Difference between revisions of "Timeline of mobile telephony"
(→Visual data) |
(→Google Scholar) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Mobile telephony google schoolar.png|thumb|center|700px]] |
=== Google Trends === | === Google Trends === | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 11 August 2021
This is a timeline of mobile telephony, attempting to describe the evolution of mobile phone networks, as well as crucial mobile device releases in relation to novel functionality.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 1900s | Radio transmission is achieved by creating bursts of sparks generated by electrical voltages.[1] |
| 1930s | The idea of a cell phone begins.[2] |
| 1940s | Communication by mobile radios becomes more common. Most government agencies, as well as the rich people, own mobile radios.[3] AT&T and Bell Labs introduce cellular technology. However, mobile phones would not develop widespread use at the time.[4] US Signal Corps communicate via radio in field during World War 2.[5] |
| 1960s | Researchers develop the technology systems (like frequency reuse and handoff) that would lead to modern cellular networks.[4] In the United States, Bell Labs prepares a detailed plan for implementing the cellular system.[6] Soviet engineer Leonid Kupriyanovich develops very small mobile phones. |
| 1970s | 1G is developed by AT&T and Bell Labs early in the decade.[7] Nippon Telephone and Telegraph (NTT) in Japan and Ericsson in Sweden begin testing cellular technology and start designing equipment that would facilitate commercial service provision in their respective home markets.[8] The first mobile call is made.[9] |
| 1980s | 1G is deployed.[7][6] Mobile phone technology starts to be released commercially.[10] Adding text messaging functionality to mobile devices begins. |
| 1990s | Mobile telephony revolutionizes telecommunications during the decade.[11] 2G Second–generation wireless telephone technology becomes available, [12] bringing the first digital systems to be deployed.[10][7] Mobile phone operators start offering prepay mobile phones. European and American networks start to split apart and compete against one another.[4] The IBM Simon is introduced, being possibly the world’s first smartphone.[13] |
| 2000s | Apple introduces the iPhone. Android operating system launches. 3G technology starts deployment.[7] Between 2000 and 2003, the mobile phone experiences two of the biggest changes in its physical configuration: The introduction of QWERTY keyboard by BlackBerry as a popular standard, and the arrival of LCD touchscreens.[14] |
| 2010s | A massive development in smartphone technology takes place. 4G technology starts deployment.[7] Mobile telephony keeps extending into developing and least developed countries. 5G technology is still in development phase as no standard for its deployment has been concreted.[15] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
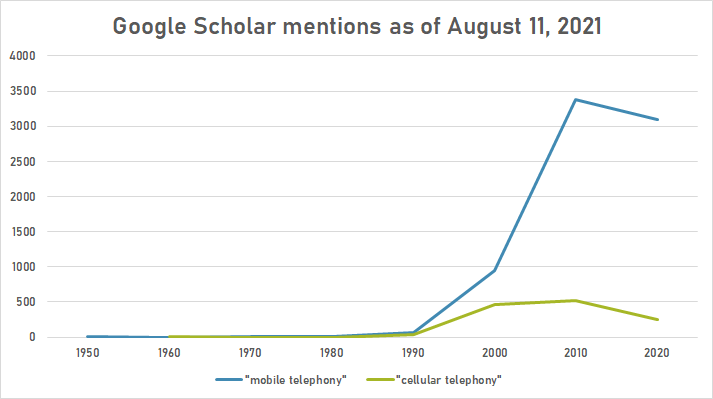
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of August 11, 2021.
| Year | "mobile telephony" | "cellular telephony" |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 3 | |
| 1960 | 1 | 2 |
| 1970 | 2 | 1 |
| 1980 | 11 | 1 |
| 1990 | 65 | 43 |
| 2000 | 954 | 468 |
| 2010 | 3,380 | 517 |
| 2020 | 3,090 | 244 |
Google Trends
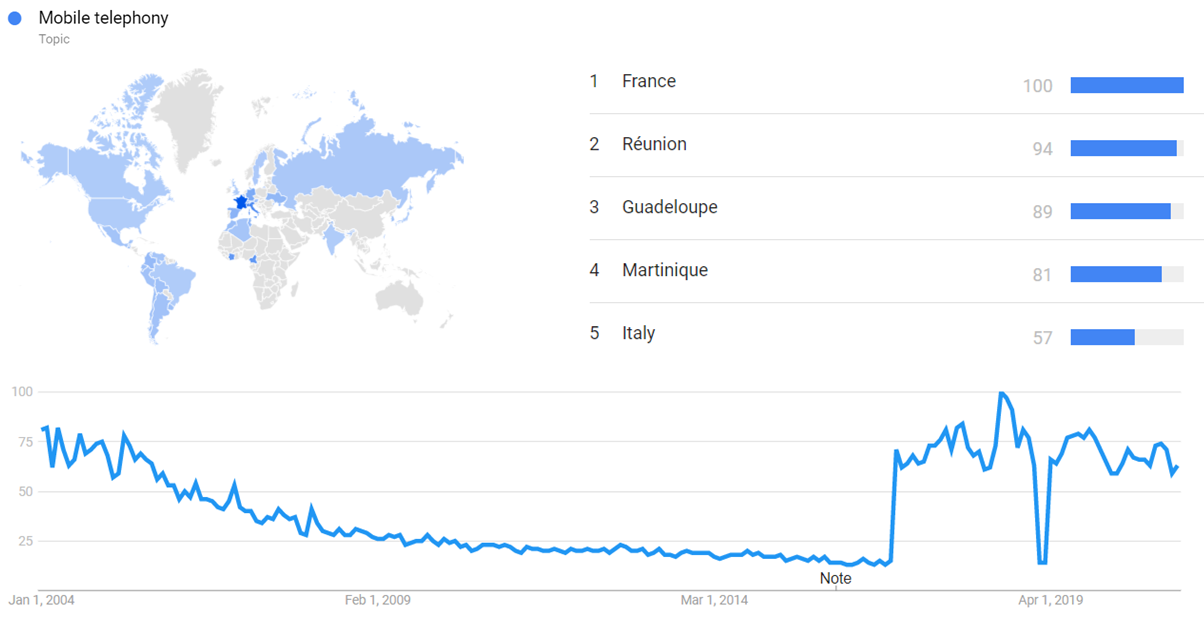
The image below shows Google Trends data for Mobile telephony (Topic), from January 2004 to March 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[16]
Google Ngram Viewer
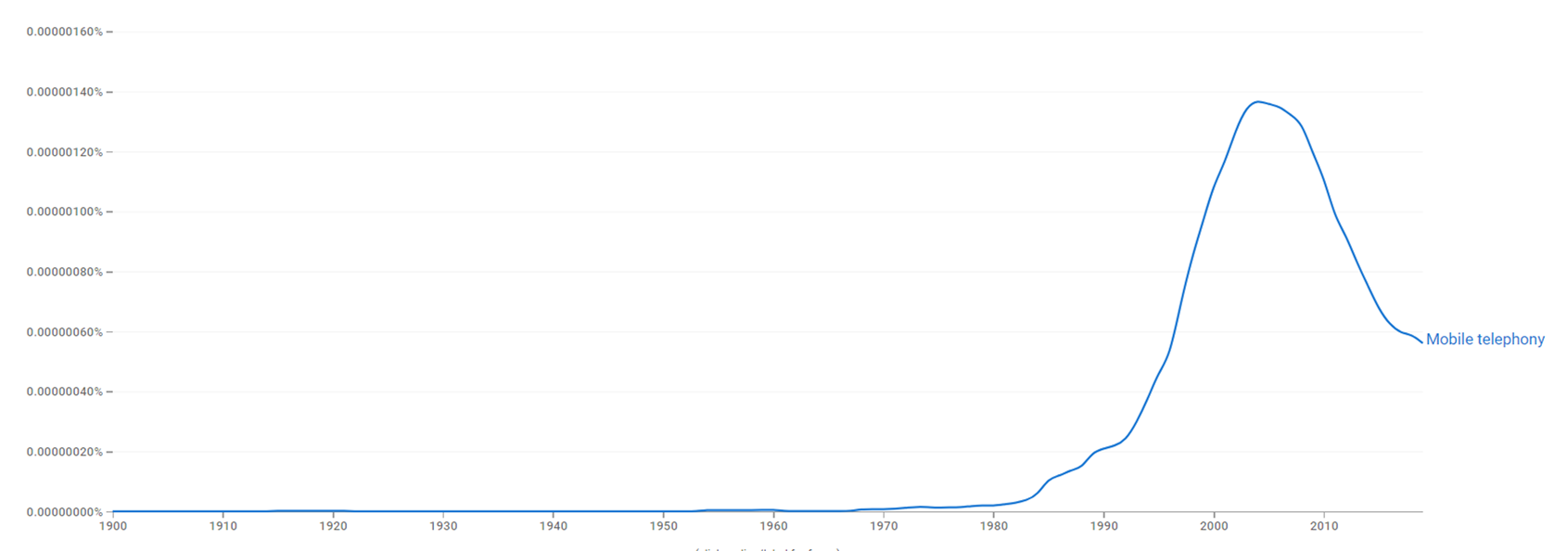
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for Mobile telephony, from 1900 to 2019.[17]
Wikipedia Views
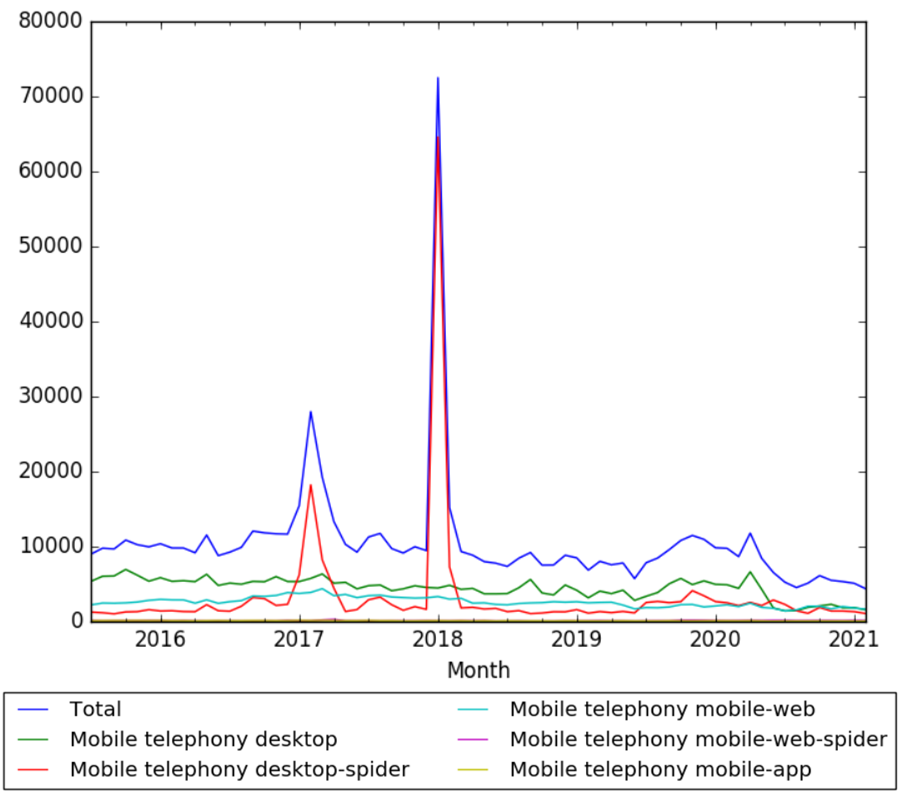
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Mobile telephony, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to February 2021.[18]
Full timeline
| Year | Event type | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1876 (March 10) | Prelude | Scottish-born Alexander Graham Bell, the inventor of the telephone, makes the first phone call.[9] | United States |
| 1894 | Prelude | Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi transmits signals over the distance of 2 kms.[19] | |
| 1906 | Prelude | Canadian-born inventor Reginald Fessenden manages to broadcast music through radio.[19] | United States |
| 1908 | Prelude | A man claims to have invented a wireless telephone. Being considered so crazy for this time, he is accused of fraud. The charges are later dropped.[4] | |
| 1921 | Prelude | The Detroit Police Department introduce mobile radios in their police cars, giving rise to the car–to–car radios. However, the system doesn't work very well at the time.[3][20] | United States |
| 1924 | Network technology | Wireless phones are tested on trains running between Berlin and Hamburg.[21] | Germany |
| 1926 | The first successful mobile telephony service is offered to first class passengers in trains of the Deutsche Reichsbahn on the route between Berlin and Hamburg.[22] | Germany | |
| 1940 | Technology | Second World War: Hand-held radio receivers become widely available, opening up communications in battlefields around the world.[4] | |
| 1945 | Network technology | The first service created just for mobile phones launches in Saint Louis, but the service doesn't work well and it does not last.[3][20] | United States |
| 1946 (June) | Network technology | American company Bell Labs begins to offer mobile telephone services on vehicles in Saint Louis. A few weeks later, AT&T matches Bell Labs, offering its Mobile Telephone Service (0G equivalent), at the time a wide range of mostly incompatible mobile telephone services with limited coverage areas and a small number of available channels.[4] | United States |
| 1946 | Network technology | Interconnection of mobile transmitters and receivers with the Public switched telephone network (PSTN) begins in the United States, with the introduction of Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company.[23] | United States |
| 1947 | Technology | Engineers at Bell Labs seek ways to implement cell service in vehicles, theorizing that hexagonal cells would work best for them. The first car phone service is attempted. A car phone service opens between Boston and New York, but this service soon fails.[3] The same year, base stations for mobile phones come into being when engineers from Bell Labs develop the first stations.[4] | United States |
| 1947 | Network technology | Bell Labs is the first company to propose a cellular radio telephone network.[1][6] | United States |
| 1948 | Service coverage | The Mobile Telephone Service, initially only available in Saint Louis, becomes now available in about 100 towns in the United States. Using this service, an estimated 5,000 customers place approximately 30,000 calls each week. Each call has to be manually connected by an operator. The system also functions similar to a Walkie-Talkie: a button must be pushed down talk, then released to listen. The Mobile Telephone Service requires about 36kg of equipment in the vehicle. Expensive, it costs approximately US$ 15 per month (same buying power as $154.76 in 2017) plus an additional $0.30 to $0.40 per local call. [4] | United States |
| 1952 | Network technology | A-Netz network is launched as a Mobile Radio Network in West Germany.[4][24] | West Germany |
| 1956 | Service launch | The first ever partly automatic car phone system, Mobile System A (MTA), is introduced in Sweden. [25][26][3] | Sweden |
| 1957–1961 | Product development | Soviet engineer Leonid Kupriyanovich develops a number of mobile phones that look surprisingly similar to modern mobile devices. One of these devices weighs just 70 grams and can fit into the palm of the hand.[4] | |
| 1959 | Network technology | The Post Office Radiophone Service is launched in Manchester. The system requires callers to connect through an operator. However, that operator could connect users to any subscriber across all of Great Britain.[4] | United Kingdom |
| 1960 | Network technology | Ericsson Company releases the first fully automated mobile telephone. Introduced in Sweden, the system, known in Swedish as Mobiltelefonisystem A (MTA), allows for automated connection from a rotary handset (that’s the circular dialing knob to me and you) mounted within a car, but requires an operator to forward calls.[19][27][27] | Sweden |
| 1962 | Network technology | AT&T develops a prototype for the first generation cellular mobile communications technology.[28] | United States |
| 1962 | Network technology | Swedish Mobiltelefonisystem A (MTA) is replaced by Mobiltelefonisystem B (MTB), which uses transistorized mobile sets. This system would last until 1983.[27] | Sweden |
| 1963 | Network technology | Altai mobile telephone system (системы "Алтай") is introduced as a pre-cellular 0G radiotelephone service in the Soviet Union.[29] | Soviet Union |
| 1964 | Pre-cellular VHF/UHF radio system launch | Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS) is introduced by AT&T as a replacement to Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) and improved on most MTS systems by offering direct-dial rather than connections through a live operator.[23] | |
| 1965 | Network technology | AT&T introduces the first major improvement to mobile telephony, creating the Improved Mobile Telephone Service, which allows more simultaneous calls in a given geographic area, introducing customer dialing, and reducing the size and weight of the equipment.[13] | |
| 1968 | Network technology | Bell Labs starts developing the Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) standard.[6] | United States |
| 1969 | Network technology | Penn Central Railroad equips commuter trains along the New York-Washington route with special pay phones that allow passengers to place telephone calls while the train is moving.[30] | United States |
| 1969 | Organization | The Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) Group is established in Scandinavia and Finland with the purpose to develop a mobile phone system that, unlike the systems being introduced in the United States, focuses on accessibility.[21] | Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland |
| 1969 | PNetwork technology | Engineers from the Nordic countries meet and set up the first mobile phone system international standard, the Nordic Mobile Telephony (NMT).[31] | Scandinavia |
| 1971 | Terminology | The term cell comes into play when AT&T proposes splitting phone service into different areas across the cities. These areas are called cells.[3][20] | United States |
| 1971 | Network technology | Autoradiopuhelin (ARP) network is launched in Finland. It is one of the first successful public commercial mobile phone networks.[28] | Finland |
| 1972 | Network technology | B-Netz mobile radio network is launched in West Germany.[4] | Germany |
| 1973 | Technology milestone | 10 years before a cell phone is first released onto the market, Martin Cooper, a Motorola researcher and executive, makes the first analog mobile phone call using a heavy prototype model. The communication is carried out between Cooper and Joel S. Engel of Bell Labs.[32][4][9] | United States |
| 1973 | Handset release | Motorola becomes the first company to mass produce the the first handheld mobile phone.[22] | |
| 1973 | Mobile phone service | A cellular telephone switching plan is described by Fluhr and Nussbaum.[33] | |
| 1977 | Network technology | A cellular telephone data signaling system is described by Hachenburg et al.[34] | |
| 1979 (December) | Network technology | 1G, the first generation of wireless telephone technology, is launched in Japan by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT). It becomes the world's first mobile phone network to be launched.[9] Initially deployed in the metropolitan area of Tokyo, within five years, the NTT network expand to cover the whole population of Japan and becomes the first nationwide 1G network.[23][12][4][8] | Japan |
| 1981–1986 | Network technology | The Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system opens in Sweden and Norway. NMT is the first mobile phone network to feature international roaming. The system is introduced in Denmark and Finland in 1982, and in Iceland in 1986.[35][9][23][28] | Scandinavia, Finland |
| 1981 | Network technology | The Saudi mobile phone network becomes operational.[6] | Saudi Arabia |
| 1982 | Policy | The European standard for protorypes is established.[31] | |
| 1982 | Network technology | Ericsson constructs the first European cellular systems for use by service providers in Scandinavia.[8] | |
| 1983 | Network technology | The Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) is officially introduced in North America.[36][28][37] The system would further expand into Canada in 1985, later in Mexico, Colombia, Korea, Australia, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, New Zealand, Pakistan, the Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam and finally all Latin American countries.[38] | |
| 1983 (March 6) | Handset release | The Motorola DynaTAC 8000X becomes the first mobile for sale in the United States. It costs US$ 4000 (equivalent to $9,894.75 in 2017). 1G network launches in the country, with Chicago-based Ameritech using the Motorola DynaTAC mobile phone.[9][23][4] American engineer Martin Cooper is credited with developing the device.[5] | United States |
| 1983 | Network technology | The Total Access Communication System (TACS) (1G) is released in the United Kingdom as a variant of the Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS).[38][23][6] | United Kingdom |
| 1983 | Network technology | AMR radiotelephone network (Automatizovaný Městský Radiotelefon in Czech language) enters full mode as the very first analog mobile radio telephone in Czechoslovakia.[39] | Czechoslovakia |
| 1984 | Network technology | Airborne cellular systems: The North American terrestrial system (NATS) is introduced in the United States by GTE Corporation.[23] | United States |
| 1985 | Network technology | The Nordic Mobile Telephone grows to 110,000 subscribers in Scandinavia and Finland, 63,300 in Norway alone, which makes it the world's largest mobile network at the time.[40] | Scandinavia |
| 1985 | Technology milestone | The first mobile call in the United Kingdom is made.[9] | United Kingdom |
| 1985 | Network technology | The Radio Telephone Network C (C-Netz), is introduced in Germany as a first generation analog cellular phone system.[41] | Germany |
| 1985 | Study | A study group of the Geneva-based International Telecommunication Union (ITU) begins to consider specifications for Future Public Land Mobile Telephone Systems (FPLMTS). These specifications would eventually become the basis for a set of “third-generation” (3G) cellular standards, known collectively as IMT-2000.[23] | |
| 1987 | Network technology | The Technical specifications for the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) standard are approved. Based on digital technology, it focuses on interoperability across national boundaries and consequent different frequency bands, call quality and low costs.[21] | |
| 1988 | Program launch | A group of government-owned public telephone bodies within the European Community announce the creation of a digital Global System for Mobile Communications (originally Groupe Spécial Mobile), referred to as GSM, the first such system that would permit any cellular user in one European country to operate in another European country with the same equipment. GSM would soon become ubiquitous throughout the continent.[23] | |
| 1989 | Handset release | Motorola MicroTAC 9800X is released. It becomes the first phone to feature a flip–down, and also the smallest and lightest phone available at the time.[42][9] | |
| 1990 | Network technology | The old AMPS networks are replaced by Digital AMPS (D-AMPS).[4] | |
| 1990 | Expansion | There are 12.5 millions subscriptions to mobile telephony worldwide.[43] | |
| 1991 | Network technology | Second-generation (2G) cellular telecom networks are commercially launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja (now part of Elisa Oyj).[44] The first wireless Internet access becomes available as part of this generation.[12]. Developed to serve voice communication, 2G is first digital transmission system in mobile communication in history.[7] Also, the first GSM call is made by the Finnish prime minister in the country.[6] | Finland |
| 1992 | Handset release | The Nokia 1011 launches. It is the world’s first mass produced phone using the new GSM digital standard. It includes a monochrome LCD screen, extendable antenna and a memory capable of storing 99 phone numbers.[21] | |
| 1992 (December 3) | Technology milestone | Software architect Neil Papworth sends the first text message saying "Merry Christmas" to Richard Jarvis, a director at Vodafone.[45][9][20] | United Kingdom |
| 1992 | Network technology | The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) adopts a terrestrial Aeronautical Public Correspondence (APC) system known as the terrestrial flight telephone system (TFTS).[23] | |
| 1992 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Andorra, Denmark, Finland, France, Gabon, Germany, Hong Kong, Portugal, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.[46] | Andorra, Denmark, Finland, France, Gabon, Germany, Hong Kong, Portugal, Sweden, United Kingdom |
| 1993 | Technology milestone | An early SMS text message is sent in Finland.[4] | Finland |
| 1993 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Australia, Austria, Greece. Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Norway, Singapore, Switzerland, United States and Nicaragua.[46] | Australia, Austria, Greece. Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, New Zealand, Norway, Singapore, Switzerland, United States, Nicaragua |
| 1994 (August 16) | Handset release | The IBM Simon is released, featuring a touchscreen and is the first phone to feature apps. It costs US$ 899.[9] The IBM Simon is considered by many to be the world’s first smartphone.[4] | United States |
| 1994 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Belgium, the Channel Islands, Hungary, Iceland, Israel, Kuwait, Malaysia, Netherlands, Qatar, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Cameroon, China, Fiji, Indonesia, Iran, Madagascar, Morocco, Pakistan, Philippines, Russia, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.[46] | Belgium, the Channel Islands, Hungary, Iceland, Israel, Kuwait, Malaysia, Netherlands, Qatar, South Africa, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, Cameroon, China, Fiji, Indonesia, Iran, Madagascar, Morocco, Pakistan, Philippines, Russia, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam |
| 1994 (November) | Mobile phone service | A patent for prepaid mobile phones (Patent Number 5826185) is filed in the United States.[47] | United States |
| 1995 | Mobile phone service | Fax, data, and SMS messaging services are launched commercially.[48] | |
| 1995 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Bahrain, Canada, Costa Rica, Croatia, Cyprus, Estonia, French Polynesia, Lebanon, Macao, New Caledonia, Puerto Rico, Seychelles, Spain, Bulgaria, Colombia, Republic of Congo, Georgia, Gibraltar, India, Jordan, Kyrgyzistan, Lao, Latvia, Lithuania, Malawi, Myanmar, Namibia, Reunion, Sri Lanka, Suriname, Tanzania, Tonga, Uganda and Uzbekistan.[46] | Bahrain, Canada, Costa Rica, Croatia, Cyprus, Estonia, French Polynesia, Lebanon, Macao, New Caledonia, Puerto Rico, Seychelles, Spain, Bulgaria, Colombia, Republic of Congo, Georgia, Gibraltar, India, Jordan, Kyrgyzistan, Lao, Latvia, Lithuania, Malawi, Myanmar, Namibia, Reunion, Sri Lanka, Suriname, Tanzania, Tonga, Uganda, Uzbekistan |
| 1995–1999 | Network technology | Europe and Asia become the first regions to deploy mobile connectivity in their underground assets.[49] | Europe, Asia |
| 1996 | Handset release | The Nokia Communicatoris released. It is the first mobile phone to enable internet connectivity and wireless email creating a new category of multi-use devices called smartphones.[50] | |
| 1996 | Mobile operating system | Palm OS is launched as a discontinued mobile operating system, designed for ease of use with a touchscreen-based graphical user interface. | |
| 1996 (January) | Handset release | The Motorola StarTAC is released as a clamshell mobile phone. Manufactured by Motorola is the first ever clamshell/flip mobile phone.[51][9][4] | United States |
| 1996 | Handset release | The Nokia 8110 is launched. Its distinctive styling is the first example of a 'slider' form factor.[9] | |
| 1996 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Argentina, Brazil, Brunei, Czechia, Dominica, Guam, South Korea, Libya, Mauritius, Oman, Panama, Poland, Saudi Arabia, Slovenia, Venezuela, Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bosnia Herzegovina, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Cote D'Ivoire, Ecuador, Egypt, Ghana, Guadalupe, Guernsey, Kenya, Lesotho, Macedonia, Mongolia, Senegal, Sudan, Ukraine, Yugoslavia, and Zimbabwe.[46] | Argentina, Brazil, Brunei, Czechia, Dominica, Guam, South Korea, Libya, Mauritius, Oman, Panama, Poland, Saudi Arabia, Slovenia, Venezuela, Albania, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bosnia Herzegovina, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Cote D'Ivoire, Ecuador, Egypt, Ghana, Guadalupe, Guernsey, Kenya, Lesotho, Macedonia, Mongolia, Senegal, Sudan, Ukraine, Yugoslavia, Zimbabwe, |
| 1996 | Mobile phone service | MTN becomes the first mobile operator to introduce a prepaid cellular service in Africa, popularizing “pay as you go” in emerging markets.[52] | Africa |
| 1996 (September) | Mobile phone service | The first Prepaid card is called "Mimo", launched by TMN, the mobile phone operator of Portugal Telecom.[53] | Portugal |
| 1996 | Mobile phone service | MTN becomes the first mobile operator to introduce a Prepaid cellular service in Africa, popularizing “pay as you go” in emerging markets.[54] | Africa |
| 1997 | Handset release | Dutch technology company Philips introduces "The Synergy", an early attempt at a digital smartphone. The unit provides wireless access to e-mail, internet and faxes.[5][20] | |
| 1997 | Handset release | Little known German-made Hagenuk GlobalHandy becomes the first phone that has no visible external antenna.[21][55] | Germany |
| 1997 | Mobile payment | Coca Cola first introduces mobile purchasing, setting up vending machines that allow their customers to purchase drinks via text message.[56] | United States |
| 1997 (October) | Mobile phone service | Vodafone UK launches 'Pay as you Talk', packaging a GSM phone with a prepay tariff. | United Kingdom |
| 1997 (December) | Handset release | Nokia 6110 is launched. Hugely popular, It is the first phone from Nokia to have the popular Snake game pre-installed. [4] | |
| 1997 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Barbados, Bermuda, Chile, Malta, Slovakia, Uruguay, Virgin Islands, Bangladesh, Bolivia, Cape Verde, Guinea, Martinique, Mozambique, Romania, Togo and Zambia.[46] | Barbados, Bermuda, Chile, Malta, Slovakia, Uruguay, Virgin Islands, Bangladesh, Bolivia, Cape Verde, Guinea, Martinique, Mozambique, Romania, Togo, Zambia |
| 1997–1998 | Network technology | The Iridium system is introduced as the first LEO system intended for commercial service. It is designed by Motorola, and owned by Iridium LLC. The Iridium concept employs a constellation of 66 satellites orbiting in six planes around Earth, and are launched from May 1997 to May 1998. Commercial service begins in November 1998.[23] | |
| 1998 | Mobile payment | Mobile payments are trialled in Finland and Sweden.[1] | Finland, Sweden |
| 1998 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Bahamas, Botswana, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Faroe Islands, Greenland, Mexico, Trinidad and Tobago, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guyana, Moldova, Paraguay, Peru, Rwanda, Swaziland and Tunisia.[46] | Bahamas, Botswana, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Faroe Islands, Greenland, Mexico, Trinidad and Tobago, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, French Guiana, Guyana, Moldova, Paraguay, Peru, Rwanda, Swaziland, Tunisia |
| 1998 | The first downloadable mobile ringtone service is created and delivered in Finland when Radiolinja starts their service called Harmonium, invented by Vesa-Matti Pananen.[21][57] | Finland | |
| 1998 | Handset release | The Siemens S10 is launched as the first mobile phone with a colour screen.[21] | Germany |
| 1998 | Handset release | The Nokia 5110 is released. It becomes an instant success and kickstarted the vogue for customising your handset."[21] | |
| 1999 | Network technology | Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) technical standard is made available for mobile devices.[9] | |
| 1999 | Mobile operating system | Nokia Series 40 mobile operating system is introduced with the release of Nokia 7110 device.[58] | |
| 1999 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Algeria, Angola, Belarus, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of Congo, Cuba, Ethiopia, Guatemala, Haiti, Jamaica, Kazakhstan, Maldives, Nepal, Syria, West Bank and Gaza.[46] | Algeria, Angola, Belarus, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of Congo, Cuba, Ethiopia}}, Guatemala, Haiti, Jamaica, Kazakhstan, Maldives, Nepal, Syria, West Bank, Gaza |
| 1999 | Shigetaka Kurita in Japan invents the emojis.[21] | Japan | |
| 1999 | Handset release | The BlackBerry 850 launches as the first BlackBerry phone. It would become famous for its super-easy email service.[21] | |
| 1999 | Handset release | The Motorola Timeport is released. It is the first tri-band GSM phone, meaning it works "everywhere around the world".[21] | |
| 1999 | Mobile payment | Movie tickets become available for purchase through mobile payment.[59] | |
| 1999–2002 | Network technology | Globalstar is released as a LEO system, consisting in 48 satellites that are launched about the same time as the Iridium constellation. Globalstar begins offering service in October 1999, though it would go into bankruptcy in 2002. A further reorganized Globalstar LP would continue to provide service thereafter.[23] | |
| 1999 | Mobile payment | The first mobile commercial payment system to mimic banks and credit cards is launched in the Philippines, simultaneously by mobile operators Globe Telecom and Smart Communications.[2] | |
| 2000 | Network technology | Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) networks evolve into General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) (2.5G) and become available. The first GPRS-compatible handsets become available for sale.[48][6] | |
| 2000 | Handset release | The Nokia 9210 Communicator is launched as the first serious attempt at an internet-enabled mobile phone.[21] | |
| 2000 (June) | Handset release | South Korean multinational conglomerate Samsung releases SCH-V200, which integrates digital camera and mobile phone in a unit that can take up to 20 pictures at 640 x 480 (350,000 pixel CCD, 1 MB internal storage).[60] | South Korea |
| 2000 (November) | Handset release | Japanese multinational Sharp Corporation releases the J-SH04 mobile phone, the first ever phone with a built-in camera (110,000-pixel CMOS) and color display (256-color display).[61] | Japan |
| 2000 | Digital mobile telephony introduction | Digital mobile telephony is commercially introduced in Dominica, Grenada, Santa Lucia, Anguilla, Benin, Burundi, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, Honduras, Mali, Marshall Islands, Mauritania, Sierra Leone, Tajikistan and Turkmenistan.[46] | Dominica, Grenada, Santa Lucia, Anguilla, Benin, Burundi, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, Honduras, Mali, Marshall Islands, Mauritania, Sierra Leone, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan |
| 2000 | Mobile phones on aircraft | A study by the British Civil Aviation Authority finds that a mobile phone, when used near the cockpit or other avionics equipment location, will exceed safety levels for older equipment (compliant with 1984 standards). Such equipment is still in use, even in new aircraft. Therefore, the report concludes, the current policy, which restricts the use of mobile phones on all aircraft while the engines are running, should remain in force.[62] | United Kingdom |
| 2001 (October) | Handset release | Nokia 5510 is released, featuring a full QWERTY keyboard.[20] | |
| 2001 (October) | Network technology | The third generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology 3G (FOMA W-CDMA services on the 2GHz) is launched in Japan, with a system offered by NTT DoCoMo.[23] For the first time, mobile devices are fast enough to support online video and music streaming.[4] Developed to serve data communication, 3G can send 10 times more data than 2G.[63] | Japan |
| 2001 | Mobile payment | Mobile commerce reaches $2.4 billion worldwide.[59] | |
| 2001 | Technology | The popularity of voice over IP grows with startlingly rapid progress, with the number of installed voice-over-IP networks, the number of players in the voice-over-IP arena, the dollars spent on voice-over-IP products, the number of channels shipped and even the capacity of voice-over-IP products, all having doubled within a year.[64] | |
| 2002 | Handset release | Handspring (company)|Handspring]]'s Treo 180 is released. It is the first smartphone that fully integrates the Palm OS on a GSM mobile phone having telephony, SMS messaging and Internet access built into the OS. The 180 model has a thumb-type keyboard and the 180g version has a Graffiti handwriting recognition area, instead.[65][3][20] | |
| 2002 (June) | Organization | The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is formed as a standards body with aims at developing open standards for the mobile phone industry.[66] | |
| 2002 | Handset release | The Sanyo SCP–5300 is released. It allows users to view photos on a screen for the first time, instead of plugging it into a computer.[3][9] | |
| 2002 | Research | Finnish scientists claim that the electromagnetic radiation affect brain tissue.[1] | |
| 2002 | Mobile payment | Mobile payment is introduced in China.[67] | China |
| 2003 | Handset release | The Nokia 1100 is released. It would become the biggest–selling phone of all time.[9] | |
| 2003 | Handset release | A Blackberry phone, integrating a phone with fully functioning email, web browsing and the Blackberry Messenger, is launched.[21] | |
| 2003 | Mobile payment | An estimated 95 million users worldwide make purchases with their mobile phones.[59] | |
| 2003–2007 | Expansion | Mobile phone users surpass those using landline telephone in the United States.[43] | United States |
| 2004 | Research | German–led European laboratory study using mouse models announces that mobile radiation could cause genetic damage.[1] | |
| 2004 | Handset release | The Motorola Razr V3 is released. It would be the last great flip phone. Very thin at only 14mm.[21] | |
| 2005 | Handset release | The Casio GZ'One is released as the first waterproof phone.[9] | |
| 2005 | Mobile operating system | Android is acquired by Google. This step shows that Google is serious about developing mobile technology.[9] | United States |
| 2005 | Policy | The Cell Phone Recycle Act is passed in California.[3] | United States |
| 2005 | Policy | The Finnish government decides that the fastest way to warn citizens of disasters is the mobile phone network.[68] | Finland |
| 2005 | Handset release | Nokia launches the first Near-field communication (NFC)-enabled phone.[59] | |
| Mid-2000s | Network technology | Underground systems in the Americas start deploying mobile connectivity in their underground assets.[49] | Americas |
| 2006 | Study | British researcher at the University of Staffordshire links mental wellbeing issues, such as stress, to mobile use.[1] | United Kingdom |
| 2006 (June) | Network technology | The world's first commercial mobile WiMAX service is opened by KT in Seoul. [69] | South Korea |
| 2006 (August) | Mobile phones on aircraft | Irish airline Ryanair announces that it would introduce a facility to allow passengers to use their mobile phones in-flight.[70] | |
| 2006 | Mobile payment | Mobile payment is introduced in India.[71] | India |
| 2007 | Handset release | Steve Jobs unveils the Apple Iphone, which is released. It has finger–input touchscreen, no keyboard, intuitive interface and apps[3][9][1] | |
| 2007 | Policy | Google opens Android operating system for free development and use, making its own services default for search, video and email.[9] | |
| 2007 | Network technology | The first 4G network is launched in South Korea.[9] | South Korea |
| 2007 | Technology | T-Mobile US rolls out a service, T-Mobile HotSpot@Home, that allows a single handset to switch seamlessly from cellular to Wi-Fi access in the home and at the 8,900 T-Mobile Hotspot locations in the United States.[72] | United States |
| 2007 (June 29) | Handset/mobile operating system release | Apple Inc. launches the first-generation iPhone, along with its mobile operating system iOS.[73] | |
| 2007 | Coverage | The total number of mobile phone subscribers in the world is estimated at 3.3 billion, equivalent of over half the planet's population.[68] 295 million 3G users are estimated around the world. This number accounts for 9% of the total worldwide number of mobile users.[4] | |
| 2007 | Network technology | Hong Kong and Buenos Aires become the first cities to install Wi-Fi in their subway systems.[74] | Hong Kong, Argentina |
| 2008 | Policy | The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) sets forward a list of requirements for what it calls IMT Advanced, or 4G. These requirements include data rates of 1 gigabit per second for a stationary user and 100 megabits per second for a moving user.[23] | |
| 2008 (March) | Mobile phones on aircraft | Emirates airline flights begin allowing in-flight voice calls on some commercial airline flights.[75] | |
| 2008 | Network shutdown | The whole Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) service is shut down across North America. This would be considered the end of an era.[4] | |
| 2008 | Handset release | HTC corporation releases the HTC Dream the first commercially released device to use the Linux-based Android operating system.[9] | |
| 2008 (july 10) | Handset release | The App Store (iOS) is launched, featuring 552 apps, 135 of which are free.[9] | |
| 2008 | Product shutdown | Microsoft deprecates windows mobile, saying that it can't compete with iPhone and Android. The development of Windows Phone begins.[9] | United States |
| 2008 | Technology | Several mobile phone providers in the United States start to include IPv6 capabilities in their phones.[76] IPv6 is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. | United States |
| 2009 (January) | Mobile application | Whatsapp is launched.[9][77] | |
| 2009 | Network technology | Swedish telephone company TeliaSonera introduces the first 4G LTE network in Stockholm.[23] | Sweden |
| 2009 | Mobile payment | The mobile payment market reaches US$69 billion in sales.[59] | |
| 2010 | Handset release | Samsung Galaxy S smartphone is launched. Usurping former Android giant HTC, the Samsung Galaxy S range is still the most popular Android brand.[21] | |
| 2010 (June 7) | Technology | Apple announces FaceTime in conjunction with iPhone 4. A videotelephony product, FaceTime uses the device's front-facing camera to show the caller to the receiver, and vice versa. FaceTime works anywhere there is Wi-Fi.[78] | United States |
| 2010 | Samsung, Nokia, LG Electronics, ZTE Corporation and Apple Inc. altogether control more than 70% of the world mobile phone market.[31] | ||
| 2010 | Policy | The International Telecommunication Union decides that two technologies, LTE-Advanced (Long Term Evolution; LTE) and WirelessMan-Advanced (also called WiMAX), meet the requirements for a 4G.[23] | |
| 2011 | Health | The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), an agency of the World Health Organization, classifies wireless radiation as Group 2B – possibly carcinogenic. This means that there "could be some risk" of carcinogenicity, so additional research into the long-term, heavy use of wireless devices needs to be conducted.[79] | |
| 2011 | Mobile as a modem | The Verizon iPhone is released. It includes the 'Personal Hotspot" feature which allows a user to use the iPhone as a wireless hotspot, with up to five devices connecting at one time.[80][81][82][83] | United States |
| 2011 | Network technology | As of date, 90% of the world's population live in areas with 2G coverage, while 45% live in areas with 2G and 3G coverage, and 5% live in areas with 4G coverage. By 2017 more than 90% of the world's population is expected to have 2G coverage, 85% is expected to have 3G coverage, and 50% will have 4G coverage.[84] | |
| 2012 | Organization | The British Government announces the establishment of a 5G Innovation Centre at the University of Surrey.[85] | United Kingdom |
| 2012 | Health | A study of low-frequency radiation on humans finds "no evidence for acute effects of short-term mobile phone radiation on cerebral blood flow".[86][87] However, several animal studies demonstrate damage to the blood-brain barrier from phone radiation.[88][89] | |
| 2012 | Statistics | At the end of the year there are roughly 1.5 billion mobile broadband subscriptions, growing at a 50% year-on-year rate.[90] | |
| 2013 | Technology | Apple introduces FaceTime Audio. A version of FaceTime simply featuring audio-only, so only the user's voice is transmitted in the call.[91] | United States |
| 2014 | Acquisition | American corporation Facebook acquires Whatsapp for US$ 19 billion.[9] | United States |
| 2014 (June) | Technology | Apple announces WiFi calling for iPhone users with iOS 8. The new feature allows users to make and receive calls as well as send messages through a WiFi connection rather than using their voice or data plan.[92] | |
| 2015 (April) | Technology | WhatsApp Call is introduced for Android and iOS as a new voice calling service, enabling users to make phone calls over the Internet.[93] | |
| 2015 (August) | Technology | Deutsche Telekom starts to roll out IPv6 (dual stack) in their mobile network.[94] | Germany |
| 2015 (September) | Program launch | Verizon Communications announces a roadmap to begin testing 5G in field trials in the United States in 2016.[95] | |
| 2015 (October) | Technology | AT&T first introduces Wi-Fi calling, a feature that allows customers to place calls over Wi-Fi in instances where a cellular connection is poor.[96] | United States, Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands |
| 2015 | Mobile payment | Samsung Pay launches in South Korea as a mobile payment and digital wallet service that lets users make payments using compatible phones and other Samsung-produced devices.[97][59] | South Korea |
| 2015 (September 11) | Mobile payment | Android Pay is released as a digital wallet platform and online payment system developed by Google to power in-app and tap-to-pay purchases on mobile devices.[98] | United States |
| 2016 (February) | NTT DoCoMo and Ericsson succeed in World's first trial to achieve a cumulative 20Gbit/s with two simultaneously connected mobile devices in 5G outdoor trial.[99] | ||
| 2016 | Mobile application | The Pokemon Go app launches worldwide, using a free augmented reality game by means of the smartphone camera and location to show Pokemon characters in the real world. The game is massively adopted worldwide.[21] | |
| 2017 (April) | Network technology | Huawei announces having jointly with Telenor conducted successful 5G tests with speeds up to 70 Gbit/s in a controlled lab environment in Norway.[100] | Norway |
| 2017 (April) | Technology | All Regional Internet Registries confirm that IPv4 addresses are exhausted and cannot be allocated any more, implying all new organizations requesting a block of Internet addresses would be allocated IPv6 addresses.[101] | |
| 2017 (July) | Network technology | Telecom Italia Mobile signs a memorandum of understanding with the government of San Marino to upgrade its 4G network to 5G. It would be the first nationwide 5G network in the world.[102] | Italy, San Marino |
| 2017 | Mobile operating system | KaiOS launches as a Mobile operating system based on Linux.[103] | |
| 2017 | Network technology | As of date, more than 90% of the world's population is expected to have 2G coverage, 85% is expected to have 3G coverage, and 50% 4G coverage.[104] | |
| 2020 (March) | Network technology | The London Underground is expected to get 4G access in its tunnels and stations by this time.[105][106] | United Kingdom |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
- Timeline of WhatsApp
- Timeline of Wi-Fi
- Timeline of NTT Docomo
- Timeline of Xiaomi
- Timeline of money transfer
- Timeline of IPv6 adoption
- Timeline of 5G
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Agar, Jon. Constant Touch: A Global History of the Mobile Phone. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "cellular phone". prezi.com. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 "cell phone Timeline". softschools.com. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 4.20 4.21 4.22 "History of Mobile Cell Phones, The First Cell Phone To Present Time". bebusinessed.com. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "A Photographic History of the Cell Phone". time.com. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 O'Regan, Gerard. Introduction to the History of Computing: A Computing History Primer. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 "Wireless communications first-to-second-generation-1g-to-2g". coursera.org. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Global Competitiveness of U.S. Advanced-Technology Industries: Cellular Communications (Information Gatekeepers Inc ed.). Retrieved 21 November 2017.
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 9.17 9.18 9.19 9.20 9.21 9.22 9.23 9.24 "1876 to 2015 – the History of the Mobile Phone". mcs-testequipment.com. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "History of Mobile / Cell Phone". radio-electronics.com. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ "The Case of Cellular Mobile Telephony". springer.com. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Hilbert, Jeffrey L. Tunable RF Components and Circuits: Applications in Mobile Handsets. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "A BIG CHANGE FOR HUMANITY". phoneevolution.wordpress.com. Retrieved 27 August 2019.
- ↑ Technical Innovation in American History: An Encyclopedia of Science and Technology [3 volumes] (Rosanne Welch, Peg A. Lamphier ed.).
- ↑ "ITU towards "IMT for 2020 and beyond" - IMT-2020 standards for 5G". International Telecommunications Union. Retrieved 19 August 2017.
- ↑ "Mobile telephony". Google Trends. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ↑ "Mobile telephony". books.google.com. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ↑ "Mobile telephony". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 "Invention Story of Cell Phones". engineersgarage.com. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 "Week 3- Timeline of the cell-phone". timetoast.com. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ↑ 21.00 21.01 21.02 21.03 21.04 21.05 21.06 21.07 21.08 21.09 21.10 21.11 21.12 21.13 21.14 21.15 "History of mobile phones and the first mobile phone". physicslover.in. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 "History of mobile phones and the first mobile phone". uswitch.com. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ↑ 23.00 23.01 23.02 23.03 23.04 23.05 23.06 23.07 23.08 23.09 23.10 23.11 23.12 23.13 23.14 23.15 "Mobile telephone". britannica.com. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ Berg, Christian. Smartphones und Tablets. Ihre Auswirkungen auf den privaten Alltag. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ "Evolution of Mobile Phones from 1956 - 2007". techeblog.com. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ "Car phone". pinterest.com. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 "A Brief History Of Mobile Phones". makeuseof.com. Retrieved 24 July 2017.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 28.3 Evolution and Standardization of Mobile Communications Technology (Seo, DongBack ed.). Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ "Мобильная связь в СССР (7 фото)". vasi.net. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ Gordon A. Gow, Richard K. Smith Mobile and wireless communications: an introduction, McGraw-Hill International, 2006 Template:ISBN page 23
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Boutellier, Roman; Heinzen, Mareike. Growth Through Innovation: Managing the Technology-Driven Enterprise. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ Shiels, Maggie (April 21, 2003). "BBC interview with Martin Cooper". BBC News.
- ↑ "Switching Plan for a Cellular Mobile Telephone System":, Z. Fluhr and E. Nussbaum, IEEE Transactions on Communications volume 21, #11 p. 1281 (1973)
- ↑ Hachenburg, V.; Holm, B.D.; Smith, J.I. (1977). "Data signaling functions for a cellular mobile telephone system". IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 26: 82–88. doi:10.1109/T-VT.1977.23660.
- ↑ "Mobiltelefonens historie i Norge". archive.org. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ↑ AT&T Tech Channel (2011-06-13). "AT&T Archives : Testing the First Public Cell Phone Network". Techchannel.att.com. Archived from the original on 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2013-09-28.
- ↑ MilestonesPast.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Huurdeman, Anton A. The Worldwide History of Telecommunications. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ "First Czechoslovak radiotelephone networks: AMR". medium.com. Retrieved 19 August 2017.
- ↑ Nordsveen, Arve M (28 November 2005). "Mobiltelefonens historie i Norge" (in Norwegian). Norsk Telemuseum. Archived from the original on 13 February 2007.
- ↑ "Das C Netz in der Mobilfunk Geschichte". mobilfunk-geschichte.de. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ Motorola Has a Pocket-Size Cellular Phone Los Angeles, April 26, 1989
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 "L'Histoire du Wi-Fi". ucopia.com. Retrieved 30 May 2018.
- ↑ "Radiolinja's History". 20 April 2004. Archived from the original on 23 October 2006. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ↑ "The First Text Message Ever Was Sent 21 Years Ago Today". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 46.4 46.5 46.6 46.7 46.8 "Diffusion of Digital Mobile Telephony: Are Developing Countries Different?" (PDF). econstor.eu. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ↑ Wise, Andrew. "Prepaid Cellular Patent". 5826185. USPTO. Retrieved January 24, 2012.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 El Khoury, Franjieh; Zgheib, Antoine. Building a Dedicated GSM GPS Module Tracking System for Fleet Management: Hardware and Software.
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 "Internet connectivity in underground rail systems" (PDF). uitp.org. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "Nokia 9000 Communicator". computinghistory.org.uk. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ Tynan, Dan (2005-12-24). "The 50 Greatest Gadgets of the Past 50 Years". PC World. p. 2. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ "MTN Group - Annual Report 2008 - Chairman's statement". www.mtn-investor.com. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ↑ "Portugal Telecom FAQ". Archived from the original on February 3, 2015. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- ↑ "MTN Group - Annual Report 2008 - Chairman's statement". www.mtn-investor.com. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- ↑ "Hagenuk GlobalHandy". mobilephonehistory.co.uk. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ Martins, Flavio. "The History of the Mobile Payment Experience". winthecustomer.com. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ↑ Time Magazine Europe: The Sweet Sound Of Success
- ↑ "Nokia Series 40: over 1.5 billion served". engadget.com. Retrieved 19 August 2017.
- ↑ 59.0 59.1 59.2 59.3 59.4 59.5 "The History of Mobile Pay". emspayments.com. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ↑ "Samsung integrate digital camera and phone". dpreview.com. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ↑ "Sharp J-SH04: World's First Ever Phone With Integrated Camera". Digitizor Media & Web, Inc. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- ↑ "Interference Levels In Aircraft at Radio Frequencies used by Portable Telephones" (PDF). web.archive.org. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ "Third generation system. wireless-communications". coursera.org. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ Network World 29 Jan 2001.
- ↑ Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:Citation/CS1/Suggestions' not found.
- ↑ "The Open Mobile Alliance: Delivering Service Enablers for Next-Generation Applications". acm.org. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- ↑ "To Pay or Not to Pay: The Dilemmas of an Emerging Business Ecosystem – The Case of Mobile Payments" (PDF). doria.fi. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Beer, Tom. Geophysical Hazards: Minimizing Risk, Maximizing Awareness. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ Shukla, Anuradha (October 10, 2011). "Super-Fast 4G Wireless Service Launching in South Korea". Asia-Pacific Business and Technology Report. Retrieved 28 July 2017.
- ↑ "RTÉ Business: Ryanair signs OnAir deal for in-flight mobiles". Rte.ie. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ "Globsyn Management lobsyn Management lobsyn Management Conference 2018" (PDF). globsyn.edu.in. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
- ↑ Plunkett's Telecommunications Industry Almanac 2009 (Jack W. Plunkett ed.).
- ↑ "June 29, 2007: Apple Introduces the iPhone (First Apple Cell Phone)". historyandheadlines.com. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ "Why It's So Damn Hard to Put Internet in the Subway". popularmechanics.com. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "Emirates offers first mobile phone service onboard A380 Aircraft" (Press release). Emirates. October 4, 2012. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ "IPv6 on Your Mobile Phone". networkworld.com. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- ↑ "Whatsapp Success Story". successstory.com. Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ↑ "Apple Presents iPhone 4". apple.com. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ "IARC classifies radiofrequency electromagnetic fields as possibly carcinogenic to humans" (PDF). World Health Organization press release N° 208 (Press release). International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2011-05-31. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "Verizon Wireless Has Record Sales On First Day Of iPhone 4" (Press release). Verizon Wireless. February 4, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2011.
- ↑ "Liveblog: The Verizon iPhone". The Washington Post.
- ↑ Memmott, Mark (January 11, 2011). "It's Official: Verizon Has The iPhone 4: The Two-Way". NPR. Retrieved 31 July 2019.
- ↑ Raice, Shayndi (January 12, 2011). "Verizon Unwraps iPhone". The Wall Street Journal.
- ↑ "The World in 2011: ITC Facts and Figures", International Telecommunications Unions (ITU), Geneva, 2011
- ↑ "5G Innovation Centre". University of Surrey - Guildford. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ What has research shown about the possible cancer-causing effects of radiofrequency energy?, United States National Cancer Institute
- ↑ Kwon MS, Vorobyev V, Kännälä S, et al. (2012). "No effects of short-term GSM mobile phone radiation on cerebral blood flow measured using positron emission tomography". Bioelectromagnetics. 33 (3): 247–56. PMID 21932437. doi:10.1002/bem.20702.
- ↑ Nittby, Henrietta; Brun, Arne; Eberhardt, Jacob; Malmgren, Lars; Persson, Bertil R. R.; Salford, Leif G. (August 2009). "Increased blood-brain barrier permeability in mammalian brain 7 days after exposure to the radiation from a GSM-900 mobile phone". Pathophysiology: The Official Journal of the International Society for Pathophysiology. 16 (2–3): 103–112. ISSN 0928-4680. PMID 19345073. doi:10.1016/j.pathophys.2009.01.001.
- ↑ Tang, Jun; Zhang, Yuan; Yang, Liming; Chen, Qianwei; Tan, Liang; Zuo, Shilun; Feng, Hua; Chen, Zhi; Zhu, Gang (2015-03-19). "Exposure to 900 MHz electromagnetic fields activates the mkp-1/ERK pathway and causes blood-brain barrier damage and cognitive impairment in rats". Brain Research. 1601: 92–101. ISSN 1872-6240. PMID 25598203. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.01.019.
- ↑ Ericsson Mobility Report: Interim Update, Ericsson, February 2013
- ↑ "FaceTime: What It Is & How to Use It". lifewire.com. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ Kahn, Jordan. "T-Mobile confirms WiFi calling arriving for iPhone users with iOS 8". 9to5mac.com. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ Patkar, Mihir. "WhatsApp Voice Call: Everything You Need to Know". makeuseof.com. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ Zivadinovic, Dusan (2015-07-08). "Telekom startet IPv6-Einführung im Mobilfunknetz". Heise Online (in Deutsch). Archived from the original on 2019-01-27. Retrieved 2019-01-27.
- ↑ "Verizon sets roadmap to 5G technology in U.S.; Field trials to start in 2016". Verizon. 8 September 2015. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ "AT&T Expands Wi-Fi Calling to Cover International Calls to U.S. When Traveling". macrumors.com. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ↑ "Samsung Pay Now Available in Six Continents, Accelerating Global Expansion". news.samsung.com. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "Google officially launches new NFC payment service Android Pay". extremetech.com. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "DOCOMO and Ericsson Succeed in World's first trial to achieve a cumulative 20Gbps with two simultaneously connected mobile devices in 5G Outdoor Trial". NTT DoCoMo. February 22, 2016. Retrieved July 14, 2017.
- ↑ "Telenor and Huawei Jointly Announce First 5G Demo in Norway". huawei.com. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ "IPv6 Is A Failure - Time To Move On". i-programmer.info. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ "San Marino set to get Europe's first super-fast 5G mobile network". cnbc.com. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ↑ "Meet The Devices That Are Powered by KaiOS". kaiostech.com. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ Ericsson Mobility Report, Ericsson, November 2012
- ↑ Porter, Jon. "4G is coming to the London Underground's tunnels next year". theverge.com. Retrieved 29 July 2019.
- ↑ "4G on Jubilee line tunnel section from March 2020". tfl.gov.uk. Retrieved 29 July 2019.