Timeline of DeepSeek
This is a timeline of DeepSeek, a Chinese artificial intelligence company founded in 2023 by Liang Wenfeng, specializing in the development of open-source large language models (LLMs).
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- What are the key product and model releases by DeepSeek?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Product launch".
- You will see a number of major product launches, including model names and key features. You will see brief descriptions of model's capabilities, benchmarks, and intended use cases.
- What major updates or improvements were made to DeepSeek’s models and services over time?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Update".
- You will see a list of key updates related to DeepSeek’s AI models, highlighting technical improvements, architectural innovations, and enhanced capabilities in areas like instruction-following, coding, efficiency, and performance benchmarks.
- What are major competitive events involving DeepSeek and its rivals in the AI industry?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Competition".
- You will see a number of key competitive moments involving DeepSeek, showing how it challenged rivals like OpenAI, Alibaba, and Baidu. The results highlight app dominance, market disruptions, model comparisons, and investor reactions. These events illustrate DeepSeek’s rising influence and the shifting balance in global AI competition and innovation.
- How have global regulators responded to DeepSeek’s operations?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Regulatory action".
- You will see a list of government actions taken against DeepSeek, including bans, service suspensions, and investigations. These actions are primarily due to concerns over data privacy, security risks, and the potential misuse of personal information, reflecting growing international scrutiny of AI technologies, especially those with ties to China.
- Other events are described under the following types: "Company launch", "Financial disclosure", "Impact", "Legal dispute", "Notable comment", "Prelude", "Recognition", "Research development", "Research insight".
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| 2016-2019 | Early AI research | Chinese quantitative hedge fund High-Flyer Capital concentrates on AI trading algorithms, which lays the foundation for the eventual creation of DeepSeek. Liang Wenfeng's strategic acquisition of up to 50,000 Nvidia A100 GPUs, ahead of anticipated U.S. export restrictions, reflects his commitment to advancing AI technology.[1] DeepSeek traces its origins to a collective of AI researchers and engineers who had previously contributed to advancements in transformer architectures and large-scale language modeling. |
| 2023 | Initial releases | DeepSeek enters the public sphere in early 2023 with the release of its first language models, which benchmark competitively against contemporary models like LLaMA and Falcon. Notably, the company adopts an open-weight policy, releasing model weights under permissive licenses—a move praised by the open-source community. By mid-2023, DeepSeek secures Series A funding led by prominent tech venture firms, enabling rapid team expansion.[1] |
| 2024 | Multimodal expansion | The launch of DeepSeek-V2 in Q1 2024 introduces multimodal capabilities, combining text, image, and audio processing in a unified framework. Strategic collaborations with cloud providers (e.g., Alibaba Cloud, AWS) facilitate enterprise adoption. The release of DeepSeek-V2 disrupts the AI market by delivering high-performance capabilities at a competitive price, sparking a price war among leading Chinese tech companies such as ByteDance, Tencent, and Baidu.[1] The DeepSeek-Coder model, released later that year, achieves top rankings on coding benchmarks like HumanEval, rivaling GitHub’s Copilot. |
| 2025 | Global scale | DeepSeek emerges as a major global AI actor, gaining international attention with its reasoning-focused R1 model. Launched in January, DeepSeek-R1 achieves notable results in mathematics, coding, and analytical benchmarks, in some cases matching or surpassing leading Western models while being significantly cheaper and released under an open-source license. Its success is driven by efficiency-focused innovations such as mixture-of-experts architectures, sparsity, and later generative reward modelling (GRM), developed with Tsinghua University. DeepSeek rapidly disrupts the market, briefly overtaking ChatGPT as the top app in the U.S. App Store and expanding access through platforms such as Microsoft Azure and Google Vertex AI. At the same time, its rise triggers geopolitical and regulatory responses, including bans and investigations in multiple countries and allegations from OpenAI regarding model distillation. Overall, DeepSeek’s rapid innovation and low-cost strategy reshapes global debates on AI competition, regulation, and technological leadership. |
Full timeline
Inclusion criteria
We include:
- Impactful performance improvements and feature expansions. Technical updates that significantly enhance model architecture, efficiency, instruction-following, code generation, and API capabilities.
- Major competitors that significantly impact DeepSeek’s position in the AI market.
We do not include:
- Team
- Minor bug fixes, internal tests, or incremental updates lacking broader relevance or measurable improvements in benchmarks or usability.
- Minor competitors
Timeline
| Year | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | Prelude | Liang Wenfeng, a millennial hedge fund entrepreneur from Guangdong, founds High-Flyer Capital, a hedge fund that would finance DeepSeek’s research focus.[2] |
| 2022 | Prelude (background) | United States president Joe Biden introduces extensive export controls on semiconductors destined for China, aiming to prevent the country from obtaining the equipment needed for rapid AI development. The powerful H100 chip from Nvidia is included in the ban. In response, Nvidia creates the less powerful H800 chips for the Chinese market, which DeepSeek would use to train its model. However, these chips would be also banned in 2023.[2] |
| 2023 (May | Company launch | DeepSeek is officially launched by Liang Wenfeng, marking its entry into the competitive field of artificial intelligence and large language models.[2] |
| 2023 (December 2 | Product launch | DeepSeek AI releases DeepSeek LLM, an open-source family of large language models, including 7B and 67B parameter versions in base and chat variants. The 67B Base model surpasses Llama2 70B in reasoning, coding, math, and Chinese comprehension. DeepSeek Chat achieves a 73.78% pass rate on HumanEval and 84.1% on GSM8K without fine-tuning. The models had undergone rigorous training, emphasizing data quality and efficiency. While DeepSeek Chat's web interface includes censorship to comply with Chinese regulations, the downloadable models remain unrestricted.[3][4][5] |
| 2024 (February 1 | Product launch | DeepSeek-AI, in collaboration with Peking University, introduces DeepSeek-Coder, an open-source series of code models ranging from 1.3B to 33B parameters. Trained on 2 trillion tokens across 87 programming languages, these models address the limitations of prior open-source alternatives. Utilizing a "fill-in-the-middle" training approach and extended context windows, they enhance code completion and handle complex coding scenarios. The 33B Base model outperforms other open-source models, while the Instruct variant rivals closed-source solutions like GPT-3.5 Turbo.[6] |
| 2024 (March 13 | Product launch | DeepSeek-AI introduces DeepSeek-VL, an open-source vision-language (VL) model designed for real-world applications. The model bridges the gap between visual data and natural language, leveraging a diverse dataset to improve contextual understanding. Its hybrid vision encoder efficiently processes high-resolution images, addressing computational challenges while maintaining accuracy. Performance evaluations show state-of-the-art or competitive results across various benchmarks. DeepSeek-VL sets a new standard in multimodal AI, enhancing accessibility and automated assistance. This advancement underscores the growing role of VL models in artificial intelligence, offering innovative solutions to longstanding challenges in integrating vision and language processing.[7] |
| 2024 (May 8 | Update | DeepSeek-V2 introduces a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) to enhance AI performance. This model activates only a fraction of its parameters per task, reducing computational costs while maintaining high efficiency. Trained on 8.1 trillion tokens, DeepSeek-V2 improves upon its predecessor, DeepSeek 67 B, with a 42.5% reduction in training costs and a 93.3% decrease in Key-Value cache size. It also increases maximum generation throughput by 5.76 times. DeepSeek-V2 outperforms other open-source models in benchmark tests, setting a new standard for efficient, scalable language models in natural language processing.[8] |
| 2024 (May 17 | Update | A DeepSeek-V2-0517 upgrade improves instruction-following capabilities, increasing IFEval Benchmark Prompt-Level accuracy from 63.9% to 77.6% and JSON parsing accuracy from 78% to 85% (up to 97% with regular expressions). This update enhances the model’s ability to execute complex instructions reliably and improves its usefulness for developers working with structured data.[9] |
| 2024 (June 14 | Update | A DeepSeek-Coder-V2-0614 upgrade enhances code generation, debugging, and completion, achieving performance comparable to leading models. It also demonstrates strong mathematical and reasoning abilities. This update positions DeepSeek-Coder-V2 as a top-tier AI coding tool, making it a preferred choice for developers seeking advanced assistance.[9] |
| 2024 (June 18 | Product launch | DeepSeek-AI launches DeepSeek-Coder-V2, an open-source language model aimed at competing with commercial models like GPT-4 and Claude. It supports 338 programming languages and can process contexts of up to 128,000 tokens. Trained on 10.2 trillion tokens, including 60% source code, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 performs well in code generation, mathematics, and language tasks. In benchmarks, its 236-billion-parameter version achieves 75.3%, slightly behind GPT-4.[10] |
| 2024 (July 20 | Product launch | DeepSeek releases DeepSeek-V2-Chat-0628. This update significantly enhances performance, as demonstrated by its top ranking of #11 in the LMSYS Chatbot Arena. Notable improvements include a 3.7-point increase in HumanEval, a 17.1-point jump in MATH, and a 26.7-point rise in Arena-Hard benchmarks. Optimized instruction-following capabilities enhance tasks like translation and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The model requires high-performance GPUs for inference and is available under the MIT License, making it suitable for both research and commercial use.[11] |
| 2024 (July 25 | Update | New API features are introduced, including JSON mode, function calling, chat prefix completion (beta), and support for 8K max_tokens (beta). These additions expand the API's capabilities, providing developers with more tools to create advanced applications. The support for longer context windows (8K max_tokens) is especially significant, allowing for more complex and detailed interactions.[9] |
| 2024 (August 2 | Update | Context caching on disk is implemented, reducing computational costs by an order of magnitude. This innovation significantly lowers the cost of using DeepSeek’s API, making it more accessible to a wider user base. It also highlights DeepSeek’s commitment to optimizing resource efficiency without compromising performance.[9] |
| 2024 (August 29 | Product launch | DeepSeek-AI introduces the Fire-Flyer AI-HPC architecture, designed to address the increasing demand for processing power in deep learning and large language models (LLMs). The system integrates hardware and software to optimize cost and energy efficiency. The Fire-Flyer 2, featuring 10,000 PCIe A100 GPUs, delivers performance comparable to the NVIDIA DGX-A100 at 50% lower cost and 40% reduced energy consumption. Innovations like HFReduce enhance communication efficiency in distributed training. Supported by tools such as HaiScale and 3FS, the system improves scalability for complex workloads, combining advanced hardware and software solutions for cost-effective AI development.[12] |
| 2024 (September 5 | Product launch | DeepSeek-V2.5 is released, introducing a highly advanced 238 billion parameter model utilizing a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture with 160 experts. This model enhances capabilities in both chat and coding, offering features like function calls, JSON output generation, and Fill-in-the-Middle (FIM) completion. With a remarkable 128k context length, DeepSeek-V2.5 improves human preference alignment and instruction-following abilities. The model is optimized for performance, demonstrated by improved benchmarks in general reasoning and coding tasks. Available for local or cloud-based inference, it offers flexible use under an MIT License for both commercial and non-commercial purposes, positioning itself as a versatile tool for developers and businesses.[13] Within a few days, it is hailed as the new leader in open-source AI models.[14] |
| 2024 (October 18 | Product launch | DeepSeek-AI, in collaboration with the University of Hong Kong and Peking University, introduces Janus, a 1.3 billion parameter multimodal AI model designed to handle both visual understanding and generation tasks efficiently. Janus uses two distinct visual encoding pathways—an Understanding Encoder for semantic feature extraction and a Generation Encoder for detailed image synthesis—processed through a shared transformer. This dual approach alleviates conflicts found in prior models, improving performance. Janus outperforms existing models like LLaVA-v1.5 in multimodal understanding and DALL-E 2 in visual generation, offering enhanced flexibility and parameter efficiency.[15] |
| 2024 (November 20 | Product launch | DeepSeek launches R1-Lite-Preview, a large language model (LLM) designed to excel in reasoning tasks such as logical inference, mathematical problem-solving, and real-time challenges. Available through DeepSeek Chat, it demonstrates performance comparable to or exceeding OpenAI's o1-preview model. Notable for its transparent "chain-of-thought" reasoning, users can follow the model's problem-solving process step by step. R1-Lite-Preview shows strong performance in benchmarks like AIME and MATH, outperforming previous models on tasks like trick questions. It is made available via DeepSeek Chat first.[16] |
| 2024 (December 10 | Update | DeepSeek-V2.5 sees significant performance improvements, including enhanced mathematical and coding capabilities. The MATH-500 benchmark performance improves from 74.8% to 82.8%, and LiveCodebench accuracy increases from 29.2% to 34.38%. Additionally, file upload and webpage summarization functionalities are optimized. These updates solidify DeepSeek-V2.5 as a top choice for users needing advanced mathematical and coding support, while expanding its practical applications through improved file handling and summarization.[9] |
| 2024 (December 26 | Update | Deepseek-chat is upgraded to DeepSeek-V3, while maintaining backward compatibility. This update allows users to access the latest advancements without disrupting their workflows and lays the groundwork for future innovations by establishing a strong foundation.[9] |
| 2024 (December 28 | Product launch | DeepSeek launches DeepSeek V3, an advanced large language model (LLM) available for free chatbot access. Building on its predecessor, DeepSeek V2, the model incorporates optimization techniques such as load balancing, 8-bit floating-point (FP8) calculations, and Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) to reduce training costs and energy consumption. Training costs are kept under $6 million, significantly lower than OpenAI’s GPT-4. Preliminary benchmarks place DeepSeek V3 among the top ten LLMs, outperforming competitors in 12 of 21 tests. While businesses can access its API, user data is stored in China, raising privacy considerations. The chatbot is freely available online.[17] |
| 2025 (January 20 | Product launch | DeepSeek-R1 is launched as a state-of-the-art model designed for advanced reasoning tasks. It achieves top performance in math, coding, and reasoning benchmarks. This release represents the pinnacle of DeepSeek’s advancements, positioning it as a competitor with the best models in the industry. The focus on reasoning tasks opens up new possibilities for complex problem-solving applications.[9] |
| 2025 (January 22 | Product launch | DeepSeek unveils its reasoning model, DeepSeek-R1, which outperforms OpenAI o1 in several benchmarks, including math, coding, and general knowledge. DeepSeek-R1, built with a mixture-of-experts architecture, demonstrates exceptional problem-solving and analytical capabilities, with impressive scores such as 93% accuracy in the MATH-500 benchmark and a 79.8% pass rate in AIME 2024. It also ranks in the 96.3rd percentile in coding benchmarks like Codeforces. DeepSeek-R1 is notably 90-95% more affordable than o1, marking a significant advancement in AI technology with its open-source availability and superior performance at a fraction of the cost.[18] |
| 2025 (January 23 | Recognition | DeepSeek-R1 garners attention for its affordability and open availability. Unlike OpenAI's o1, DeepSeek-R1 performs reasoning tasks in fields like chemistry, mathematics, and coding with comparable results. The model, released under an MIT license, is open for researchers to explore and build upon, though its training data is not fully disclosed. DeepSeek prices R1 at a fraction of the cost of similar models, making it accessible to more researchers. Despite US export controls limiting access to top AI chips, DeepSeek's efficiency showcases China's growing prowess in AI development.[19][20] |
| 2025 (January 25 | Recognition | DeepSeek attracts significant attention for its rapid advancements in AI model development. Despite facing challenges from U.S. export restrictions on advanced chips, by this time the company had managed to achieve top-tier performance in global AI rankings, positioning itself among the world’s top 10 AI developers. DeepSeek's models are praised for their efficiency, with the cost of training one model reported to be $5.6 million, significantly lower than the $100 million to $1 billion estimated for similar models by American companies. This development highlights China's growing capability in AI innovation, despite technological constraints.[19][21] |
| 2025 (January 26 | Notable comment | American businessman and former software engineer Marc Andreessen tweets, “DeepSeek R1 is AI's Sputnik moment,” comparing DeepSeek's development of the AI model DeepSeek-R1 to the Soviet Union's launch of Sputnik 1 in 1957, which sparked the space race between the US and the Soviet Union.[22] By this time, DeepSeek's success challenges U.S. export controls and raises concerns over China's AI ambitions, which are bolstered by domestic resources and military objectives. Meanwhile, the U.S. seeks to restrict China's access to advanced technology and prioritize domestic AI development.[23] |
| 2025 (January 27 | Competition | DeepSeek gains significant attention by dethroning ChatGPT as the top app on the U.S. App Store. The company offers its chatbot with an integrated reasoning model for unlimited use at no cost, unlike OpenAI, which charges $20 to $200 per month for access. This advancement causes concern among U.S. investors, with some questioning the sustainability of U.S. companies' AI spending and their ability to maintain a lead in the field. The DeepSeek rollout causes stock market shifts as investors reconsider the competitive landscape in AI development.[24][25] |
| 2025 (January 28 | Research insight | Apple researchers highlight how DeepSeek leverages "sparsity" to improve performance while reducing computational costs. Sparsity refers to the strategy of turning off certain neural network parameters that do not significantly affect the AI's output, optimizing the use of computing power. This approach allows DeepSeek to deliver results comparable to more powerful models, despite using less computational resources. Apple's research, along with collaborations from Microsoft and Google, suggests that adjusting the level of sparsity can lead to more efficient and accurate AI models, marking a significant shift in AI optimization techniques.[26] |
| 2025 (January 29 | Product launch | DeepSeek R1 becomes available on Azure AI Foundry and GitHub, joining over 1,800 AI models. Hosted on Microsoft’s enterprise-ready platform, it enables seamless AI integration with strong security and compliance measures. Developers can quickly experiment, benchmark, and deploy AI-powered applications with built-in tools. DeepSeek R1 had undergone extensive safety evaluations, with default content filtering via Azure AI Content Safety. Users can access the model through a serverless endpoint, GitHub resources, or local deployment on Copilot+ PCs. Microsoft continues expanding its AI model catalog, supporting businesses in leveraging AI for innovation and transformative applications.[27] |
| 2025 (January 29 | Notable comment | Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei states in a blog post that he does not see DeepSeek as an adversary but emphasizes the importance of U.S. export controls in maintaining AI leadership. By this time, DeepSeek’s rise, including topping Apple’s App Store and disrupting tech markets, had drawn political scrutiny, with U.S. lawmakers labeling it a “serious threat.” Amodei argues that while DeepSeek researchers are talented, they operate under an authoritarian government. He calls for stronger restrictions on AI-related exports to China, asserting that the U.S. must maintain a technological edge to prevent strategic advantages for the Chinese Communist Party.[28][29] |
| 2025 (January 30 | Competition | Alibaba Group launches Qwen 2.5, an AI model it claims outperforms DeepSeek V3. The release, coinciding with the Lunar New Year, underscores competition in China's AI sector, particularly with DeepSeek, whose recent advancements have unsettled Silicon Valley. By this time, DeepSeek's ability to operate with lower development and operational costs had led to a decline in the stock prices of major tech companies, prompting investors to question the sustainability of high spending in AI development by U.S. firms. The rivalry between Chinese companies like Alibaba and DeepSeek and Western tech giants starts reshaping the AI landscape, with cost-effective approaches challenging the dominance of Silicon Valley. This shift is expected to have far-reaching effects on global market dynamics and AI regulations.[30] |
| 2025 (January 31 | Regulatory action | Italy's Data Protection Authority, known as the Garante, orders DeepSeek to block its chatbot service within the country due to concerns over insufficient transparency regarding user data processing. The Garante highlights a lack of information on how DeepSeek collects and utilizes personal data, leading to the suspension of the service. Following this directive, the DeepSeek app becomes unavailable on both Apple and Google app stores in Italy. This action reflects broader apprehensions within the European Union regarding data privacy and the operations of AI services.[31][32][33] |
| 2025 (February 3 | Regulatory action | Taiwan officially bans government departments from using DeepSeek AI, citing security risks. The decision, announced by Premier Cho Jung-tai, strengthens earlier guidance that discouraged its use. Taiwan had long been cautious of Chinese technology due to Beijing’s sovereignty claims and political threats. Concerns include potential censorship and the risk of sensitive data being transferred to China. The ban aligns with broader global scrutiny, as authorities in South Korea, France, Italy, and Ireland also investigate DeepSeek’s data practices. Taiwan's move reflects growing international concerns over security and data privacy in AI technologies.[34] |
| 2025 (February 4 | Regulatory action | Australia bans DeepSeek from all government devices and systems, citing national security risks. The government insists the decision is based on security concerns rather than DeepSeek’s Chinese origins. The ban requires the removal and prevention of DeepSeek’s applications and services on government systems, affecting agencies like the Australian Electoral Commission. The move follows growing scrutiny of DeepSeek’s data practices, with regulators in Italy, South Korea, Ireland, and France investigating its data storage in China. Similar concerns had previously led to restrictions on Huawei and TikTok. At this time, the US also examines DeepSeek’s security implications.[35] |
| 2025 (February 4 | Legal dispute | OpenAI accuses DeepSeek of inappropriately copying its ChatGPT model through a technique known as model distillation. This process involves training a new model by querying an existing one at scale. By this time, DeepSeek’s R1 model had gained global attention for offering performance comparable to OpenAI’s leading models at a lower cost. Despite OpenAI’s allegations, the company itself faces multiple lawsuits over its use of copyrighted materials in training its AI models. DeepSeek's rapid development had also been aided by innovations in AI hardware, driven in part by U.S. restrictions on exporting high-performance chips to China. The legal and ethical disputes surrounding AI development highlight the broader challenge of regulating intellectual property in the industry. Meanwhile, competition among AI companies continues to grow, with OpenAI releasing its o3-mini model in response to DeepSeek’s emergence, potentially benefiting consumers through increased model efficiency and affordability.[36] |
| 2025 (February 13) | Impact | It is reported that many young Chinese turn to DeepSeek for emotional support, given economic uncertainty, high unemployment, and limited access to affordable mental health services. By this time DeepSeek had gained popularity for its empathetic and insightful responses, outperforming other Chinese AI models. Users describe feeling deeply moved by its messages, with some considering it a superior alternative to human therapists. While AI chatbots help fill a psychological support gap, experts caution they cannot replace professional care for severe mental health conditions. DeepSeek’s rise reflects both China’s technological advances and the growing emotional needs of its youth.[37][38] |
| 2025 (March 5) | Financial disclosure | DeepSeek discloses that its AI models, V3 and R1, can theoretically achieve a profit margin of 545%. This figure is based on a 24-hour period analysis, where the daily inference cost was approximately $87,072, while the potential revenue stood at $562,027. However, DeepSeek clarified that actual revenues are significantly lower due to factors such as limited monetization of services and off-peak discounts. The company's innovative approach, including the use of cost-effective Nvidia H800 chips, has positioned it as a notable competitor in the AI industry, challenging established models like OpenAI's ChatGPT.[39][40][41][42] |
| 2025 (March 16) | Competition | Baidu launches Ernie X1, a reasoning AI model designed to compete with DeepSeek R1, known for its high performance at low cost. The company also upgrades its flagship model to Ernie 4.5, claiming it surpasses OpenAI’s GPT-4.5 in text generation. Baidu announces it would open-source its Ernie models from June 30, signaling a major strategic shift in response to DeepSeek's rise. It also integrates the R1 model into its search engine. While the AI boom boosts Baidu’s cloud revenue, weak ad sales offset gains.[43] |
| 2025 (April 9) | Research development | In collaboration with Tsinghua University, DeepSeek introduces a new reasoning technique for large language models. This method combines generative reward modelling (GRM) with self-principled tuning to enhance both the speed and quality of model outputs. A paper indicates that the resulting DeepSeek-GRM models achieves competitive results, outperforming several public reward models.[44] |
| 2025 (May 27) | Impact | DeepSeek ranks as the #1 most downloaded app in the App Store in over 156 countries following the January 2025 release of DeepSeek-R1. The startup reports 96.88 million monthly active users as of April 2025 and approximately 22.15 million daily active users in January 2025. Total downloads across Google Play and the App Store exceed 57 million. China, India, and Indonesia together account for just over half of the global user base, which skews younger and predominantly male.[45] |
| 2025 (June 27) | Regulatory action | Germany’s data protection authority asks Apple and Google to review whether to block DeepSeek’s AI app, citing unlawful transfers of German user data to China under EU GDPR rules. Berlin’s data protection commissioner states that DeepSeek unlawfully transfers personal data of German users to China, in violation of the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). According to the authority, DeepSeek had not convincingly demonstrated that user data sent to China is protected at a level equivalent to EU standards, particularly given the broad access rights Chinese authorities may have to data held by Chinese companies.[46] |
| 2025 (July 17) | Expansion | DeepSeek R1 becomes available to all users through Google’s Vertex AI Model Garden as a fully managed Model-as-a-Service offering, expanding access to open models alongside earlier additions such as Llama 4. The announcement emphasizes flexibility and choice for enterprises building AI applications. By delivering large models via serverless APIs, Vertex AI removes the need to provision and manage complex GPU infrastructure, reducing operational and financial burdens. The platform provides scalable, enterprise-grade deployment with built-in security, data privacy, compliance features, and flexible pay-as-you-go pricing.[47] |
| 2025 (August 20) | Update | DeepSeek unveils an updated version of its flagship AI model, V3.1, expanding its context window to 128,000 tokens and improving token efficiency. The model contains 685 billion parameters, uses a hybrid architecture, and balances speed with generation quality across dialogue, reasoning, and programming tasks. In benchmarks such as Aider Polyglot, V3.1 reportedly outperforms Claude 4 Opus. DeepSeek removes references to its R1 reasoning network from the chatbot, later stating that V3.1 introduces hybrid reasoning, faster responses, and enhanced agent capabilities.[48] |
| 2025 (September 30) | Product launch | DeepSeek releases DeepSeek-V3.2-Exp, an experimental open-source large language model intended as a precursor to its next-generation architecture. The model introduces DeepSeek Sparse Attention, a fine-grained sparse attention mechanism designed to improve efficiency in long-context training and inference while preserving output quality. Benchmarks show performance comparable to the V3.1-Terminus model under aligned training conditions.[49] |
| 2025 (October 3) | Regulatory action | A report by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Center for AI Standards and Innovation warns that DeepSeek models pose national security risks despite lagging behind leading U.S. models in performance and cost. The assessment compares DeepSeek with OpenAI and Anthropic systems, finding that DeepSeek models are more susceptible to malicious prompts and more likely to echo Chinese Communist Party narratives. The findings bolster bipartisan efforts in Congress to restrict or ban DeepSeek on U.S. government devices.[50] |
| 2025 (December) | Controversy | DeepSeek is accused of smuggling banned Nvidia Blackwell chips into China to train advanced AI models, allegedly bypassing U.S. export controls through intermediaries and overseas data centers. Reports suggest the chips were acquired in permitted countries and covertly transferred, highlighting enforcement challenges in global semiconductor trade. Nvidia denies involvement and states it would investigate potential violations. The case underscores escalating geopolitical tensions over AI hardware access and accelerates China’s push toward domestic chip development and greater technological self-reliance.[51] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Trends
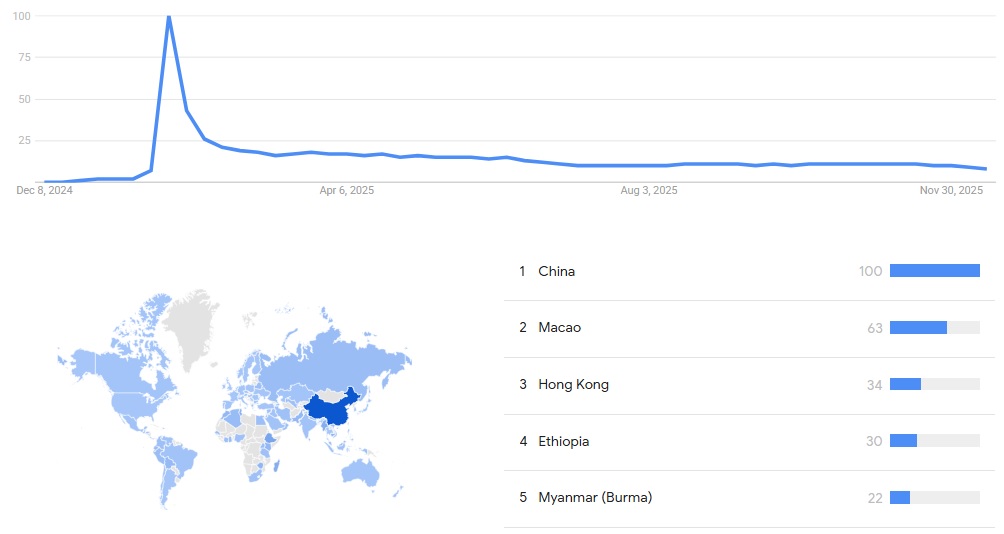
The Google Trends graph below covers the period from December 2024 to November 2025 and shows that interest in “DeepSeek” surged sharply in early 2025, reaching a brief peak before declining and stabilizing at a lower level for the rest of the year. The initial spike reflects intense attention following the DeepSeek chatbot release. Geographic interest is dominated by China, with notable secondary interest in Macao and Hong Kong, indicating strong regional concentration and limited sustained global attention.[52]
Wikipedia views
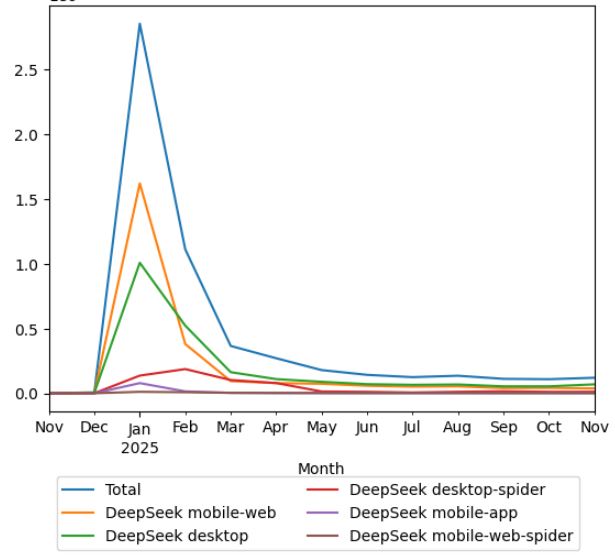
The graph below shows Wikipedia pageviews for the article DeepSeek from November 2024 to November 2025. Views spike sharply in January 2025, indicating a surge of public attention following a major media coverage. After February, views decline rapidly and stabilize at a low but steady level through mid to late 2025.[53]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
- Timeline of ChatGPT
- Timeline of Mistral AI
- Timeline of Bing Chat
- Timeline of Google Bard
- Timeline of large language models
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "The History of Deepseek". Redress Compliance. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Who is behind Deepseek and how did it achieve its AI Sputnik moment?". The Guardian. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ "Chinese Startup Unveils Impressive New AI Chatbot Deepseek". Maginative. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ "China Open-Sources Deepseek LLM, Outperforms Llama 2 and Claude 2". Analytics India Magazine. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ "Meet Deepseek Chat, China's latest ChatGPT rival with a 67B model". VentureBeat. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ "Author Reveals Using ChatGPT for Award-Winning Novel". AI Business. Retrieved 29 January 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek AI Introduces DeepSeek-VL, an Open-Source Vision-Language (VL) Model Designed for Real-World Vision and Language Understanding Applications". MarkTechPost. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ↑ "This AI Paper by DeepSeek AI Introduces DeepSeek-V2: Harnessing Mixture of Experts for Enhanced AI Performance". MarkTechPost. Retrieved 8 May 2024.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 "A History of DeepSeek: Software Updates, Key Milestones, and Their Significance". NewSpaceEconomy. 27 January 2025. Retrieved 1 February 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek Coder V2: Open-Source Model Beats GPT-4 and Claude Opus". The Decoder. Retrieved 8 May 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek V2.0628 Released: An Improved Open-Source Version of DeepSeek V2". MarkTechPost. Retrieved 20 July 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek V2.0628 Released: An Improved Open-Source Version of DeepSeek V2". MarkTechPost. Retrieved 20 July 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek V2.5 Released by DeepSeek AI: A Cutting-Edge 238B-Parameter Model Featuring Mixture of Experts (MoE) with 160 Experts, Advanced Chat, Coding, and 128K Context-Length Capabilities". MarkTech Post. Retrieved 7 September 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek V2.5 Wins Praise as the New True Open-Source AI Model Leader". VentureBeat. Retrieved 7 September 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek AI Releases Janus: A 1.3B Multimodal Model with Image Generation Capabilities". MarkTech Post. Retrieved 18 October 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek's First Reasoning Model R1 Lite Preview Turns Heads, Beating OpenAI O1 Performance". VentureBeat. Retrieved 18 October 2024.
- ↑ "DeepSeek unveils DeepSeek V3 AI LLM with free chatbot access". NotebookCheck. Retrieved 30 January 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek R1: A reasoning model that beats OpenAI O1". Indian Express. 22 January 2025. Retrieved 30 January 2025.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Matt Phillips. "A Quick and Dirty Timeline of the Market's DeepSeekFreak". Sherwood News. Retrieved January 27, 2025.
- ↑ "The deep-sea research expedition that showed the power of teamwork". Nature. 2025-01-29. Retrieved 2025-01-30.
- ↑ "China's AI DeepSeek chatbot". WSJ. The Wall Street Journal. January 29, 2025. Retrieved January 30, 2025.
- ↑ Marc Andreessen (January 27, 2025). "Deepseek R1 is AI's Sputnik moment". Retrieved January 30, 2025.
- ↑ "AI's Sputnik Moment: Chinese AI Model DeepSeek R1 Reportedly Surpasses Leading U.S. AI Models". Foundation for Defense of Democracies. January 30, 2025. Retrieved January 30, 2025.
- ↑ David Goldman, Matt Egan (27 January 2025). "A Shocking Chinese AI Advancement Called DeepSeek Is Sending US Stocks Plunging". CNN. Retrieved 27 January 2025.
- ↑ South China Morning Post (30 January 2025). "Chinese AI Disrupter DeepSeek Claims Top Spot in US App Store, Dethroning ChatGPT". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 30 January 2025.
- ↑ "Apple researchers reveal the secret sauce behind DeepSeek AI". ZDNet. Retrieved January 31, 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek R1 is now available on Azure AI Foundry and GitHub". Microsoft Azure Blog. Retrieved January 31, 2025.
- ↑ Dario Amodei. "On DeepSeek and Export Controls". Dario Amodei's Blog. Retrieved 30 January 2025.
- ↑ "Anthropic CEO Amodei says he doesn't view DeepSeek as adversaries". CNBC. 29 January 2025. Retrieved 30 January 2025.
- ↑ "Alibaba launches Artificial Intelligence model that it says is superior to DeepSeek". AzerNews. 30 January 2025. Retrieved 1 February 2025.
- ↑ "Italy's Data Protection Authority (Garante) blocked DeepSeek". Security Affairs. Retrieved January 31, 2025.
- ↑ "Italy's privacy watchdog blocks Chinese AI app DeepSeek". Reuters. Retrieved January 31, 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek AI blocked by Italian authorities as other member states open probes". Euronews. Retrieved January 31, 2025.
- ↑ "Taiwan bans government departments from using DeepSeek AI". Reuters. 3 February 2025. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- ↑ "BBC News Article". BBC News. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- ↑ "OpenAI says DeepSeek inappropriately copied ChatGPT – but it's facing copyright claims too". The Conversation. Retrieved 4 February 2025.
- ↑ "'DeepSeek moved me to tears': How young Chinese find therapy in AI". BBC News. BBC. Retrieved 11 April 2025.
- ↑ "Why Youths In China Are Turning To DeepSeek For Emotional Support". NDTV. NDTV. Retrieved 11 April 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek reveals theoretical margin on its AI models is 545%". ET CIO. The Economic Times. 2 March 2025. Retrieved 2 March 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek claims 545% profit margin for AI models based on theoretical income". Social Samosa. 2 March 2025. Retrieved 2 March 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek announces 545% theoretical profit margin for AI models". Taipei Times. 3 March 2025. Retrieved 3 March 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek reveals theoretical margin on its AI models is 545%". The Economic Times. 2 March 2025. Retrieved 2 March 2025.
- ↑ "Baidu launches ERNIE-X1 reasoning AI model and DeepSeek R1 chatbot". Fortune. March 16, 2025. Retrieved March 20, 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek teases next big AI model". Digital Watch Observatory. April 9, 2025. Retrieved April 9, 2025.
- ↑ [[1](https://backlinko.com/deepseek-stats) "DeepSeek AI Usage Stats"]. Backlinko. Semrush. Retrieved 13 December 2025.
{{cite web}}: Check|url=value (help) - ↑ Arjun Kharpal (2025-06-27). "Germany tells Apple, Google to block DeepSeek as the Chinese AI app faces rising pressure in Europe". CNBC. Retrieved 2025-12-13.
- ↑ "DeepSeek R1 is available for everyone in Vertex AI Model Garden". Google Cloud Blog. Google. 2025-07-17. Retrieved 2025-12-13.
- ↑ "DeepSeek Unveils Updated AI Model V3.1". ForkLog. Retrieved 2025-12-14.
- ↑ "DeepSeek releases V3.2-Exp experimental model, cuts API prices by over 50%". TechNode. 30 September 2025. Retrieved 13 December 2025.
- ↑ Maria Curi (October 3, 2025). "AI standards institute sounds alarm over DeepSeek". Axios. Retrieved 2025-12-14.
- ↑ "Chinese AI Startup DeepSeek Accused of Smuggling Banned Nvidia Chips". WebProNews. Retrieved 14 December 2025.
- ↑ "DeepSeek – Google Trends". trends.google.com. Retrieved 14 December 2025.
- ↑ "Wikipedia pageviews for "DeepSeek"". WikipediaViews.org. Retrieved 14 December 2025.