Timeline of DeepMind
This is a timeline of DeepMind, a leading artificial intelligence company based in the United Kingdom. DeepMind is subsidiary of Google.
Contents
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary |
|---|---|
| 2010–2014 | DeepMind initiates as a British AI startup. Before being acquired by Google, it remains relatively unknown.[1] |
| Since 2014 | Google's DeepMind era. The acquired company starts being known worldwide. Since being acquired by Google, DeepMind's AI would be used to beat humans at board games and create free apps with the British National Health Service.[2] |
| Since 2016 | DeepMind becomes renowned after its AlphaGo program beats a human professional Go player for the first time and again when AlphaGo beats Lee Sedol, the world champion, in a five-game match.[3] |
| Present time | DeepMind is considered today one of the leading AI companies in the world. It has a team of around 700 people, with most of those based out of Google's headquarters in King's Cross, London.[4] |
Numerical and visual data
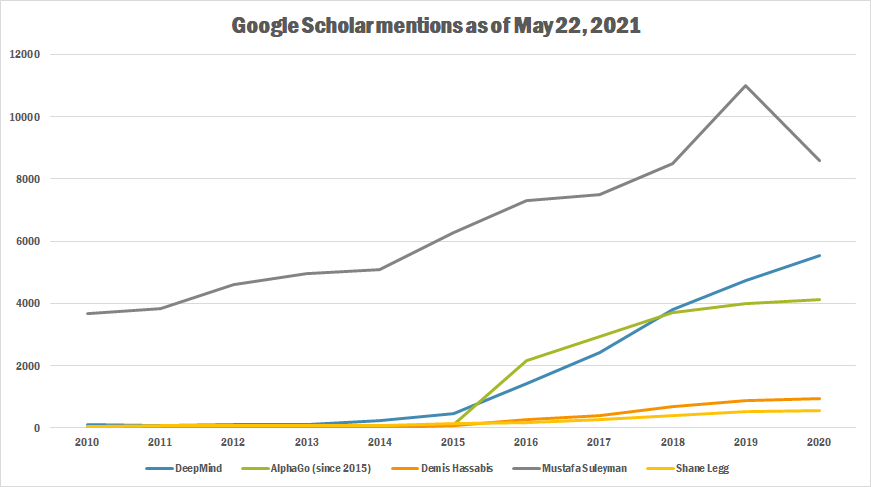
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of May 22, 2021.
| Year | DeepMind | AlphaGo (since 2015) | Demis Hassabis | Mustafa Suleyman | Shane Legg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 97 | 17 | 3,670 | 55 | |
| 2011 | 84 | 15 | 3,840 | 63 | |
| 2012 | 108 | 26 | 4,600 | 87 | |
| 2013 | 111 | 12 | 4,960 | 68 | |
| 2014 | 251 | 25 | 5,100 | 91 | |
| 2015 | 478 | 110 | 87 | 6,270 | 143 |
| 2016 | 1,440 | 2,180 | 274 | 7,300 | 167 |
| 2017 | 2,430 | 2,950 | 406 | 7,490 | 269 |
| 2018 | 3,800 | 3,720 | 699 | 8,500 | 408 |
| 2019 | 4,740 | 3,990 | 887 | 11,000 | 535 |
| 2020 | 5,540 | 4,120 | 930 | 8,580 | 545 |
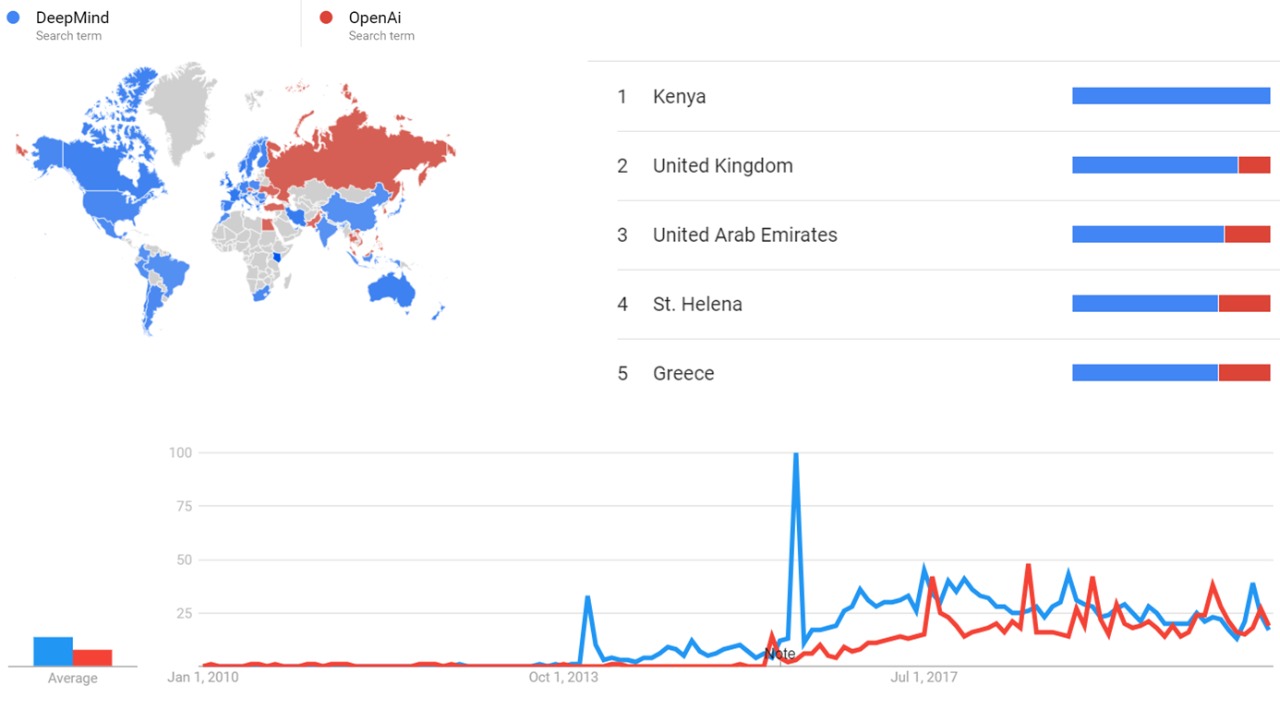
Google Trends
The comparative chart below shows Google Trends data for DeepMind (Search term) and OpenAi (Search term), from January 2010 to February 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[5]
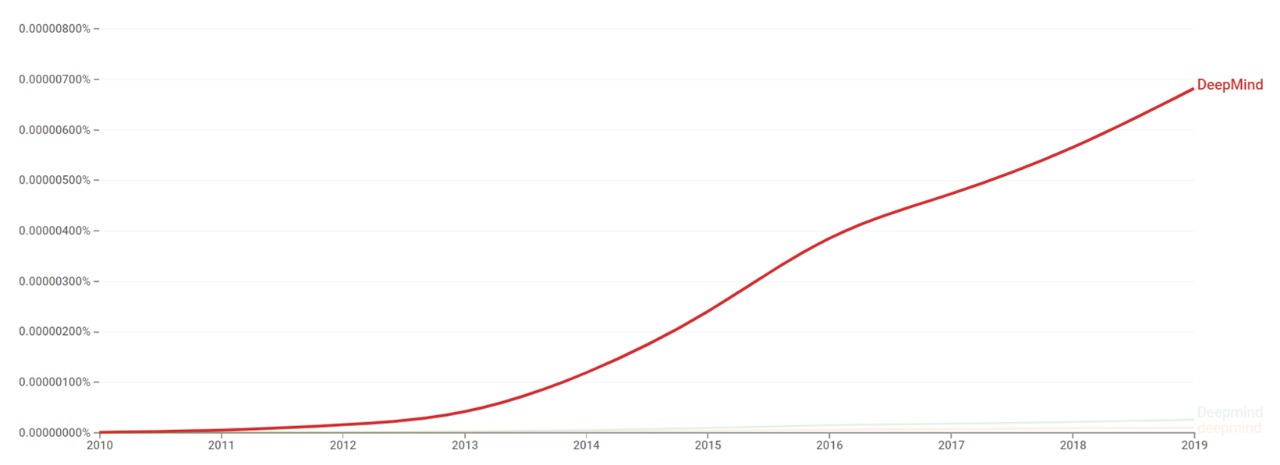
Google Ngram Viewer
The chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for DeepMind, from 2010 to 2019.[6]
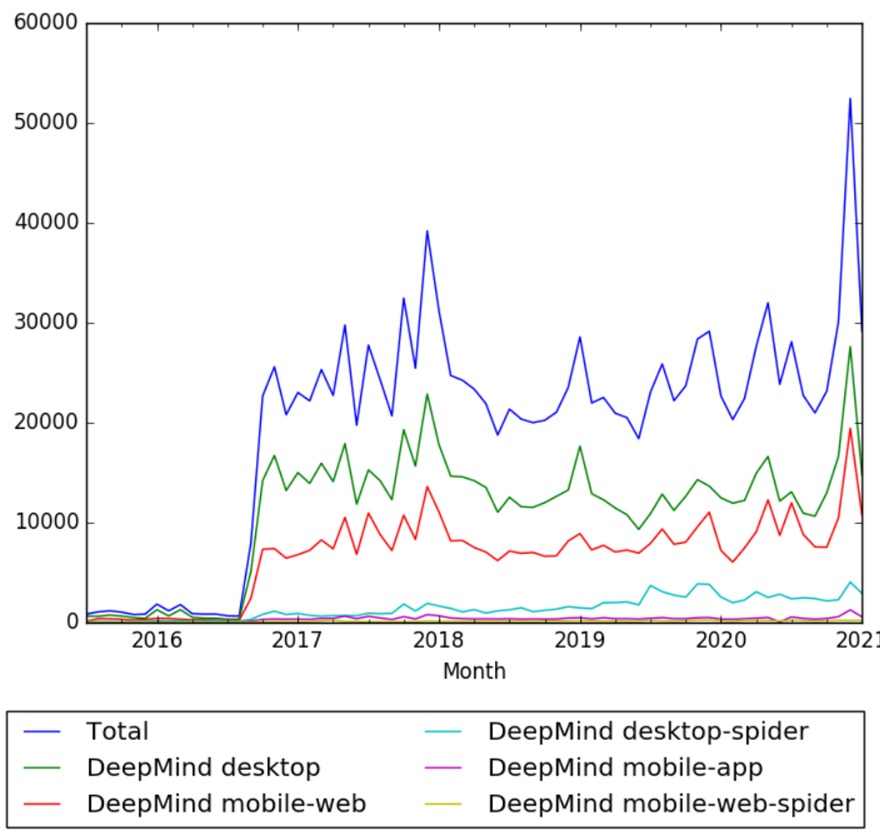
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article DeepMind, on desktop, mobile-web, desktop-spider, mobile-web-spider and mobile app, from July 2015 to January 2021.[7]
Full timeline
| Year | Month and date | Event type | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 | Prelude | British student Demis Hassabis, a chess child prodigy, attains a double first in Computer Science at Cambridge University.[8] | |
| 2009 | Prelude | Demis Hassabis attains a doctorate in Cognitive Neuroscience from University College London.[8] | |
| 2010 | September | Creation | DeepMind Technologies is co-founded by Demis Hassabis alongside Shane Legg, a machine learning researcher from New Zealand, and childhood friend Mustafa Suleyman.[9][10][11] |
| 2011 | February 1 | Funding | DeepMind raises an undisclosed amount from Founders Fund and Horizons Ventures.[12] |
| 2012 | December | Acquisition | Facebook reportedly fails to acquire DeepMind, according to Forbes.[8] Discussions between DeepMind and Facebook about the acquisition happen around this time.[13] |
| 2013 | December | AI development | DeepMind reveals having developed an AI algorithm able to learn how to play iconic early video games like Breakout and Pong simply by watching them being played on a vintage 1977 Atari 2600 games console. The algorithm deduces the rules and rewards from the way the pixels are batted about the screen, then it is able to beat human opponents at playing the games.[14] |
| 2013 | December | Team | DeepMind reportedly has around 75 employees.[13] |
| 2013 | Team | David Silver joins DeepMind as a full-time research scientist.[15] | |
| 2014 | January 27 | Acquisition | Google engages in its largest European acquisition to date with a deal to buy DeepMind for £400 million (US$650 million). From then on, DeepMind starts becoming known worldwide.[2][16][9][14][17] |
| 2014 | October 29 | AI development | DeepMind unveils a neural network that can access an external memory like a conventional Turing machine. The project mimics properties of the human brain's short-term working memory. The result is a computer able to mimic some of the brain’s memory skills and even program like a human.[18][19][20][21] |
| 2014 | November | Notable comment | Elon Musk submits a comment to edge.com about the threat of AI:
The pace of progress in artificial intelligence (I'm not referring to narrow AI) is incredibly fast. Unless you have direct exposure to groups like Deepmind, you have no idea how fast-it is growing at a pace close to exponential. The risk of something seriously dangerous happening is in the five year timeframe. 10 years at most. This is not a case of crying wolf about something I don't understand.[22] |
| 2014 | Recognition | DeepMind receives the "Company of the Year" award from Cambridge Computer Laboratory.[23] | |
| 2015 | June | Notable comment | Mustafa Suleyman describes DeepMind's work during a machine learning conference in London: "Our deep learning tool has now been deployed in many environments, particularly across Google in many of our production systems."[9] |
| 2015 | June | Team | Alex Graves joins DeepMind as a research scientist.[24] |
| 2015 | September | Partnership | DeepMind partners with the Royal Free NHS Trust to develop a patient safety application aimed at reviewing test results for signs of sickness and sending staff instant alerts if an urgent assessment is required. The app would also help clinicians to quickly check for other serious conditions such as acute kidney injury and display results of blood tests, scans, and x-rays at the touch of a button.[9][25] |
| 2015 | October | Achievement | DeepMind's AlphaGo beats the European Go champion Fan Hui, a 2 dan (out of 9 dan possible) professional, five to zero.[26] This is the first time an artificial intelligence defeats a professional Go player.[27] |
| 2015 | February 25 | AI development | DeepMind develops an artificial intelligence capable of learning how to successfully play 49 classic Atari games by itself, with minimal input. The researchers claim software that learns to play video games could graduate to the real world before long.[28][29][30][31] |
| 2016 | February | Partnership | DeepMind announces that it is teaming with the National Health Service to build an app called Streams to help hospital staff monitor patients with kidney disease.[32] |
| 2016 | February 24 | Team | DeepMind launches a new division called DeepMind Health, an initiative aimed at creating apps for medical professionals that can help identify patients at risk of complications.[33][34][35][36] |
| 2016 | April | Controversy | New Scientist obtains a copy of a data-sharing agreement between DeepMind and the Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust. The latter operates three London hospitals where an estimated 1.6 million patients are treated annually. The agreement shows DeepMind Health had access to admissions, discharge and transfer data, accident and emergency, pathology and radiology, and critical care at these hospitals, including personal details such as whether patients have been diagnosed with HIV, suffered from depression or have ever undergone an abortion in order to conduct research to seek better outcomes in various health conditions.[37][38] |
| 2016 | June 3 | AI development | DeepMind develops a ‘big red button’ to stop AIs from causing harm, using a framework in the form of "safely interruptible" artificial intelligence. It guarantees that a machine will not learn to resist attempts by humans to intervene in its learning processes.[39][40][41]. The system is described in a paper by Laurent Orseau from DeepMind and Stuart Armstrong from the Future of Humanity Institute.[42] |
| 2016 | July | AI development | DeepMind announces the ability to cut Google's data centers' energy consumption by 15%, using a machine learning algorithm.[43][44] |
| 2016 | August 30 | Partnership | DeepMind announces a partnership with University College London Hospital to explore using artificial intelligence to treat patients with head and neck cancers. The goal is to develop tools to automatically identify cancerous cells for radiology machines.[45][46][47][48] |
| 2016 | September 9 | AI development | DeepMind claims having significantly improved computer-generated speech with its new system called WaveNet, an AI technology making machines sound more like humans. The system generates voices by sampling real human speech and directly modeling audio waveforms based on it, as well as its previously generated audio.[49][50][51][52] |
| 2016 | October 12 | AI development | DeepMind unveils an AI “working memory” able to learn how to solve tasks for itself, such as how best to get from A to B on the London tube network. The AI combines both data processing with self-learning code. The new algorithm is able to retain information in its memory and use its learnings to solve problems in some areas.[53][54][55] |
| 2016 | November 4 | Partnership | DeepMind teams with Blizzard Entertainment to release an open test environment within the StarCraft II game for artificial intelligence researchers to use worldwide. DeepMind would use deep reinforcement learning to develop an AI agent that can play StarCraft II effectively.[56][57][58] |
| 2016 | November 22 | Partnership | DeepMind announces a five-year agreement with a UK National Health Service trust that would give it access to patient data to develop and deploy its healthcare app, Streams. The agreement lasts until at least 2021.[59][60][61] |
| 2016 | December 5 | Userbase | DeepMind announces open-sourcing DeepMind Lab, its 3D game-like platform for agent-based AI research, so that others can try and make advances in the field of AI. The DeepMind Lab project was used to create enviroments capable of testing AI systems’ ability to achieve goals in a wide range of environments. Tasks such as navigation in mazes, collecting fruit, traversing dangerous passages, laser tag and interaction with bots have been developed to refine the programs. The development of mazes and challenges were designed using video game Quake III Arena’s 17-year-old software, to teach its artificial intelligence programs how to operate in 3D spaces.[62][63][64][65] |
| 2016 | December | International expansion | DeepMind Applied is anounced as a sub-team to be forming in Mountain View, California. This team is expected to be more closely involved with Google, working with the various product teams to help implement AI-based solutions.[66] |
| 2016 | Financial | DeepMind records £40.3 million (US$ 52 million) in revenue in the year.[67] | |
| 2017 | January | Collaboration | DeepMind's experts pledge to pass on their knowledge to students enrolled on machine learning master's programs at University College London.[68] |
| 2017 | March | AI development | DeepMind announces development of a new way to protect confidential health data from itself, in an attempt to assure hospitals, and the public at large, that patient confidentiality isn’t compromised as DeepMind processes the sensitive medical health records entrusted to it.[69][70] |
| 2017 | March | AI development | DeepMind develops algorithms that can anticipate energy demand and supply, with the potential to cut the United Kingdom energy consumption by up to 10%.[71][72][73][74] |
| 2017 | April 17 | Userbase | DeepMind open sources TensorFlow library Sonnet, its object-oriented neural network library. Sonnet is a higher-level library that meshes well with DeepMind’s internal best-practices for research.[75][76] |
| 2017 | May | Controversy | Sky News publishes a leaked letter from the National Data Guardian, Dame Fiona Caldicott, revealing that in her "considered opinion" the data-sharing agreement between DeepMind and the Royal Free took place on an "inappropriate legal basis".[77] |
| 2017 | June | Partnership | DeepMind’s safety team partners with OpenAI in the development of an algorithm which can infer what humans want by being told which of two proposed behaviors is better. The learning algorithm uses small amounts of human feedback to solve modern reinforcement learning environments.[78] |
| 2017 | July | International expansion | DeepMind announces its first international research lab in Edmonton, Canada.[79][80][81][82] |
| 2017 | July | Controversy | The UK Information Commissioner's Office rules that the Royal Free has breached the Data Protection Act by providing DeepMind with the personal data of around 1.6 million patients.[9] |
| 2017 | Kuly 10 | AI development | DeepMind uses reinforcement learning to master parkour, using a virtual course designed by the researchers which features drops, hurdles, and ledges. All of the navigation is self-taught by the AI using a trial-and-error approach to working out how to move forward and progress across the course as fast as possible.[83][84] |
| 2017 | July 19 | AI development | DeepMind releases a paper describing new developments for "imagination-based planning" to AI and algorithms that simulate the human ability to construct plans. The AI can reason through decisions and make plans for the future, without being bound by human instructions.[85][86][87][88] |
| 2017 | October 4 | Team | DeepMind launches DeepMind Ethics & Society (DMES), a new research group recruiting advisers from academia and charity sector with the purpose to ‘help technologists put ethics into practice’ and help coping with artificial intelligence to consider the “real-world impacts” of replicating human intelligence. The group consists of six independent research fellows, eight full-time researchers, and nine partnerships with other research institutions. It would explore topics such as algorithmic bias, accountability, and autonomous killing machines.[89][90][91] |
| 2017 | October 18 | AI development | DeepMind announces AlphaGo Zero, a software capable of mastering the Chinese game of Go without help from human players. The new version is an improvement on the original AlphaGo, which had to be trained over time using large quantities of human knowledge and supervision.[92][93][94][95][96] |
| 2017 | October 20 | Recognition | The DeepMind team behind AlphaGo is awarded the inaugural Marvin Minsky Medal by the International Joint Conference On Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) in Stockholm, for outstanding achievements in the field of AI.[97][98][99][100] |
| 2017 | October | International expansion | DeepMind opens new research office in Montreal, led by McGill University professor Doina Precup.[101] |
| 2017 | November | Partnership | DeepMind announces a research partnership with the Cancer Research UK Center at Imperial College London with the goal of improving breast cancer detection by applying machine learning to mammography.[102] |
| 2017 | December 5 | AI development | DeepMind team introduces AlphaZero, a program using generalized AlphaGo Zero's approach, which achieved within 24 hours a superhuman level of play in chess, shogi, and Go, defeating world-champion programs, Stockfish, Elmo, and 3-day version of AlphaGo Zero in each case.[103] |
| 2017 | Financial | DeepMind records £54.4 million (US$ 71 million) in revenue in 2017, up 35% from £40.3 million (US$ 52 million) in 2016.[67] | |
| 2018 | February | Partnership | DeepMind announces that it is teaming with the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs in an attempt to use machine learning to predict the onset of acute kidney injury in patients, and also more broadly the general deterioration of patients during a hospital stay so that doctors and nurses can more quickly treat patients in need.[104] |
| 2018 | February | AI development | DeepMind develops an artificial intelligence capable of an ability that most children only develop at around age 4, which is to infer what someone else is thinking. This new technology is thought to have useful application in the future, from warfare to elderly care.[105][106][107] |
| 2018 | March | International expansion | DeepMind announces a new research lab in Paris, led by Remi Munos.[108] |
| 2018 | May 9 | AI development | DeepMind develops a neural network loosely modeled on mammalian brains, that is better at navigating a maze than humans.[109][110][111][112] |
| 2018 | June 14 | AI development | DeepMind develops a neural network that teaches itself to ‘imagine’ a scene from different viewpoints, based on just a single image. The new type of computer vision algorithm can generate 3D models of a scene from 2D snapshots, unraveling details from the static images and solving spatial relationships, including the camera’s position. Dubbed a Generative Query Network (GQN), the system gets rid of labels and focuses on what's known as unsupervised learning.[113][114][115][116] |
| 2018 | June 15 | Controversy | The DeepMind Health Independent Reviewers’ 2018 report warns about the potential for DeepMind Health to be able to “exert excessive monopoly power” as a result of the data access and streaming infrastructure that’s bundled with provision of the Streams app, which would position DeepMind as the access-controlling intermediary between the structured health data and any other third parties.[117][118] |
| 2018 | June 26 | Demis Hassabis is enlisted by the British government's Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS), as an adviser to the Government’s new Office for Artificial Intelligence.[119][120] | |
| 2018 | November 19 | Partnership | DeepMind partners with OpenAI in a new paper that proposes a new method to train reinforcement learning agents in ways that enables them to surpass human performance. The paper, titled Reward learning from human preferences and demonstrations in Atari, introduces a training model that combines human feedback and reward optimization to maximize the knowledge of RL agents.[121] |
| 2018 | July | AI development | Researchers from DeepMind train one of its systems to play the famous computer game Quake III Arena.[122] |
| 2018 | July 11 | AI development | DeepMind presents a paper titled "Measuring abstract reasoning in neural networks", which details its attempt to measure various AIs’ abstract reasoning capabilities, much like IQ tests for humans.[123][124] |
| 2018 | July 18 | Commitment | DeepMind, along with tech leaders, including Elon Musk, sign a pledge promising to not develop “lethal autonomous weapons.” They also call on governments to institute laws against such technology. The pledge is organized by the Future of Life Institute, an outreach group focused on tackling existential risks.[125][126][127] |
| 2018 | August 13 | AI development | DeepMind announces an AI capable of detecting over 50 eye diseases and making correct diagnoses 94.5% of the time after trial with Moorfields Eye Hospital in London.[128][129][130][131] |
| 2018 | September 26 | Partnership | DeepMind announces a partnership with Unity Technologies with the purpose to accelerate machine learning and artificial intelligence research. The new collaboration would focus on "virtual environments" that DeepMind can use to test and visualize experimental algorithms.[132][133][134][135] |
| 2018 | October 4 | AI development | DeepMind furthers cancer research and announces having been given access to mammograms from roughly 30,000 women that were taken at Jikei University Hospital in Tokyo, Japan between 2007 and 2018. The data would be used to refine DeepMind's AI breast cancer detection algorithms.[136][137] |
| 2018 | November 13 | Team | Google announces DeepMind’s health care unit to be absorbed to the holding company to create an ‘AI assistant for nurses and doctors’.[138][139] |
| 2018 | November 19 | AI development | DeepMind safety research team publishes a paper on scalable agent alignment via reward modeling. The paper gives a summary of a research direction for solving the agent alignment problem.[140][141] |
| 2018 | December 2 | AI development | DeepMind unveils AlphaFold, an algorithm able to predict the complex, three-dimensional shapes into which proteins can be folded. The prediction is based solely on their genetic sequence.[142][143][144][145] |
| 2018 | December | Notable comment | Demis Hassabis announces: "I'd be much more pessimistic about the way the world is going to go if I didn't know there was something as game-changing as AI on the way."[9] |
| 2019 | February | Achievement | DeepMind's AI AlphaStar is revealed to outperform human professionals at StarCraft II, beating the humans 10 games in a row.[146][147][148][149] |
| 2019 | February | AI development | DeepMind develops an algorithm aimed at boosting wind energy efficiency. Google reports having increased energy production by 20% after installing its own AI software across its largest renewable energy facilities in the United States.[150][151] |
| 2019 | March | Team | As of date, DeepMind has about 700 employees.[152] |
| 2019 | April | Team | Google disbands the advisory board for DeepMind Health. It is the second disbanded review panel related to Alphabet's AI dealings.[153][154][155] |
| 2019 | April | AI development | DeepMind researchers develop an AI tasked with teaching itself to solve arithmetic, algebra and probability problems, among others. However, the neural network performs poorly when tested on a maths exam taken by 16-year-olds in the United Kingdom, getting just 14 out of 40 questions correct, or the equivalent of an E grade.[156][157] |
| 2019 | June | AI development | DeepMind medical director Dominic King says AI could soon be used in predictive medicine, achieving this by looking at a medical record and electronic health record data to make predictions.[158] |
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "How Google's Amazing AI Start-Up 'DeepMind' Is Making Our World A Smarter Place". forbes.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Shead, Sam. "Google's $500+ million purchase of DeepMind just got very interesting". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind". paganresearch.io. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind Built An iPhone Space Simulation Game, But Never Released It". forbes.com. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind and OpenAi". Google Trends. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ↑ "DeepMind". books.google.com. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ↑ "DeepMind". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 19 February 2021.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Google buys UK artificial intelligence startup Deepmind for £400m". theguardian.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 "Google DeepMind: the story behind the world's leading AI startup". techworld.com. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind's elusive third cofounder is the man making sure that machines stay on our side". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "Neuroscience, intuition and superhumans - how DeepMind co-founder and UCL alumnus Demis Hassabis is leading the Artificial Intelligence revolution". ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind > Recent News & Activity". crunchbase.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Google To Acquire Artificial Intelligence Company DeepMind". forbes.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Google buys AI firm DeepMind to boost image search". newscientist.com. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Computer Science News". cs.ucl.ac.uk. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ↑ "Google buys UK artificial intelligence startup Deepmind for £400m". theguardian.com. Retrieved 5 June 2019.
- ↑ "Google acquires artificial intelligence company DeepMind". computerworld.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google's Secretive DeepMind Startup Unveils a "Neural Turing Machine"". technologyreview.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Hornyak, Tim. "Google's DeepMind AI project apes human memory and programming skills". pcworld.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Computer with human-like learning will program itself". newscientist.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google reveals it is developing a computer so smart it can program ITSELF". dailymail.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "28 Best Quotes About Artificial Intelligence". bernardmarr.com. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ↑ "Hall of Fame Awards: To celebrate the success of companies founded by Computer Laboratory graduates.". University of Cambridge. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "The 21 smartest AI scientists working at Google DeepMind". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ↑ Lomas, Natasha. "Documents detail DeepMind's plan to apply AI to NHS data in 2015". TechCrunch. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google achieves AI 'breakthrough' by beating Go champion". BBC News. 27 January 2016.
- ↑ "Première défaite d'un professionnel du go contre une intelligence artificielle". Le Monde (in French). 27 January 2016.
- ↑ Twilley, Nicola. "Artificial Intelligence Goes to the Arcade". newyorker.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Clark, Liat. "DeepMind's AI is an Atari gaming pro now". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google's AI Masters Space Invaders (But It Still Stinks at Pac-Man)". technologyreview.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Devlin, Hannah. "Google develops computer program capable of learning tasks independently". theguardian.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Revealed: Google AI has access to huge haul of NHS patient data". newscientist.com. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google's DeepMind AI group unveils health care ambitions". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "Google's London AI powerhouse has set up a new healthcare division and acquired a medical app called Hark". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google AI group that's mastering Go is now taking on healthcare". theverge.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Smart care: how Google DeepMind is working with NHS hospitals". theguardian.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Hodson, Hal (29 April 2016). "Revealed: Google AI has access to huge haul of NHS patient data". New Scientist. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Leader: If Google has nothing to hide about NHS data, why so secretive?". New Scientist. 4 May 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ Byrne, Michael. "Google DeepMind Researchers Develop AI Kill Switch". vice.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Li, Abner. "Google DeepMind has developed a 'big red button' to stop AIs from causing harm". 9to5google.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "Google has developed a 'big red button' that can be used to interrupt artificial intelligence and stop it from causing harm". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Safely Interruptible Agents" (PDF). intelligence.org. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ↑ Burgess, Matt. "Google's DeepMind trains AI to cut its energy bills by 40%". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Wakefield, Jane. "Google uses AI to save on electricity from data centres". bbc.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google is teaming up with a London hospital to inject AI into cancer treatment". qz.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google DeepMind targets NHS head and neck cancer treatment". bbc.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google DeepMind and UCLH collaborate on AI-based radiotherapy treatment". theguardian.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google DeepMind wants to use machine learning to help treat certain cancers". theverge.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google's DeepMind artificial intelligence has figured out how to talk". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Gallego, Jelor. "At Last, Google's DeepMind AI Can Make Machines Sound Like Humans". futurism.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Robertson, Adi. "Google's DeepMind AI fakes some of the most realistic human voices yet". theverge.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Krumins, Aaron. "Robots receive a scary-accurate new voice, courtesy of Google's DeepMind". extremetech.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind's AI has learned to navigate the Tube using memory". newscientist.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Burgess, Matt. "DeepMind's AI learned to ride the London Underground using human-like reason and memory". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Hsu, Jeremy. "Google's Deep Mind Gives AI a Memory Boost That Lets It Navigate London's Underground". spectrum.ieee.org. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Byford, Sam. "Google DeepMind's next gaming challenge: can AI beat StarCraft II?". theverge.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Reichert, Corinne. "Google's DeepMind turns to StarCraft II after conquering Go". zdnet.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Galeon, Dom. "DeepMind: AI is Heading to StarCraft". futurism.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Pelaez, Jose Luis. "Google's DeepMind agrees new deal to share NHS patient data". newscientist.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Collins, Katie. "Google DeepMind knows you well enough to save your life". cnet.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Lomas, Natasha. "Patient data API pivotal to DeepMind's push into UK's NHS". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ McCarthy, John. "Google DeepMind releases source code to the Quake III levels its using to train AIs". thedrum.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Condon, Stephanie. "OpenAI, DeepMind open source AI training platforms". zdnet.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "DeepMind is opening up its 'flagship' platform to AI researchers outside the company". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Kahn, Jeremy. "Google DeepMind Makes AI Training Platform Publicly Available". bloomberg.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ "New DeepMind Applied Team Being Formed In Mountain View". androidheadlines.com. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 "DeepMind Losses Grew To $368 Million In 2017". forbes.com. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "DeepMind's AI experts have pledged to pass on their knowledge to students at UCL". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Wong, Joon Ian. "Google's DeepMind has a plan for protecting private health data—from itself". qz.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ "Trust, confidence and Verifiable Data Audit". deepmind.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "Google's Deepmind wants to cut 10% off the entire UK's energy bill". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Thompson, Avery. "Google Wants to Use AI to Cut the UK's Electric Bill by 10 Percent". popularmechanics.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google Wants To Use AI To Cut the UK's Electric Bill By 10 Percent". hardware.slashdot.org. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google's Deepmind wants to cut 10% off the entire UK's energy bill". businessinsider.nl. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Mannes, John. "Google DeepMind open sources Sonnet so you can build neural networks in TensorFlow even quicker". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Quach, Katyanna. "DeepMind hopes its TensorFlow lib Sonnet is music to ears of AI devs". theregister.co.uk. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Martin, Alexander J (15 May 2017). "Google received 1.6 million NHS patients' data on an 'inappropriate legal basis'". Sky News. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Learning from Human Preferences". openai.com. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ↑ Vincent, James. "Google's AI powerhouse DeepMind is opening its first international lab in Canada". theverge.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Fingas, Jon. "Google's next DeepMind AI research lab opens in Canada". engadget.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Kahn, Jeremy. "DeepMind Goes to Alberta For First International Lab". bloomberg.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Semeniuk, Ivan. "AI company that conquered Go game opens office in Edmonton". theglobeandmail.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Vincent, James. "DeepMind's AI is teaching itself parkour, and the results are adorable". theverge.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Daws, Ryan. "Google's DeepMind uses reinforcement learning to master parkour". developer-tech.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Plummer, Libby. "Google's DeepMind creates an AI with 'imagination'". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Locklear, Mallory. "DeepMind researchers create AI with an 'imagination'". engadget.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Nield, David. "Google Has Started Adding Imagination to Its DeepMind AI". sciencealert.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Prigg, Mark. "Google's DeepMind researchers create AI with an 'imagination'". dailymail.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Gershgorn, Dave. "DeepMind now has two ethics groups, but one of them is still secret". qz.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Hern, Alex. "DeepMind announces ethics group to focus on problems of AI". theguardian.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ Sawers, Paul. "Alphabet's DeepMind sets up 'ethics and society' unit to research real-world impact of AI". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ↑ "AI versus AI: Self-Taught AlphaGo Zero Vanquishes Its Predecessor". scientificamerican.com. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ↑ Cellan-Jones, Rory. "Google DeepMind: AI becomes more alien". bbc.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Burgess, Matt. "DeepMind's latest AI breakthrough is its most significant yet". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Cuthbertson, Anthony. "Deepmind AlphaGo: AI Teaches Itself 'Thousands of Years of Human Knowledge' Without Help". newsweek.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "DeepMind's human-bashing AlphaGo AI is now even stronger". businessinsider.com. Retrieved 30 May 2019.
- ↑ Gorey, Colm. "DeepMind team behind AlphaGo wins inaugural 'Nobel Prize for AI'". siliconrepublic.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind team behind AlphaGo wins inaugural 'Nobel Prize for AI'". lionra.ie. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "IJCAI 2018 Kicks Off; DeepMind AlphaGo Wins Marvin Minsky Medal". medium.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind wins the Minsky medal for AlphaGo". celi.it. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind opens new AI research office in Montreal". linkedin.com. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ↑ "Google DeepMind announces new research partnership to fight breast cancer with AI". Silicon Angle. 24 November 2017.
- ↑ Silver, David; Hubert, Thomas; Schrittwieser, Julian; Antonoglou, Ioannis; Lai, Matthew; Guez, Arthur; Lanctot, Marc; Sifre, Laurent; Kumaran, Dharshan; Graepel, Thore; Lillicrap, Timothy; Simonyan, Karen; Hassabis, Demis (5 December 2017). "Mastering Chess and Shogi by Self-Play with a General Reinforcement Learning Algorithm".
- ↑ "Google's DeepMind wants AI to spot kidney injuries". Venture Beat. 22 February 2018.
- ↑ Revell, Timothy. "DeepMind AI is learning to understand the 'thoughts' of others". newscientist.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "Will A.I. Ever Be Smarter Than a Four-Year-Old?". smithsonianmag.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "'Deep Mind' AI As Advanced as a 4yr old!". trebuchet-magazine.com. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ↑ "A return to Paris". deepmind.com. Retrieved 5 July 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind AI developed navigation neurons to solve a maze like us". newscientist.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Sample, Ian. "Google DeepMind's AI program learns human navigation skills". theguardian.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Gent, Edd. "This DeepMind AI Spontaneously Developed Digital Navigation 'Neurons' Like Ours". singularityhub.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Quach, Katyanna. "DeepMind: Get a load of our rat-like AI. 'Ere, look. It solves mazes and stuff". theregister.co.uk. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Whyte, Chelsea. "DeepMind's AI can 'imagine' a world based on a single picture". newscientist.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Bogle, Ariel. "Who needs humans? Google's DeepMind algorithm can teach itself to see". abc.net. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Wiggers, Kyle. "Google's DeepMind develops AI that can render 3D objects from 2D pictures". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "Neural scene representation and rendering". science.sciencemag.org. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Lomas, Natasha. "UK report warns DeepMind Health could gain 'excessive monopoly power'". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Lomas, Natasha. "Building health AIs should be UK ambition, says strategy review". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind co-founder among experts to advise Government on using AI". eveningexpress.co.uk. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "UK enlists DeepMind's Demis Hassabis to advise its new Government Office for AI". zdnet.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Rodriguez, Jesus. "What's New in Deep Learning Research: OpenAI and DeepMind Join Forces to Achieve Superhuman Performance in Reinforcement Learning". towardsdatascience.com. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind AI’s new trick is playing ‘Quake III Arena’ like a human". Engadget. 3 July 2018.
- ↑ Wiggers, Kyle. "Google's DeepMind developed an IQ test for AI models". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Houser, Kristin. "DeepMind created an IQ test for AI, and it didn't do too well". weforum.org. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Vincent, James. "Elon Musk, DeepMind founders, and others sign pledge to not develop lethal AI weapon systems". theverge.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Locklear, Mallory. "DeepMind, Elon Musk and others pledge not to make autonomous AI weapons". engadget.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Quach, Katyanna. "Elon Musk, his arch nemesis DeepMind swear off AI weapons". theregister.co.uk. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Burgess, Matt. "Now DeepMind's AI can spot eye disease just as well as your doctor". wired.co.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Major, Mario L. "AI System by Google's DeepMind Can Diagnose Over 50 Common Eye Diseases". interestingengineering.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Kelly, Éanna. "DeepMind's AI doctor predicted to transform eye disease diagnosis". sciencebusiness.net. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ Vincent, James. "DeepMind's AI can detect over 50 eye diseases as accurately as a doctor". theverge.com. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind and Unity will work together on AI research". engadget.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "Google's DeepMind teams with leading 3D game dev platform Unity". zdnet.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Johnson, Khari. "Google's DeepMind and Unity join forces to create simulated environments for AI training". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ "How Google's DeepMind will train its AI inside Unity's video game worlds". fastcompany.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Wiggers, Kyle. "DeepMind expands AI cancer research program to Japan". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Shead, Sam. "Google DeepMind Given Access To Mammograms Of 30,000 Women By Japanese Hospital". forbes.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Vincent, James (13 November 2018). "Google is absorbing DeepMind's health care unit to create an 'AI assistant for nurses and doctors'". The Verge. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ "Google Is Absorbing DeepMind's Health Care Unit To Create An 'AI Assistant For Nurses and Doctors'". science.slashdot.org. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ↑ Leike, Jan. "Scalable agent alignment via reward modeling". medium.com. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ↑ Leike, Jan; Krueger, David; Everitt, Tom; Martic, Miljan; Maini, Vishal; Legg, Shane. https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.07871. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Lomas, Natasha. "DeepMind claims early progress in AI-based predictive protein modelling". techcrunch.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Wiggers, Kyle. "Deepmind's AlphaFold wins CASP13 protein-folding competition". venturebeat.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Kahn, Jeremy. "Alphabet's DeepMind AI Algorithm Wins Protein-Folding Contest". bloomberg.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Sample, Ian. "Google's DeepMind predicts 3D shapes of proteins". theguardian.com. Retrieved 1 June 2019.
- ↑ Grayson, Nathan. "Google's DeepMind AI Just Beat Two Pros At StarCraft II". kotaku.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind Beats Pros at StarCraft in Another Triumph for Bots". wired.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind AI AlphaStar goes 10-1 against top 'StarCraft II' pros". engadget.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind - StarCraft II Demonstration". starcraft2.com. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ↑ Cuff, Madeleine. "Google and DeepMind deploy AI to predict wind energy output". businessgreen.com. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind: Google uses AI technology to boost wind energy efficiency". edie.net. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- ↑ Webb, Amy. The Big Nine: How the Tech Titans and Their Thinking Machines Could Warp Humanity.
- ↑ Fuertes, Rechelle Ann. "Google Disbands Advisory Board for DeepMind Health". edgy.app. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Fuertes, Rechelle Ann. "Google Disbands Advisory Board for DeepMind Health". edgy.app. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Merriman, Chris. "DeepMind becomes the second Alphabet company to disband an AI ethics panel". theinquirer.net. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Vaughan, Adam. "DeepMind created a maths AI that can add up to 6 but gets 7 wrong". newscientist.com. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ Srivastava, Smriti. "DeepMind Examined AI Neural Net Over High School Maths, but Lacked Success". analyticsinsight.net. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ↑ "DeepMind health lead says AI could soon be used in predictive medicine". digitalhealth.net. Retrieved 29 June 2019.