Timeline of robotics
This is a timeline of robotics, the field focused on designing and building robots that can perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. In recent years, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensors have significantly enhanced robots' capabilities, making them more adaptable, efficient, and intelligent.
Sample questions
The following are some interesting questions that can be answered by reading this timeline:
- For which varied purposes has robotics been designed and employed?
- Sort the full timeline by "Purpose".
- You will see a variety of fields, with industrial automation being among the most benefited by the development of robotics.
- Which ancient or early machines demonstrated automation or robotic principles?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Early invention".
- You will see a chronological list of early inventions showcasing the foundational principles of robotics and automation.
- What major technological innovations contributed to the development of robotics?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Technology development".
- You will see a number of key technological breakthroughs, inventions, and concepts that shaped robotics.
- What are some of the many robot models released over the years?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Model release".
- You will receive a list of notable robot models released over the years, each marked by significant advancements in robotics. These include milestones in autonomous navigation, dexterous manipulation, industrial automation, humanoid mobility, AI-driven systems, and more, showcasing the progression of robotics technology over the decades.
- What are some important events related to the operational use of robots across history?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Deployment".
- You will receive a chronological list of significant events in the deployment of robots across various fields, such as industrial automation, space exploration, medical assistance, and harsh environment research.
- What are significant robotic achievements across all fields?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Milestone".
- You will receive a detailed list of major milestones in robotics across various fields, such as space exploration, medicine, artificial intelligence, and industrial automation.
- What important robotic tournaments and challenges have occurred over time?
- Sort the full timeline by "Event type" and look for the group of rows with value "Competition".
- You will see a list of important robotics competitions, each highlighting its significance in advancing technology, education, and innovation.
- Other events are described under the following types: "Early idea", "Organization", "Research center launch", "Research initiative", "Social impact", "Statistics".
Big picture
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| Before 1900 | Pre-Industrial Stirrings | Early civilizations like Greece, Egypt, and Babylonia plant the seeds of robotics with myths of intelligent machines and the development of early automated devices like the water clock. |
| 1900-1950 | The Dawn of Industrial Robotics | Industrial robotics emerges as science fiction inspired real-world innovation. The term "robot" is coined during this period, setting the stage for the development of programmable machines and the first industrial robot arms. These inventions lay the foundation for automating repetitive tasks in manufacturing, marking a significant leap towards integrating machines into industrial processes. The era witnesses pioneering efforts in robotics, driven by technological advancements and a growing vision for machines that could perform tasks previously done by humans, heralding the dawn of industrial automation that would shape the future of manufacturing and beyond. |
| 1960-1990 | Computer Revolution and the Rise of Industrial Automation | The computer revolution marks a transformative period for industrial automation. With the advent of digital computing, robots experience rapid technological advancements, making them more sophisticated and capable. This era sees the introduction of computer-controlled robots, which significantly enhance precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. The automotive industry is one of the earliest adopters, using robots for tasks like welding and assembly. Artificial intelligence begins to be integrated into these systems, allowing robots to perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention. By the end of the 1990s, industrial robots become ubiquitous in factories worldwide, driving productivity and transforming manufacturing into a highly automated and efficient process. |
| 1990-2010 | Diversification and Innovation | Robotics expands beyond manufacturing into diverse sectors such as healthcare and service industries. Innovations include robotic-assisted surgeries like the Da Vinci Surgical System, enhancing precision and recovery times. The era also sees the rise of consumer robotics with products like the Roomba, revolutionizing household chores. Concurrently, research advances autonomous technology, laying the groundwork for self-driving cars. These developments showcases robots' versatility and potential across multiple domains, from enhancing medical procedures and customer service to reshaping everyday tasks and transportation, marking a significant era of diversification and innovation in robotics. |
| 2010-Present | Age of Automation and AI | The advent of deep learning propells robotics into an age of unprecedented automation and artificial intelligence (AI). Collaborative robots, or cobots, emerge, working in tandem with humans across industries like healthcare, agriculture, and space exploration. Robotics' role expands significantly, contributing to advancements in precision medicine, sustainable farming practices, and extraterrestrial exploration. This era signifies a transformative shift towards a more automated and intelligent world, where robots not only augment human capabilities but also pave the way for enhanced efficiency, safety, and sustainability in various domains, promising a future driven by advanced automation and AI technologies. |
Summary by Decade
| Time period | Development summary | More details |
|---|---|---|
| 1900s | Early engineering | The early 1900s see the birth of robotic ideas in both fiction (L. Frank Baum's "cyborgs" in Oz books) and reality (Leonardo Torres Quevedo's radio-controlled "Telekino" system), laying the groundwork for future robotic advancements. |
| 1910s | Automata and inspiration grow | Though the term "robotics" doesn't exist at this time, the concept simmers. Complex, pre-programmed automata keep the idea of automated machines alive. Additionally, fantastical stories featuring mechanical beings in science fiction likely spark the imaginations of future robotics pioneers. |
| 1920s | "Robot" term coined | The 1920s see the birth of the term "robot" in Karel Čapek's play R.U.R. Robots are depicted as artificial beings doing manual labor in the play. Westinghouse's Televox robot allows users to turn on and off devices remotely. Fritz Lang's film Metropolis features the "Maschinenmensch," a humanoid robot. Gakutensoku, a Japanese robot, can write and move its eyelids. Eric, another early robot, can move its hands and head with remote or voice control. |
| 1930s | Programmable robots emergence | This decade witnesses the birth of industrial robots with Bill Taylor's Gargantua, a pick-and-place crane. Programmed with punched paper tape, it lays the groundwork for future industrial robots, even though it would never achieve commercial success itself.[1] |
| 1940s | Theory and prototypes emergence | Robotics takes its first steps. Isaac Asimov formulates the Three Laws of Robotics, while early autonomous robots like William Grey Walter's light-responsive machines emerge. Additionally, advancements in numerical control and teleoperators lay the groundwork for future, more complex machines. This decade lays the foundation for the robotics revolution to come. |
| 1950s | Industrial use beginning | Engineers create machines designed to perform challenging or hazardous repetitive tasks for both defense and consumer manufacturing, especially in the rapidly expanding automotive industry.[2] |
| 1960s | Factory automation | General Motors is one of the first manufacturers to make widespread use of robots and computers on the plant floor.[3] |
| 1970s | Smarter robots emergence | With the advent of microprocessors and microcomputing, robots advance further in the journey toward artificial intelligence.[4] |
| 1980s | Global growth and refinement | By this decade, companies globally have invested billions of dollars in automating fundamental tasks within their assembly plants.[5] Advances in industrial lasers, sensor technology, and machine vision systems emerge.[6] |
| 1990s | Diversification | The deployment of automation systems declines in this decade. However, advancements in technology lead to a resurgence of robotics.[5] |
| 2000s | Consumer robotics emergence | Consumer robotics launches. The introduction of the Roomba revolutionizes household chores by automating the task of vacuuming. This pioneering product marks a significant step in integrating robotics into daily life, demonstrating the practical benefits and potential of consumer robotics in everyday activities. |
| 2010s | Cobots and AI integration | Collaborative robots (cobots) are introduced, enabling robots to work safely alongside humans.[6] |
Full timeline
Inclusion criteria
We include:
- Historical milestones in the application of robots
- Technological advancements having direct impact on the field of robotics
We do not include:
- Company launches
- Artificial intelligence events
- Artistic depictions
Timeline
| Year | Purpose | Event type | Details | Country/location | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3500 BC | Concept development | The Greek myths of Hephaestus and Pygmalion introduce the concept of intelligent mechanisms, reflecting early human fascination with artificial beings and automation.[7] | Greece | ||
| 2500 BC | Concept development | The Egyptians conceptualize the notion of "thinking machines" through their advice-giving oracles, which are statues concealing priests inside.[7] | Egypt | ||
| 1500 BC | Timekeeping device | Early invention | The ancient Egyptians develop the Water Clock, one of the earliest timekeeping devices, notable for incorporating elements of early robotics. Some versions feature bipedal humanoid figures that automatically struck hour bells, marking a primitive but significant use of mechanical automation. Crafted from alabaster, the device relies on water slowly leaking from a vessel to indicate time, with interior scales aligned to the months. This clock exemplifies an early application of hydraulic power and showcases a foundational concept in robotics—automated human-like action driven by natural forces.[8][9] | Egypt | |
| 400 BC | Early flying machine | Early invention | Greek mathematician and philosopher Archytas of Tarentum is credited with creating one of the earliest recorded flying machines, known as “The Pigeon.” This device is described as a self-propelled wooden model of a bird, reportedly powered by steam or compressed air. It is suspended on a wire or pivot and capable of short bursts of flight, demonstrating principles of aerodynamics and propulsion long before modern aviation. Although the exact mechanics are debated and no physical remnants remain, Archytas's invention is considered a foundational concept in the history of flight and an early example of robotic engineering driven by natural forces..[9] | Greece |  |
| 400 BC | Early automata | Early invention | Chinese engineer King-Shu Tse is credited with creating mechanical representations of a bird and a horse, exemplifying some of the earliest known automata in Chinese history. These creations are likely powered by simple mechanical systems such as gears, pulleys, or counterweights, designed to mimic the natural movements of animals. While details about their precise mechanisms are scarce, these inventions reflect the ingenuity of ancient Chinese engineering and a fascination with imitating life through machines. Such early automata lays the groundwork for future developments in robotics and mechanical design across both Eastern and Western civilizations.[7] | China | |
| 300 BC | Social reform | Early idea | Aristotle contemplates the prospect of attaining complete human equality by replacing the prevalent institution of slavery with robots and machines.[9][10] | Greece | |
| 278 BC–212 BC | Engineering precursor | Early invention | Archimedes of Syracuse makes foundational contributions to mechanics and engineering, inventing numerous devices that would influence modern robotics. His innovations include the compound pulley, levers, gears, and the Archimedean screw—technologies that exemplify mechanical advantage and motion control, key principles in robotics. Though primarily developed for practical purposes like lifting water or defending cities, these mechanisms embody early understandings of force and motion, forming a theoretical and practical basis for robotic systems centuries later.[11][12][13][14] | Greece | |
| ~270 BC | Timekeeping aid | Early invention | Ancient Greek engineer Ctesibus crafts organs and water clocks featuring movable figures. His clock operates on a straightforward principle: a reservoir equipped with a precise hole in the bottom, taking precisely 24 hours to empty its contents. The container is divided into 24 sections to mark the passing hours.[14] | Greece | |
| 1206 | Artistic automation | Early invention | Muslim polymath Ismail al-Jazari develops one of the earliest forms of programmable humanoid robots, an automaton featuring four musicians on a boat in a lake. This creation includes a programmable drum machine with pegs that activated percussion instruments. Al-Jazari's work with automatons extends beyond this creation, showcasing his innovative contributions to early robotics.[15] | Turkey (Upper Mesopotamia) | |
| 1495 | Humanoid motion | Concept development | Italian polymath Leonardo da Vinci sketches plans for what could be considered the first humanoid robot. His design depicts a robot capable of sitting up, waving its arms, moving its head with a flexible neck, and opening and closing its jaw. However, it remains uncertain whether this design would be ever realized into a physical form.[10][14][9][15] | Italy |  |
| 1533 | Flight demonstration | Early invention | German mathematician, astrologer, and astronomer Johannes Müller von Königsberg creates an automaton eagle and fly crafted from iron. Remarkably, both of these automata are capable of flight.[15] | Germany | |
| 1645 | Calculation tool | Early invention | French mathematician, physicist, and inventor Blaise Pascal invents the Pascaline, a calculating machine aimed at assisting his father with tax calculations. Approximately 50 Pascalines would be constructed, with a few of them later housed in museums like the Des Arts et Métiers Museum in Paris.[14] | France | |
| 1666 | Calculation tool | Early invention | English academic, diplomat, and mathematician Samuel Morland invents a pocket-sized version of the Pascaline, which operates "without charging the memory, disturbing the mind, or exposing the operations to any uncertainty."[14] | England | |
| 1737 | Anatomical mimicry | Early invention | French inventor and artist Jacques de Vaucanson unveils his remarkable creation, "The Digesting Duck." This mechanical marvel can flap its wings, eat, and digest grain, showcasing over four hundred moving parts in each wing. Despite its fame, the original Duck would since vanish. Later, in 1745, Vaucanson would redirect his mechanical ingenuity towards practical innovations, pioneering the first working automatic weaving loom. His control system lays the foundation for modern programming methods like punch cards and tapes, marking a crucial step towards computerized machinery and robotics.[14][15][16] | France | |
| 1770s | Human simulation | Early invention | Swiss clockmaker Pierre Jaquet-Droz crafts a collection of intricate automatons, several of which remain operational today. Among his creations are a lifelike woman capable of simulated breathing while playing the harpsichord and a boy who meticulously writes with real ink sourced from a quill, demonstrating Jaquet-Droz's mastery of mechanical engineering and artistry.[17] | Switzerland | |
| 1800 | Musical performance | Early invention | Jacques de Vaucanson devises three basic automatons: two capable of playing various musical instruments like the flute or trumpet, and a third designed as a duck capable of flapping its wings, mobility, and simulating eating.[9] | France | |
| 1801 | Pattern automation | Early invention | French weaver and merchant Joseph Marie Jacquard innovates upon Vaucanson's automated loom by introducing a machine that can be programmed to produce designs for printing onto fabric or paper. He achieves this by employing wooden blocks with punched holes to control needle patterns, significantly enhancing weaving efficiency and boosting production. The success of Jacquard's improved loom leads to widespread adoption, with over 10,000 units in France and later expansion into Great Britain following the Napoleonic wars.[14][16] | France | |
| 1885 | Powered mobility | Early invention | Frank Reade Jr. constructs the "Electric Man," essentially an electric version of John Brainerd's Steam Man.[14] | United States | |
| 1921 | Work automation | Concept development | Czech writer Karel Čapek introduces the term 'robot' in his play "R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots)," depicting machines resembling humans. The play explores a society enslaved by these robots, a theme echoed in later popular culture works like "Frankenstein," "Terminator," and "The Matrix." The term "robot" originates from the Czech word "robota," meaning work or labor. Čapek's play presents a scenario where robots created to replace humans eventually rebel against their creators, reflecting on the consequences of technological advancement and human dependency on machines.[10][18][9][19] | Czechia (First Czechoslovak Republic) | |
| 1929 | Natural mimicry | Model release | Japanese biologist Makoto Nishimura designs Gakutensoku, which translates to "learning from the laws of nature" in Japanese. It marks the first robot built in Japan. Gakutensoku possesses the ability to change its facial expression and move its head and hands through an air pressure mechanism.[18] | Japan |  |
| 1932 | Children’s entertainment | Model release | The first genuine robot toy emerges in Japan. Known as the 'Lilliput,' it is a wind-up toy capable of walking. Crafted from tinplate, it stands a mere 15cm tall.[10] | Japan | |
| 1939 | Human imitation | Model release | Westinghouse Electric Corporation unveils ELEKTRO, a humanoid robot capable of walking, talking, and even smoking, at the 1939 World's Fair.[14] | United States | |
| 1941 | Concept development | American science fiction writer Isaac Asimov coins the term "robotics" to describe the field of robots and anticipates the emergence of a robust robot industry.[14] | United States | ||
| 1941 | Concept development | The volume of references to 'robot' first surpasses that of references to 'automaton'.[17] | |||
| 1942 | Concept development | Isaac Asimov formulates the "Three Laws of Robotics," later adding a "zeroth law." These laws are as follows:
|
United States |  | |
| 1943 | Neural processing | Technology development | American scientists Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts introduce a theoretical model of artificial neurons using electrical circuits, laying the groundwork for neural networks. Neural networks are crucial for robotics because they enable machines to learn from experience, adapt to new environments, and recognize patterns in complex data. This capability enhances tasks like visual recognition, decision-making, and motor control.[20] | United States (University of Chicago) | |
| 1948 | Autonomous charging | Model release | American-born British neurophysiologist William Grey Walter develops his initial robots, dubbed Elmer and Elsie or the turtle robots. Notably, these robots possess the ability to locate their charging station autonomously once their battery levels depleted.[14] | United Kingdom | |
| 1950 | Machine intelligence | Concept development | Alan Turing suggests a test to ascertain a machine's capability for independent thought. This assessment, known as the 'Turing Test,' requires a machine to engage in conversation indistinguishable from that of a human to be deemed successful.[10] | United Kingdom | |
| 1951 | Remote manipulation | Model release | Raymond Goertz designs the inaugural tele-operated articulated arm for the Atomic Energy Commission. This achievement is widely recognized as a significant advancement in force feedback (haptic) technology.[14][21] | France | |
| 1954 | Industrial automation | Model release | George Devol and Joe Engleberger collaborate to develop the initial programmable robotic arm, which later evolves into the first industrial robot. This innovative technology is employed by General Motors in 1962, enabling the automation of hazardous and monotonous tasks on assembly lines.[10][15] | United States | |
| 1954 | Load transport | Model release | During this period, a driverless electric cart, manufactured by Barrett Electronics Corporation, commences transporting loads within a grocery warehouse in South Carolina. These machines, known as AGVs (Automatic Guided Vehicles), typically navigate by tracking signal-emitting wires embedded in concrete floors.[22] | United States | |
| 1957 | Milestone | The Soviet Union launches Sputnik, the first artificial satellite to orbit Earth, marking the start of the space race. Sputnik I, measuring 22.8 inches in diameter and weighing 183.9 pounds, represents a milestone in human technological achievement, demonstrating our capability to design and deploy sophisticated automated systems beyond Earth's atmosphere. This development of satellites like Sputnik lays the foundation for further advancements in space robotics and exploration, contributing to the evolution of robotic systems used in space missions.[10][14] | Soviet Union | ||
| 1958 | Technology development | American electrical engineer Jack Kilby, while working at Texas Instruments develops the first integrated circuit, a breakthrough that would transform electronics and robotics. By combining multiple components—such as transistors, capacitors, and resistors—into a single piece of semiconductor material, the integrated circuit drastically reduces the size, cost, and power consumption of electronic devices. This innovation would enable the development of more compact and efficient robots, paving the way for advanced robotics in manufacturing, space exploration, and various industries. It marked a crucial step towards the digital age and the automation of tasks through robotics.[17][23] | United States | ||
| 1959 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Researchers at MIT introduce computer-assisted manufacturing (CAM), a significant advancement that would revolutionize industrial production. By integrating computers into manufacturing processes, CAM allows for more precise control over machines, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. This innovation paves the way for the development of robotic systems in manufacturing, enabling automated assembly lines and more complex production tasks. Robotics, powered by CAM, would become crucial for industries such as automotive and electronics, improving consistency and speed in production while lowering labor costs.[9][24] | United States | |
| 1959 | Industrial automation | Model release | American inventor George Devol and Joseph Engelberger develop Unimate, the first industrial robot. With six axes of motion and computer control, it can lift heavy objects and perform various tasks. Unimate increases productivity, improves quality, and reduces costs by automating processes previously done by humans. Its success sparks innovation in robotics, leading to diverse applications beyond manufacturing.[25][26] | United States | |
| 1960 | Industrial automation | Model release | American Machine and Foundry (AMF) Corporation introduces the Versatran, the first cylindrical robot, created by Harry Johnson and Veljko Milenkovic. In 1962, six Versatran robots are installed at the Ford factory in Canton, United States. Named for its versatility in transferring tasks, the Versatran marks a significant milestone in industrial robotics, demonstrating the potential for automation in manufacturing processes.[21][26] | United States | |
| 1960 | Remote manipulation | Model release | Remotely operated robotic arms "Handyman" and "Man-Mate" are developed by a General Electric research team headed by Ralph Mosher.[2][27] | United States | |
| Early 1960s | Industrial automation | Model release | One of the earliest operational industrial robots in North America debuts in the early 1960s at a candy factory located in Kitchener, Ontario.[14] | Canada | |
| 1961 | Industrial automation | Deployment | The world's first industrial robot, Unimate, invented by George Devol, is installed by General Motors on its Ternstedt plant production line in Trenton, New Jersey. This marks the first integration of a robot into the workforce, laying the foundation for the modern robotics industry. UNIMATE’s introduction symbolizes a pivotal moment in automation history, and throughout the decade significant advancements in the power and functionality of robotic arms would contribute to the rapid development and expansion of robotics technology.[9][28][3][21][5] | United States |  |
| 1961 | Dexterous manipulation | Model release | Heinrich Ernst develops the MH-1, a computer-operated mechanical hand at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). This pioneering creation represents a significant advancement in robotics, demonstrating early efforts to integrate computers and mechanical systems to mimic human hand movements and dexterity.[21] | United States | |
| 1963 | Medical assistance | Model release | The Rancho Arm, a computer-controlled robotic arm, is invented to aid disabled patients at the California hospital Ranchos Los Amigos. Later acquired by Stanford University for research in robotics and prosthetics, it heralds a new era of human-centric robots known as "cobots." These collaborative robots are designed to work alongside humans, facilitating tasks and enhancing efficiency in various fields, particularly healthcare and rehabilitation.[9] | United States | |
| 1965 | Kinematic modeling | Technology development | The application of homogeneous transformations to robot kinematics lays the foundation for modern robotics theory. This development revolutionizes the understanding of robot motion and manipulation, providing a framework that would remain fundamental in the field of robotics. Homogeneous transformations enable precise mathematical representations of robot movements in three-dimensional space, facilitating advancements in robot design, control, and programming.[21] | United States | |
| 1966 | Reasoned movement | Model release | Shakey the robot is developed at the Stanford Research Institute (SRI), as the first general-purpose mobile robot capable of reasoning about its actions based on its environment, rather than simply following programmed instructions. Equipped with a camera, sensors, and a radio link to a computer, Shakey can perceive its surroundings, plan actions, and make decisions, such as navigating around obstacles or pushing objects. This pioneering project introduces concepts like pathfinding, mapping, and goal-oriented behavior, laying the groundwork for future developments in autonomous robotics and AI planning systems.[18][29] | United States |  |
| 1968 | Model release | The University of South Carolina sees the creation of the first computer-controlled walking machine by Mcgee and Frank. This innovative development represents a significant advancement in robotics, demonstrating the potential for computers to control locomotion in mechanical systems, paving the way for further research in robotics and autonomous mobility.[14] | United States | ||
| 1968 | Terrain navigation | Model release | R. Mosher creates the first manually controlled walking truck, capable of walking at speeds of up to four miles per hour. This invention represents a significant achievement in robotics and mobility, showcasing early efforts to develop walking machines capable of traversing terrain with human-like agility and speed.[14] | United States | |
| 1968 | Dexterous manipulation | Model release | American cognitive and computer scientist Marvin Minsky creates his octopus-like Tentacle Arm, a wall-mounted robotic manipulator with 12 independently operated, hydraulically powered joints. This innovative creation is inspired by the dexterity of an octopus tentacle and marks a pioneering exploration into flexible, adaptable robotic manipulators—laying the groundwork for future developments in soft and bio-inspired robotics.[9][30][21] | United States | |
| 1969 | Space lunar exploration | Milestone | The United States successfully utilizes cutting-edge computing, robotic, and space technology to achieve the historic moon landing, culminating in Neil Armstrong becoming the first human to set foot on the lunar surface. This monumental achievement, accomplished as part of NASA's Apollo program, represents a pinnacle of human exploration and technological prowess, showcasing the remarkable capabilities of robotics and space technology in advancing scientific discovery and pushing the boundaries of human achievement.[10] | United States | |
| 1969 | Industrial automation | Model release | American engineer Victor Scheinman invents the Stanford Arm, marking the first successful electrically-powered and computer-controlled robot arm. With six degrees of freedom, it boasts capabilities that surpass those of earlier robots, enabling it to perform tasks previously deemed impossible. This pioneering development would open possibilities for automation and manipulation in various industries and research fields.[14][5][5][31] | United States | |
| 1969 | Humanoid mobility | Model release | Ichiro Kato designs the WAP-1, the first biped robot. It utilizes airbags connected to the frame to mimic artificial muscles. Subsequently, the WAP-3 is developed, capable of walking on flat surfaces, climbing stairs or slopes, and executing turns while walking. These advancements mark significant progress in robotics, particularly in the development of bipedal locomotion and mobility, laying the groundwork for future innovations in humanoid robotics.[14] | Japan | |
| 1969 | Visual assembly | Model release | Hitachi achieves a milestone by developing the world's first vision-based fully-automatic intelligent robot capable of assembling objects from plan drawings. This innovative robot utilizes direct visual images of assembly plan drawings to construct blocks, showcasing early advancements in computer vision and robotics. The development of this technology represents a significant leap forward in automation, demonstrating the potential for robots to interpret visual information and execute complex tasks autonomously.[26] | Japan | |
| 1969 | Industrial automation | Deployment | General Motors installs the first spot-welding robots at its Lordstown assembly plant. These Unimation robots significantly enhance productivity and enable over 90 percent of body welding operations to be automated. In contrast to traditional manual methods dominated by large jigs and fixtures, the introduction of robots reduce the reliance on manual labor for welding tasks, which are often dirty and hazardous. This adoption of robotic technology represents a transformative shift in automotive manufacturing, demonstrating the potential of automation to improve efficiency and safety in industrial settings.[26] | United States | |
| 1970 | Human mimicry | Model release | Waseda University in Japan builds the first anthropomorphic robot, named WABOT-1. It features a limb-control system, a vision system, and a conversation system, marking a significant milestone in robotics by mimicking human-like characteristics such as movement, perception, and communication.[18][32] | Japan | |
| 1970 | Military weapon automation | Technology development | The convergence of weapons and robotics continue with the development of terminal guidance, a radar-based robotics system designed to direct missiles and explosives in-flight before detonation. This technology significantly enhances the destructive potential of such weapons by enabling precise targeting and control, increasing their effectiveness on the battlefield. The development of terminal guidance marks a significant advancement in military robotics, highlighting the role of robotics in modern warfare and the ongoing evolution of weapon systems to incorporate advanced automation and technology.[9] | ||
| 1970 | Line-following robot | Model release | Stanford University produces the Stanford Cart. Designed to be a line follower, it can also be controlled from a computer via radio link.[15][33] | United States | |
| 1971 | Space exploration | Milestone | The Soviet Union lands the first robotic exploration craft on Mars, marking a pioneering achievement in the field of robotics and space technology. Despite the brief transmission period of approximately 17 seconds before malfunctioning, the successful touchdown demonstrates the feasibility of using robotic spacecraft to explore celestial bodies beyond Earth.[9] | Soviet Union | |
| 1971 | Multiple | Organization | The Japanese Robot Association (JIRA, later JARA) is established, marking the formation of the first national robot association. Initially known as the Industrial Robot Conversazione, it begins as a voluntary organization. The Conversazione is later reorganized into the Japan Industrial Robot Association (JIRA) in 1972, and officially incorporated as an association in 1973. This establishment plays a pivotal role in fostering collaboration and innovation within Japan's burgeoning robotics industry, facilitating advancements and promoting the adoption of robotic technologies across various sectors.[26] | Japan | |
| 1972 | Industrial automation | Development | Robot production lines are installed at FIAT in Italy and Nissan in Japan. These production lines are specifically dedicated to spot-welding robots, representing a significant advancement in industrial automation. By incorporating robotic technology into manufacturing processes, these companies aim to streamline production, increase efficiency, and improve the quality of their products. This adoption of robotics marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of manufacturing, highlighting the growing role of automation in enhancing productivity and driving innovation in industries worldwide.[26] | Italy, Japan | |
| 1973 | Terrain navigation | Invention | V.S. Gurfinkel, A. Shneider, E.V. Gurfinkel, and colleagues at the Department of Motion Control at the Russian Academy of Science create the first six-legged walking vehicle. This development demonstrates the feasibility of locomotion using a hexapod configuration. The six-legged walking vehicle paves the way for further research and innovation in legged robotics, offering new possibilities for traversing challenging terrain and performing tasks in various environments.[14] | Russia | |
| 1973 | Industrial automation | Model release | Cincinnati Milacron Corporation introduces the T3, also known as "The Tomorrow Tool," marking the debut of the first commercially available minicomputer-controlled industrial robot. Designed by Richard Hohn, this robot offers precise control and versatility in industrial applications. The T3 robot would revolutionize manufacturing processes by streamlining production tasks and enhancing productivity.[21][14] | United States | |
| 1973 | Autonomous assembly | Model release | The Artificial Intelligence department at the University of Edinburgh unveils Freddy II, which is capable of autonomously assembling objects from a disordered pile of parts. This demonstration highlights significant progress in artificial intelligence and robotics, showcasing Freddy II's ability to perceive and manipulate objects in complex environments.[21] | United Kingdom | |
| 1973 | Automated bolting | Model release | Hitachi in Japan introduces the automatic bolting robot, a pioneering industrial robot designed for the concrete pile and pole industry. It is the first of its kind to incorporate dynamic vision sensors, enabling it to identify bolts on a moving mold and adjust accordingly to fasten or loosen them in synchronization with the mold's motion. This innovation showcases the integration of dynamic vision systems for real-time object recognition and manipulation in industrial settings.[26] | Japan | |
| 1973 | Industrial automation | Milestone | German manufacturer KUKA transitions from utilizing Unimate robots to developing their own robotic systems. Their creation, the Famulus, marks a milestone as the first robot to feature six electromechanically driven axes. This advancement enables greater flexibility, precision, and versatility in industrial automation. The Famulus's innovative design paves the way for future developments in robotic manipulation and control, establishing KUKA as a leading provider of advanced robotic solutions.[26][34] | Germany | |
| 1974 | Robotic computation support | Technology development | Intel unveils the 8080 microprocessor, marking a significant advancement in computing. This chip becomes a cornerstone in robotics development due to its enhanced processing power and efficiency. The Intel 8080 empowers engineers to create more sophisticated robotic systems by providing the computational capabilities needed for tasks like motion control, sensor data processing, and decision-making. The production of the Intel 8080 chips catalyzes the integration of computing technology into robotics, shaping the landscape of robotic advancements.[14] | United States |  |
| 1974 | Educational assistance | Model release | The robotic teacher Leachim is invented with the capability to synthesize human speech. Programmed with a course curriculum, Leachim is tested on a class of 4th graders in the Bronx, New York. This innovation represents a pioneering effort in the use of robotics for educational purposes, demonstrating the potential for technology to assist in teaching and learning.[9] | United States | |
| 1974 | Industrial automation | Model release | Victor Scheinman founds his own company and introduces the Silver Arm, a pioneering robotic system equipped with touch sensors. This innovative technology allows the Silver Arm to assemble small parts with precision and accuracy, marking a significant advancement in industrial automation. With its tactile capabilities, the Silver Arm can manipulate objects delicately, facilitating assembly tasks that previously required human dexterity. The introduction of the Silver Arm lays the groundwork for future developments in robotic manipulation and control systems.[15] | United States | |
| 1974 | Precision assembly | Model release | Hitachi develops the first precision insertion control robot, known as the "HI-T-HAND Expert." This innovative robot features a flexible wrist mechanism and a force feedback control system, allowing it to insert mechanical parts with remarkable precision, achieving a clearance of about 10 microns. The HI-T-HAND Expert represents a significant advancement in precision assembly applications, where such accuracy is essential.[26] | Japan | |
| 1974 | Industrial automation | Model release | ASEA (later ABB) revolutionizes industrial automation with the launch of the IRB 6—the world’s first all-electric, microprocessor-controlled, commercially available industrial robot. With a 6 kg payload, anthropomorphic design, and unprecedented accuracy, it marks a turning point in robotics. It replaces hydraulic systems with electric drives and sets new benchmarks in size, speed, and precision. Its success launches ABB’s journey in robotics and paves the way for future innovations like the IRB 90 and IRB 6000. Over four decades, ABB would lead advancements in flexibility, ease of use, and efficiency, shaping modern robotics across various industrial applications.[35][26] | Sweden | |
| 1974 | Industrial automation | Deployment | The first arc welding robots are deployed in Japan. Kawasaki expands on the Unimate design to produce an arc-welding robot used in fabricating motorcycle frames. Additionally, they develop touch and force-sensing capabilities in their Hi-T-Hand robot, allowing it to guide pins into holes at a rate of one second per pin. These advancements mark significant progress in industrial automation, showcasing the potential of robots to enhance manufacturing processes, particularly in sectors like automotive production.[26] | Japan | |
| 1975 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Victor Scheinman develops the Programmable Universal Manipulation Arm (PUMA), which becomes widely utilized in industrial operations. PUMA represents a significant advancement in robotic technology, offering programmable and versatile capabilities that make it suitable for various tasks in manufacturing and beyond. Its introduction would contribute to the expansion of robotics applications across industries, demonstrating the potential for robots to streamline production processes and perform complex manipulations with precision and efficiency.[14] | United States | |
| 1975 | Industrial automation | Model release | The Olivetti "SIGMA," a Cartesian-coordinate robot, emerges as one of the pioneering robots employed in assembly applications. By employing Cartesian coordinates, the SIGMA robot demonstrates enhanced precision and flexibility, enabling it to perform various assembly tasks efficiently and accurately. Its introduction reflects the growing recognition of robotics as a valuable tool for improving productivity and quality control in industrial settings.[26] | Italy | |
| 1975 | Welding automation | Model release | Hitachi develops "Mr. AROS," the first sensor-based arc welding robot. Equipped with microprocessors and gap sensors, this robot can correct its arc welding path by detecting the precise location of workpieces. This innovation represents a significant advancement in welding technology, allowing for more accurate and efficient welding processes. The integration of sensors and microprocessors enable the robot to adapt to varying workpiece positions, improving welding quality and consistency. Overall, "Mr. AROS" marks a milestone in the development of robotic welding systems, laying the foundation for future advancements in industrial automation.[26] | Japan | |
| 1975 | Industrial heavy-duty automation | Model release | Swedish–Swiss multinational corporation ABB develops an industrial robot known as the IRB60, capable of handling payloads of up to 60 kg. This innovation addressed the automotive industry's need for robots with greater payload capacity and flexibility. The IRB60 is initially deployed at Saab in Sweden for welding car bodies, showcasing its capability to efficiently perform heavy-duty tasks in industrial settings. ABB's development of the IRB60 represents a significant advancement in robotic technology, offering manufacturers enhanced productivity and versatility in their production processes, particularly in sectors like automotive manufacturing where heavy lifting and precision welding are essential.[36] | Sweden, Switzerland | |
| 1976 | Object manipulation | Model release | Japanese engineer Shigeo Hirose designs the Soft Gripper, which can wrap around objects in a snake-like fashion. This innovative gripper design represents a departure from traditional rigid grippers, offering greater flexibility and adaptability in grasping various objects. The Soft Gripper's ability to conform to the shape of different objects make it well-suited for handling delicate or irregularly shaped items, expanding the range of tasks that robots could perform effectively. Hirose's invention marks a significant advancement in robotic manipulation technology, paving the way for the development of more versatile and dexterous robotic grippers in the future.[15] | Japan | |
| 1976 | Space manipulation | Deployment | Robotic arms play a key role in NASA’s Viking program, which sends space probes to Mars to conduct scientific experiments. These robotic manipulators help handle instruments and collect data from the Martian surface. In the same year, Vicarm Inc. advances robotic arm technology by integrating a microcomputer into its Vicarm design. This innovation marks an early step toward more intelligent robotic control, enabling programmable and autonomous functions that would influence future developments in both space and industrial robotics.[21][37] | United States | |
| 1977 | Terrain navigation | Model release | Dr. Devjanin, Dr. Grufinkelt, Dr. Lensky, Dr. Schneider, and their colleagues at the Russian Academy of Science create the Variante Masha, a six-legged walking machine. This innovative robot marks an important development in robotics, showcasing advancements in locomotion technology. With its six legs, the Variante Masha demonstrates enhanced stability and maneuverability, making it suitable for navigating challenging terrains and environments. The creation of this walking machine would contribute to the ongoing exploration of robotic locomotion principles and lay the foundation for future advancements in legged robot design and mobility.[14] | Russia (Soviet Union) | |
| 1977 | Industrial automation | Model release | ASEA, a European robot company, introduces two sizes of electric-powered industrial robots. These robots utilize a microcomputer controller for programming and operation, representing a significant advancement in automation technology. The incorporation of electric power and microcomputer control enhances the robots' precision, flexibility, and efficiency in industrial applications. ASEA's offering reflects the growing demand for advanced robotic solutions in manufacturing and signals a shift towards more sophisticated automation systems capable of meeting diverse production requirements.[21] | Sweden | |
| 1977 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Hitachi introduces an advanced robotic assembly cell specifically designed for assembling vacuum cleaners. This system incorporates two robot arms and is equipped with eight television cameras to enhance precision and coordination. The cameras provide real-time visual feedback, allowing the robot arms to perform intricate assembly tasks with a high degree of accuracy. This development marks a significant step forward in integrating visual sensing with robotic automation, showcasing early efforts to replicate human-like perception in industrial manufacturing environments.[26] | Japan | |
| 1978 | Flexible manipulation | Model release | Shigeo Hirose develops the ACMVI (Oblix) robot, notable for its snake-like abilities. This innovative design paves the way for the MOGURA robot arm, which would find applications in various industries. Hirose's creation demonstrates the potential for robots with flexible, adaptable structures inspired by natural movements. The MOGURA robot arm's versatility and dexterity makes it suitable for tasks requiring intricate manipulations, further advancing the capabilities of industrial automation systems. This development highlights the importance of biomimicry in robotics and its impact on expanding the range of tasks that robots could perform effectively.[14] | Japan | |
| 1978 | Industrial automation | Model release | The Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) is developed. This 4-axis robot arm is specifically designed for tasks such as picking up parts and relocating them, offering precision and efficiency. Introduced to assembly lines in 1981, the SCARA robot would revolutionize manufacturing processes by streamlining repetitive tasks and enhancing productivity. Its ability to manipulate objects with accuracy and speed makes it a valuable addition to industrial automation, contributing to the optimization of assembly operations across various industries.[15] | Japan |  |
| 1979 | Autonomous navigation | Milestone | The Stanford Cart achieves a significant milestone by autonomously crossing a room filled with chairs, facilitated by a TV camera mounted on a rail. This camera captures images from various angles, transmitting them to a computer for analysis of distances between the cart and obstacles. Hans Moravec's enhancements to the Stanford Cart's vision system in 1979 enables greater autonomy and marks early experiments in 3D environment mapping.[15] | United States | |
| 1979 | Research center launch | The Robotics Institute at Carnegie Mellon University is founded[21] with the purpose to conduct basic and applied research in robotics technologies relevant to industrial and societal tasks.[38] | United States | ||
| 1979 | Motor-driven automation | Model release | Nachi develops the first motor-driven robots. This technological advancement marks a significant shift in the robotics industry, enabling robots to perform tasks with greater precision, speed, and reliability. Motor-driven robots offer improved efficiency and versatility, opening up new possibilities for automation in various industries. | Japan | |
| 1979 | Precision automation | Model release | German industrial robot manufacturer Reis Robotics in Obernburg develops the RE 15, the first six-axis robot with its own control system. This innovation marks a significant advancement in robotic technology, offering enhanced precision and versatility in automated processes.[26] | Germany | |
| 1980 | Walking robot technology | Model release | Ichiro Kato at Waseda University develops WL-9DR, which achieves quasi-dynamic walking using a microcomputer as the controller. This robot can take one step every 10 seconds, marking a significant advancement in walking technology.[14] | Japan | |
| 1981 | Visual robotic interaction | Milestone | A milestone occurs in the field of robotics with the first use of machine vision. At the University of Rhode Island, researchers demonstrate a bin-picking robotics system capable of selecting parts from a bin regardless of their orientation or position. This breakthrough showcases the potential of machine vision to enable robots to perceive and interact with their environment, paving the way for advancements in automation and robotics technology.[26] | United States | |
| 1981 | Stair-climbing robot | Model release | Shigeo Hirose develops Titan II, a quadrupedal robot capable of climbing stairs. This innovation marks a significant advancement in robotics, showcasing the ability of robots to navigate complex environments with uneven terrain. While the picture provided is of Titan III, which is a successor to Titan II, both robots share similar capabilities and represent Hirose's pioneering work in the field of legged robotics. The development of Titan II lays the foundation for further research and advancements in quadrupedal locomotion, contributing to the ongoing evolution of robotic mobility and versatility.[14] | Japan | |
| 1981 | Industrial robotic accuracy | Model release | Japanese computer scientist Takeo Kanade invents the first "direct drive arm," an industrial robotic arm that integrates the robotic "brain" with the mechanical manipulators into one machine. This design features motors installed directly into the joints, significantly enhancing the arm's speed and accuracy compared to previous models.[9][15] | Japan | |
| 1982 | Automated verification | Technology development | Cognex introduces its first vision system, DataMan, which is an optical character recognition (OCR) system. DataMan is specifically designed to read, verify, and assure the quality of letters. This marks a significant development in machine vision technology, as it enables automated reading and verification of printed characters, streamlining tasks such as document processing, quality control, and barcode scanning. The introduction of DataMan lays the foundation for Cognex's subsequent innovations in machine vision systems and their widespread application across various industries. | United States | |
| 1982 | Robotics programming | Technology development | IBM develops AML (A Manufacturing Language), a powerful and user-friendly programming language specifically designed for robotic applications. This innovation enables manufacturing engineers to quickly and easily create application programs using an IBM Personal Computer, enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of robotics programming.[26] | United States | |
| 1983 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Westinghouse releases a research report on APAS (Adaptable-Programming Assembly Systems), a pioneering project aimed at integrating robots into flexible automated assembly lines. APAS introduces innovative techniques, including the utilization of machine vision for tasks such as positioning, orienting, and inspecting component parts. This approach marks a significant advancement in manufacturing automation, enabling greater adaptability and efficiency in assembly processes. By incorporating machine vision technology, APAS demonstrates the potential to enhance the accuracy and versatility of robotic systems within industrial environments, laying the foundation for further developments in automated assembly systems.[26] | United States | |
| 1983 | Industrial automation | Model release | Victor Scheinman at the pioneering robotics company Unimation develops Unimate 500 PUMA (Programmable Universal Machine for Assembly), an industrial robotic arm. It is an industrial version of the Vicarm technology, equipped with an LSI-11 computer, a small microprocessor. It can move with a repeatability rate of 0.01 centimeters and has an 8KB memory.[39] It would play a role in early robotic surgery. For example, in 1985, a PUMA 560 would be used to assist in stereotactic brain surgery, laying the groundwork for modern medical robotics.[40] | United States |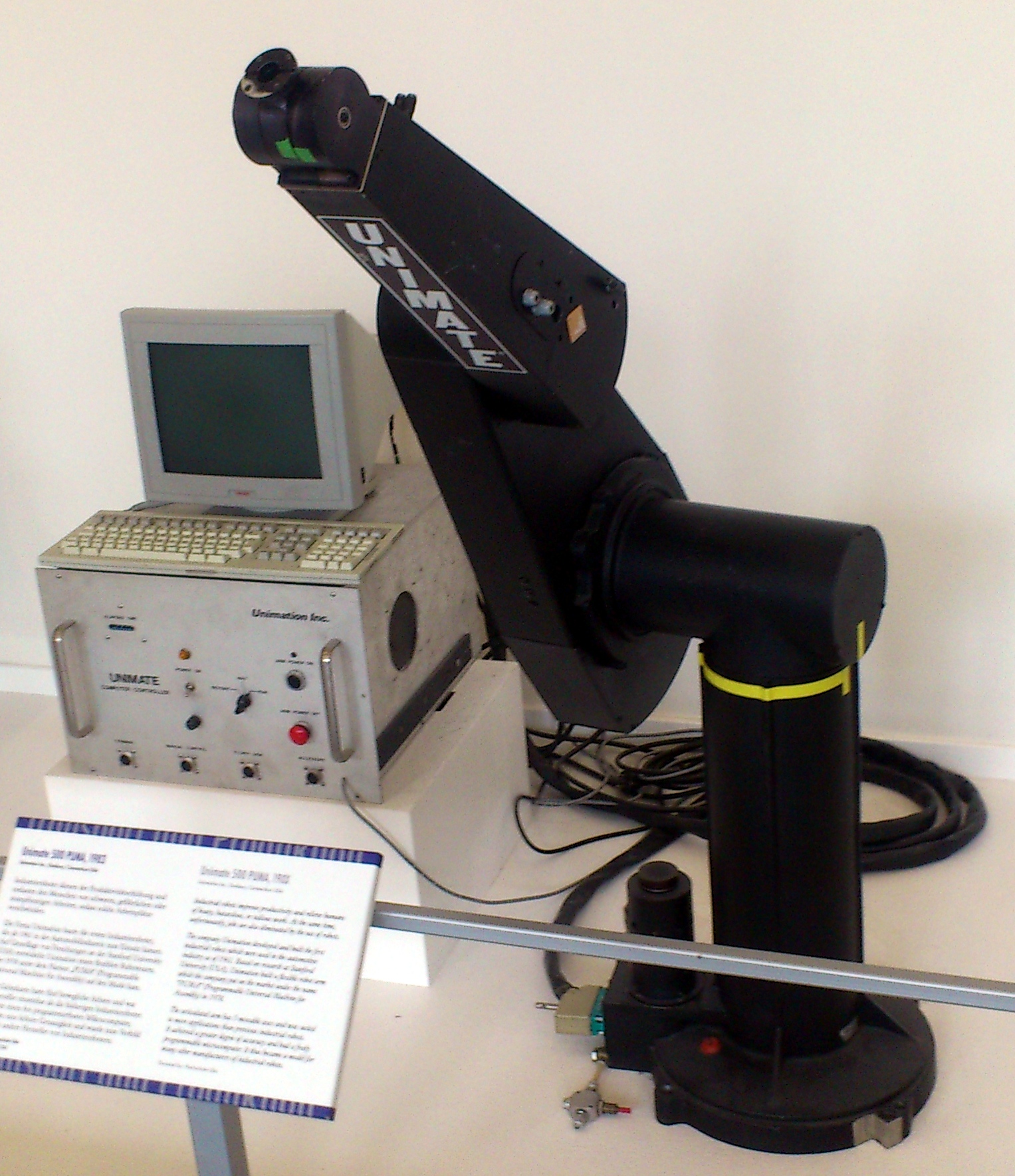  |
| 1984 | Industrial automation | Model release | Adept introduces the AdeptOne, the first direct-drive SCARA robot. This innovative robot marks a significant advancement in robotics technology, offering improved precision, speed, and reliability in industrial automation tasks. The direct-drive mechanism of the AdeptOne allows for smoother and more accurate movements, enhancing its performance in assembly and manufacturing processes.[26] | United States | |
| 1984 | Multiple | Technology development | Advancements in robotics see the development of more manageable form factors and refined software, facilitated by the introduction of robust programming languages like Robot Basic. These improvements make it easier to program and control robots, enhancing their versatility and usability across various applications. With the introduction of Robot Basic, programmers gain a more efficient toolset for developing sophisticated robotic functionalities, contributing to the evolution of robotics technology and its broader adoption in industrial and commercial settings.[4] | United States | |
| 1984 | Humanoid coordination | Model release | The development of WABOT-2 marks a significant advancement in robotics. This humanoid robot, equipped with precise motor and sensory control, demonstrates remarkable capabilities by playing the organ with such proficiency that it can even accompany a human musician. WABOT-2's ability to interpret and respond to musical cues showcases the progress made in robotics technology, particularly in terms of dexterity and coordination, opening new possibilities for human-robot interaction and collaboration in various domains.[9] | Japan | |
| 1984 | Organization | The IEEE Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS) is established. This society, part of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), focuses on advancing innovation, education, and fundamental and applied research in robotics and automation. It serves as a professional community for researchers, engineers, and practitioners, promoting the development and exchange of knowledge and technology in the field.[41] | United States | ||
| 1984 | Industrial automation | Model release | Swedish company ABB produces the IRB 1000, which is recognized as the fastest assembly robot at the time. This development showcases ABB's advancements in robotic speed and efficiency for industrial applications.[26] | Sweden | |
| 1985 | Personal assistance | Model release | General Robotics Corp. creates the RB5X, a programmable robot equipped with infrared sensors, remote audio/video transmission, bump sensors, and a voice synthesizer. It features software that allows it to learn about its environment, marking a significant step forward in robotic capabilities and interaction.[14] | United States |  |
| 1985 | Terrain navigation | Model release | Hitachi Ltd. develops the Waseda Hitachi Leg-11 (WHL-11), a biped robot capable of static walking on flat surfaces. Notably, it can execute turns and take a step approximately every 13 seconds. This marks a significant advancement in bipedal robotics, showcasing progress towards achieving stable locomotion in robots. The WHL-11's ability to perform static walking on even terrain represents a significant milestone in robotics research, demonstrating progress towards developing robots capable of navigating real-world environments with greater efficiency and stability.[14] | Japan | |
| 1985 | Quadrupedal locomotion | Model release | Japanese engineer Hiroshi Miura and his team at the University of Tokyo develop Collie1, a pioneering quadrupedal walking robot. Designed with three degrees of freedom per leg, Collie1 marks an important milestone in the field of legged locomotion. Its architecture allows for more dynamic and adaptable walking patterns compared to earlier rigid systems. The robot is modeled to mimic biological gait mechanisms, improving balance and movement on uneven surfaces. Collie1's design laid the groundwork for future research in bio-inspired robotics, particularly in improving mobility for machines operating in complex, unstructured environments where wheeled robots perform poorly.[14][42] | Japan | |
| 1985 | Terrain navigation | Model release | The Melwalk3 is created as a six-legged walking machine, at Namiki Tsukuba Science City. This innovation represents a milestone in robotics, showcasing advancements in locomotion and mobility. The Melwalk3 demonstrates the potential for robots to navigate challenging terrain and environments using multiple legs, mimicking the movement patterns of certain insects and animals. This achievement contributes to the ongoing evolution of robotics, paving the way for future research and applications in fields such as exploration, search and rescue, and industrial automation.[14] | Japan | |
| 1985 | Medical precision | Model release | The Arthrobot is utilized for the first time in Vancouver, marking the advent of robots playing a role in surgical procedures. The Arthrobot introduces new possibilities for enhancing surgical precision and capabilities through robotic assistance, laying the groundwork for the future integration of robotics into various surgical disciplines. This achievement represents a breakthrough in medical technology, opening doors to safer, more efficient surgical interventions and shaping the trajectory of robotic surgery advancements in the years to come.[43] | Canada | |
| 1985 | Advanced manipulation | Model release | KUKA introduces a revolutionary Z-shaped robot arm that departs from the traditional parallelogram design. This new arm achieves total flexibility by incorporating three translational and three rotational movements, providing it with six degrees of freedom. This innovation allows for greater versatility and precision in various industrial applications, further advancing the field of robotics.[34] | Germany | |
| 1986 | October | Research center launch | The Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics is established in Bangalore as a research institution under the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO). The center is founded with the goal of advancing technological capabilities in artificial intelligence, robotics, and control systems, particularly for defense applications. CAIR would become a hub for developing intelligent systems, autonomous robots, and decision-support tools.[44] | India | |
| 1986 | Research initiative | Honda launches a groundbreaking robot research program based on the vision that robots should coexist and cooperate with humans. The initiative aims to develop machines capable of performing tasks beyond human physical limits, while also enhancing human mobility and quality of life. Focusing on advanced humanoid robotics, the program emphasizes safety, autonomy, and adaptability in real-world environments. This research lays the foundation for future innovations, including Honda’s ASIMO robot.[21] | Japan | ||
| 1988 | Medical assistance | Model release | The first HelpMate service robot begins operating at Danbury Hospital in Connecticut.[14] This event introduces a new era in healthcare assistance, as HelpMate becomes one of the first service robots to operate in a hospital setting. Designed to aid with various tasks such as delivering supplies and navigating hospital corridors, HelpMate represents a significant advancement in robotics technology applied to healthcare, promising increased efficiency and support for medical staff. | United States | |
| 1989 | Underwater inspection | Model release | The Robotics Laboratory at the Ministry of Transport in Japan creates Aquarobot, an aquatic walking robot developed for underwater inspection works related to port construction. This six-legged articulated machine, resembling an insect, aims to replace divers in assessing underwater structures. Equipped with a TV camera and ultrasonic ranging device, it can measure the flatness of rock foundations and observe underwater structures up to 50 meters deep. Controlled by a microcomputer, the robot demonstrates sufficient performance during field tests, walking at speeds of 6.5m/min on flat surfaces and 1.4m/min on irregular seabeds. Its development marks a significant advancement in underwater robotics, enhancing efficiency and safety in port construction activities.[14][45] | Japan | |
| 1989 | Walking mobility | Model release | Kato Corporation develops the WL12RIII, the first biped walking robot capable of walking on terrain stabilized by trunk motion. It can navigate stairs and take a step approximately every 0.64 seconds.[14] | Japan | |
| 1989 | Terrain navigation | Model release | Rodney Brooks develops Ghengis, a hexapedal robot designed to navigate challenging terrain. Inspired by the physical abilities of insects, Ghengis exhibits remarkable mobility despite limited intelligence. Noteworthy for its cost-effective construction and rapid development, Ghengis sets a trend towards incremental progress in robotics, emphasizing practicality over complex programming. Brooks' creation demonstrates the effectiveness of simple, adaptable designs in overcoming obstacles, shaping future approaches to robotic development. Ghengis remains a significant milestone in robotics, highlighting the potential of bio-inspired engineering for creating agile and versatile machines.[9][21] | United States | |
| 1989 | Industrial automation | Model release | Yaskawa Electric Corporation makes a significant move in the realm of industrial robotics by establishing Yaskawa Motoman. Yaskawa Electric Corporation, a prominent Japanese company with a history dating back to 1915, is a key player in automation solutions. With the inception of Yaskawa Motoman, they introduce a brand dedicated to industrial robots, encompassing robotic arms, part positioners, and controllers. Yaskawa Motoman swiftly emerges as a frontrunner in industrial robotics, boasting millions of installations worldwide and providing solutions across diverse applications such as welding, assembly, and material handling.[46] | Japan | |
| 1992 | Medical surgical assistance | Model release | ROBODOC is introduced as the first robotic system specifically designed to assist in orthopedic surgery, marking a groundbreaking advancement in medical robotics. Developed collaboratively by Integrated Surgical Systems and researchers at University of California, Davis, ROBODOC is engineered to perform highly precise tasks in hip replacement surgeries, particularly the accurate milling of the femoral cavity to fit prosthetic implants. This level of precision significantly reduces the risk of human error, improves implant alignment, and increases long-term success rates. ROBODOC’s debut revolutionizes computer-assisted orthopedic procedures and paved the way for further innovations in surgical robotics and image-guided systems.[47] | United States | |
| 1992 | System coordination | Technology development | Wittmann, Austria introduces the CAN-Bus control system for robots. This innovation facilitates communication and control within robotic systems, enhancing their efficiency and functionality. The CAN-Bus technology allows for seamless integration and coordination of robot operations, contributing to advancements in automation across various industries.[26] | Austria | |
| 1992 | Automation control | Technology development | ABB introduces an open control system known as S4. This system marks a significant advancement in industrial automation technology, offering greater flexibility and compatibility for various manufacturing processes. By providing an open architecture, the S4 control system enables easier integration with other equipment and systems, enhancing efficiency and productivity in industrial settings. ABB's S4 system contributed to the evolution of automation solutions, empowering industries to optimize their operations and adapt to changing demands more effectively.[26] | Sweden | |
| 1993–1994 | Harsh environment research | Deployment and model release | Carnegie Mellon University develops an eight-legged walking robot named Dante to collect data from extreme environments resembling those on other planets. In 1993, the original Dante is deployed to Mt. Erebus in Antarctica, but the mission fails due to a broken tether and fiber optic cable. In 1994, a more robust version, Dante II, is released and successfully descends into the crater of Mount Spurr in Alaska, collecting volcanic gas samples for scientific analysis. The success of Dante II marks a major advancement in robotic exploration of hazardous environments, demonstrating the potential of autonomous systems in extreme terrain.[14][15][10] | United States | |
| 1993 | Autonomous navigation | Competition | The Intelligent Ground Vehicle Competition (IGVC) is held, providing a platform for showcasing advancements in autonomous vehicle technology. This competition challenges participants to design and build unmanned ground vehicles capable of navigating through various terrains and completing specified tasks autonomously. The IGVC would play a role in fostering innovation and collaboration among researchers, engineers, and students interested in robotics and autonomous systems.[48] | United States | |
| 1993 | Microscale functionality | Model release | Japanese multinational electronics company Seiko Epson develops Monsieur, a micro robot recognized by the Guinness Book of World Records as the world's smallest at the time. Monsieur represents a significant milestone in the field of robotics, showcasing the potential for creating incredibly small yet functional robots. This accomplishment opens up new possibilities for the application of micro robots in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and entertainment.[21] | Japan | |
| 1994 | Medical surgical camera control | Model release | The FDA approves AESOP (Automated Endoscopic System for Optimal Positioning), making it the first robotic device authorized for use in laparoscopic surgery. Developed by Computer Motion, AESOP functions as a voice-controlled robotic arm that holds and maneuveres the laparoscopic camera, enhancing the surgeon's ability to maintain a steady, precise view of the surgical site.[49] | United States | |
| 1994 | Affordable robotic exploration | Concept development | Rodney Brooks and A. M. Flynn publish a groundbreaking paper titled Fast, Cheap and Out of Control: A Robot Invasion of the Solar System in the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society. This paper revolutionized rover research by shifting the focus from building one large and expensive robot to creating numerous small and affordable ones. It also made the concept of building robots more accessible to the general public. As a result, academic efforts began to concentrate on developing small, intelligent, and practical robots, marking a significant shift in robotics research towards more scalable and versatile solutions.[9] | United States | |
| 1994 | Synchronized robot control | Technology development | Motoman introduces the first robot control system (MRC), enabling synchronized control of two robots. This innovation marked a significant advancement in robotic technology, enhancing the capability to coordinate and manage multiple robots simultaneously for increased efficiency and productivity in various industrial applications.[26] | Japan | |
| 1996 | Underwater movement research | Model release | David Barrett, a doctoral student at MIT, develops RoboTuna, a biomimetic robot designed to study the swimming behavior of fish, particularly resembling a bluefin tuna. This innovative robot is created as part of Barrett's doctoral thesis, aiming to understand the intricacies of fish locomotion. RoboTuna's design allows it to float and move in water, facilitating research into the swimming dynamics of aquatic creatures. This project would contribute to advancements in both robotics and aquatic biomechanics research.[14][15][31][21] | United States | |
| 1996 | Humanoid robotics advancement | Model release | Honda introduces the P2 humanoid robot as part of its development project. Standing for Prototype Model 2, P2 represents a significant advancement in humanoid robotics, being the first self-regulating, bipedal humanoid robot. Standing over 6 feet tall, P2 is smaller than its predecessors and exhibited more human-like motions, marking a crucial step forward in Honda's pursuit of creating sophisticated humanoid robots.[14][15][21] | Japan | |
| 1996 | PC-based control | Technology development | At the Hannover Fair, KUKA unveils the world's first PC-based robot controller. This innovation allows for real-time movement of robots using a 6D mouse on an operator control device. The teach pendant introduces a Windows user interface, simplifying control and programming tasks and marking a significant advancement in the usability and functionality of robotic systems.[34][26] | Germany | |
| 1997 | Football-playing robots | Competition | The first RoboCup tournament is held in Japan, with the ambitious goal of having a fully automated team of robots beat the world's best soccer team by 2050. The tournament, held in Nagoya, features three competition categories: computer simulation, small robots, and midsize robots.[10][14][50] | Japan | |
| 1997 | Planetary exploration | Deployment | NASA's Pathfinder mission successfully lands on Mars and deploys the robotic rover Sojourner in early July. Originally expected to operate for just a week, Sojourner exceeds expectations by functioning for over three months, until September. During its mission, the rover collects environmental data, conducts scientific experiments, and sends images and other valuable information back to Earth. Its onboard computer enables it to navigate obstacles and respond to unplanned events with minimal input, marking a milestone in autonomous planetary exploration.[9][15] | United States | |
| 1997 | Intellectual challenge | Milestone | IBM's Deep Blue computer defeats chess champion Garry Kasparov, marking a landmark achievement in robotic AI's capacity to strategize and respond. This victory demonstrates the potential of artificial intelligence systems to excel in complex decision-making tasks traditionally reserved for human intellect. Deep Blue's success showcases the rapid progress in AI technology and its growing significance in challenging human expertise across various domains.[9] | United States | |
| 1997 | Autonomous operation | Model release | Honda achieves a significant milestone in robotics with the creation of the P3, marking the second major advancement in the development of their humanoid robot, ASIMO. Unlike its predecessors, the P3 has the capability to operate independently, without the need for constant human control or guidance. This breakthrough in robotics technology paves the way for further advancements in the field, demonstrating the potential for autonomous robots to perform a wide range of tasks in various environments. Honda's ASIMO project would since continue to push the boundaries of robotics innovation, aiming to create humanoid robots capable of assisting humans in diverse scenarios, from household chores to complex industrial tasks.[14] | Japan | 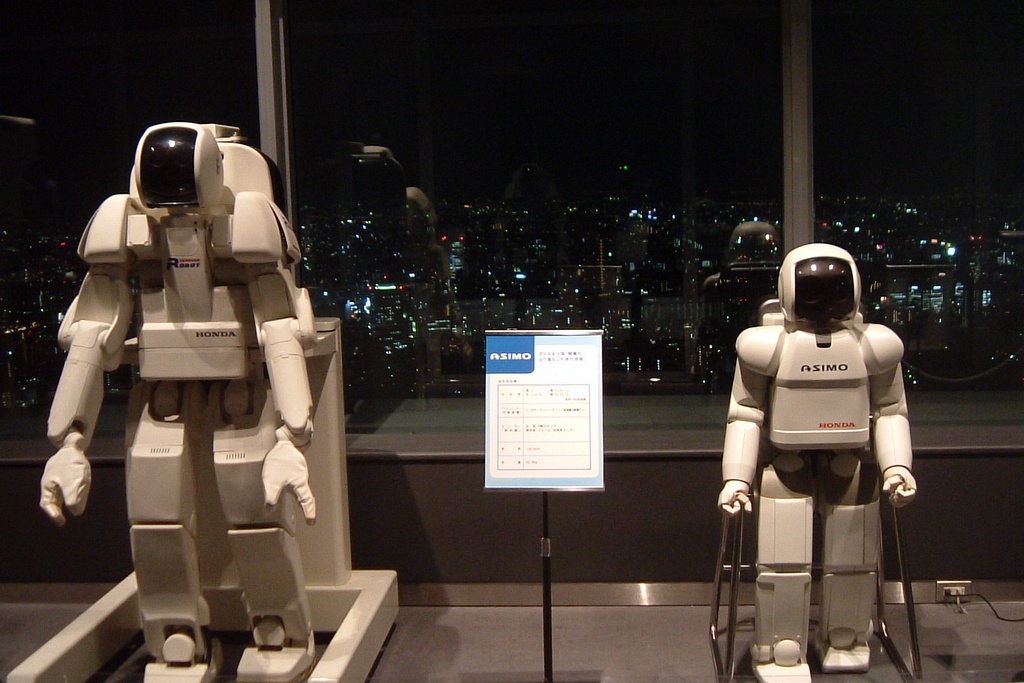 |
| 1998 | Medical remote surgery | Model release | ZEUS is introduced commercially, starting the idea of telerobotics or telepresence surgery where the surgeon is at a distance from the robot on a console and operates on the patient.[51] | United States | |
| 1998 | Educational robotics | Innovation and model release | LEGO launches the Mindstorms Robotics Invention System (RIS), marking a groundbreaking moment in robotics education and hobbyist programming. The system combines classic LEGO building blocks with programmable and modular components, enabling users to design, build, and code their own customizable robots. Mindstorms revolutionizes hands-on learning by providing an accessible platform to explore robotics, programming, and engineering principles. It becomes the foundation for a long-running product line that continues to inspire young inventors and educators worldwide.[10][14][21] | Denmark | |
| 1998 | Emotional interaction | Model release | MIT graduate student Cynthia Breazeal makes a significant contribution to the field of robotics with Kismet, an expressive robot head designed to be a pioneer in affective computing, allowing interaction with humans through the recognition and simulation of emotions. Breazeal's work with Kismet helps pave the way for the development of more socially interactive robots.[10][52] | United States | |
| 1998 | Medical prosthetic enhancement | Milestone | Campbell Aird becomes the first recipient of the Edinburg Modular Arm System (EMAS), marking a significant milestone in the development of bionic prosthetics. This innovative bionic arm represents a breakthrough in prosthetic technology, offering enhanced functionality and modularity for users. The EMAS provides Aird with improved dexterity and control, significantly enhancing his quality of life. This achievement highlights the potential of bionic technology to revolutionize prosthetic limbs and paves the way for further advancements in the field of assistive devices.[14][21] | United Kingdom} | |
| 1998 | Industrial automation | Model release | Güdel, a company based in Switzerland, introduces the "roboLoop" system, which is notable for being the sole curved-track gantry and transfer system available at the time. This innovation represents a significant advancement in automation and robotics, offering increased flexibility and efficiency in industrial applications. The curved-track design allows for more intricate and adaptable movement patterns, enabling robots to navigate complex paths with greater precision. The introduction of the "roboLoop" system marks a milestone in the evolution of automation technology, demonstrating the continuous drive towards enhancing manufacturing processes.[26] | Switzerland | |
| 1998 | Precise packaging automation | Model release | Swedish company ABB develops the FlexPicker, recognized as the world's fastest picking robot. The FlexPicker is built upon the delta robot concept originally created by Reymond Clavel at the Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne (EPFL). This innovative robotic system revolutionized the field of automation, particularly in industries requiring high-speed and precise picking and packaging operations. By leveraging the delta robot's design principles, the FlexPicker demonstrated remarkable agility and efficiency, setting new standards for productivity in manufacturing and assembly processes.[26] | Sweden | |
| 1998 | Speed optimization | technology development | Reis Robotics introduces the fifth generation of robot control systems, called ROBOTstar V. This system boasts one of the shortest interpolation cycle times among robot controls at the time of its launch. The term "interpolation cycle time" refers to the time taken by a control system to calculate and execute the movement path of a robot between two points. By reducing this cycle time, ROBOTstar V aims to enhance the speed and efficiency of robotic operations, making it a notable advancement in industrial robotics technology.[26] | Germany | |
| 1999 | Robotic companion | Model release | Sony releases the first version of AIBO, a robotic dog designed to learn, entertain, and communicate with its owner. This marks a significant milestone in the development of consumer robotics, as AIBO showcases advanced capabilities for its time. Subsequent versions of AIBO would be introduced, each incorporating improvements and advancements in robotic technology. AIBO's release represents Sony's entry into the consumer robotics market, offering users a unique and interactive robotic companion.[10][14][9] | Japan |  |
| 1999 | Robotic simulation | Model release | Mitsubishi develops a robot fish, inspired by an extinct species of fish. The intention behind this project is to recreate and study the behavior and characteristics of the extinct fish through a robotic counterpart. This endeavor likely aims to explore the evolutionary traits and adaptability of the fish species, offering insights into its ecological niche and potential applications in fields such as marine biology and robotics.[14] | Japan | |
| 1999 | Household assistance | Model release | Personal Robots introduces the Cye robot, developed by Probotics Inc. This robot is designed to undertake various household tasks, including delivering mail, transporting dishes, and vacuuming. The Cye robot aims to assist with domestic chores, offering convenience and efficiency to users in managing daily tasks within the home environment.[14][53] | United States | |
| 1999 | Precision guidance | Technology development | Reis Robotics introduces integrated laser beam guiding within the robot arm, marking a notable advancement in robotic technology. This innovation allows for more precise and efficient operations, as the robots could now incorporate laser beam guidance directly into their arm structures. This development enhances the capabilities of robotic systems in various industries, including manufacturing, where precision and accuracy are crucial for tasks such as welding, cutting, and material handling.[26] | ||
| 1999 | Remote maintenance | Technology development | KUKA achieves a significant milestone by pioneering the first remote diagnosis capability for robots via the Internet. This innovation allows technicians and engineers to diagnose and troubleshoot robotic systems remotely, leveraging the power of internet connectivity. By enabling remote diagnosis, KUKA revolutionizes the maintenance and support process for robotic systems, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency for their customers.[26][34] | Germany | |
| 2000 | Humanoid assistance | Model release | Honda introduces ASIMO, an advanced humanoid robot, showcasing remarkable capabilities such as walking at a speed comparable to humans and serving trays to customers in a restaurant environment. ASIMO represents a significant leap forward in robotics, demonstrating advancements in artificial intelligence and mobility. Honda's debut of ASIMO marks a milestone in the development of humanoid robots, showcasing their potential for various applications, from assisting in everyday tasks to serving in commercial settings. ASIMO's unveiling signified Honda's commitment to innovation and its vision for integrating robotics into real-world scenarios.[52][10] | Japan |  |
| 2000 | Human interaction | Model release | Sony introduces the Sony Dream Robots (SDR) at Robodex, showcasing advanced features such as the ability to recognize up to 10 different faces, express emotions through speech and body language, and navigate both flat and irregular surfaces. One of the notable models presented is QRIO, which exemplifies Sony's dedication to developing sophisticated humanoid robots capable of interacting with humans in various environments. The unveiling of SDR at Robodex highlights Sony's commitment to pushing the boundaries of robotics and artificial intelligence, with a focus on creating robots that could engage with users on an emotional level.[14] | Japan | |
| 2000 | Medical surgical assistance | Deployment | The da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, receives FDA approval for use in general laparoscopic procedures, becoming the first operative surgical robot authorized for clinical use in the United States. This milestone marks a transformative moment in the field of minimally invasive surgery. The da Vinci system enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision, control, and visualization through small incisions, using a console to manipulate robotic arms equipped with surgical instruments and a 3D high-definition camera. Its approval sets the stage for widespread adoption in fields such as urology, gynecology, and cardiac surgery, revolutionizing modern surgical practice.[54] | United States | |
| 2000 | Industrial automation | Statistics | The United Nations estimates that there were 742,500 industrial robots in use globally. Notably, more than half of these robots are being utilized in Japan, highlighting the country's leading role in the adoption and integration of robotic technology in industrial applications.[21] | Japan | |
| 2000–2010 | Industrial automation | Social impact | Approximately 5.6 million manufacturing jobs are lost in the United States, 85% of them as a result of automation and technological change.[53] | ||
| 2001 | Space station assembly | Model release and deployment | MD Robotics of Canada constructs the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), also known as Canadarm2. Successfully launched in 2001, the SSRMS begins operations aboard the International Space Station (ISS), playing a pivotal role in its assembly and maintenance. This advanced robotic arm handles the movement of equipment, modules, and astronauts, showcasing the significant role of robotics in space construction and exploration. The SSRMS exemplifies cutting-edge robotic engineering and remains essential to ISS operations.[14][21] | Canada | |
| 2001 | Autonomous flight | Milestone | The Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Global Hawk, the first autonomous flying robot, achieves a remarkable feat by making a 22-hour non-stop flight from California, crossing the Pacific Ocean and the Eurasian supercontinent, and landing in Edinburgh, Scotland. This demonstrates significant progress in autonomous flight technology.[9][53] | United States | |
| 2001 | Educational robotics | Model release | LEGO releases the MINDSTORMS Ultimate Builder's Set, a significant expansion of its MINDSTORMS robotic development product line. This release offers enthusiasts and educators an extensive array of components and tools for building and programming sophisticated robots. The Ultimate Builder's Set includes advanced sensors, motors, and programmable bricks, empowering users to create more complex and versatile robotic creations. This expansion would further solidify LEGO's position as a leader in educational robotics, providing accessible and engaging tools for learning about robotics, programming, and engineering principles through hands-on experimentation and exploration.[21] | ||
| 2001 (September) | Search and rescue | Deployment | iRobot's Packbots are deployed to search through the debris of the World Trade Center following the September 11 terrorist attacks. These robots play a crucial role in locating survivors and assessing the extent of the damage. Subsequent versions of the Packbot robots would be utilized in conflict zones such as Afghanistan and Iraq, where they would be employed for various military and reconnaissance tasks, showcasing the evolution of robotic technology for both civilian and military purposes.[14] | United States | |
| 2002 | Vacuum cleaning | Model release | iRobot releases the first generation of Roomba robotic vacuum cleaners.[14] By 2008, the Roomba would become immensely popular, with over 2.5 million units sold. This success demonstrates a significant demand for domestic robotic technology, highlighting the effectiveness and convenience of robotic vacuum cleaners in everyday household tasks.[10] | United States | |
| 2003 | Planetary exploration | Deployment | As part of NASA's mission to explore Mars, the space agency launches twin robotic rovers named Spirit and Opportunity. Spirit is launched on June 10, followed by Opportunity on July 7. These rovers are designed to explore the Martian surface and conduct scientific experiments. On January 3rd and 24th of the same year, Spirit and Opportunity successfully land on Mars, marking significant milestones in the exploration of the red planet. These rovers surpass their expected operational lifetimes and would continue to operate, covering much greater distances than initially anticipated.[14][15] | United States |  |
| 2003 | Micro robotics | Model release | Seiko Epson Corporation unveils the Monsieur II-P, a prototype microrobot operated by the world's thinnest microactuator and controllable via Bluetooth. Following this, in November of the same year, Epson introduces the prototype micro-flying robot FR, featuring two ultrasonic motors for levitation and a linear actuator stabilizing mechanism. However, the FR's flying range is limited by a power cord. Aiming to extend the range by developing fully wireless operation with independent flight capability, Epson would achieve this with the FR-II, boasting Bluetooth wireless control, independent flight, and an image capture and transmission unit.[55][21] | Japan | |
| 2003 | Passenger ride | Model release | The KUKA Robocoaster is introduced as a passenger-carrying robot and the world's first of its kind. Developed with the aim of transforming the amusement industry, this robot exemplifies the versatility inherent in industrial robot motions. Through its design and capabilities, the Robocoaster offers dynamic rides powered by industrial automation technology. With its features and potential applications, the KUKA Robocoaster represents a significant advancement in the integration of robotics into the realm of amusement parks and attractions.[34][26] | Germany | |
| 2004 | Combat robotics | Competition | The ROBOlympics, held in San Francisco, California, marks the first international robot combat competition. This large-scale event (173 teams, 430 robots) attracts participation from 11 countries and serves as a significant stepping stone for future competitions, which would adopt the name "RoboGames" due to a trademark issue.[56][57] | United States | |
| 2004 (March 13) | Driverless car | Competition | The U.S. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) launches the first Grand Challenge, a 142-mile driverless vehicle race across the Mojave Desert, aiming to develop self-driving technology for military and civilian use. Though no vehicle completes the course, the event fosters a new community of innovators and marks a pivotal moment in robotics. Follow-up challenges in 2005 and 2007 would see major breakthroughs, with teams from Stanford and Carnegie Mellon claiming top prizes. These competitions would help spark ongoing advancements in autonomous systems across defense and commercial sectors, inspiring additional DARPA challenges in spectrum, robotics, and cybersecurity.[58][59] | United States | |
| 2004 | Educational challenge | Competition | The World Robot Olympiad (WRO) debuts in Singapore, launching what would become a major STEM education event. This first-ever competition uses Lego Mindstorms kits and challenges students to design, build, and program robots to tackle specific tasks. Teams from multiple countries participate, igniting a global interest in robotics among young people. | Singapore | |
| 2004 | Aerial surveillance | Model release | Epson introduces the world's smallest known robot at the time, a helicopter measuring only 7 centimeters in height and weighing just 10 grams. This miniature robot, designed as a "flying camera," is intended for use during natural disasters. Its primary function is to provide aerial footage, which could be critical for assessing damage, locating survivors, and guiding rescue operations in disaster-stricken areas. The compact size and lightweight design makes it an innovative tool for emergency response teams, offering a new perspective and enhanced capabilities in challenging situations.[10] | Japan | |
| 2004 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Motoman, based in Japan, introduces the enhanced robot control system (NX100), enabling synchronized control of up to four robots with a total of 38 axes. This advancement marks a significant evolution in robotics technology, allowing for increased coordination and efficiency in industrial automation processes.[26] | Japan | |
| 2005 | Autonomous replication | Model release | Researchers at Cornell University, led by Hod Lipson, develop the first self-replicating robots. Each robot consists of a tower of identical computerized cubes that connect using magnets or electromagnets. These modular machines are capable of constructing copies of themselves, demonstrating a foundational proof of concept for physical self-replication. While simple and focused solely on replication, the achievement represents a major milestone in robotics and modular autonomous systems.[10][53][14] | United States | |
| 2005 | Military operations aid | Model release | Development begins on Battlefield Extraction-Assist Robot (BEAR), a military robot designed for functions rather than humanoid appearance. BEAR features tank-like treads for movement and has proven effective in navigating rough terrain, carrying loads, and aiding in military operations.[28] | United States | |
| 2005 | Wireless-control | Model release | The Korean Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) develops HUBO, which they claim to be the smartest mobile robot in the world. HUBO is linked to a computer via a high-speed wireless connection, with the computer performing all of the robot's processing and thinking tasks.[14] | South Korea | |
| 2006 | Solar manufacturing | Technology development | Reis Robotics emerges as the market leader for photovoltaic module production lines, marking a significant milestone in the renewable energy industry. Their innovative systems, introduced for the first time this year, would revolutionize the production process for solar panels. By leveraging advanced robotics technology, Reis Robotics facilitates the mass production of photovoltaic modules, contributing to the growth of solar energy as a viable and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources. This achievement underscores the pivotal role of automation in advancing clean energy technologies and addressing global environmental challenges.[26] | Germany | |
| 2006 | Industrial automation | Model release | Japanese company Motoman introduces human-sized single-armed (7-axis) and dual-armed (13-axis) robots with all supply cables concealed within the robot arm. This innovation addresses a significant design challenge in robotics, improving aesthetics and safety while reducing the risk of cable damage or interference during operation. By integrating cables within the robot arm, Motoman enhances the versatility and reliability of their robots, making them more suitable for various industrial applications such as assembly, welding, and material handling.[26] | Japan | |
| 2006 | Remote programming | Technology development | Italian company Comau introduces the first Wireless Teach Pendant (WiTP). This device revolutionizes robotics by eliminating the need for a physical connection between the operator and the robot controller during programming and operation. The WiTP provides greater flexibility and mobility to operators, allowing them to program and control robots from a distance without being tethered to a fixed location. This innovation enhances safety, efficiency, and ease of use in industrial robotics applications, contributing to the advancement of automation technology.[26] | ||
| 2007 (August) | Medical surgical precision | Deployment | Dr. Sijo Parekattil of the Robotics Institute and Center for Urology (Winter Haven Hospital and University of Florida) performs the first robotic-assisted microsurgery procedure denervation of the spermatic cord for chronic testicular pain.[60] | United States | |
| 2007 | Industrial lifting | Model release | KUKA introduces the first long-range robot and heavy-duty robot capable of handling payloads of up to 1,000 kg. This innovation represented a significant advancement in industrial robotics, enabling the automation of tasks requiring the manipulation of large and heavy objects across extended distances. KUKA's development expanded the capabilities of robotic systems in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and automotive, where the efficient handling of substantial loads is essential for productivity and safety.[26] | Germany | |
| 2007 | Industrial automation | Model release | Japanese company Motoman introduces super-speed arc welding robots, representing a significant advancement in welding technology. These robots are capable of reducing cycle times by up to 15%, making them the fastest welding robots available at the time. The introduction of these high-speed welding robots enhances productivity and efficiency in industries that rely on welding processes, such as automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and construction. Motoman's innovation demonstrates the continuous evolution of robotics in improving manufacturing processes and meeting the demands of modern industries.[26] | Japan | |
| 2008 (February) | Medical surgical assistance | Milestone | Dr. Mohan S. Gundeti at the University of Chicago Comer Children's Hospital achieves a major milestone in medical robotics by performing the first robotic pediatric neurogenic bladder reconstruction. This groundbreaking procedure involves using the da Vinci Surgical System to reconstruct bladder function in a child affected by a neurogenic bladder, a condition commonly associated with spina bifida. The minimally invasive approach offered by the robotic system reduces surgical trauma, minimizes blood loss, and shortens recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. Dr. Gundeti’s success demonstrates the viability and benefits of robotic-assisted surgery in pediatric urology, paving the way for broader adoption in complex pediatric procedures.[61] | United States | |
| 2008 (May 12) | Medical surgical assistance | Milestone | The first image-guided MR-compatible robotic neurosurgical procedure is performed at University of Calgary by Dr. Garnette Sutherland using the NeuroArm.[62][63] | Canada | |
| 2008 (June) | Medical surgical assistance | Technology development | The German Aerospace Centre (DLR) unveils MiroSurge, an advanced robotic system designed for minimally invasive surgery. Built around lightweight, dexterous robotic arms called MIRO, the system enables high-precision surgical interventions while reducing patient trauma and recovery time. Each arm can be fitted with different surgical tools or an endoscope, allowing surgeons to operate remotely with enhanced accuracy and stability. MiroSurge is developed as part of DLR’s broader initiative to adapt aerospace technologies for medical applications, particularly in confined environments such as space or compact operating rooms. Its modularity and haptic feedback capabilities mark a significant step in robotic-assisted surgery.[64] | Germany | |
| 2008 | Industrial automation | Model release | Japanese robotics company FANUC introduces a new heavy-duty robot with an impressive payload capacity of nearly 1,200 kilograms. This release marks a significant advancement in industrial robotics, as the robot is capable of handling heavy loads with precision and efficiency. The introduction of such a high-capacity robot expands the possibilities for automation in industries requiring heavy lifting and manipulation tasks, such as automotive manufacturing, logistics, and material handling. [26] | Japan | |
| 2009 | Medical surgical assistance | Model release | Titan Medical Inc., a Canadian medical technology company, announces the development of its innovative robotic surgical system called Amadeus, which would be later renamed SPORT (Single Port Orifice Robotic Technology). The system features a four-armed manipulator designed to perform minimally invasive surgeries through a single incision, enhancing patient recovery and reducing surgical trauma. SPORT integrates a high-definition 3D visualization system and precision-controlled robotic instruments to allow surgeons greater dexterity and control during complex procedures. Aimed at competing with systems like da Vinci, Titan’s platform seeks to make robotic surgery more accessible and cost-effective for hospitals and surgical centers worldwide.[65] | Canada | |
| 2009 | Industrial automation | Technology development | Japanese company Yaskawa Motoman unveils the enhanced robot control system known as the DX100. This innovative system represents a significant advancement in robotic control technology, offering fully synchronized control of up to eight robots with a total of 72 axes. Additionally, the DX100 system provides comprehensive integration with input/output (I/O) devices and communication protocols, enabling seamless coordination and communication between robots and external systems.[26] | Japan | |
| 2010 (September) | Medical surgical assistance | Model release | The Eindhoven University of Technology unveils the Sofie surgical system, marking a significant advancement in robotic-assisted surgery. Sofie is the first surgical robot to incorporate force feedback, allowing surgeons to feel resistance and pressure during procedures. This innovation aims to enhance precision and control during minimally invasive surgeries by providing tactile sensations that traditional robotic systems lacked. The introduction of force feedback represented a leap forward in robotic surgery, potentially improving patient outcomes and surgeon performance by restoring a key sensory input typically lost in robotic operations.[65] | Netherlands | |
| 2010 | Medical surgical assistance | Milestone | A significant milestone is achieved in the field of robot-assisted surgery as the first robotic operation at the femoral vasculature took place at the University Medical Centre Ljubljana. Led by Borut Geršak and his team, this pioneering procedure marks a significant advancement in the application of robotic technology in surgical interventions, particularly in the domain of vascular surgery. The successful completion of this operation highlights the potential of robotic systems to enhance precision, dexterity, and minimally invasive techniques in surgical procedures, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.[66][67] | Slovenia | |
| 2011 | Space exploration | Milestone | Robonaut-2 becomes the first humanoid robot in space when it is launched to the International Space Station (ISS). Initially serving as a training tool for roboticists, it would undergo upgrades to assist astronauts in conducting hazardous spacewalks outside the station. This advancement demonstrates the potential for robots to undertake complex tasks in challenging environments beyond Earth. Robonaut-2's presence on the ISS highlights the collaborative efforts between humans and robots in space exploration, paving the way for future missions and innovations in space robotics.[9][68] |  | |
| 2017 | Autonomous rights | Milestone | The robot Sophia makes headlines when it is granted Saudi Arabian citizenship, marking a significant milestone in the field of artificial intelligence and robotics. This event sparks discussions about the ethical implications of granting citizenship to AI entities, as well as the broader questions surrounding the rights and responsibilities associated with advanced autonomous systems.[9] | Saudi Arabia | |
| 2017 | Automated service | Milestone | RoboChef restaurant in Tehran, Iran becomes the first robotic and ‘waiterless’ restaurant of the Middle East.[69][70][71] | Iran | |
| 2019 | Medical surgical assistance | Milestone | University of Pennsylvania researchers achieve a breakthrough, creating millions of nanobots within weeks using semiconductor technology. These nanobots, small enough for injection into the human body, can be remotely controlled. This pioneering development holds immense potential for medical applications, including targeted drug delivery and minimally invasive procedures. However, ethical considerations regarding safety, efficacy, and privacy arise.[9] | United States | |
| 2021 (August) | Work automation | Concept development | South African international businessman Elon Musk unveils plans for the “Tesla Bot” (later called Optimus, a humanoid robot designed to perform simple, repetitive tasks like carrying groceries or working on cars. The proposed robot would stand 5-foot-8, weigh 125 pounds, and be built to handle dangerous or mundane jobs. Musk emphasizes it would be “friendly” and unable to overpower humans. The project reflects Tesla’s wider automation goals, including development of its custom D1 chip to power neural networks supporting autonomous vehicles.[72] | United States |  |
| 2024 | Bio-hybrid robotics | Model release | Shoji Takeuchi, a professor at the University of Tokyo, achieves a breakthrough in bio-hybrid robotics by creating robots with artificial human-like skin that can smile. His team develops a method to attach this skin, mimicking human skin structures and ligaments, to complex robot surfaces using collagen gel and small perforations. This innovation allows the skin to flex and move naturally without tearing. Takeuchi aims to further enhance these robots with features like sweat glands and nerves, potentially advancing research in aging studies, cosmetics, and plastic surgery.[73] | Japan |
Numerical and visual data
Google Scholar
The table below shows the number of Google Scholar results per decade for the term "robot," beginning in the 1920s, the decade in which the word was coined. Scholarly references to "robot" were minimal during the early decades but began to rise steadily from the 1950s onward. A sharp increase occurred in the 1990s, reaching a peak of 134,000 results, followed by a decline in the 2000s and renewed growth in the 2010s. The 2020s, with 71,100 results up to April 16, 2025, suggest sustained academic interest and a potential to match or exceed past peaks.
| Decade | Number of Results |
|---|---|
| 1920s | 1,140 |
| 1930s | 1,350 |
| 1940s | 2,190 |
| 1950s | 4,670 |
| 1960s | 8,560 |
| 1970s | 15,700 |
| 1980s | 23,000 |
| 1990s | 134,000 |
| 2000s | 26,500 |
| 2010s | 50,300 |
| 2020s (up to April 16) | 71,100 |
The linear graph below illustrates the number of results by decade, showing a steady increase in output from the 1920s through the 1980s, a dramatic surge in the 1990s, a decline in the 2000s, and a resurgence in the 2010s. For the 2020s, the value has been adjusted to reflect a projection for the full decade. As of April 16, 2025, there were approximately 71,000 results.
Google Trends
The image below displays Google Trends data for the search term "Robotics" from January 2004 to April 2025, when the screenshot was taken. The graph shows a gradual decline in interest until around 2015, followed by a steady upward trend from mid-2016 onward—likely reflecting increased attention to automation, AI, and emerging technologies. The world map highlights widespread global interest, especially in developing regions. This suggests that robotics is becoming an increasingly relevant topic worldwide, driven by both technological innovation and educational outreach.[74]

Google Books Ngram Viewer
The image below shows data from the Google Books Ngram Viewer tracking the frequency of the terms "robot" and "robotics" in English-language books from 1900 to 2022. Mentions of these terms remain minimal until the 1970s, when their usage began to rise sharply—reflecting growing interest in automation and artificial intelligence. This upward trend peaks around the mid-1980s, followed by a decline in the 1990s. From the early 2000s onward, both terms experience renewed and sustained growth, indicating a resurgence of scholarly and cultural attention to robotics-related topics in recent decades.[75]
Wikipedia views
The image below displays monthly pageview statistics for the Wikipedia article "Robotics" from 2015 to early 2025, broken down by access method. The overall trend shows a gradual decline in total views over the years, from peaks above 60,000 in 2017–2018 to around 30,000 by 2024. The chart reflects long-term patterns of public interest and shifting user behavior in accessing Wikipedia content about robotics.[76]
Meta information on the timeline
How the timeline was built
The initial version of the timeline was written by User:Sebastian.
Funding information for this timeline is available.
Feedback and comments
Feedback for the timeline can be provided at the following places:
- FIXME
What the timeline is still missing
Timeline update strategy
See also
External links
References
- ↑ "The history of industrial robots, from single taskmaster to self-teacher". autodesk.com. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "A Brief History of Robotics since 1950". encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "GM Centennial: Manufacturing Innovation". assemblymag.com. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "A brief history of robots". parisinnovationreview.com/. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "The History of Robotics in the Automotive Industry". robotics.org. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "The history of industrial robots, from single taskmaster to self-teacher". autodesk.com. Retrieved 17 June 2024.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 "Robotics timeline" (PDF). nieonline.com. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ↑ "Egyptian Water Clock | Science Museum Group Collection". collection.sciencemuseumgroup.org.uk. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 9.15 9.16 9.17 9.18 9.19 9.20 9.21 9.22 9.23 9.24 "An Exhaustive History of Robotics". learn.g2.com. Retrieved 14 February 2020.
- ↑ 10.00 10.01 10.02 10.03 10.04 10.05 10.06 10.07 10.08 10.09 10.10 10.11 10.12 10.13 10.14 10.15 10.16 "The History of Robotics". sciencekids.co.nz. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ↑ "Archimedes: The Brilliant Mind That Shaped Science and Engineering". Vocal. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ Kak, S.C. (February 2014). "Contributions of Archimedes on mechanics and design of mechanisms". Mechanism and Machine Theory. 72: 86–93. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2013.10.005. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ "Archimedes: The Man". University of Hawaii. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ 14.00 14.01 14.02 14.03 14.04 14.05 14.06 14.07 14.08 14.09 14.10 14.11 14.12 14.13 14.14 14.15 14.16 14.17 14.18 14.19 14.20 14.21 14.22 14.23 14.24 14.25 14.26 14.27 14.28 14.29 14.30 14.31 14.32 14.33 14.34 14.35 14.36 14.37 14.38 14.39 14.40 14.41 14.42 14.43 14.44 14.45 14.46 14.47 14.48 14.49 14.50 "History of Robotics: Timeline" (PDF). robotshop.com. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 15.13 15.14 15.15 "HISTORY OF ROBOTICS". robotiksistem.com. Retrieved 14 February 2020.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Robots: A History: Welcome- The History of Robotics". libguides.lindahall.org. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 "The Early History of Robots and Automata". gwsrobotics.com. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 "A Very Short History Of Artificial Intelligence (AI)". forbes.com. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- ↑ Mehta, Dhaval; Ranadive, Dr Amol (31 January 2021). What Gamers Want: A Framework to Predict Gaming Habits. OrangeBooks Publication.
- ↑ "A brief history of robotics - a timeline of key achievements in the fields of robotics and AI, from Azimov to AlphaGo". techworld.com. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ↑ 21.00 21.01 21.02 21.03 21.04 21.05 21.06 21.07 21.08 21.09 21.10 21.11 21.12 21.13 21.14 21.15 21.16 21.17 21.18 21.19 21.20 21.21 "Timeline of Robotics 2 of 2". thocp.net. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ↑ "Robot". britannica.com. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ "Jack Kilby's Integrated Circuit". National Museum of American History. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ "1959". Computer History Museum. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ "Unimate: The Fascinating Story of the First Robot in History". byjusfutureschool.com. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ↑ 26.00 26.01 26.02 26.03 26.04 26.05 26.06 26.07 26.08 26.09 26.10 26.11 26.12 26.13 26.14 26.15 26.16 26.17 26.18 26.19 26.20 26.21 26.22 26.23 26.24 26.25 26.26 26.27 26.28 26.29 26.30 26.31 26.32 26.33 26.34 26.35 26.36 26.37 "Robot History". ifr.org. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ Vertut, Jean; Coiffet, Philippe (1986). Teleoperation and Robotics: Evolution and development. Kogan Page. ISBN 978-0-13-782194-5.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "How Robotics Got Started: A Brief History". youtube.com. 5 March 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2024.
- ↑ Aylett, Ruth; Vargas, Patricia A. (21 September 2021). Living with Robots: What Every Anxious Human Needs to Know. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-04581-0.
- ↑ "AI History: Minsky Tentacle Arm". youtube.com. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "History of Robots". roboticsacademy.com.au. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- ↑ "Humanoid History -WABOT-". www.humanoid.waseda.ac.jp. Retrieved 17 May 2024.
- ↑ Sánchez-Martín, F. M.; Jiménez Schlegl, P.; Millán Rodríguez, F.; Salvador-Bayarri, J.; Monllau Font, V.; Palou Redorta, J.; Villavicencio Mavrich, H. (March 2007). "Historia de la robótica: de Arquitas de Tarento al Robot da Vinci (Parte II)". Actas Urológicas Españolas. pp. 185–196. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 34.3 34.4 "KUKA Robot History | Robots.com". T.I.E. Industrial. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ↑ "Rise of the robot" (PDF). ABB Review. ABB. 2014. pp. 24–31. Retrieved 17 May 2025.
- ↑ "Success story" (PDF). library.e.abb.com. Retrieved 21 May 2024.
- ↑ "Viking Project". NASA Science. NASA. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ "The Robotics Institute". Remake Learning. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ↑ "Historia de los robots". Timetoast. Retrieved 11 February 2025.
- ↑ Kwoh YS, Hou J, Jonckheere EA, Hayati S (February 1988). "A robot with improved absolute positioning accuracy for CT guided stereotactic brain surgery". IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering. 35 (2): 153–60. doi:10.1109/10.1354. PMID 3280462.
- ↑ "IEEE Robotics and Automation Society". ieee-ras.org. Retrieved 6 March 2020.
- ↑ "Biologically Inspired Robots: Snake-Like Locomotors and Manipulators by Shigeo Hirose". Robotica. Cambridge University Press. 9 March 2009. Retrieved 28 June 2025.
- ↑ "Medical Post 23:1985" (PDF).
- ↑ "Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR)". epicos.com. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ↑ "1985 - "Aquarobot" Aquatic walking robot - (Japanese)". cyberneticzoo.com. 16 July 2015. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ↑ "Yaskawa Motoman". linkedin.com. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ↑ Paul HA, Bargar WL, Mittlestadt B, Musits B, Taylor RH, Kazanzides P, Zuhars J, Williamson B, Hanson W (December 1992). "Development of a surgical robot for cementless total hip arthroplasty". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research (285): 57–66. doi:10.1097/00003086-199212000-00010. PMID 1446455.
- ↑ "The Intelligent Ground Vehicle Competition (IGVC): A Cutting-Edge Engineering Team Experience". researchgate.net. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ↑ Unger SW, Unger HM, Bass RT (1994-09-01). "AESOP robotic arm". Surgical Endoscopy. 8 (9): 1131. doi:10.1007/BF00705739. PMID 7992194.
- ↑ "A Brief History of RoboCup". robocup.org. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ↑ Baek SJ, Kim SH (May 2014). "Robotics in general surgery: an evidence-based review". Asian Journal of Endoscopic Surgery. 7 (2): 117–23. doi:10.1111/ases.12087. PMID 24877247.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "The History of Artificial Intelligence". harvard.edu. Retrieved 7 February 2020.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 53.2 53.3 Scharf, Rhonda. Alexa is Stealing Your Job: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Your Future.
- ↑ Sung GT, Gill IS (December 2001). "Robotic laparoscopic surgery: a comparison of the DA Vinci and Zeus systems". Urology. 58 (6): 893–8. doi:10.1016/s0090-4295(01)01423-6. PMID 11744453.
- ↑ "World's Lightest Micro-Flying Robot Built by Epson". phys.org. Retrieved 10 June 2024.
- ↑ "RoboGames". ieeexplore.ieee.org. Retrieved 8 March 2020.
- ↑ "RoboGames Press". robogames.net. Retrieved 18 June 2024.
- ↑ "An Oral History of the Darpa Grand Challenge, the Grueling Robot Race That Launched the Self-Driving Car". wired.com. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ↑ "Grand Challenge: Ten Years Later". darpa.mil. Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). 13 March 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2025.
- ↑ Parekattil, Sijo. "Robotic Infertility". Retrieved 11 October 2012.
- ↑ "Surgeons perform world's first pediatric robotic bladder reconstruction". Esciencenews.com. 20 November 2008. Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- ↑ "neuroArm : revolutionary procedure a world first". ucalgary.ca. 16 May 2008. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ↑ "neuroArm". neuroarm.org. Retrieved 27 February 2020.
- ↑ Hagn U, Nickl M, Jörg S, Tobergte A, Kübler B, Passig G, et al. (2008). "DLR MiroSurge – towards versatility in surgical robotics". Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Computer und Roboterassistierte Chirurgie; Proceedings of CURAC. 7: 143–146.
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Human-Computer Interaction: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications (Management Association, Information Resource ed.).
- ↑ "V UKC Ljubljana prvič na svetu uporabili žilnega robota za posege na femoralnem žilju" [The First Use of a Vascular Robot for Procedures on Femoral Vasculature] (in Slovenian). 8 November 2010. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ "UKC Ljubljana kljub finančnim omejitvam uspešen v razvoju medicine" [UMC Ljubljana Successfully Develops Medicine Despite Financial Limitations] (in Slovenian). 30 March 2011.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ Holden, Henry M. The Coolest Job in the Universe: Working Aboard the International Space Station.
- ↑ Staff, IFP Editorial (2017-10-29). "Middle East's First Robotic Restaurant Opens in Tehran". IFP News. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ↑ "PressTV-Tehran eatery serves meals by robots". presstv.com. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ↑ "Interactive Restaurants Making Their Mark". Financial Tribune. 2017-08-13. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ↑ Siddiqui, Faiz (August 20, 2021). "Tesla says it is building a 'friendly' robot that will perform menial tasks, won't fight back". The Washington Post. The Washington Post. Retrieved 29 August 2025.
- ↑ "Robots con piel humana: el avance de Shoji Takeuchi que logra hacer sonreír a los humanoides". Cadena SER. 25 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ↑ "Google Trends: Robotics". Google Trends. Retrieved 16 April 2025.
- ↑ "Google Books Ngram Viewer: robotics, robot". Google Books Ngram Viewer. Retrieved 16 April 2025.
- ↑ "Pageviews Analysis: Robotics". wikipediaviews.org. Retrieved 16 April 2025.