Timeline of vitamin D
This is a timeline of vitamin D, attempting to describe significant and illustrative events in the history of vitamin D.
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- What are some important events preceeding the discovery of vitamin D?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Prelude".
- You will see some important events related to the history of vitamin D, like the first description of rickets, and early treatments involving vitamin D, such as cod liver oil.
- What are some health conditions related to vitamin D named in this timeline?
- Sort the full timeline by "Related health condition (when applicable)".
- You will see a range of conditions, often rickets, but also cancer and kidney disease, among others.
- What are some significant or illustrative studies being conducted on Vitamin D?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Research".
- You will see a variety of studies of different types, from cohort studies indicating the effect of vitamin D in subjects, to laboratory studies such as molecular cloning.
- What are some Vitamin D recommended intakes published by competent institutions?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Recommendation".
- Check table of recommendations for vitamin D for adults in Canada and United States.
- What are some vitamin D-related drugs having been launched to the market?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Drug launch".
- You will see a list of marketed analogs of vitamin D.
- What are some illustrative books specializing in vitamin D?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Literature".
- You will see a number of publications, some by notable authors such as Michael F. Holick.
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| 2nd century–1890s | Recognition & empiricism | Vitamin D history begins as a clinical problem long before a biochemical explanation exists. Physicians in antiquity and early modern Europe identify rickets as a distinct childhood bone disorder, carefully describing its deformities and prevalence. By the 18th and 19th centuries, cod liver oil becomes an established empirical treatment for both rickets and tuberculosis, despite ignorance of its active component. Observational insights gradually accumulate: children in crowded, sun-poor urban environments are disproportionately affected, while those in sunnier regions are largely spared. These patterns lead to early hypotheses about sunlight as a protective factor. By the late 19th century, rickets is well defined clinically, effective remedies exist, and environmental determinants are suspected—but the underlying substance and mechanism remain unknown. |
| 1890s–1937 | Vitamin discovery & UV biology | This period transforms scattered observations into nutritional science. The emergence of the vitamin concept enables researchers to classify “accessory food factors” essential for health. Experiments distinguish vitamin D from vitamin A and show that cod liver oil contains a rickets-preventing factor resistant to heating. Parallel work demonstrates that ultraviolet light alone can cure rickets, implying endogenous synthesis. Animal models reveal that skin irradiation generates a precursor later stored in tissues. By the early 1930s, vitamin D₂ is purified and crystallized, and its chemical structure clarified. The isolation of 7-dehydrocholesterol and identification of vitamin D₃ as the natural skin-derived form complete the discovery phase. Vitamin D is now recognized as both diet-derived and sunlight-generated.[1] |
| 1940s–late 1970s | Endocrine system & regulation | With rickets largely controlled, research shifts from discovery to mechanism, safety, and policy. Governments establish intake recommendations and fortification programs, but excessive dosing leads to toxicity episodes, forcing reassessment of public health strategies. Mechanistic advances overturn the belief that vitamin D acts directly: it is shown to undergo liver and kidney activation and to function like a steroid hormone. Key metabolites, including calcifediol and calcitriol, are identified, along with specific nuclear receptors mediating gene regulation. Vitamin D becomes understood as a tightly regulated endocrine system central to calcium homeostasis, bone metabolism, and neuromuscular function. Definitive proof of cutaneous vitamin D₃ synthesis resolves long-standing debates, marking the conceptual maturation of vitamin D biology. |
| 1980s–2025 | Expansion, controversy & precision | From the 1980s onward, vitamin D research expands beyond bone into cancer, immunity, cardiovascular disease, autoimmunity, and aging. Epidemiological studies link low vitamin D levels to diverse chronic conditions, while laboratory work reveals receptor expression across many tissues. Vitamin D analogs enter clinical use for kidney disease, psoriasis, and osteoporosis. However, large randomized trials increasingly show mixed or context-dependent benefits, challenging earlier optimism. Evidence accumulates that responses vary by baseline deficiency, age, BMI, pregnancy status, and comorbidities. Recent guidelines favor conservative supplementation for healthy adults while recognizing benefits in specific populations. Contemporary research emphasizes personalized dosing, metabolic complexity, and mechanistic pathways, reframing vitamin D as neither panacea nor trivial nutrient, but a context-sensitive biological regulator. |
Full timeline
| Year | Related health condition (when applicable) | Event type | Details | Location/researcher affiliation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd century AD | Rickets | Clinical description | Rickets, the bone disease caused by vitamin D deficiency, is described by Soranus of Ephesus’s in Roman children.[2] | |
| 1650 | Rickets | Clinical description | Rickets is described in detail by British physician Francis Glisson.[3] | United Kingdom |
| 1770 | Tuberculosis | Therapeutic practice | Cod liver oil, rich in vitamin D, is first advocated for the treatment of tuberculosis.[4] Derived from liver of cod fish (Gadidae), today it is a dietary supplement. | |
| 1822 | Rickets | Hypothesis (etiology) | Polish physician Jędrzej Śniadecki observes that lack of sunlight exposure is likely a cause of rickets.[5] | Poland |
| 1824 | Rickets | Therapeutic practice | Although having been used medicinally for a long time, cod liver oil (which has vitamin D) is first prescribed by D. Scheutte for the treatment of rickets.[3] | |
| 1849 | Tuberculosis | Clinical evidence (observational) | English physician Charles Theodore Williams reports the results of administering fish liver oil (vitamin D) to 234 patients with tuberculosis. He notes an important improvement in a few days and concludes that ”the pure fresh oil from the liver of the cod is more beneficial in the treatment of pulmonary consumption than any agent, medicinal, dietetic, or regiminal, that has yet been employed“.[6] | United Kingdom |
| 1849 | Tuberculosis | Prelude (medical development) | Cod liver oil is recognized in Europe as beneficial in the treatment of tuberculosis.[7] | Europe |
| 1890 | Rickets | Prelude (research) | British medical missionary and epidemiologist Theodore Palm notes through his travels that children living in equatorial countries do not develop rickets.[8] | |
| 1903 | Tuberculosis | Prelude (research) | Faroese physician Niels Ryberg Finsen is awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery that shortwave ultraviolet light is effective in the treatment of cutaneous tuberculosis.[9] | |
| 1906 | Rickets | Prelude (research) | English biochemist Frederick Gowland Hopkins postulates the existence of essential dietary factors necessary for the prevention of diseases such as scurvy or rickets.[3][10] | United Kingdom |
| 1912 | Prelude (research) | Frederick Gowland Hopkins describes the vitamins.[2] | United Kingdom | |
| 1913 | Discovery/identification | The identification of vitamin A by McCollum and Davis marks the beginning of the concept of accessory food factors, ultimately enabling a full understanding of nutritional requirements. This development paves the way for the discovery of vitamin D, including the recognition that it is produced in the skin through exposure to ultraviolet light.[11] | ||
| 1914 | Rickets | Discovery / identification | McCollum and co-workers conduct a series of experiments that would lead to the discovery of vitamin D. The team manages to isolate a substance from butterfat, necessary for prevention of xerophthalmia in rats, and name it “fat-soluble factor A”. They subsequently report that heated oxidized cod-liver oil could not prevent xerophthalmia but could cure rickets in rats, and conclude that “fatsoluble factor A” consists of two entities, one which could prevent xerophthalmia (subsequently called vitamin A) and one which cured rickets (subsequently called vitamin D, as the terms vitamin B and vitamin C have already been coined).[9][12] | United States (Wisconsin Agricultural Experiment Station, University of Wisconsin–Madison) |
| 1919 | Clinical evidence (observational) | British biochemist Edward Mellanby observes that dogs who were fed a diet of mostly oatmeal and kept indoors away from the sun could be cured of the disease by providing cod liver oil.[13] | United Kingdom | |
| 1921 | Rickets | Epidemiologic observation | Hess and Unger observe that “seasonal incidence of rickets is due to seasonal variations of sunlight.”[3] | |
| 1922 | Rickets | Discovery/identification | American biochemist Elmer McCollum at Johns Hopkins University discovers Vitamin D from cod liver oil as a dietary substance that could prevent rickets.[14] | United States |
| 1922 | Rickets | Clinical evidence (observational) | British microbiologist Hariette Chick and her co-workers, working with malnourished children in a clinic in Vienna, show that rickets prevalent in the children could be cured by whole milk or cod-liver oil.[3] | Austria |
| 1923 | Rickets | Mechanism/pathway | Harry Goldblatt and Katharine Marjorie Soames show the conversion of a precursor to vitamin D in the skin under the effect of ultraviolet light. They also observe that livers of irradiated rats are curative when fed to rachitic rats.[15][2] | |
| 1926 | Mechanism / pathway | Rosenheim and Webster, at a meeting of the Biochemical Society in London, announce that “the precursor of vitamin D is not cholesterol itself, but a substance which is associated with and follows ‘chemically pure' cholesterol in all its stages of purification by the usual methods (saponification and recrystallization).”[3] | United Kingdom | |
| 1928 | Tooth decay | Clinical evidence (observational) | An experiment by Mellanby and Pattison with children finds that oral vitamin D intake reduces the risk of dental caries.[14] | |
| 1930 | Drug/analog launch | Vitamin D prodrug dihydrotachysterol is developed as a method of stabilizing the triene structure of one of the photoisomers of vitamin D. This represents the oldest vitamin D analog.[7] | ||
| 1931 | Discovery / identification | Vitamin D2 is purified and crystallized simultaneously by researchers in London and the Netherlands.[9][3] | United Kingdom, Netherlands | |
| 1932 | Discovery / identification | The structure of vitamin D is identified when Askew et al. manage to isolate vitamin D2 from a mixture of ergosterol (a compound found in fungi).[13] | ||
| 1933 | Drug/analog launch | Holtz develops dihydrotachysterol,[16] a synthetic analog of vitamin D that does not require renal activation like vitamin D2 or vitamin D3.[17] | ||
| 1936 | Discovery / identification | Cholecalciferol is first described.[18] Also known as vitamin D3, it is a type of vitamin D which is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is also found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.[19] | ||
| 1936 | Skin cancer | Epidemiologic observation | S. Peller observes that U.S. Navy personnel who experiences skin cancer has a much lower incidence of nonskin cancers. This leads him to hypothesize that the development of skin cancer confers protection against other cancers. This marks the beginning of the emergence of the epidemiologic role of sunlight in cancer prevention.[8] | United States |
| 1937 | Rickets | Clinical evidence (observational) | The term "rickets resistant to vitamin D" is coined by Albright et al., as the patients they describe present with changes in mineral metabolism that could only be overcome by very large daily doses of vitamin D.[2] | |
| 1935 | Discovery / identification | Researchers led by German chemist Adolf Windaus isolate 7-dehydrocholesterol, a key precursor in vitamin D biology.[20] | Germany | |
| 1937 | Discovery / identification | Vitamin D₃ is identified by Adolf Windaus and his colleague Franz Bock as the natural form of vitamin D produced in human skin through ultraviolet irradiation of 7-dehydrocholesterol, isolated two years earlier. This discovery prompts debate over whether vitamin D is truly a dietary vitamin or primarily an endogenously synthesized compound. Although skin production is inferred, direct proof would come only in 1978, when vitamin D₃ is isolated by mass spectrometry.[20] The isolation and identification of the vitamin D nutritional compounds are completed, drawing to a close an important era of vitamin D investigation.[11] | ||
| 1940 | Guideline / recommendation | The first recommendation for vitamin D is established in the United States, determining the value of 400 IU (i.e., the lower value of a range for infants at the time), for adults in a footnote only, that states “When not available from sunshine, [vitamin D] should be provided up to the minimal amounts recommended for infants”.[7] | United States | |
| 1942 | Cancer (internal) | Epidemiologic observation | Apperly first observes that there are lower overall mortality rates from internal cancers in sunnier regions of the United States.[8] | United States |
| 1946 | Lupus vulgaris | Clinical evidence (observational) | Dowling et al. report the treatment of patients with lupus vulgaris with oral vitamin D. Eighteen of 32 patients appear to be cured, with nine improved.[9] | |
| 1952 | Drug/analog launch | Synthetic vitamin D2 and D3 compounds start being produced.[21] | ||
| 1952 | Mechanism / pathway | Arvid Carlsson, Heinz Bauer and their colleagues demonstrate that vitamin D does not directly induce mineral deposition in bone but instead mobilizes calcium from bone into the bloodstream. Although this process might seem to weaken bone, it reveals a crucial role for vitamin D in maintaining adequate serum calcium levels. This function is essential not only for skeletal mineralization but also for neuromuscular activity, redefining vitamin D’s mechanism of action in calcium homeostasis.[20] | ||
| 1953–1955 | Safety signal | Nutrition surveys indicate that the normal British infant could ingest from various sources as much as 4,000 IU of vitamin D per day. This is coincident with numerous cases of infantile hypercalcemia mainly of the mild form. In the following years the food enrichment policies would change and subsequently make the incidence of infantile hypercalcemia fall.[22] | United Kingdom | |
| 1955 | Mechanism / pathway | The complete photochemical and thermal reaction steps from ergosterol to calciferol are elucidated by Velluz et al.[3] | France | |
| 1957 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Medical Association’s Council on Foods and Nutrition recommends that milk should contain 400 IU (10 μg) per quart and that the vitamin D content be measured at least twice yearly by an independent laboratory.[7] | United States | |
| 1960s | Skin cancer | Epidemiologic observation | An increasing trend of skin cancer incidence rates starts being observed from this time, leading to large sun-safety campaigns.[7] | |
| 1960 | Mechanism / pathway | 25,26-Dihydroxyvitamin D3(25,26-dihydroxycholecalciferol) becomes the first dihydroxylated metabolite to be identified.[23] It is a metabolite of vitamin D3 with intestinal calcium transport activity.[24] | ||
| 1960s | Supravalvular stenosis | Hypothesis | During this time, vitamin D is considered the cause of supravalvular stenosis.[7] The published hypothesis is that “toxic” amounts of vitamin D during pregnancy gave rise to a clinical condition titled “infantile hypercalcemia syndrome”.[25] | |
| 1963 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Committee on Nutrition recommends a dose of vitamin D of 10 micrograms (400 IU) daily as the standard of care for children.[26] | ||
| 1963 | Guideline / recommendation | The US Food and Drug Administration's Daily Recommended Allowance of vitamin D is determined to be 400 IU, consistent with the recommendations of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Committee on Nutrition.[27] | United States | |
| 1963 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition recommends that all infants receive 10μg (400 IU) of vitamin D per day.[2] | United States | |
| 1965–1975 | Mechanism / pathway | In this period, the elements of the vitamin D endocrine system that regulate calcium and phosphorus become clear.[28] | ||
| Mid–1960s | Assay / standardization | New techniques using radioactively labeled substances are developed. Before this, scientists did not have the tools to follow vitamin D metabolism in living subjects.[2] | ||
| 1966 | Receptor / gene regulation | Wasserman and his colleagues discover the existence of a calcium-binding protein in the intestines of chicks given vitamin D.[11] | ||
| 1967 | Hypothesis | Loomis suggests that melanin pigmentation evolved for protection from vitamin intoxication because of excessive exposure to sunlight.[7] | ||
| 1968 | Mechanism / pathway | Team led by Hector DeLuca at the University of Wisconsin isolate an active substance identified as 25-hydroxyvitamin D3, which the team later proves to be produced in the liver.[2] | United States | |
| 1968 | Mechanism / pathway | The long-held belief that vitamin D functions without metabolic conversion is overturned. Until then, vitamin D research had entered a relatively quiet phase following the successful control of rickets, while attention shifted toward the increasingly complex water-soluble vitamin B group. Although vitamin D was briefly considered a possible coenzyme, this approach had failed. The 1968 shift marks a conceptual turning point, recognizing that vitamin D requires metabolic transformation to exert its biological effects.[20] | ||
| 1968 | Kidney disease | Research | The idea that vitamin D might function as a steroid-like hormone emerges.[21] | |
| 1968–1971 | Mechanism / pathway | During this period, researchers make great progress in understanding the metabolic processing of vitamin D and its physiological activity.[2] | ||
| 1969 | Receptor / gene regulation | The vitamin D receptor (VDR) is discovered in the intestine of vitamin D deficient chicks.[21] | ||
| 1969 | Mechanism / pathway | The chemical synthesis of calcifediol is determined by J. W. Blunt and Hector F. DeLuca.[11][29] | United States | |
| 1971 | Discovery / identification | Calcitriol, an active form of vitamin D, is identified by American adult endocrinologist Michael F. Holick working in the laboratory of Hector DeLuca.[30][31] | United States | |
| 1971 | Mechanism / pathway | D. R. Fraser and E. Kodicek first identify the kidney as the source of calcitriol.[32] | ||
| 1972 | Mechanism / pathway | The chemical synthesis of 1α,25-(OH)2D3 (calcitriol) is achieved.[11] | ||
| 1974 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Clinical evidence (observational) | Researchers report vitamin D deficiency in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis who have suffered fractures compared with postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis who have not suffered fractures.[33] | |
| 1974 | Receptor / gene regulation | The existence of a chromosomal receptor for vitamin D is demonstrated.[2] | ||
| 1975 | Receptor / gene regulation | Mark Haussler at the University of Arizona discovers a protein receptor that binds calcitriol to the nucleus of cells in the intestine.[2][34] | United States | |
| 1977 | Discovery / identification | A report from the laboratory of Elsie Widdowson in Cambridge, England, describes a new form of water-soluble vitamin D in human milk. This metabolite, vitamin D sulfate, is present at concentrations of 400–950 IU/L. This would prompt the gained credibility of the idea that breast-fed infants do not need supplemental vitamin D.[26] | United Kingdom | |
| 1978 | Mechanism / pathway | Robert P. Esvelt and colleagues provide definitive proof that vitamin D₃ is synthesized in human skin by directly isolating and identifying it using mass spectrometry. This achievement conclusively confirms earlier hypotheses that ultraviolet irradiation of 7-dehydrocholesterol produces vitamin D₃ in vivo. The finding resolves longstanding uncertainty over whether vitamin D is strictly a dietary vitamin or an endogenously produced compound, firmly establishing cutaneous synthesis as a central component of human vitamin D physiology.[20] | ||
| 1979 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Anthony W. Norman publishes Vitamin D: The Calcium Homeostatic Steroid Hormone.[35] | ||
| 1980 | Mechanism / pathway | Holick et al. report on the exact sequence of steps leading to the photoproduction of cholecalciferol in the skin.[3][36] | United States | |
| 1980 | Short gestation and low birth weight | Clinical trial (RCT) | In response to recognition of a high incidence of pregnancy-associated osteomalacia and decreased fetal size in association with vitamin D deficiency among Asian (primarily Indian) women in England, O.G. Brooke et al. evaluate vitamin D supplementation in Asian women. The study includes 59 pregnant women given 1,000 IU/day in their last trimester and a matched group of 67 women given placebo. The researchers report modest increase in birth weight of 123 g in the treatment group.[37] | United Kingdom |
| 1980 | Cancer | Hypothesis | The solar UVB/vitamin D/cancer theory is proposed by brothers Cedric Garland and Frank C. Garland. The researchers hypothesize that the potential benefit of sun exposure is attributed to vitamin D. Initially, the hypothesis is centered on colon cancer, but later it is extended to breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, and to multiple cancer types.[38] | United States |
| 1980 | Hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, osteodystrophy, rickets, osteomalacia | Drug/analog launch | Alfacalcidol is first introduced in Canada. It is a vitamin D analogue used for the management of hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and osteodystrophy in patients with chronic renal failure, as well as some types of rickets and osteomalacia.[39] | Canada |
| 1980 | Cancer (colon) | Epidemiologic observation | C. F. Garland and F. C. Garland publish a seminal article on the relationship between vitamin D, calcium and colon cancer risk in the International Journal of Epidemiology. In this ecologic analysis, they propose that vitamin D and calcium are protective factors against colon cancer.[8] The authors also find a clear positive association between latitude and mortality from colon cancer in the United States. They hypothesize that this might be related to sun-induced vitamin D.[40] | United States |
| 1980 | Mechanism / pathway | Michael F. Holick describes the dermal synthesis of vitamin D.[14] | United States | |
| 1981 | Birth weight | Clinical trial (RCT) | R. K. Marya et al. study 25 pregnant women treated with 1,200 IU of vitamin D a day in their third trimester, 20 women treated with two doses of 600,000 IU in the seventh and eighth months of pregnancy, and 75 women who received no supplemental vitamin D. The researchers report a significantly greater increase in birth weight with either vitamin D supplementation, but greater increase with the 600,000 IU doses.[41] | |
| 1981 | Cardiovascular disease | Hypothesis | Drawing on ecological studies of variations in cardiovascular disease by season, latitude, and altitude, Robert Scragg publishes a hypothesis that sunlight and vitamin D may protect against cardiovascular disease.[42] | Australia |
| 1981 | Cancer (melanoma, leukemia) | Mechanism / pathway | The classical consideration of vitamin D as a regulator of calcium and phosphate metabolism and bone biology begins when David Feldman’s[43] and Tatsuo Suda’s[44] groups show that the most active vitamin D metabolite, calcitriol, inhibits the proliferation of melanoma cells and induces the differentiation of leukemic cells.[7] | |
| 1981 | Cystic fibrosis | Clinical evidence (observational) | Reduced vitamin D binding protein levels in people with cystic fibrosis is first reported.[9] | |
| 1982 | Rickets | Receptor / gene regulation | The role of the vitamin D receptor in vitamin D-dependent rickets type-2 is realized.[2] | |
| 1983 | Epidemiologic observation | S. H. Sedrani et al. find unexpectedly low vitamin D levels in Saudi university students as well as in elderly subjects suggesting that up to 100% of the Saudi population may have vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency.[45] | Saudi Arabia | |
| 1984 | Kidney disease | Clinical evidence (observational) | Research by B. P. Halloran et al. reports conclusive evidence of the importance of correcting the impaired 25(OH)D availability in chronic kidney disease.[46] | |
| 1984 | Breastfeeding | Mechanism / pathway | In a study, Greer et al. expose lactating white women to UVB exposure equivalent to 30 min of sunshine at midday on a clear summer day at temperate latitudes. With this exposure, the vitamin D content of the milk significantly increases with a peak at 48 h and with a return to baseline at 7 days.[47] | |
| 1984 | Safety signal | A paper by Narang et al. states that 2,400 IU/day is the dose of vitamin D that statistically increases serum calcium, but not quite into the hypercalcemia range.[7] | ||
| 1985 | Tuberculosis, pulmonary disease | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study conducted on 40 Indonesian patients with active tuberculosis and treated with anti-tuberculosis chemotherapy, reports that 10 patients with the highest calcifediol levels at the outset of therapy had “less active pulmonary disease”.[9] | Indonesia |
| 1985 | Tuberculosis | Epidemiologic observation | Davies observes that people migrating to the United Kingdom from countries with a high incidence of latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection experience rates of active tuberculosis that exceeds rates in their countries of origin, and that this increased risk coincide with the development of vitamin D deficiency, probably arising as a result of decreased sun exposure.[9] | United Kingdom |
| 1985 | Psoriasis | Clinical evidence (observational) | S. Morimoto and Y. Kumahara report that a patient who was treated orally with 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 for osteoporosis had a dramatic remission of psoriatic skin lesions.[48] | Japan (Osaka University) |
| 1986 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Mechanism / pathway | Experiments by Rook become the first to suggest vitamin D-induced antimicrobial activity by human monocytes and macrophages against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[7] | |
| 1986 | Cancer (melanoma, leukemia) | Mechanism / pathway | Colston et al. become the first to demonstrate that 1α,25(OH)2D3 (calcitriol) inhibits human melanoma cell proliferation significantly in vitro at nanomolar concentrations. Parallel studies in the same year also find that 1α25(OH)2D3 could induce differentiation in cultured mouse and human myeloid leukemia cells.[49] | |
| 1987 | Receptor / gene regulation | Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding chick vitamin D receptor is achieved for the first time by McDonnell et al.[2] | ||
| 1988 | Receptor / gene regulation | The successful cloning of the cDNA encoding the human vitamin D receptor is achieved.[2] | ||
| 1988 | Receptor / gene regulation | A research group led by Bert W. O'Malley from California Biotechnology Inc. manages to clone the vitamin D receptor.[2] | United States | |
| 1989 | Kidney disease (hyperparathyroidism) | Drug/analog launch | Paricalcitol is patented. It is an analog of 1,25-dihydroxyergocalciferol, the active form of vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).[50] It is a vitamin D analog used to treat hyperparathyroidism associated with stage 3 or greater chronic kidney disease.[51] | United States |
| 1989 | Assay / standardization | DEQAS (Vitamin D External Quality Assessment Scheme) is launched to compare the performance of assays for vitamin D measurement. It monitors the performance of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) and 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D) assays.[52] DEQAS would grow to be the dominant proficiency testing scheme with more than 470 laboratories participating from over 30 countries.[7] | ||
| 1989 | Cancer (breast and colon) | Hypothesis | E.D. Gorham et al. postulate an association between ultraviolet-B blocking air pollution and increased risk of breast and colon cancer, based on inhibition by sulfurrelated air pollution of cutaneous vitamin D photosynthesis, resulting in vitamin D deficiency.[53][8] | |
| 1989 | Receptor / gene regulation | The sequence elements in the human osteocalcin gene conferring basal activation and inducible response of this gene promoter to hormonal 1,25(OH) 2 D 3 are described.[21] | ||
| 1989 | Guideline / recommendation | The US Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of vitamin D is determined at 200 IU to guarantee a protecting effect against malignancies and other diseases. However, several subsequent investigations would show that 200 IU/day has no effect on bone status, with adults needing five times the RDA, or 1,000 IU, to adequately prevent bone fractures, protect against some malignancies, and derive other broad-ranging health benefits.[7] | United States | |
| 1989 | Cancer (colon) | Clinical evidence (observational) | Garland et al. report that prediagnostic serum 25(OH)D concentration inversely correlates with colon cancer.[14] | |
| 1990 | Cancer (prostate) | Hypothesis | Researchers note that the major risk factors for prostate cancer, older age, Black race, and residence at northern latitudes, are all associated with a decreased synthesis of vitamin D.[7] | |
| 1990 | Psoriasis | Drug/analog launch | Vitamin D derivative calcipotriol is first introduced as ointment for the treatment of psoriasis in Denmark. It is a synthetic derivative of calcitriol.[54] | Denmark |
| 1992 | Epidemiologic observation | A review of global vitamin D status from 1971 to 1990 finds lower oral vitamin D intake in Western and Central Europe (2–3 μg/day) compared with North America (5.5–7 μg/day) and Scandinavia (4–6 μg/day), reflecting differences in supplementation and fatty fish consumption. Plasma 25(OH)D levels show strong seasonal variation, with winter lows and persistently lower levels in Central Europe (~18 nmol/L) than in North America (~58 nmol/L) and Scandinavia (~37 nmol/L). Hypovitaminosis D and skeletal disorders are most prevalent among elderly Europeans but occurs in all aging populations.[55] | ||
| 1992 | Cancer (prostate cancer) | Epidemiologic observation | Geographic analyses show that U.S. county-wide mortality rates for prostate cancer among Caucasian men are inversely correlated with the availability of ultraviolet radiation, the major source of vitamin D.[56][57] | United States |
| 1993 | Psoriasis | Drug/analog launch | Tacalcitol ointment is first approved in Japan.[54] Tacalcitol (1,24-dihydroxyvitamin D3) is a synthetic vitamin D3 analog.[58] It is prescribed for the treatment of psoriasis.[59] | Japan |
| 1994–1999 | Muscle function, bone, and fracture risk | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study conducted in this period in Montreal of blood samples from 256 elderly (aged 65–94 years) apparently healthy, community-dwelling men and women, shows a very surprising 32% of women and 51% of men with 25(OH)D levels below 20 nmol/l[60]. This level of deficiency is likely to have an adverse effect on muscle function, bone, and fracture risk.[7] | Canada |
| 1995 | Epidemiologic observation | Dutch research team led by R. P. van der Wielen measure wintertime plasma 25(OH)D (calcifediol) in 824 elderly people from 11 European countries. The team concludes that freeliving elderly Europeans, regardless of geographical location, are at substantial risk of inadequate vitamin D status during winter. Unexpectedly, the lowest mean 25(OH)D concentrations are seen in Southern Europe.[61] | Europe | |
| 1997 | Mechanism / pathway | As the result of 25 years of research, the cytochrome P450, CYP27B1, representing the 1α-Hydroxylase enzyme is finally cloned from a rat renal cDNA library by St Arnaud’s group in Montreal.[62] 1α-Hydroxylase is the key enzyme in vitamin D metabolism.[63] | Canada | |
| 1997 | Discovery / identification | Vitamin D5 is first synthesized by researchers at the Department of Chemistry at the University of Chicago.[64] | ||
| 1997 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Canadian Pediatric Association both recommend 400 IU/day of vitamin D, which is twice what the Institute of Medicine (IOM) of the US National Academy of Sciences recommend in the same year.[7] | United States | |
| 1997 | Guideline / recommendation | The dietary reference intake panel for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D and fluoride is first established to provide intake recommendations for Americans and Canadians.[65][14] | United States, Canada | |
| 1997 | Guideline / recommendation | The U.S. Institute of Medicine (IOM) designates 2,000 IU/day as the TUIL (tolerable upper intake level) of vitamin D intake.[7] | United States | |
| 1997 | Mechanism / pathway | Researchers manage to clone the human 25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase, a secosteroid hormone which plays a crucial role in normal bone growth, calcium metabolism, and tissue differentiation.[66] | United States | |
| 1997 | Epidemiologic observation | The Norwegian National Dietary Survey shows that the vitamin D intake is 13% larger in north than in south Norway. This suggests that there is no significant north–south gradient in the level of vitamin D metabolites in serum in that country.[7] | Norway | |
| 1997 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Committee on Nutrition recommends a dose of vitamin D 400 IU daily as the standard of care for children.[7] | United States | |
| 1998 | Kidney disease (hyperparathyroidism) | Drug/analog launch | Paricalcitol (marketed under the trade name Zemplar) is introduced by Abbott Laboratories.[67] | United States |
| 1998 | Cancer (prostate cancer) | Mechanism / pathway | It is demonstrated that normal human prostate cells possess 25-hydroxyvitamin D3–1α-hydroxylase (1α(OH)ase) and indeed synthesize 1,25(OH)2D from 25(OH)D.[68] | United States (University of Miami School of Medicine) |
| 1999 | Asthma, allergy | Hypothesis | Wjst and Dold, in trying to explain the rise in asthma and allergy rates, propose their hypothesis that the introduction of vitamin D in fortified foods and in multivitamin preparations in many westernized countries is related to the asthma and allergy epidemic in these countries.[9] They propose that vitamin D supplementation might be the cause of global increases in asthma and allergies.[69] | |
| 1999 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Michael F. Holick publishes Vitamin D: Molecular Biology, Physiology, and Clinical Applications.[70] | United States | |
| 2000 | Cancer (prostate cancer) | Mechanism / pathway | Researchers show that 25(OH)D (calcifediol) inhibits the proliferation of prostate cells that possess 1α-OHase.[71] | United States (Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, North Carolina) |
| 2001 | Kidney disease (secondary hyperparathyroidism) | Drug/analog launch | Doxercalciferol (marketed under the trade name Hectorol) is first introduced in Canada by Sanofi Genzyme. It is a synthetic vitamin D2 analog used to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease with or without therapy of dialysis.[72] | Canada |
| 2003 | Guideline / recommendation | In response to the vitamin D adequate intake recommendations made by the Institute of Medicine in 1997, the Committee on Nutrition of the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends 200 IU/d vitamin D for all infants and children.[26] | United States | |
| 2005 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | David Feldman, J. Wesley Pike and Francis H. Glorieux publish Vitamin D, which includes over 100 chapters covering from chemistry and metabolism to mechanisms of action, diagnosis and management, new analogs, and emerging therapies involving vitamin D.[73] | ||
| 2006 | Cancer (digestive-system) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study by researchers at Harvard Medical School, analizing 1095 men and documents from 1986 through 2000 of 4286 incident cancers (excluding organ-confined prostate cancer and nonmelanoma skin cancer) and 2025 deaths from cancer, concludes that low levels of vitamin D may be associated with increased cancer incidence and mortality in men, particularly for digestive-system cancers.[74] | United States |
| 2007 | Cancer (breast | Clinical evidence (observational) | Garland et al. publish a breast cancer doseresponse meta-analysis, finding that individuals with the highest blood levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D has reduced risk of breast cancer.[75][8] | United States |
| 2007 | Anaphylaxis | Hypothesis | Camargo and colleagues propose that vitamin D status might influence risk of food-induced anaphylaxis (FIA) after observing a strong north–south gradient in epinephrine autoinjector prescription rates in the United States.[76] | United States (Boston) |
| 2007 | Psoriasis | Drug/analog launch | CollaGenex Pharmaceuticals licenses becocalcidiol, a vitamin D analogue for topical treatment of psoriasis and psoriatic disorders.[77][78] | United States |
| 2008 | Skin cancer | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Jörg Reichrath publishes Sunlight, Vitamin D and Skin Cancer, which provides an overview of positive and negative effects of ultraviolet-exposure, with a focus on Vitamin D and skin cancer.[79] | |
| 2008 | Guideline / recommendation | The American Academy of Pediatrics increases the recommended supplementation dose from 200 to 400 IU daily across the pediatric age spectrum.[80] | United States | |
| 2008 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | James Dowd and Diane Stafford publish The Vitamin D Cure.[81] | ||
| 2009 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Soram Khalsa publishes Vitamin D Revolution.[82] | ||
| 2010 | Pneumonia | Clinical trial (RCT) | A randomized clinical trial finds that vitamin D supplementation reduces the risk of pneumonia in children.[14] | |
| 2010 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study in Italy inversely relates rheumatoid arthritis activity and disability scores with calcifediol concentrations.[14] | Italy |
| 2011 (January) | Osteoporosis | Drug/analog launch | Eldecalcitol is approved in Japan, for the treatment for osteoporosis.[83] It is an analog of vitamin D.[84] | Japan |
| 2012 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Ian Wishart publishes Vitamin D: Is This the Miracle Vitamin?, which claims that taking vitamin D reduces up to a 77% the risk of developing cancer.[85] | ||
| 2016 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Ana Claudia Domene publishes Multiple Sclerosis and (lots Of) Vitamin D, which introduces the Coimbra Protocol, a therapeutic approach that relies on high doses of vitamin D with the purpose to boost the immune system.[86] | ||
| 2018 | Cancer (colorectal) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study by an international group of researchers using data from about 12,800 people finds that higher levels of vitamin D in the blood is associated with a lower risk for getting colorectal cancer.10.1093/jnci/djy087[87] | |
| 2018 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Emilia Pauline Liao publishes Extraskeletal Effects of Vitamin D: A Clinical Guide, which provides an examination of extraskeletal effects of vitamin D and the associations between vitamin D deficiency and various disease states.[88] | ||
| 2020 (July) | COVID-19 | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | David C. Anderson and David S. Grimes publish Vitamin D Deficiency and Covid-19: Its Central Role in a World Pandemic, which emphasizes the immunity provided by adequate levels of Vitamin D against the invasion by all new viruses.[89] | |
| 2021 (Jan) | COVID-19 Severity | Research Publication (Meta-analysis) | Meta-analysis suggests vitamin D deficiency is linked to increased COVID-19 severity and mortality risk. | University of Barcelona, Spain |
| 2021 (January 14) | Common cold, influenza, influenza-like illness | Clinical trial (RCT) | A randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplements led by QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute in Australia finds they do not protect most people from developing colds, influenza and other acute respiratory infections.[90] | Australia |
| 2021-04-13 | Vitamin D deficiency | Guideline / recommendation | USPSTF recommendation: Insufficient evidence to assess benefits/harms of screening for vitamin D deficiency in asymptomatic adults. | US Preventive Services Task Force, USA https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/vitamin-d-deficiency-screening |
| 2021 (Jun) | Cancer (advanced cancer mortality) | Clinical trial (RCT) | The VITAL trial reported that vitamin D supplementation may reduce advanced cancer mortality, particularly among normal-weight individuals. | United States (Harvard Medical School; Brigham and Women's Hospital) |
| 2023 (January 17) | Clinical evidence (observational) | New research analyzing data from the VITAL trial found that the health benefits of vitamin D supplementation vary by body mass index (BMI). Positive effects, including reduced cancer mortality and autoimmune disease, are mainly observed in individuals with BMI under 25. People with higher BMI show a blunted biological response, with smaller increases in vitamin D–related biomarkers, suggesting altered metabolism. The findings highlight the potential need for BMI-adjusted, personalized vitamin D dosing strategies.[91] | ||
| 2023 (September) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A large UK Biobank study examines over 411,000 adults to evaluate how 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and vitamin D supplement use relate to mortality from 18 cancer types. Vitamin D deficiency (21%) and insufficiency (34%) are common. Over a median 12.7-year follow-up, deficiency is found to significantly increase mortality from stomach, colorectal, lung, and prostate cancers, while insufficiency raises colorectal and lung cancer mortality. Regular vitamin D supplementation is associated with 25% lower lung cancer mortality and reduced overall cancer mortality. Multivitamin use is linked to lower melanoma mortality. The findings suggest vitamin D supplementation may help reduce cancer deaths in populations with low vitamin D levels.[92] | ||
| 2023 (October 2) | Inflammatory bowel disease | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | A review evaluates whether vitamin D is effective and safe for treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Across 22 randomized trials involving 1,874 participants, evidence quality is mostly low or very low. Some low-quality evidence suggests vitamin D may reduce relapse rates compared with placebo or no treatment, but effects on symptoms, quality of life, and safety remain unclear. Comparisons between different dosing strategies show no consistent benefits. Due to study limitations, inconsistent outcome measures, and poor reporting, firm conclusions cannot be drawn, and the effectiveness of vitamin D in IBD remains uncertain.[93] | |
| 2023 (November 12) | Clinical evidence (observational) | Two studies from Intermountain Health suggest current vitamin D dosing guidelines may be insufficient to achieve optimal blood levels, potentially undermining trials assessing cardiovascular benefits. In the Target-D trial, most patients required far more than the recommended 600–800 IU daily—often over 2,000 IU, and in some cases above 10,000 IU—to reach target levels above 40 ng/mL. Even with tailored dosing, many patients needed months of adjustment. Researchers argue that prior studies likely underdosed participants and that individualized, monitored supplementation is essential to properly evaluate vitamin D’s role in heart health.[94] | ||
| 2023 (October 26) | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | A systematic review finds a linear association between vitamin D levels and periodontal health, though current evidence remains limited and heterogeneous. Vitamin D appears to support gum health not only through bone metabolism but, more importantly, via antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory actions that help maintain oral tissues. However, underlying mechanisms are poorly defined, and available data are fragmented. The authors emphasize the need for larger, well-designed longitudinal studies to confirm causality. While dietary vitamin D intake is often insufficient, supplementation may offer potential benefits for periodontal health.[95] | ||
| 2023 (December 1) | Clinical trial (RCT) | A large randomized controlled trial led by Queen Mary University of London and Harvard finds that vitamin D supplementation does not reduce fracture risk or improve bone strength in vitamin D–deficient children. Conducted in Mongolia with 8,851 children aged 6–13, the study successfully raises vitamin D levels but observes no benefits on fractures or bone strength over three years. Results challenge assumptions about vitamin D’s role in pediatric bone health, though supplementation remains essential for preventing rickets. The findings suggest vitamin D alone is ineffective for fracture prevention without additional factors such as calcium.[96][97] | ||
| 2024 (March) | Mechanism / pathway | A study examines why vitamin D deficiency is prevalent in obesity and how metabolism and storage complicate assessment. Using a validated UHPLC-MS/MS method, researchers analyze vitamin D metabolites in 452 obese and healthy subjects. They find widespread deficiency of 25OHD2 and 25OHD3 across all groups. Although supplementation increases vitamin D3 and 25OHD3 in obese individuals, levels remain suboptimal. The findings highlight sequestration in fat tissue, dilution effects, and metabolic factors, underscoring the need to adjust vitamin D evaluation and supplementation strategies in obesity.[98] | ||
| 2024 (April 4) | Mechanism / pathway | New research highlights vitamin D’s anti-aging role by preserving stem cell health in the Drosophila gut. Scientists find that aging and disease reduce vitamin D and its receptor (VDR), impairing tissue balance. Using a fruit-fly midgut model, the study shows that VDR loss in intestinal cells accelerates stem cell aging, cell death, and abnormal proliferation. Vitamin D treatment reduces age- and oxidative stress–related damage, including excess centrosomes. The findings provide direct evidence that the vitamin D/VDR pathway protects intestinal cells and supports healthy aging, offering insights into fundamental aging mechanisms.[99] | ||
| 2024 (May 7) | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | Prof. Carsten Carlberg’s article Vitamin D in the Context of Evolution traces the 1.2-billion-year history of vitamin D, from its origins in early eukaryotes to its changing functions in humans. According to Carlberg, vitamin D initially supported detoxification, energy metabolism, and innate immunity, later becoming essential for calcium homeostasis after species moved onto land. Homo sapiens evolved with constant UV-B exposure in East Africa, maintaining high vitamin D levels until migrations to higher latitudes and modern indoor lifestyles caused widespread deficiencies. Carlberg argues that human behaviour—not evolution—made vitamin D a “vitamin,” with over one billion people now affected globally.[100] | ||
| 2024 (June 3) | Guideline / recommendation | The Endocrine Society’s 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline concludes that healthy adults under age 75 are unlikely to benefit from vitamin D intake above the recommended daily allowance set by the Institute of Medicine and do not require routine vitamin D testing. Based on evidence from clinical trials, higher vitamin D supplementation may benefit specific groups, including children, pregnant individuals, adults over 75, and people with prediabetes, due to potential reductions in defined health risks. The guideline advises against routine blood testing for vitamin D levels in any population, citing insufficient evidence for outcome-based target thresholds.[101] | ||
| 2024 (July 16) | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | An article reviews how vitamin D and arsenic interact to influence human health. Evidence suggests they may work synergistically to inhibit certain hematological cancers, highlighting a possible therapeutic pathway. Vitamin D appears to protect T-cell function and mitigate arsenic-induced toxicity, while deficiencies combined with arsenic exposure may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Arsenic shows both harmful and potentially therapeutic effects depending on the cell type, underscoring the need for targeted research. The authors emphasize further investigation into arsenic’s cell-specific actions, its clinical implications, and whether safe sunlight exposure could benefit individuals affected by arsenic poisoning.[102] | ||
| 2024 (September 20) | Clinical trial (RCT) | A study reports that high-dose oral vitamin D3 supplementation significantly reduces disease activity in adults with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), according to a randomized, double-blind trial of 303 participants presented at ECTRIMS 2024. Patients receiving 100,000 IU cholecalciferol every two weeks for 24 months showed less disease activity than placebo (60.3% vs 74.1%; HR 0.66) and a longer time to disease activity. Effects were rapid and comparable to some platform therapies. Secondary outcomes such as relapse rate and disability progression were unchanged. Vitamin D3 was safe and well tolerated, supporting its potential role as add-on therapy in early multiple sclerosis.[103] | Denmark | |
| 2024 (October 24) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study examines the relationship between vitamin D insufficiency and obesity in school-aged children, and its effects on bone and metabolic health. Clinical data from 159 children are analyzed by comparing those with deficient and normal serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D₃ levels. Vitamin D–deficient children show higher body mass index, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and alkaline phosphatase activity, alongside lower serum calcium levels and delayed bone maturation. Statistical analyses identify calcium levels, alkaline phosphatase activity, and bone age as significant predictors of vitamin D deficiency. The findings indicate that vitamin D insufficiency is strongly associated with childhood obesity and impaired skeletal development, supporting routine monitoring in at-risk pediatric populations.[104] | ||
| 2024 (November 20) | Mechanism / pathway | An article examines how vitamin D3 and the anti-inflammatory molecule IL-10 influence the development of a special type of immune cell called regulatory dendritic cells. These cells help control excessive immune responses and promote immune tolerance. Using advanced genetic analysis, the researchers show that these regulatory cells have distinct chemical markings on their DNA that differ from those of immune-activating dendritic cells. These markings affect genes linked to immune suppression and reduced inflammation, while genes that promote inflammation are less active. The study also identifies common genetic patterns shared by regulatory cells produced using different methods. Overall, the findings help explain how vitamin D contributes to immune regulation and may support the development of new treatments for autoimmune diseases and organ transplantation.[105] | ||
| 2024 (December) | Drug/analog launch | Nutriearth’s N-utra, a vitamin D3-enriched mealworm flour, receives EU Novel Food status. Produced from UV-treated yellow mealworm larvae, it naturally synthesizes vitamin D3—unlike standard mealworm flour—and provides proteins, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Protected by more than 50 patents, N-utra is designed for easy incorporation into foods such as bread, pasta, biscuits and energy bars, helping consumers reach recommended vitamin D levels. Consumer studies show increasing acceptance of insect-based foods, with over half rating them highly. Nutriearth highlights global vitamin D deficiency and positions N-utra as a sustainable solution supporting public health and food industry innovation.[106] | European Union | |
| 2024 (November 18) | Clinical trial (RCT) | A study reports that vitamin D and calcium supplementation may modestly lower blood pressure in older adults with overweight, especially those with obesity or hypertension, according to a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. The study includes 221 participants aged 65 or older with low vitamin D levels who received calcium plus either low- or high-dose vitamin D3 for 12 months. Overall, systolic and diastolic blood pressure fell significantly, with stronger effects in participants with BMI above 30 and in those with hypertension. High doses offered no clear advantage over standard doses. Effects were exploratory and warrant cautious interpretation.[107] | ||
| 2025 (May 13) | Mechanism / pathway | A publication reports that vitamin D supplementation appears to protect against liver disease progression by targeting ductular reaction. This study shows that higher vitamin D levels correlate with reduced ductular reaction in chronic liver disease patients. In mice, active vitamin D (1,25(OH)₂D₃) decreases ductular proliferation, inflammation, and fibrosis while upregulating TXNIP in ductular cells. Cholangiocyte-specific TXNIP deletion worsens injury, increasing cell proliferation, cytokine release, and fibrotic signaling, and eliminates vitamin D’s protective effects. Conversely, TXNIP overexpression reduces inflammation and fibrosis. Overall, the findings identify the vitamin D–TXNIP axis as a key mechanism limiting ductular reaction and suggest it as a promising therapeutic target.[108] | ||
| 2025 (June 6) | Cellular aging (telomere attrition) | Literature (scholarly / popularization) | A review paper highlights vitamin D’s key metabolic and immunomodulatory roles and its influence on both communicable and non-communicable diseases. Deficiency is linked to higher risks of cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory disorders, and severe COVID-19. Adequate levels may help prevent or slow NCD progression, though causality remains debated. Vitamin D comes from sunlight, limited foods, fortified products, and supplements; absorption depends on nutrient interactions, UV-B exposure, and gut health. Serum 25(OH)D is used to assess status, but ideal cutoffs vary. Worldwide deficiency is common, prompting interest in improved fortification methods, nano-delivery systems, and clearer dietary guidelines.[109] | |
| 2025 (July 4) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A cross-sectional study of 68 adults with diabetic macular edema examines associations between serum vitamin D levels and macular ischemia using OCTA imaging. Higher vitamin D levels correlate with increased superficial and deep vascular density and smaller foveal avascular zones. These associations remain significant after adjustment, indicating that vitamin D deficiency is linked to retinal microvascular damage in diabetic maculopathy.[110] | ||
| 2025 (July 11) | Clinical trial (RCT) | A publication reports that patients with Parkinson’s disease and vitamin D deficiency exhibit an imbalance between pro-inflammatory Th17 cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, three months of vitamin D3 supplementation increased serum 25(OH)D3 levels, reduced Th17 cells, and increased Tregs. These immunological changes were accompanied by improvements in motor function measured by UPDRS scales, findings not observed in the placebo group. The results are preliminary and require confirmation in larger, longer-term clinical studies.[111] | ||
| 2025 (December 4) | Clinical evidence (observational) | A study of more than 4,000 pregnant people finds that lower maternal vitamin D levels—especially in the second and third trimesters—are consistently linked to higher rates of early childhood caries up to age five. Vitamin D is crucial for fetal tooth mineralisation between weeks 13–17, and supplementation before or during pregnancy may reduce caries risk. Early childhood caries is a major global health concern, affecting up to 57% of young children.[112] |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
The following table summarizes per-year mentions on Google Scholar as of September 19, 2021.
| Year | "vitamin D" |
|---|---|
| 1920 | 16 |
| 1930 | 502 |
| 1940 | 723 |
| 1950 | 932 |
| 1960 | 950 |
| 1970 | 1,780 |
| 1980 | 3,350 |
| 1990 | 4,350 |
| 2000 | 9,600 |
| 2010 | 30,000 |
| 2020 | 45,300 |
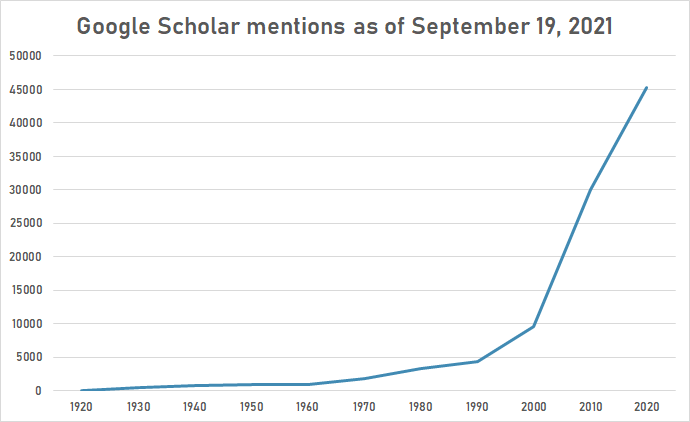
Google Trends
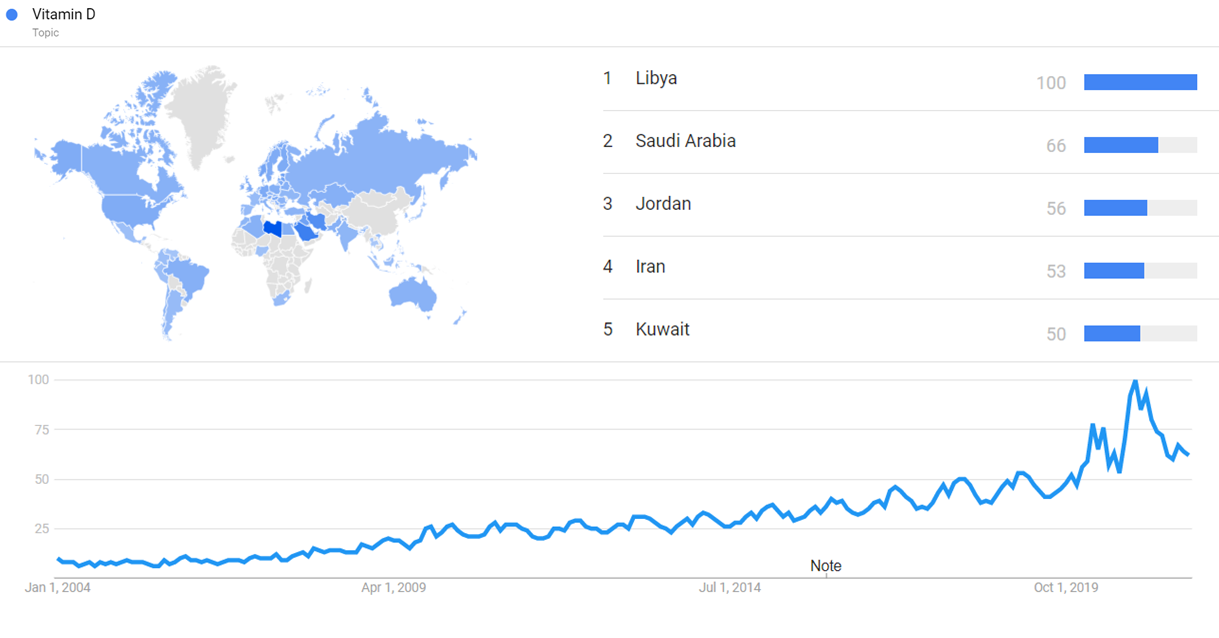
The chart below shows Google Trends data for Vitamin D, from January 2004 to September 2021, when the screenshot was taken. Interest is also ranked by country and displayed on world map.[113]
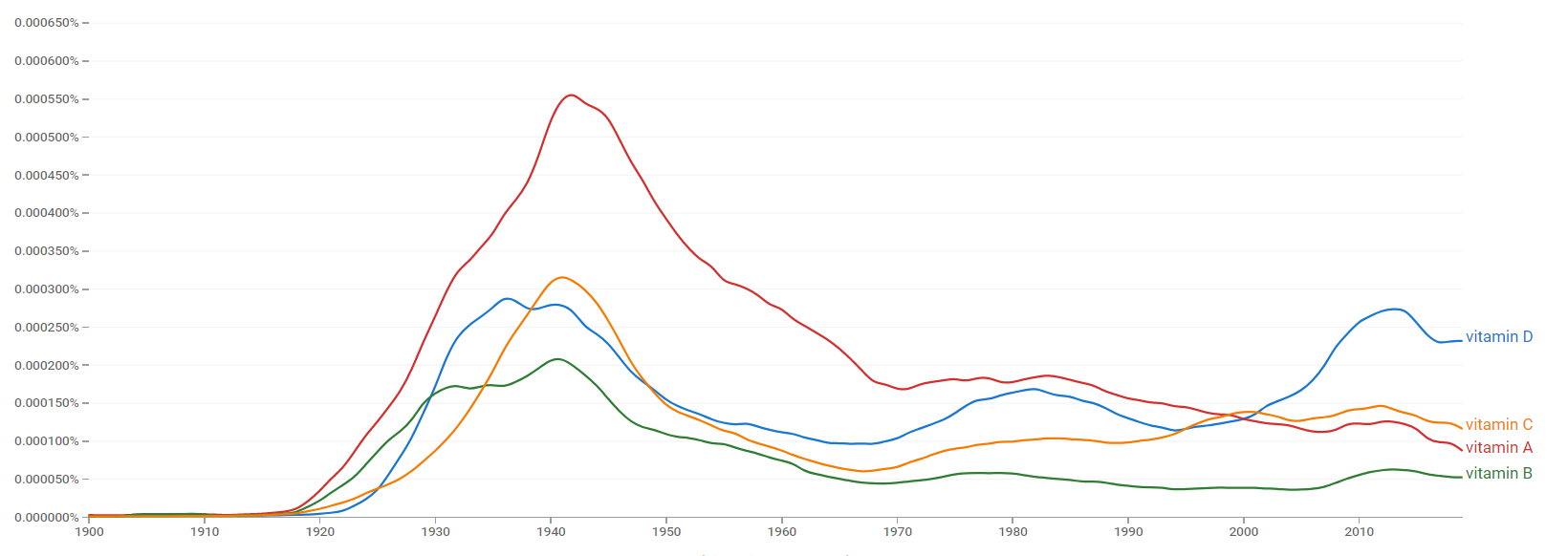
Google Ngram Viewer
The comparative chart below shows Google Ngram Viewer data for vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin B and vitamin C, from 1900 to 2019.[114]
Wikipedia Views
The chart below shows pageviews of the English Wikipedia article Vitamin D, from July 2015 to August 2021.[115]
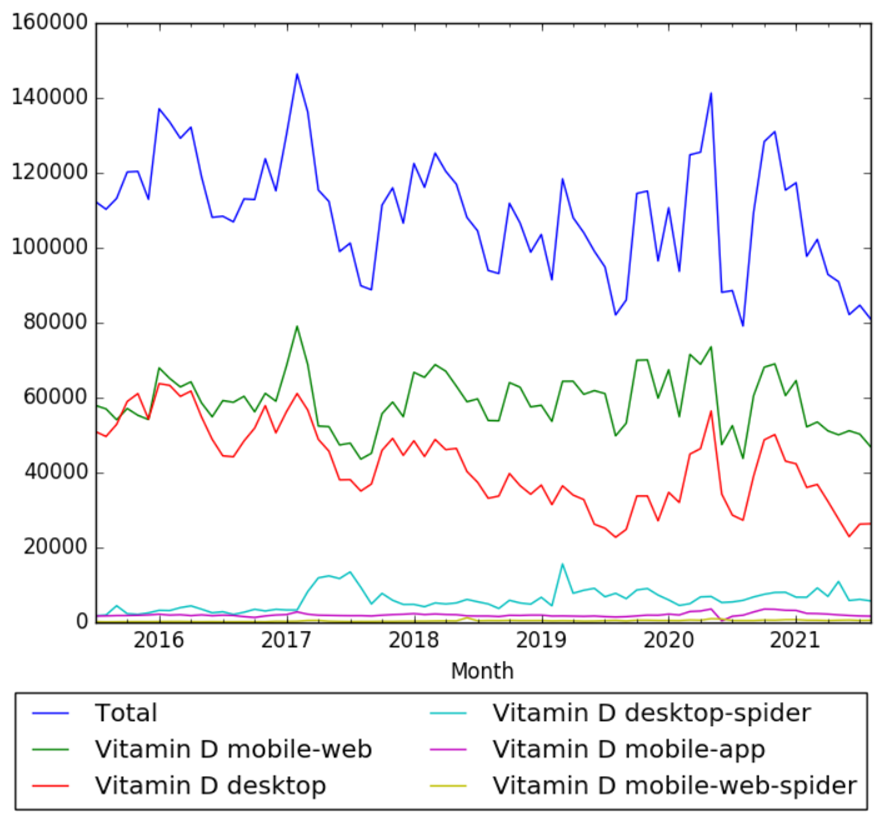
Other
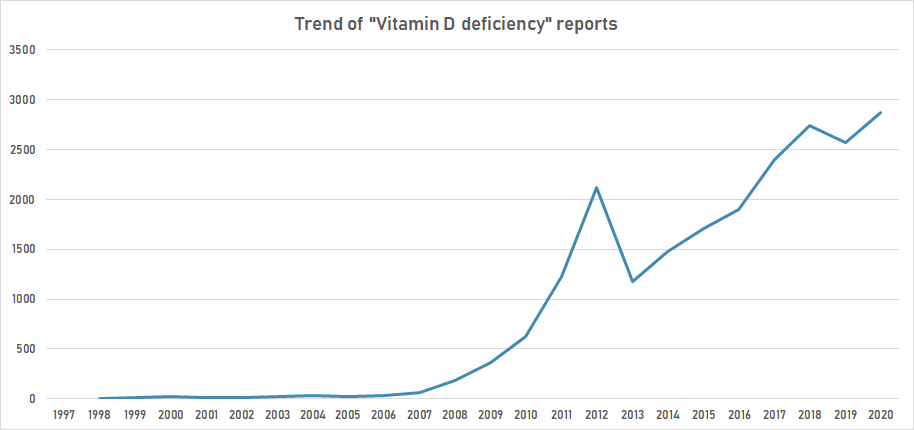
Trend of “Vitamin d deficiency” reports.[116]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
- Helpful / harmful / no effect column?
- Vitamin D Wiki (both the launch of the wiki itself, and some content in it)
- Vitamin D cofactors: relation with Vitamin A, Vitamin K, and magnesium
- Beware Mass-Produced Medical Recommendations
- [1]
- [2]
- Category:Vitamin D
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin D deficiency
- Also how vegan diets are at higher risk of vitamin D deficiency without supplementation
- [3] [6]
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ Milne, G. W. A.; Delander, M. (2008). Vitamin D Handbook: Structures, Synonyms, and Properties. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-13983-7. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 Hochberg, Z. (2003). Vitamin D and Rickets. Karger. ISBN 978-3-8055-7582-9.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Wolf, George (1 October 2004). "The Discovery of Vitamin D: The Contribution of Adolf Windaus". The Journal of Nutrition. 134 (6): 1299–1302. doi:10.1093/jn/134.6.1299.
- ↑ "Cod Liver Oil - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ↑ W. Mozolowski: Jedrzej Sniadecki (1768–1883) on the cure of rickets. Nature 143:121 (1939)
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hochberg, Ze'ev; Hochberg, Irit (15 May 2019). "Evolutionary Perspective in Rickets and Vitamin D". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 10. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00306. ISSN 1664-2392.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ↑ 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 7.15 7.16 7.17 Holick, Michael F. (23 April 2010). "Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications". Humana Press. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Mohr, Sharif B. (February 2009). "A Brief History of Vitamin D and Cancer Prevention". Annals of Epidemiology. 19 (2): 79–83. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2008.10.003.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Litonjua, Augusto A. (23 May 2012). Vitamin D and the Lung: Mechanisms and Disease Associations. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-1-61779-888-7.
- ↑ Hopkins, F. Gowland (1 January 1906). "The analyst and the medical man". Analyst. pp. 385b–404. doi:10.1039/AN906310385B. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 DeLuca, H. F. (6 December 2012). Vitamin D: Metabolism and Function. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-642-81306-1.
- ↑ McCollum, E.V.; Davis, Marguerite (October 1914). "OBSERVATIONS ON THE ISOLATION OF THE SUBSTANCE IN BUTTER FAT WHICH EXERTS A STIMULATING INFLUENCE ON GROWTH". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 19 (2): 245–250. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)88306-5.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "The History and Discovery of Vitamins Through The Ages". What's Up, USANA?. 27 April 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 Handbook of vitamin D in human health : prevention, treatment and toxicity. Wageningen: Wageningen Academic Publishers. 2013. ISBN 978-90-8686-765-3.
- ↑ Goldblatt, Harry; Soames, Katharine Marjorie (1 January 1923). "Studies on the Fat-Soluble Growth-Promoting Factor: (I) Storage. (II) Synthesis". Biochemical Journal. 17 (4–5): 446–453. doi:10.1042/bj0170446.
- ↑ McCann, S. M. (27 May 2013). Endocrinology: People and Ideas. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4614-7436-4.
- ↑ "Dihydrotachysterol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Fischer, János; Ganellin, C. Robin. Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5.
- ↑ Nutrition in the prevention and treatment of disease (3rd ed.). Amsterdam: Boston. 2013. ISBN 9780123918840.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 DeLuca, Hector F. (8 January 2014). "History of the discovery of vitamin D and its active metabolites". Bonekey Reports. 3: 479. doi:10.1038/bonekey.2013.213. PMC 3899558. PMID 24466410.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 21.3 Torres, Pablo A. Ureña; Cozzolino, Mario; Vervloet, Marc G. (21 September 2016). Vitamin D in Chronic Kidney Disease. Springer. ISBN 978-3-319-32507-1.
- ↑ Paunier, Luc. "Prevention of Rickets" (PDF). nestlenutrition-institute.org.
- ↑ DeLuca, Hector F.; Suda, Tatsuo; Schnoes, Heinrich K.; Tanaka, Yoko; Holick, Michael F. (1 November 1970). "25,26-Dihydroxycholecalciferol, a metabolite of vitamin D3 with intestinal calcium transport activity". Biochemistry. 9 (24): 4776–4780. doi:10.1021/bi00826a022.
- ↑ "25,26-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (25,26-Dihydroxycholecalciferol) | VD/VDR Activator | MedChemExpress". MedchemExpress.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Friedman, William F. (May 1967). "Vitamin D as a cause of the supravalvular aortic stenosis syndrome". American Heart Journal. 73 (5): 718–720. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(67)90186-x.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Greer, Frank R. "Issues in establishing vitamin D recommendations for infants and children" (PDF). watermark.silverchair.com.
- ↑ Huh, Susanna Y.; Gordon, Catherine M. (June 2008). "Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents: Epidemiology, impact and treatment". Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders. 9 (2): 161–170. doi:10.1007/s11154-007-9072-y.
- ↑ DeLuca, Hector F (8 January 2014). "History of the discovery of vitamin D and its active metabolites". BoneKEy Reports. 3. doi:10.1038/bonekey.2013.213.
- ↑ Blunt, J. W.; DeLuca, Hector F. (1 February 1969). "The synthesis of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. A biologically active metabolite of vitamin D3". Biochemistry. 8 (2): 671–675. doi:10.1021/bi00830a031.
- ↑ Holick MF, Schnoes HK, DeLuca HF, Suda T, Cousins RJ (July 1971). "Isolation and identification of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. A metabolite of vitamin D active in intestine". Biochemistry. 10 (14): 2799–804. doi:10.1021/bi00790a023. PMID 4326883.
- ↑ Holick MF, Schnoes HK, DeLuca HF (April 1971). "Identification of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, a form of vitamin D3 metabolically active in the intestine". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 68 (4): 803–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.4.803. PMC 389047. PMID 4323790.
- ↑ Fraser, D. R.; Kodicek, E. (November 1970). "Unique Biosynthesis by Kidney of a Biologically Active Vitamin D Metabolite". Nature. 228 (5273): 764–766. doi:10.1038/228764a0.
- ↑ Maddison, P. J.; Bacon, P. A. (23 November 1974). "Vitamin D Deficiency, Spontaneous Fractures, and Osteopenia in Rheumatoid Arthritis". BMJ. 4 (5942): 433–435. doi:10.1136/bmj.4.5942.433.
- ↑ Brumbaugh, PF; Haussler, MR (25 February 1975). "Specific binding of 1alpha,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol to nuclear components of chick intestine". The Journal of biological chemistry. 250 (4): 1588–94. PMID 163254.
- ↑ Norman, Anthony W. (1979). Vitamin D: The Calcium Homeostatic Steroid Hormone. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-521050-8.
- ↑ Holick, M.; MacLaughlin, J.; Clark, M.; Holick, S.; Potts, J.; Anderson, R.; Blank, I.; Parrish, J.; Elias, P (10 October 1980). "Photosynthesis of previtamin D3 in human skin and the physiologic consequences". Science. 210 (4466): 203–205. doi:10.1126/science.6251551.
- ↑ Brooke, O G; Brown, I R; Bone, C D; Carter, N D; Cleeve, H J; Maxwell, J D; Robinson, V P; Winder, S M (15 March 1980). "Vitamin D supplements in pregnant Asian women: effects on calcium status and fetal growth". BMJ. 280 (6216): 751–754. doi:10.1136/bmj.280.6216.751.
- ↑ Reichrath, Jörg (11 September 2020). Sunlight, Vitamin D and Skin Cancer. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-030-46227-7.
- ↑ "Alfacalcidol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 23 September 2021.
- ↑ Garland, Cedric F; Garland, Frank C (1980). "Do Sunlight and Vitamin D Reduce the Likelihood of Colon Cancer?". International Journal of Epidemiology. 9 (3): 227–231. doi:10.1093/ije/9.3.227.
- ↑ Marya, R.K.; Rathee, S.; Lata, V.; Mudgil, S. (1981). "Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation in Pregnancy". Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. 12 (3): 155–161. doi:10.1159/000299597.
- ↑ Scragg, Robert (1981). "Seasonality of Cardiovascular Disease Mortality and the Possible Protective Effect of Ultra-violet Radiation". International Journal of Epidemiology. 10 (4): 337–341. doi:10.1093/ije/10.4.337.
- ↑ Colston, Kay; Colston, M. Joseph; Feldman, David (March 1981). "1,25-DIHYDROXYVITAMIN D 3 AND MALIGNANT MELANOMA: THE PRESENCE OF RECEPTORS AND INHIBITION OF CELL GROWTH IN CULTURE". Endocrinology. 108 (3): 1083–1086. doi:10.1210/endo-108-3-1083.
- ↑ Abe, E.; Miyaura, C.; Sakagami, H.; Takeda, M.; Konno, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Yoshiki, S.; Suda, T. (1 August 1981). "Differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 78 (8): 4990–4994. doi:10.1073/pnas.78.8.4990.
- ↑ Sedrani, S H; Elidrissy, A W; El Arabi, K M (1 July 1983). "Sunlight and vitamin D status in normal Saudi subjects". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 38 (1): 129–132. doi:10.1093/ajcn/38.1.129.
- ↑ Halloran, Bernard P.; Schaefer, Phillip; Lifschitz, Meyer; Levens, Marilyn; Goldsmith, Ralph S. (December 1984). "Plasma Vitamin D Metabolite Concentrations in Chronic Renal Failure: Effect of Oral Administration of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3*". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 59 (6): 1063–1069. doi:10.1210/jcem-59-6-1063.
- ↑ Greer, Frank R.; Hollis, Bruce W.; Cripps, Derek J.; Tsang, Reginald C. (September 1984). "Effects of maternal ultraviolet B irradiation on vitamin D content of human milk". The Journal of Pediatrics. 105 (3): 431–433. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80021-9.
- ↑ Morimoto, S; Kumahara, Y (March 1985). "A patient with psoriasis cured by 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3". Medical journal of Osaka University. 35 (3–4): 51–4. PMID 4069059.
- ↑ Gombart, Adrian F. (21 November 2012). Vitamin D: Oxidative Stress, Immunity, and Aging. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4398-5021-3.
- ↑ Fischer, János; Ganellin, C. Robin. Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5.
- ↑ "Paricalcitol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Carter, G.D.; Berry, J.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Gunter, E.; Jones, G.; Jones, J.; Makin, H.L.J; Pattni, P.; Phinney, K.W.; Sempos, C.T.; Williams, E.L. (October 2017). "Quality assessment of vitamin D metabolite assays used by clinical and research laboratories". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 173: 100–104. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.03.010.
- ↑ Gorham, ED; Garland, CF; Garland, FC (March 1989). "Acid haze air pollution and breast and colon cancer mortality in 20 Canadian cities". Canadian journal of public health = Revue canadienne de sante publique. 80 (2): 96–100. PMID 2720547.
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Tarutani, M (October 2004). "[Vitamin D3 for external application--history of development and clinical application]". Clinical calcium. 14 (10): 124–8. PMID 15577144.
- ↑ McKenna, Malachi J. (July 1992). "Differences in vitamin D status between countries in young adults and the elderly". The American Journal of Medicine. 93 (1): 69–77. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(92)90682-2.
- ↑ Hanchette, Carol L.; Schwartz, Gary G. (1992). "Geographic patterns of prostate cancer mortality. Evidence for a protective effect of ultraviolet radiation". Cancer. 70 (12): 2861–2869. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(19921215)70:12<2861::aid-cncr2820701224>3.0.co;2-g.
- ↑ Schwartz, Gary G.; Hanchette, Carol L. (October 2006). "UV, latitude, and spatial trends in prostate cancer mortality: All sunlight is not the same (United States)". Cancer Causes & Control. 17 (8): 1091–1101. doi:10.1007/s10552-006-0050-6.
- ↑ Peters DC, Balfour JA (August 1997). "Tacalcitol". Drugs. 54 (2): 265–71, discussion 272. doi:10.2165/00003495-199754020-00005. PMID 9257082.
- ↑ Lecha, M; Mirada, A; Lopez, S; Artes, M (July 2005). "ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Tacalcitol in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris: the Spanish experience". Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 19 (4): 414–417. doi:10.1111/j.1468-3083.2005.01099.x.
- ↑ Vecino-Vecino, Concepción; Gratton, Miren; Kremer, Richard; Rodriguez-Mañas, Leocadio; Duque, Gustavo (2006). "Seasonal Variance in Serum Levels of Vitamin D Determines a Compensatory Response by Parathyroid Hormone: Study in an Ambulatory Elderly Population in Quebec". Gerontology. 52 (1): 33–39. doi:10.1159/000089823.
- ↑ van der Wielen, R.P.J.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; van Staveren, W.A.; Löwik, M.R.H.; van den Berg, H.; Haller, J.; Moreiras, O. (July 1995). "Serum vitamin D concentrations among elderly people in Europe". The Lancet. 346 (8969): 207–210. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91266-5.
- ↑ St-Arnaud, René; Messerlian, Serge; Moir, Janet M.; Omdahl, John L.; Glorieux, Francis H. (1 October 1997). "The 25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-Alpha-Hydroxylase Gene Maps to the Pseudovitamin D-Deficiency Rickets (PDDR) Disease Locus". Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 12 (10): 1552–1559. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.10.1552.
- ↑ Brenza, H. L.; Kimmel-Jehan, C.; Jehan, F.; Shinki, T.; Wakino, S.; Anazawa, H.; Suda, T.; DeLuca, H. F. (17 February 1998). "Parathyroid hormone activation of the 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1 -hydroxylase gene promoter". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 95 (4): 1387–1391. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.4.1387.
- ↑ Moriarty, Robert M.; Albinescu, Dragos (September 2005). "Synthesis of 1α-Hydroxyvitamin D 5 Using a Modified Two Wavelength Photolysis for Vitamin D Formation". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 70 (19): 7624–7628. doi:10.1021/jo050853f.
- ↑ "Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride". 17 September 1997. doi:10.17226/5776.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Fu, Glenn K.; Lin, Dong; Zhang, Martin Y. H.; Bikle, Daniel D.; Shackleton, Cedric H. L.; Miller, Walter L.; Portale, Anthony A. (December 1997). "Cloning of Human 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-1α-Hydroxylase and Mutations Causing Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1". Molecular Endocrinology. 11 (13): 1961–1970. doi:10.1210/mend.11.13.0035.
- ↑ "Paricalcitol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Schwartz, GG; Whitlatch, LW; Chen, TC; Lokeshwar, BL; Holick, MF (May 1998). "Human prostate cells synthesize 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 from 25-hydroxyvitamin D3". Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 7 (5): 391–5. PMID 9610788.
- ↑ Hewison, Martin; Bouillon, Roger; Giovannucci, Edward; Goltzman, David (14 December 2017). Vitamin D: Volume 2: Health, Disease and Therapeutics. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-809964-3.
- ↑ Holick, Michael F. (1999). Vitamin D: Molecular Biology, Physiology, and Clinical Applications. Humana Press. ISBN 978-0-89603-467-9.
- ↑ Barreto, AM; Schwartz, GG; Woodruff, R; Cramer, SD (March 2000). "25-Hydroxyvitamin D3, the prohormone of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, inhibits the proliferation of primary prostatic epithelial cells". Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive Oncology. 9 (3): 265–70. PMID 10750664.
- ↑ "Doxercalciferol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Feldman, David; Pike, J. Wesley; Glorieux, Francis H. (25 January 2005). Vitamin D. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-08-054364-2.
- ↑ Giovannucci, Edward; Liu, Yan; Rimm, Eric B.; Hollis, Bruce W.; Fuchs, Charles S.; Stampfer, Meir J.; Willett, Walter C. (5 April 2006). "Prospective Study of Predictors of Vitamin D Status and Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Men". JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 98 (7): 451–459. doi:10.1093/jnci/djj101.
- ↑ Garland, Cedric F.; Gorham, Edward D.; Mohr, Sharif B.; Grant, William B.; Giovannucci, Edward L.; Lipkin, Martin; Newmark, Harold; Holick, Michael F.; Garland, Frank C. (March 2007). "Vitamin D and prevention of breast cancer: Pooled analysis". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 103 (3–5): 708–711. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.007.
- ↑ Vassallo, M. F.; Banerji, A.; Rudders, S. A.; Clark, S.; Camargo, C. A. (November 2010). "Season of birth and food-induced anaphylaxis in Boston: ALLERGYNet". Allergy. 65 (11): 1492–1493. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02384.x.
- ↑ "Becocalcidiol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ "The Biologics News and Reports Portal". pipelinereview. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ↑ Reichrath, Jörg (11 September 2020). Sunlight, Vitamin D and Skin Cancer. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-030-46227-7.
- ↑ Wagner, C. L.; Greer, F. R. (1 November 2008). "Prevention of Rickets and Vitamin D Deficiency in Infants, Children, and Adolescents". PEDIATRICS. 122 (5): 1142–1152. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-1862.
- ↑ MD, James Dowd; Stafford, Diane (14 January 2008). The Vitamin D Cure. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-13155-8.
- ↑ M.D, Soram Khalsa (1 March 2009). Vitamin D Revolution. Hay House, Inc. ISBN 978-1-4019-2911-4.
- ↑ Bronson J, Dhar M, Ewing W, Lonberg N (2012). "To Market — 2011: Eldecalcitol (osteoporosis)". In Desai MC (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 47 (1st ed.). San Diego: Elsevier Inc. pp. 529–531. ISBN 9780123964922.
- ↑ Hatakeyama, Susumi; Yoshino, Madoka; Eto, Kohei; Takahashi, Keisuke; Ishihara, Jun; Ono, Yoshiyuki; Saito, Hitoshi; Kubodera, Noboru (July 2010). "Synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of 20-epi-eldecalcitol [20-epi-1α,25-dihydroxy-2β-(3-hydroxypropoxy)vitamin D3: 20-epi-ED-71]". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 121 (1–2): 25–28. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.041.
- ↑ Wishart, Ian (2012). Vitamin D: Is This the Miracle Vitamin?. Howling at the Moon Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9876573-1-2.
- ↑ Domene, Ana Claudia (18 February 2016). Multiple Sclerosis and (lots Of) Vitamin D: My Eight-Year Treatment with The Coimbra Protocol for Autoimmune Diseases. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform. ISBN 978-1-5191-6531-2.
- ↑ "Vitamin D Levels Linked to Lower Colorectal Cancer Risk". www.cancer.org. Retrieved 20 September 2021.
- ↑ Liao, Emilia Pauline (23 April 2018). Extraskeletal Effects of Vitamin D: A Clinical Guide. Humana Press. ISBN 978-3-319-73742-3.
- ↑ Vitamin D Deficiency and Covid-19: Its Central Role in a World Pandemic. ISBN 0956213278.
- ↑ "Clinical trial finds vitamin D does not ward off colds and flu". medicalxpress.com. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ↑ "Weight plays role in vitamin D's health benefits". Harvard Gazette. Harvard University. January 17, 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2025.
- ↑ Sha, Sha; Chen, Li-Ju; Brenner, Hermann; Schöttker, Ben (September 2023). "Associations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D status and vitamin D supplementation use with mortality due to 18 frequent cancer types in the UK Biobank cohort". European Journal of Cancer. 191. Elsevier: 113241. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2023.113241. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ Wallace, Chris; Gordon, Morris; Sinopoulou, Vasiliki; Limketkai, Buenden (2023). "Vitamin D for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD011806. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011806.pub2.
- ↑ "New Study Finds Current Dosing Recommendations May Not Help Patients Achieve Optimal Vitamin D Levels". Intermountain Health Newsroom. 12 November 2023. Retrieved 7 December 2025.
- ↑ Shah, Monali; Poojari, Megha; Nadig, Prasad; Kakkad, Dinta; Banerjee Dutta, Sudeshna; Sinha, Susmita; Chowdhury, Kona; Dagli, Namrata; Haque, Mainul; Kumar, Santosh (26 October 2023). "Vitamin D and Periodontal Health: A Systematic Review". Cureus. 15 (10): e47773. doi:10.7759/cureus.47773.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ↑ "Vitamin D supplements for fracture prevention in schoolchildren in Mongolia: analysis of secondary outcomes from a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial". The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 12 (1). Elsevier: —. 2024. Retrieved 30 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ↑ "New Research Shatters Vitamin D Supplementation Myth". SciTechDaily. 22 January 2024. Retrieved 7 December 2025.
- ↑ Alzohily, Bashar; AlMenhali, Asma; Gariballa, Salah; Munawar, Nayla; Yasin, Javed; Shah, Iltaf (30 March 2024). "Unraveling the complex interplay between obesity and vitamin D metabolism". Scientific Reports. 14: 7583. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-58154-z.
- ↑ "Scientists Shed New Light on the Anti-Aging Effect of Vitamin D". SciTechDaily. 4 April 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ "Evolution, human migrations and vitamin D deficiencies". Science. 7 May 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
{{cite web}}: Text "Business" ignored (help) - ↑ "Endocrine Society recommends healthy adults take the recommended daily allowance of vitamin D". Endocrine Society. 3 June 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ "Potential association between arsenic and vitamin D". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 15: 1430980. 16 July 2024. doi:10.3389/fendo.2024.1430980. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ↑ Pauline Anderson (20 September 2024). "High-Dose Vitamin D Linked to Lower Disease Activity in CIS". Medscape. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ Xu, Yue; Song, Lingyun; Zhou, Li (29 October 2024). "The association of vitamin D insufficiency with the prevalence of obesity in children: implications for serum calcium levels, alkaline phosphatase activity, and bone maturation". Frontiers in Nutrition. 11. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1466270. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|editorialsection=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ↑ "Epigenetic signature of human vitamin D3 and IL-10 conditioned regulatory DCs". Scientific Reports. 14. Nature Portfolio. 20 November 2024. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-79299-x. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}:|article=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ↑ Benjamin Ferrer (5 December 2024). "N-utra functional vitamin D3-enriched mealworm flour obtains EU Novel Food status". FoodIngredientsFirst. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ "Vitamin D May Lower Blood Pressure in Seniors With Overweight". Medscape. 18 November 2024. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ "Vitamin D supplementation ameliorates ductular reaction, liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice by upregulating TXNIP in ductular cells". Nature Communications. 16. Nature Portfolio. 13 May 2025. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}:|article=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ↑ Deepika (2025). "Vitamin D: recent advances, associated factors, and its role in combating non-communicable diseases". npj Science of Food. 9: 100. doi:10.1038/s41538-025-00460-5. Retrieved 2025-12-04.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Relation between vitamin D deficiency and diabetic maculopathy". Scientific Reports. Nature. 4 July 2025. Retrieved 4 December 2025.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ↑ "Impact of vitamin D3 supplementation on motor functionality and the immune response in Parkinson's disease patients with vitamin D deficiency". Scientific Reports. 15. Nature Portfolio. 11 July 2025. Retrieved 4 December 2025.
{{cite journal}}:|article=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - ↑ "Low vitamin D in pregnancy linked to childhood caries". Dentistry.co.uk. 4 December 2025. Retrieved 5 December 2025.
- ↑ "Vitamin D". Google Trends. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ↑ "vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin B and vitamin C". books.google.com. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ↑ "Vitamin D". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 19 September 2021.
- ↑ "Vitamin d deficiency: treatments, associated drugs and conditions (21,591 reports) - eHealthMe". www.ehealthme.com. Retrieved 13 September 2021.