 | September 24 | Organization | The Honduran Red Cross is established.[52] | Honduras |
| 1937 | Organization | The Sierra Leone Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent since 16 August 1962.[52] | Sierra Leone | |
| 1938 | Conference | The Sixteenth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in London. A convening of a Diplomatic Conference to draw up a new Geneva Convention affording better protection to civilian victims of war is requested.[17] | United Kingdom | |
| 1938 | Organization | The Kazakh Red Crescent is established as part of Soviet Alliance of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies. It would become independent on 26 March 1992.[52] | Kazakhistan | |
| 1939 | June 16 | Organization | The Mongolian Red Cross Society is established.[52][53][54] | Mongolia |
| 1939 | July 6 | Organization | The Irish Red Cross is established.[52] | Ireland |
| 1939 | Organization | The Papua New Guinea Red Cross Society is established as part of the Australian Red Cross. It would become independent on 7 April 1976.[52] | Papua New Guinea | |
| 1939 | July 12 | Organization | The Trinidad and Tobago Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent on 5 May 1963.[55] | Trinidad and Tobago |
| 1939 | Organization | The The Bahamas Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent on 23 June 1975.[52] | Bahamas | |
| 1939 | The League of Red Cross Societies moves headquarters from Paris to Geneva at outbreak of World War Two.[2] | Switzerland | ||
| 1940 | June 20 | Organization | The Suriname Red Cross is established as part of the Netherlands Red Cross. It would become independent on 1975.[52] | Suriname |
| 1941 | January | The American Red Cross is requested by the United States Government to begin a blood-donor program to provide ready and ample supplies of blood plasma and serum albumin for transfusions for wounded soldiers. More than 13 million donations are collected.[56] | United States | |
| 1941 | Organization | The Antigua and Barbuda Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent on 22 July 1983.[52] | Antigua and Barbuda | |
| 1941 | Organization | The Uganda Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent on 30 July 1964.[52] | Uganda | |
| 1941 | Organization | The Mauritius Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross. It would become independent on 18 December 1973.[52] | Mauritius | |
| 1942 | Organization | The Nigerian Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 29 September 1960.[52][57] | Nigeria | |
| 1942 | February 22 | Organization | The Saint Kitts and Nevis Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 24 July 1985.[52] | Saint Kitts and Nevis |
| 1942 | May 30 | Organization | The Syrian Arab Red Crescent is established.[52] | Syria |
| 1942 | The Red Cross reveals that Japan has refused free passage of ships carrying food, medicine, and other necessities for American prisoners of war held by Japan.[56] | Japan | ||
| 1943 | The Nazi Schutzstaffel arranges Theresienstadt concentration camp as a "model ghetto" for fooling Red Cross representatives about the ongoing Holocaust and the Nazi plan to murder all Jews. The Nazified German Red Cross visit the ghetto and file the only accurate report on the ghetto, describing overcrowding and undernourishment. | Czechia | ||
| 1944 | Recognition | The International Committee of the Red Cross is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for the second time.[31] | Sweden | |
| 1945 | March 17 | Organization | The Red Cross of Macedonia is established as part of the Yugoslav Red Cross. gaining independent on 21 May 1992.[52] | North Macedonia |
| 1945 | April 30 | Organization | The Liechtenstein Red Cross is established.[52] | Lichtenstein |
| 1945 | July 9 | Organization | The Lebanese Red Cross is established.[58] | Lebanon |
| 1945 | September 17 | Organization | The Indonesian Red Cross Society is established as the Netherlands Red Cross Indonesia Section, gaining independence on 16 January 1950.[52][59] | Indonesia |
| 1946 | October 18 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea is established.[52] | North Korea |
| 1946 | November 23 | Organization | The Vietnam Red Cross Society is established.[52] | Vietnam |
| 1947 | January 13 | Organization | The Philippine Red Cross is established.[52][60] | Philippines |
| 1947 | December 20 | Organization | The Pakistan Red Crescent Society is established.[52] | Pakistan |
| 1947 | December 27 | Organization | The Jordan National Red Crescent Society is established.[52] | Jordan |
| 1948 | Organization | The Botswana Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 17 January 1968.[52] | Botswana | |
| 1948 | March 3 | Organization | The Red Cross of Monaco is established.[61] | Monaco |
| 1948 | Organization | The Brunei Darussalam Red Crescent Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 1 August 1983.[52] | Brunei | |
| 1948 | Organization | The Gambia Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 1 October 1966.[61] | Gambia | |
| 1948 | Conference | The Seventeenth International Conference is held in Stockholm, the first after the Second World War. The representatives of 50 governments, 52 National Societies and the then League (today International Federation) endorse the ICRC's proposals for the revision of the three existing Geneva Conventions and the adoption of a fourth Convention, this last for the protection of civilians in wartime. The four Conventions would be adopted the following year.[17] | Sweden | |
| 1948 | Organization | The Malaysian Red Crescent Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 22 November 1957.[52][62] | Malaysia | |
| 1948 | Organization | The Guyana Red Cross Societ is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 29 December 1967.[52] | Guyana | |
| 1948 | Organization | The Jamaica Red Cross is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independece on 9 July 1964.[61] | Jamaica | |
| 1948–1950 | Program | The League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (LORCS), at the request of the United Nations, launches the first relief operation setting up and running refugee camps for Palestinians, in Lebanon, Syria and Jordan. | Lebanon, Syria, Jordan | |
| 1949 | March 16 | Organization | The Saint Lucia Red Cross is established.[61] | Saint Lucia |
| 1949 | August 12 | Treaty | The Second, Third and Fourth Geneva Convention are adopted. The Second Geneva Convention "for the Amelioration of the Condition of Wounded, Sick and Shipwrecked Members of Armed Forces at Sea" protects wounded, sick and shipwrecked military personnel at sea during war.[63][64] The Third Geneva Convention, relative to the treatment of prisoners of war, precisely defines the conditions and places of captivity, particularly with regard to the labour of prisoners of war, their financial resources, the relief they receive, and the judicial proceedings instituted against them.[64] The Third Geneva Convention replaces the 1929 Geneva Convention that deals with prisoners of war.[65] The Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War (Fourth Geneva Convention) affords protection to civilians, including in occupied territory. It is composed of 159 articles, and contains a short section concerning the general protection of populations against certain consequences of war. While the first three conventions deal with combatants, the Fourth Geneva Convention is the first to deal with humanitarian protections for civilians in a war zone.[6][64][66] | Switzerland |
| 1949 | Organization | The Zambia Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 22 April 1966.[61][67] | Zambia | |
| 1949 | Organization | The Tanzania Red Cross National Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 7 December 1962.[61] | Tanzania | |
| 1949 | September 30 | Organization | The Singapore Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 6 April 1973.[61] | Singapore |
| 1949 | July 15 | Organization | The Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Red Cross is established as part of the British Red Cross committee, gaining independence on 15 May 1984.[61] | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines |
| 1949 | October 8 | Organization | The Red Cross of the Republic of San Marino is established.[61] | San Marino |
| 1950 | Organization | The Belize Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 18 August 1983.[61] | Belize | |
| 1950 | Organization | The Cyprus Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 1 November 1969, and recognition by the ICRC on 23 February 2012.[61] | Cyprus | |
| 1950 | Organization | The Lesotho Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 17 November 1967.[61] | Lesotho | |
| 1950 | July 12 | Organization | The Hong Kong Red Cross is established as a branch of the British Red Cross. On 1 July 1997, upon the return of Hong Kong's sovereignty to China, the HKRC would change its affiliation to become a highly autonomous branch of the Red Cross Society of China.[68] | Hong Kong |
| 1951 | October 27 | Organization | The Republic of Vietnam Red Cross is established.[61] | Vietnam |
| 1951 | Organization | The Solomon Islands Red Cross is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 15 July 1983.[61] | Solomon Islands | |
| 1952 | Organization | The Burkinabe Red Cross Society is established as part of the French Red Cross, gaining independence on 31 July 1961.[61] | Burkina Faso | |
| 1952 | July–August | Conference | The Eighteenth International Conference is held in Toronto. It revises the " Statutes of the International Red Cross".[17] | Canada |
| 1952 | October 23 | Organization | The German Red Cross (East Germany) is established, reuniting with the German Red Cross on 3 January 1991.[61] | Germany |
| 1952 | Organization | The Malta Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 24 October 1991.[61] | Malta | |
| 1952 | Organization | The Samoa Red Cross Society is established as part of the New Zealand Red Cross, gaining independence on 1 January 1983.[61] | Samoa | |
| 1954 | Organization | The Fiji Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 27 September 1971.[61] | Fiji | |
| 1954 | Organization | The Somali Red Crescent Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 27 April 1963.[61] | Somalia | |
| 1955 | January 1 | Organization | The Lao Red Cross Society is established.[61] | Lao |
| 1955 | February 18 | Organization | The Cambodian Red Cross is established.[61] | Cambodia |
| 1955 | Organization | The Grenada Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 21 August 1981.[61] | Grenada | |
| 1956 | January 11 | Organization | The Algerian Red Crescent Society is established.[61][69] | Algeria |
| 1956 | Organization | The Tunisian Red Crescent is established.[61] | Tunisia | |
| 1956 | October 30 | Organization | The Sudanese Red Crescent is established.[61] | Sudan |
| 1957 | October–November | Conference | The Nineteenth Conference of the Red Cross is held in New Delhi.[11] | India |
| 1957 | October 1 | Organization | The Ghana Red Cross Society is established.[61][70] | Ghana |
| 1957 | October 5 | Organization | The Libyan Red Crescent is established.[61] | Libya |
| 1957 | December 24 | Organization | The Moroccan Red Crescent is established.[61] | Morocco |
| 1958 | January 28 | Organization | The Dominica Red Cross Society is established.[61] | Dominica |
| 1958 | Organization | The Yemen Red Crescent Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 16 July 1970.[61] | Yemen | |
| 1959 | February 26 | Organization | The Togolese Red Cross is established.[71][61] | Togo |
| 1959 | July | Organization | The Red Cross of Benin is established.[61] | Benin |
| 1960 | February 17 | Organization | The Barbados Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 31 July 1969.[61] | Barbados |
| 1960 | April 30 | Organization | The Cameroon Red Cross Society is established.[72] | Cameroon |
| 1960 | October 30 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Côte d’Ivoire is established.[72] | Côte d’Ivoire |
| 1961 | Organization | The Tonga Red Cross Society is established.[72] | Tonga | |
| 1962 | July | Organization | The Rwandan Red Cross is established.[72] | Rwanda |
| 1963 | Organization | The International Committee of the Red Cross is awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for the third time.[31] | Sweden | |
| 1963 | January 29 | Organization | The Senegalese Red Cross Society is established.[72] | Senegal |
| 1963 | The League of Red Cross Societies launches a mass development program, involving countries recently-independent or about to gain independence, in the Caribbean and Africa.[2] | Caribbean, Africa | ||
| 1963 | June 8 | Organization | The Saudi Red Crescent Authority is established.[72][73] | Saudi Arabia |
| 1963 | July 16 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Niger is established.[72] | Niger |
| 1963 | July 31 | Organization | The Burundi Red Cross is established.[72] | Burundi |
| 1963 | September 4 | Organization | The Nepal Red Cross Society is established.[72] | Nepal |
| 1963 | Organization | The Red Cross of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is established.[74] | Congo DR | |
| 1964 | Organization | The Uganda Red Cross Society is established.[75] | Uganda | |
| 1964 | February 22 | Organization | The Congolese Red Cross (Brazzaville) is established.[72] | Republic of the Congo |
| 1965 | Organization | The Kiribati Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 12 December 1989.[72] | Kiribati | |
| 1965 | Organization | The Kenya Red Cross Society is established.[76] | Kenya | |
| 1965 | Renaming | The League of Red Cross Societies is renamed to the "League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies" to reflect the growing number of national societies operating under the Red Crescent symbol.[4] | ||
| 1965 | August 24 | Organization | The Mali Red Cross is established.[72] | Mali |
| 1965 | Conference | The Twentieth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Vienna. Seven basic principles are adopted, which should be shared by all parts of the Movement.[17] | Austria | |
| 1965 | The Fundamental Principles of the Red Cross are proclaimed in Vienna: Humanity, Impartiality, Neutrality, Independence, Voluntary Service, Unity, Universality. The principles would be incorporated in 1986 into the Statutes of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement.[2][77] | Austria | ||
| 1966 | January 10 | Organization | The Kuwait Red Crescent Society is established.[78] | Kuwait |
| 1966 | October 25 | Organization | The Central African Red Cross Society is established.[72] | Central African Republic |
| 1967 | January 13 | Organization | The Malawi Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Malawi |
| 1968 | December 26 | Organization | The Palestine Red Crescent Society is established.[79][72] | Palestine |
| 1969 | Conference | The Twenty-first International Conference is held in Istanbul. The "Principles and Rules for Red Cross Disaster Relief" are adopted. Also, a mandate is introduced to begin drafting new instruments to adapt humanitarian law to new forms of armed conflict.[17] | Turkey | |
| 1970 | January 28 | Organization | The Bahrain Red Crescent Society is established.[72] | Bahrain |
| 1970 | October 13 | Organization | The Baphalali Swaziland Red Cross Society is established.[80] | Swaziland |
| 1970 | September 22 | Organization | The Mauritanian Red Crescent is established.[72] | Mauritania |
| 1970 | Organization | The Red Cross of Chad is established as a provisional committee, being granted legal status in 1972 and becoming a National Society on 1 June 1983.[72] | Chad | |
| 1972 | Reform | Canadian civil servant Donald Tansley is appointed to lead study into future role and other aspects of the Red Cross.[2] | ||
| 1973 | March 31 | Organization | The Bangladesh Red Crescent Society is established.[81][82] | Bangladesh |
| 1973 | Conference | The Twenty-second International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Teheran. The ICRC presents two draft protocols additional to the Geneva Conventions.[17] | Iran | |
| 1975 | July 19 | Organization | The Red Cross of Cape Verde is established.[82] | Cape Verde |
| 1975 | Conference | The First World Red Cross Conference on Peace is held in Belgrade.[2] | Yugoslavia | |
| 1975 | Reform | The "Tansley Report" is published. It defines basic role of Red Cross as "provision of emergency help, on an unconditional and impartial basis, whenever and wherever human needs for protection and assistance exist because of natural disaster and conflict".[2] | ||
| 1976 | January 20 | Organization | The Sao Tome and Principe Red Cross is established.[82][83] | São Tomé and Príncipe |
| 1977 | Organization | The Tuvalu Red Cross Society is established as part of the British Red Cross, gaining independence on 1 May 1981.[82] | Tuvalu | |
| 1977 | August 1 | Organization | The Red Crescent Society of Djibouti is established.[82] | Djibouti |
| 1977 | Conference | The Twenty-third International Conference is held in Bucharest. Measures to expedite international relief are adopted.[17] | Romania | |
| 1977 | December 2 | Organization | Red Cross Society of Guinea-Bissau is established.[82] | Guinea-Bissau |
| 1978 | Organization | The Qatar Red Crescent Society is established.[82] | Qatar | |
| 1978 | March 16 | Organization | The Angola Red Cross are formed.[82] | Angola |
| 1980 | December 20 | Organization | The Andorran Red Cross is established.[82] | Andorra |
| 1981 | Organization | The Zimbabwe Red Cross Society is established.[84] | Zimbabwe | |
| 1981 | July 10 | Organization | The Mozambique Red Cross Society is established.[82] | Mozambique |
| 1981 | Conference | The Twenty-fourth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Manila.[32] | Philippines | |
| 1982 | June | Organization | The The Comoros Red Crescent is established.[82] | Comoros |
| 1983 | January 31 | Organization | The Red Crescent Society of the United Arab Emirates is established.[82] | United Arab Emirates |
| 1983 | Renaming | The League of Red Cross Societies is renamed League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies on 11 October 1983.[82][5] | ||
| 1984 | January 26 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Guinea is established. It would be renamed Red Cross of Equatorial Guinea on 16 October 1985.[82] | Equatorial Guinea |
| 1986 | Conference | The Twenty-fifth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva, amidst a deteriorating socio-political situation worldwide. The Conference adopts the revised "Statutes of the International Red Cross ", which become the Statutes of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement.[17] | Switzerland | |
| 1989 | Organization | The Seychelles Red Cross Society is established.[30] | Seychelles | |
| 1989 | May 5 | Organization | The Cook Islands Red Cross Society is established.[82] | Cook Isands |
| 1989 | Growth | With an average of 590 delegates working in 48 delegations, ICRC is active in nearly 90 countries in Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America and the Middle East providing protection and assistance to the victims of armed conflicts.[3] | ||
| 1990 | October 16 | The United Nations General Assembly decides to invite the ICRC to take part in its proceedings as an observer. A resolution to this effect, which is sponsored by 138 United Nations members, is adopted without a vote.[3] | ||
| 1991 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Eritrea is established.[82] | Eritrea | |
| 1991 | November 27 | Renaming | The League of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is renamed International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies.[5][82] | |
| 1992 | February 8 | Organization | The Namibia Red Cross Society is established.[82] | Namibia |
| 1992 | December | Policy | Non-Swiss individuals are allowed to serve as ICRC delegates abroad, a task which was previously restricted to Swiss citizens.[85] | |
| 1993 | June 5 | Organization | The Czech Red Cross is established.[82] | Czechia |
| 1995 | January 1 | Staff | The ICRC has twenty-two members, all of whom are Swiss.[86] | |
| 1995 | June 2 | Organization | The Palau Red Cross Society is established.[87] | Palau |
| 1995 | July 12 | Conference | The Twenty-sixth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva. It focuses on practical measures to enhance respect for international humanitarian law with special attention to the needs of the civilian population and the most vulnerable groups such as children and women.[17] | Switzerland |
| 1996 | July 3 | Organization | The Gabonese Red Cross Society is established.[87] | Gabon |
| 1997 | Treaty | The ICRC and the IFRC sign the Seville Agreement which provides a framework for effective cooperation and partnership between members of the Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement.[88] | ||
| 1998 | January 31 | Organization | The Micronesia Red Cross is established.[87] | Micronesia |
| 1999 | Conference | The Twenty-seventh International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 1999 | Program | The 1999 International Conference asks the International Federation of Red Cross Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) to study “humanitarian impacts of climate change.”[4] | ||
| 2000 | Organization | The Timor-Leste Red Cross Society is established.[87] | East Timor | |
| 2001 | Organization | The Red Cross Society of Bosnia and Herzegovina is established.[30] | Bosnia and Herzegovina | |
| 2002 | Background | Switzerland joins the United Nations.[85] | Switzerland | |
| 2003 | Conference | The Twenty-eighth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 2004 | The IFRC begins huge campaign, its largest mission to date after the tsunami disaster in South Asia, raising more than 3.1 billion Swiss Francs for the relief and recovery operation.[89] | |||
| 2006 | Conference | The Twenty-ninth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva. It amends the statutes of the Movement to take into account the creation of the new emblem.[10] | Switzerland | |
| 2007 | Conference | The Thirtieth International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 2009 | August 16 | Organization | The Maldivian Red Crescent is established.[90][87] | Maldives |
| 2011 | July 9 | Organization | The South Sudan Red Cross Society is established.[87] | South Sudan |
| 2011 | Conference | The Thirty-first International Conference of the Red Cross is held in Geneva.[32] | Switzerland | |
| 2013 | Study | According to the IFRC’s World Disasters Report for the year, which focuses on technology and humanitarian action, the communications revolution is having a profound impact on the way people respond to emergencies.[72] | ||
| 2015 | Financial | The overall budget of the ICRC for the year stands at US$ 1.85 billion.[91] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
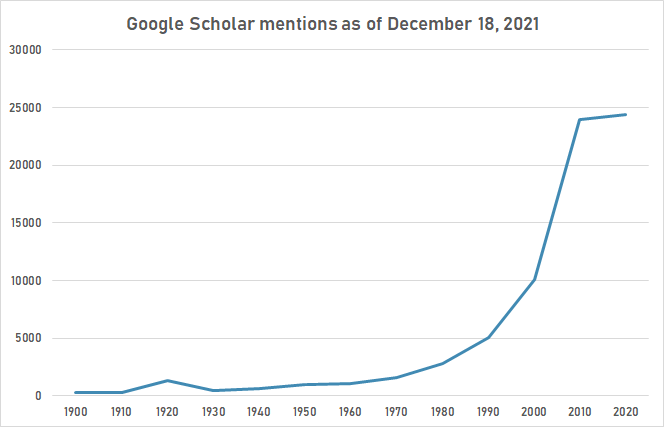
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of December 18, 2021.
| Year | "Red Cross" |
|---|---|
| 1900 | 315 |
| 1910 | 291 |
| 1920 | 1,330 |
| 1930 | 491 |
| 1940 | 670 |
| 1950 | 987 |
| 1960 | 1,030 |
| 1970 | 1,600 |
| 1980 | 2,810 |
| 1990 | 5,060 |
| 2000 | 10,100 |
| 2010 | 24,000 |
| 2020 | 24,400 |
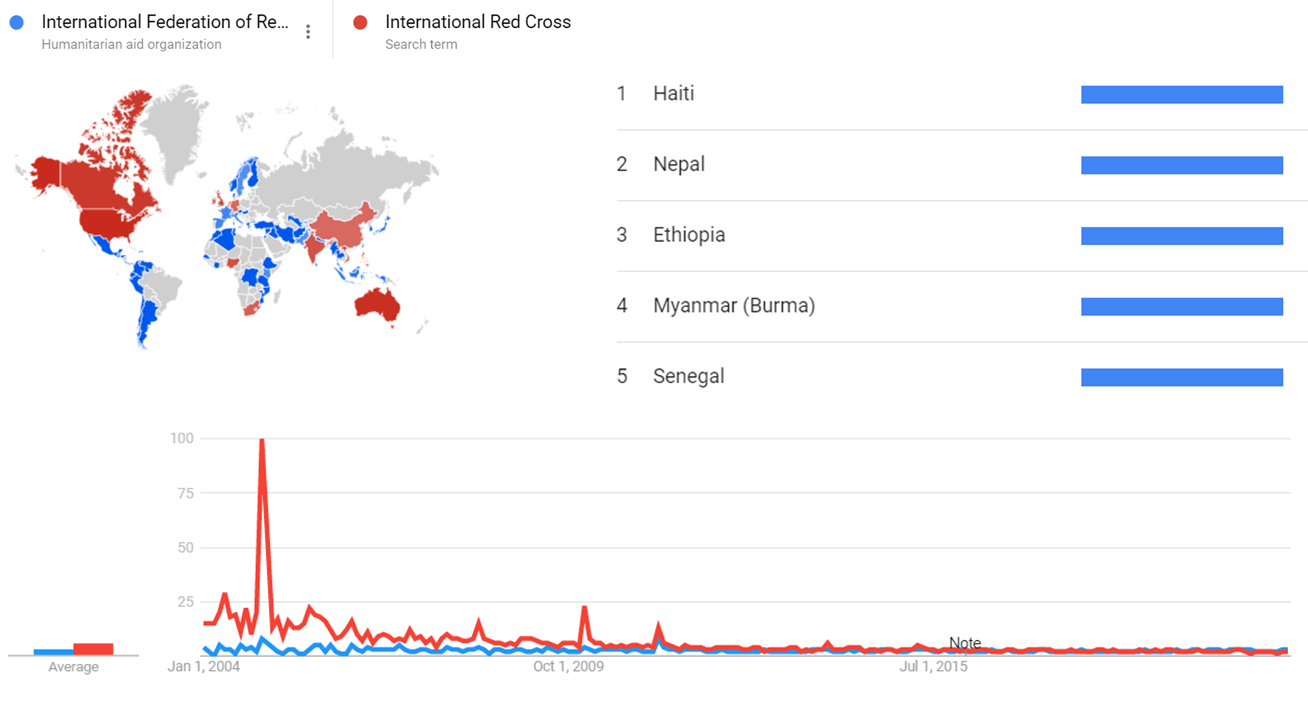
Google Trends
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (Humanitarian aid organization) and International Red Cross (Search Term) from January 2004 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[92]
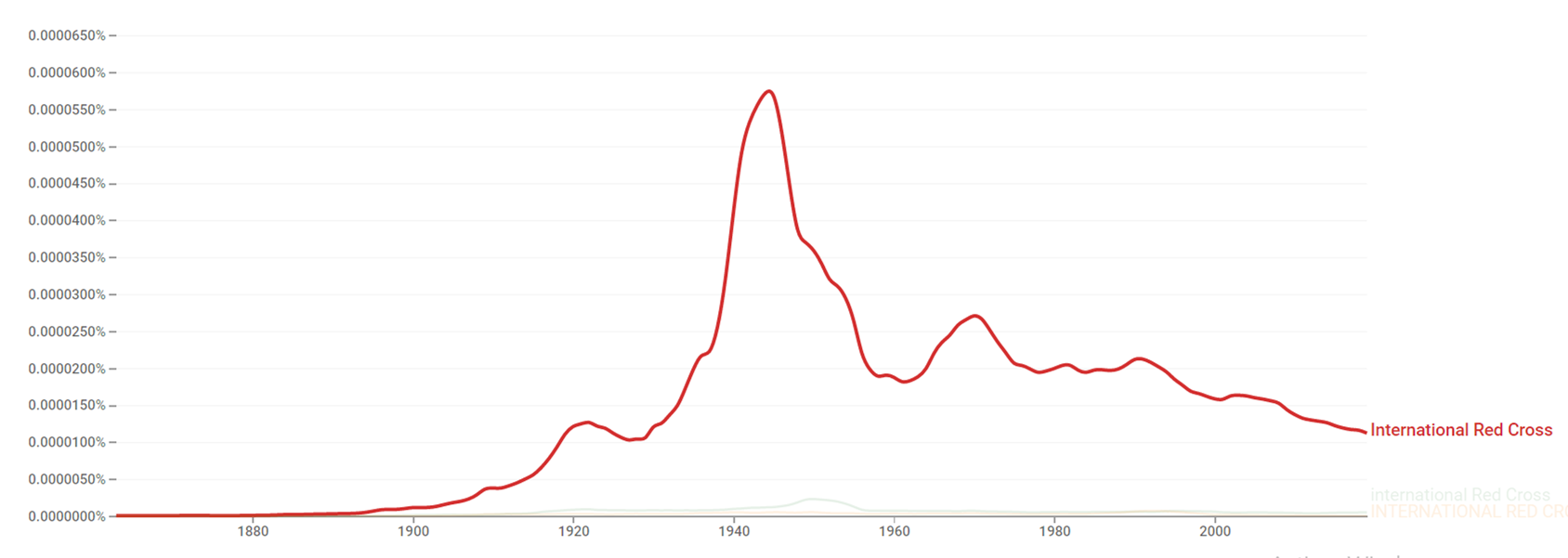
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for International Red Cross adoption from 1863 to 2019.[93]
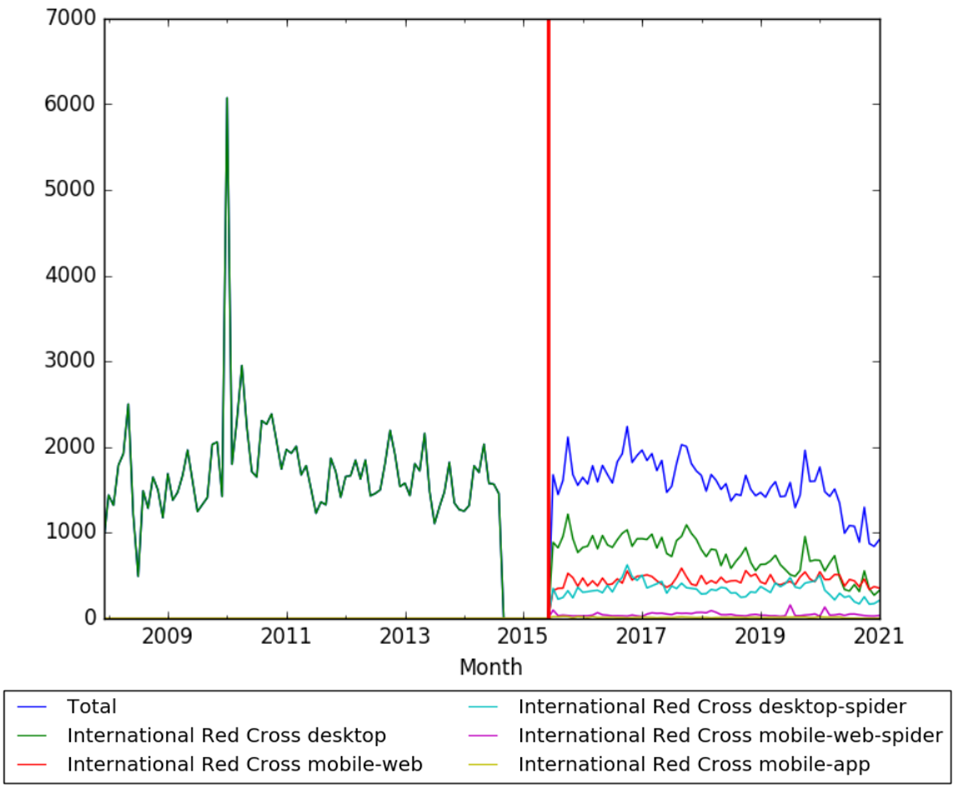
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article International Red Cross on desktop from December 2007, and on mobile-web, desktop-spider,mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015; to January 2021.[94]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "History". ifrc.org. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "A timeline of the Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement". redcross.int. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "The ICRC is granted observer status at the United Nations". icrc.org. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 "100 YEARS OF HOPE". media.ifrc.org. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "The Formation of the IFRC". ifrc.org. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "About the International Committee of the Red Cross". icrc.org. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "The beginning of the Red Cross". redcross.org.uk. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ 8.00 8.01 8.02 8.03 8.04 8.05 8.06 8.07 8.08 8.09 8.10 8.11 8.12 8.13 8.14 8.15 8.16 8.17 8.18 8.19 8.20 8.21 8.22 8.23 8.24 8.25 8.26 8.27 8.28 8.29 8.30 8.31 8.32 8.33 8.34 8.35 8.36 8.37 "A movement is born". redcross.int. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 "International Red Cross founded". history.com. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "The history of the emblems". icrc.org. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "The International Conference of the Red Cross and Red Crescent: challenges, key issues and achievements" (PDF). icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "WHAT WE DO". croix-rouge.fr. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Italian Red Cross". linkedin.com. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 "A timeline of the Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement". redcross.int. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ↑ "Swedish Red Cross". media.ifrc.org. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "150 years of humanitarian aid – with a dark side". swissinfo.ch. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 17.00 17.01 17.02 17.03 17.04 17.05 17.06 17.07 17.08 17.09 17.10 17.11 17.12 17.13 "The four-yearly International Conference of the Red Cross and Red Crescent". icrc.org. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "150 years of the Red Cross in the Netherlands – and a history lesson in the 'Hall of Knights'". climatecentre.org. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Türk Kızılayı Aydın Şube Başkanlığı (Turkish Red Crescent Aydin City Branch)". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "British Red Cross Society". culture24.org.uk. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Romanian Red Cross Marks 140th Anniversary". romaniajournal.ro. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ The European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia (Spencer C. Tucker ed.).
- ↑ "CROSS OF MERIT OF THE FINNISH RED CROSS, SILVER MEDAL". medalbook.com. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Hellenic Red Cross". redcross.gr. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "American National Red Cross is founded, May 21, 1881". politico.com. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "American Red Cross founded". history.com. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "The King who gave birth to the Thai Red Cross". english.redcross.or.th. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Getting Started: 1896-1913". redcross.ca. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Convention (IV) respecting the Laws and Customs of War on Land and its annex: Regulations concerning the Laws and Customs of War on Land. The Hague, 18 October 1907". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ 30.00 30.01 30.02 30.03 30.04 30.05 30.06 30.07 30.08 30.09 30.10 30.11 30.12 30.13 30.14 30.15 30.16 30.17 30.18 30.19 30.20 30.21 30.22 30.23 "Making history". redcross.int. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 31.3 "International Committee of the Red Cross History". nobelprize.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ 32.00 32.01 32.02 32.03 32.04 32.05 32.06 32.07 32.08 32.09 32.10 "International Conferences of the Red Cross and Red Crescent, 1867 - 2007". icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ Simon, Karla W. Civil Society in China: The Legal Framework from Ancient Times to the "New Reform Era".
- ↑ "Geneva Convention". history.com. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "Convention (X) for the Adaptation to Maritime Warfare of the Principles of the Geneva Convention. The Hague, 18 October 1907". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "Timeline of Australian Red Cross". redcross.org.au. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "ICRC in WWI: overview of activities". icrc.org. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "The Beginnings". croix-rouge.lu. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "RED CROSS SOCIETY". teara.govt.nz. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Cruz Roja Colombiana, 100 años de historias". humanitarianresponse.info. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Red Cross is awarded Nobel Peace Prize". history.com. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "Ukrainian Red Cross Society". redcross.org.ua. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "The exhibition Latvian Red Cross - 100". mvm.lv. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "About Us". eng.redcrescent.az. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "Origin". indianredcross.org. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "The Historical and Legal Development of Nonprofit Sector in Albania: Case Study - Red Cross Albania". researchgate.net. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "IRC". rcs.ir. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Red Crescent Society of Turkmenistan". tgymj.gov.tm. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War. Geneva, 27 July 1929". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent". data2.unhcr.org. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "150 years of humanitarian action". redcross.int. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ 52.00 52.01 52.02 52.03 52.04 52.05 52.06 52.07 52.08 52.09 52.10 52.11 52.12 52.13 52.14 52.15 52.16 52.17 52.18 52.19 52.20 52.21 52.22 52.23 52.24 52.25 52.26 "150 years of humanitarian action". redcross.int. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "IFRC Mongolia Program Overview 2019". reliefweb.int. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "Mongolian Red Cross Society" (PDF). preventionweb.net. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "BLINK BMOBILE DONATES 15 NETBOOKS TO TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO RED CROSS". tstt.co.tt. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 "Red Cross announces Japan refuses passage of supplies for U.S. POWs". history.com. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "WHO WE ARE". redcrossnigeria.org. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "History of Lebanese Red Cross". redcross.org.lb. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "Cross Red Indonesian" (PDF). rcrc-resilience-southeastasia.org. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Today in Philippine History, April 15, 1947, the Philippine National Red Cross was established". kahimyang.com. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 61.00 61.01 61.02 61.03 61.04 61.05 61.06 61.07 61.08 61.09 61.10 61.11 61.12 61.13 61.14 61.15 61.16 61.17 61.18 61.19 61.20 61.21 61.22 61.23 61.24 61.25 61.26 61.27 61.28 61.29 61.30 61.31 61.32 61.33 "Keeping it clean". redcross.int. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "Malaysian Red Crescent At A Glance". redcrescent.org.my. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "Treaties, States Parties and Commentaries". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 64.2 "The Geneva Conventions of 1949 and their Additional Protocols". icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ ICRC. "Convention (III) relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War. Geneva, 12 August 1949". Retrieved 5 March 2017.
The undersigned Plenipotentiaries of the Governments represented at the Diplomatic Conference held at Geneva from April 21 to August 12, 1949, for the purpose of revising the Convention concluded at Geneva on July 27, 1929, relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War [...]
- ↑ "Convention (IV) relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War. Geneva, 12 August 1949". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "An Integrated Approach to Combining a Measles Campaign with a Bed Net, Vitamin A and Mebendazole Campaign in Zambia" (PDF). coregroup.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Red Cross". redcross.org.hk. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ↑ "Presentation of the Algerian Red Crescent". fotw.info. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Ghana Red Cross Society Act, 1958". ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Togo 1959 100th Anniversary of International Red Cross". jppstamps.fandom.com. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 72.00 72.01 72.02 72.03 72.04 72.05 72.06 72.07 72.08 72.09 72.10 72.11 72.12 72.13 72.14 72.15 72.16 72.17 "The digital humanitarian". redcross.int. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ↑ "Emergency medicine in Saudi Arabia: a century of progress and a bright vision for the future". intjem.biomedcentral.com. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "Red Cross of the Democratic Republic of the Congo". media.ifrc.org. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ↑ Akaki, Tony. Mabira Forest Giveaway: A Path to Degenerative Development.
- ↑ "Kenya Red Cross Society (Kenya)". crwflags.com. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ "The Fundamental Principles of the Red Cross : commentary". icrc.org. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ↑ "A Journey of Philantrophy (1966 – 2018)". krcs.org.kw. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ "Palestine Red Crescent Society". palestinercs.org. Retrieved 2 July 2019.
- ↑ "BaphalaIi Swaziland Red Cross Society" (PDF). ihl-databases.icrc.org. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ↑ "Bangladesh Red Crescent Society". media.ifrc.org. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ 82.00 82.01 82.02 82.03 82.04 82.05 82.06 82.07 82.08 82.09 82.10 82.11 82.12 82.13 82.14 82.15 82.16 82.17 82.18 "Fundamental Principles". redcross.int. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ↑ Willemin, Georges; Heacock, Roger; Freymond, Jacques. The International Committee of the Red Cross.
- ↑ "Zimbabwe RC". redcrosszim.org.zw. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 "Swiss neutrality as viewed by the International Committee of the Red Cross". icrc.org. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- ↑ "The composition of the International Committee of the Red Cross". icrc.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 87.2 87.3 87.4 87.5 "Independence: one size does not fit all". redcross.int. Retrieved 12 July 2019.
- ↑ "Reinforcing Red Cross / Red Crescent cooperation in emergencies: the Seville Agreement". icrc.org. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ↑ "Indian Ocean tsunami". ifrc.org. Retrieved 18 July 2019.
- ↑ "Maldivian Red Crescent rises from the Tsunami". ifrc.org. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "The ICRC's funding and spending". reliefweb.int. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ↑ "International Red Cross". Google Trends. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ↑ "International Red Cross". books.google.com. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ↑ "International Red Cross". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 28 February 2021.